
PROSPECTUS
2,900,000 Shares

Common Stock
______________________
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. is a full service, vertically integrated, self-administered and self-managed real estate investment trust, or REIT, focused on the acquisition, ownership and management of single and multi-tenant Class B industrial properties, including distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties, primarily located in secondary and select primary markets across the U.S. Upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions (as defined herein), we will own 100% of the interests in 20 industrial properties located in seven states with an aggregate of approximately 4.0 million rentable square feet.
This is our initial listed public offering. We are selling 2,900,000 shares of our common stock, $0.01 par value per share in this offering. In addition, concurrently with the closing of this offering, we will be privately issuing 263,158 shares of our common stock and warrants to acquire 250,000 shares of our common stock to affiliates of Torchlight Investors, LLC, or Torchlight, in connection with the Torchlight Transactions, as described herein.
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock. Our common stock has been approved for listing, subject to official notice of issuance, on the NYSE MKT, under the symbol “PLYM.”
We were formed as a Maryland corporation in March 2011. We elected to be taxed as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2012. To assist us in maintaining our qualification as a REIT, stockholders are generally restricted from beneficially or constructively owning more than 9.8% in value or number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of the outstanding shares of any class or series of our capital stock. Our charter contains additional restrictions on the ownership and transfer of shares of our common stock. See “Description of Stock—Restrictions on Ownership and Transfer.”
We are an “emerging growth company” under the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, or the JOBS Act, and will be subject to reduced public company reporting requirements. Investing in our common stock involves significant risks. You should read the section entitled “Risk Factors” beginning on page 16 of this prospectus for a discussion of certain risk factors that you should consider before investing in our common stock.
| Per share | Total | |||||||
| Public offering price | $ | 19.00 | $ | 55,100,000 | ||||
| Underwriting discount (1) | $ | 1.33 | $ | 3,857,000 | ||||
| Proceeds, before expenses, to us | $ | 17.67 | $ | 51,243,000 | ||||
________________
| (1) | See “Underwriting” for additional disclosure regarding the compensation payable to the underwriters. |
The underwriters may also exercise their option to purchase up to an additional 435,000 shares from us, at the public offering price, less the underwriting discount, for 30 days after the date of this prospectus to cover over-allotments of shares, if any.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or determined if this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
Delivery of the shares of our common stock in book-entry form is expected to be made on or about June 14, 2017.
| D.A. Davidson & Co. | BB&T Capital Markets | Oppenheimer & Co. |
| National Securities Corporation | Wedbush Securities |
Janney Montgomery Scott
The date of this prospectus is June 8, 2017.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| PROSPECTUS SUMMARY | 1 |
| RISK FACTORS | 16 |
| CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS | 39 |
| USE OF PROCEEDS | 40 |
| DISTRIBUTION POLICY | 41 |
| CAPITALIZATION | 43 |
| DILUTION | 44 |
| SELECTED FINANCIAL INFORMATION | 46 |
| MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS | 49 |
| MARKET OVERVIEW | 64 |
| BUSINESS | 82 |
| MANAGEMENT | 98 |
| EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION | 106 |
| CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS | 112 |
| STRUCTURE OF OUR COMPANY | 113 |
| POLICIES WITH RESPECT TO CERTAIN ACTIVITIES | 115 |
| PRINCIPAL STOCKHOLDERS | 120 |
| DESCRIPTION OF CAPITAL STOCK | 121 |
| MATERIAL PROVISIONS OF MARYLAND LAW AND OF OUR CHARTER AND BYLAWS | 126 |
| SHARES ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE | 130 |
| DESCRIPTION OF THE PARTNERSHIP AGREEMENT OF PLYMOUTH INDUSTRIAL OP, LP. | 133 |
| MATERIAL U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS | 136 |
| UNDERWRITING | 156 |
| LEGAL MATTERS | 158 |
| EXPERTS | 158 |
| WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION | 158 |
| INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS | F-1 |
You should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus, any free writing prospectus prepared by us or any information to which we have referred you. We have not, and the underwriters have not, authorized any other person to provide you with different or additional information. If anyone provides you with different or inconsistent information, you should not rely on it. We are not, and the underwriters are not, making an offer to sell these securities in any jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted. You should assume that the information appearing in this prospectus, in any free writing prospectus prepared by us and in any information to which we have referred you is accurate only as of their respective dates or on the date or dates which are specified in those documents. Our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may have changed since those dates.
i
Industry and Market Data
We use market data and industry forecasts and projections throughout this prospectus, including data from publicly available information and industry publications. These sources generally state that the information they provide has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, but that the accuracy and completeness of the information are not guaranteed. The forecasts and projections are based on industry surveys and the preparers’ experience in the industry, and there is no assurance that any of the projections or forecasts will be achieved. We believe that the surveys and market research others have performed are reliable, but we have not independently investigated or verified this information. Any forecasts prepared by REIS, Inc., or REIS, are based on data (including third-party data), models and experience of various professionals, and are based on various assumptions, all of which are subject to change without notice. In addition, the projections obtained from REIS that we have included in this prospectus have not been expertized and are, therefore, solely our responsibility. As a result, REIS does not and will not have any liability or responsibility whatsoever for any market data and industry forecasts and projections that are contained in this prospectus or otherwise disseminated in connection with the offer or sale of our common stock. If you purchase our common stock, your sole recourse for any alleged or actual inaccuracies in the forecasts and projections used in this prospectus will be against us. Forecasts and other forward-looking information obtained from these sources are subject to the same qualifications and uncertainties as the other forward-looking statements contained in this prospectus.
Glossary
In this prospectus:
| • | “annualized rent” means the monthly base rent for the applicable property or properties as of March 31, 2017, multiplied by 12 and then multiplied by our percentage ownership interest for such property, where applicable, and “total annualized rent” means the annualized rent for the applicable group of properties; | |
| • | “capitalization rate” means the ratio of a property’s annual net operating income to its purchase price; | |
| • | “Class A industrial properties” means industrial properties that typically possess most of the following characteristics: 15 years old or newer, square footage generally in excess of 300,000 square feet, concrete tilt-up construction, clear height in excess of 26 feet, a ratio of dock doors to floor area that is more than one door per 10,000 square feet and energy efficient design characteristics suitable for current and future tenants; | |
| • | “Class B industrial properties” means industrial properties that typically possess most of the following characteristics: more than 15 years old, clear heights between 18 and 26 feet, square footage between 50,000 and 300,000 square feet, and adequate building systems (mechanical, HVAC and utility) to deliver services currently required by tenants but which may need upgrades for future tenants; | |
| • | “Company Portfolio” means the 20 distribution centers, warehouse and light industrial properties in which our company currently has an interest and, upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, will own 100% of the interests; | |
| • | “net operating income” or “NOI” means total revenue (including rental revenue, tenant reimbursements, management, leasing and development services revenue and other income) less property-level operating expenses including allocated overhead. NOI excludes depreciation and amortization, general and administrative expenses, impairments, gain/loss on sale of real estate, interest expense and other non-operating expenses; | |
| • | “on a pro forma basis” means after giving effect to the completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions and the application of the net proceeds of this offering as described under “Use of Proceeds;” | |
| • | “OP units” means units of limited partnership interest in our operating partnership; | |
ii
| • | “our operating partnership” means Plymouth Industrial OP, LP, a Delaware limited partnership, and the subsidiaries through which we will conduct substantially all of our business; | |
| • | “Plymouth,” “our company,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc., a Maryland corporation, and its consolidated subsidiaries, except where it is clear from the context that the term only means Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc., the issuer of the shares of common stock in this offering; | |
| • | “Preferred Interests” means the preferred membership interests issued by our subsidiary, Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC, to DOF IV Plymouth PM, LLC, an affiliate of our mezzanine lender; |
| • | “primary markets” means gateway cities and the following six largest metropolitan areas in the U.S., each generally consisting of more than 300 million square feet of industrial space: Los Angeles, San Francisco, New York, Chicago, Washington, DC and Boston; | |
| • | “secondary markets” means for our purposes non-gateway markets, each generally consisting of between 100 million and 300 million square feet of industrial space, including the following metropolitan areas in the U.S.: Atlanta, Austin, Baltimore, Charlotte, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Columbus, Dallas, Detroit, Houston, Indianapolis, Jacksonville, Kansas City, Memphis, Milwaukee, Nashville, Norfolk, Orlando, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, Raleigh/Durham, San Antonio, South Florida, St. Louis and Tampa; | |
| • | “Torchlight” means Torchlight Investors, LLC and the Torchlight Entities, as applicable; | |
| • | “Torchlight Entities” means DOF IV REIT Holdings, LLC and DOF IV Plymouth PM, LLC, both of which are managed by Torchlight Investors, LLC; and | |
| • | “Torchlight Transactions” means the redemption of the Preferred Interests for $25.0 million, which will be paid by a combination of $20.0 million in cash with a portion of the net proceeds of this offering and 263,158 shares of common stock issued to Torchlight in a private placement, and the private issuance of warrants to Torchlight to acquire 250,000 shares of common stock, in each case concurrently with the closing of this offering. See “Prospectus Summary—Torchlight Transactions.” |
Our definitions of Class A industrial properties, Class B industrial properties, primary markets and secondary markets may vary from the definitions of these terms used by investors, analysts or other industrial REITs.
See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” for more detailed explanations of NOI, Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization, or EBITDA, and reconciliations of NOI, EBITDA and Funds from Operations, or FFO, to net income computed in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP.
iii
PROSPECTUS SUMMARY
The following summary highlights information contained elsewhere in this prospectus. You should read carefully the entire prospectus, including “Risk Factors,” our financial statements, pro forma financial information, and related notes appearing elsewhere in this prospectus, before making a decision to invest in our common stock.
Unless indicated otherwise, the information included in this prospectus assumes (i) no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase up to 435,000 additional shares of our common stock to cover over-allotments, if any, and (ii) the completion of the Torchlight Transactions.
In addition, on April 21, 2017, our stockholders approved a one-for-four reverse stock split of our common stock. Effective May 1, 2017, we amended our charter to give effect to the reverse stock split with respect to all of our then-outstanding common stock. All share data included in this prospectus give retroactive effect to the stock split and related amendment to our charter. The reverse stock split had no effect on the shares authorized under our charter.
Overview
We are a full service, vertically integrated, self-administered and self-managed Maryland corporation focused on the acquisition, ownership and management of single and multi-tenant Class B industrial properties, including distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties, primarily located in secondary and select primary markets across the U.S. For our definition of Class B industrial properties, see “—Our Investment and Growth Strategies—Investment Strategy.” The Company Portfolio, which consists of 20 industrial properties located in seven states, is currently held through Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC, a joint venture with Torchlight in which we own a 0.5% interest. In connection with the completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, we will redeem Torchlight’s interest in Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC, or Plymouth Industrial 20, and, as a result, we will own 100% of the interests in the Company Portfolio. See “—Torchlight Transactions.” As of March 31, 2017, the Company Portfolio was 98.4% leased to 37 different tenants across 17 industry types.
We intend to continue to focus on the acquisition of Class B industrial properties primarily in secondary markets with net rentable square footage ranging between approximately 100 million and 300 million square feet, which we refer to as our target markets. We believe industrial properties in such target markets will provide superior and consistent cash flow returns at generally lower acquisition costs relative to industrial properties in primary markets. Further, we believe there is a greater potential for higher rates of appreciation in the value of industrial properties in our target markets relative to industrial properties in primary markets.
We believe our target markets provide us with opportunities to acquire both stabilized properties generating favorable cash flows, as well as properties where we can enhance returns through value-add renovations and redevelopment. We focus primarily on the following investments:
| • | single-tenant industrial properties where tenants are paying below-market rents with near-term lease expirations that we believe have a high likelihood of renewal at market rents; and | |
| • | multi-tenant industrial properties that we believe would benefit from our value-add management approach to create attractive leasing options for our tenants, and as a result of the presence of smaller tenants, obtain higher per-square-foot rents. |
We believe there are a significant number of attractive acquisition opportunities available to us in our target markets and that the fragmented and complex nature of our target markets generally make it difficult for less-experienced or less-focused investors to access comparable opportunities on a consistent basis. See “Market Overview.”
Our company, which was formerly known as Plymouth Opportunity REIT, Inc., was founded in March 2011 by two of our executive officers, Jeffrey Witherell and Pendleton White, Jr., each of whom has at least 25 years of experience acquiring, owning and operating commercial real estate properties. Specifically, both were members of a team of senior investment executives that was responsible for the acquisition and capital formation of commercial properties for Franklin Street Properties (NYSE: FSP), or Franklin Street, a REIT based in Boston, MA, from 2000 to 2007, during which time Franklin Street listed its stock on the American Stock Exchange. Following their time at Franklin Street, our founders recognized a growing opportunity in the Class B industrial space, particularly in secondary markets and select primary markets, following the 2008-2010 recession, and founded our company to participate in the cyclical recovery of the U.S. economy. Between March 2011 to April 2014, we prepared for and engaged in a non-listed public offering of our common stock. We used the proceeds from that offering to acquire equity interests in five industrial properties. In 2014, we used the proceeds of a senior secured loan to acquire 100% fee ownership in three of these properties and 100% fee ownership in the remaining 17 properties that comprise the Company Portfolio. In July 2015 and January 2017, we sold our equity interests in the two properties in which we did not have 100% fee ownership.
1
Competitive Strengths
We believe that our investment strategy and operating model distinguish us from other owners, operators and acquirers of industrial real estate in several important ways, including the following:
High-Quality Portfolio with Strong Fundamentals: Since 2014, we have acquired a portfolio of 20 industrial assets with an aggregate of over four million square feet of rentable space. As of March 31, 2017, the Company Portfolio was 98.4% leased to 37 different tenants across 17 diversified industries, which we believe reduces our exposure to tenant default risk and earnings volatility. We have realized consistent increases in rental rates since the acquisition of the properties comprising the Company Portfolio. Rental rates on new leases signed in 2016 were approximately 57.1% higher than rental rates on prior leases, and rental rates for renewing tenants increased 3.8%. In addition, our tenant retention rate increased from 17.3% in 2015 to 73.7% in 2016. We believe that high occupancy rates across the Company Portfolio, as well as strong rental growth, are indicative of the consistent execution of our business strategy.
Strong Alignment of Interests: We believe the interests of our management team, our board of directors and our stockholders are strongly aligned. We will grant an aggregate of 131,579 restricted shares of common stock to our executive officers and independent directors upon the closing of this offering. In addition, following the completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, the Torchlight Entities will own approximately 7.3% of our common stock (13.2% assuming the full exercise of the warrants to be issued in the Torchlight Transactions). Each of the members of our management team, our board of directors and Torchlight has entered into a lock-up agreement restricting the direct or indirect sale of such securities for 180 days after the date of this prospectus without the prior written consent of D.A. Davidson & Co.
Strategic Focus on Class B Industrial Properties in Secondary Markets with Stable and Predictable Cash Flows: We focus on Class B distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties rather than Class A industrial or other commercial properties for the following reasons, among others: fewer capital expenditure requirements, generally greater investment yields, overall greater tenant retention, generally higher current returns and lower earnings volatility. We believe the Company Portfolio is, and our future acquisitions will be, attractively positioned to participate in the recovering rental rates in our target markets while providing our stockholders with consistent, stable cash flows. For further discussion of our target markets, see “Market Overview—Our Target Markets.”
We intend to continue to focus on the acquisition of distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties in our target markets across the U.S. We believe that our target markets have exhibited, or will exhibit in the near future, positive demographic trends (i.e., population growth, decreasing unemployment rates, personal income growth and/or favorable tax climates), scarcity of available industrial space and favorable rental growth projections, which should help create superior long-term risk-adjusted returns.
Superior Access to Deal Flow: We believe our management team’s extensive personal relationships and research-driven origination methods will provide us access to off-market and lightly marketed acquisition opportunities, many of which may not be available to our competitors. Off-market and lightly marketed transactions are characterized by a lack of a formal marketing process and a lack of widely disseminated marketing materials. Our executive management and acquisition teams maintain a deep, broad network of relationships among key market participants, including property brokers, lenders, owners and tenants, and greater than 50% of the Company Portfolio was sourced in off-market or lightly marketed transactions. We believe that our sourcing approach will provide us access to a significant number of attractive investment opportunities.
Experienced Management Team: Each of the three senior members of our executive management team has over 25 years of significant real estate industry experience, with each member having previous public REIT or public real estate company experience. Led by Mr. Witherell, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Mr. White, our President and Chief Investment Officer, and Mr. Wright, our Chief Financial Officer, our management team has significant experience in acquiring, owning, operating and managing commercial real estate, with a particular emphasis on industrial assets. Throughout their careers, Mr. Witherell and Mr. White have had primary responsibility for overseeing the acquisition, financing, ownership and management of more than ten million square feet of office and industrial properties in our target markets, while over the past 18 years Mr. Wright has served as the Chief Financial Officer of two real estate companies, one of which had approximately $8 billion in assets.
2
Our Investment and Growth Strategies
Our primary objective is to generate attractive risk-adjusted returns for our stockholders through dividends and capital appreciation primarily through the acquisition of Class B industrial properties located in secondary markets. We intend to focus our acquisition activities on our core property types, which include warehouse/distribution facilities and light manufacturing facilities, because we believe they generate higher tenant retention rates and require lower tenant improvement and re-leasing costs. To a lesser extent, we intend to focus on flex/office facilities (light assembly and research and development). We believe that pursuing the following strategies will enable us to achieve our investment objectives.
Our investment strategy will also focus on the burgeoning e-commerce industry by acquiring industrial properties that may service tenants’ e-commerce fulfillment needs, or “last mile” delivery requirements. These properties, termed “in-fill” properties, are typically located in highly populated areas, near city centers or populous suburban areas.
Investment Strategy
Our primary investment strategy is to acquire and own Class B industrial properties predominantly in secondary markets across the U.S. We generally define Class B industrial properties as industrial properties that are typically more than 15 years old, have clear heights between 18 and 26 feet and square footage between 50,000 and 300,000 square feet, with building systems that have adequate capacities to deliver the services currently needed by existing tenants, but may need upgrades for future tenants. In contrast, we define Class A industrial properties as industrial properties that typically are 15 years old or newer, have clear heights in excess of 26 feet and square footage in excess of 300,000 square feet, with energy efficient design characteristics suitable for current and future tenants.
We intend to own and acquire properties that we believe can achieve high initial yields and strong ongoing cash-on-cash returns and that exhibit the potential for increased rental growth in the near future. In addition, we may acquire Class A industrial properties that offer similar attractive return characteristics if the cost basis for such properties are comparable to those of Class B industrial properties in a given market or sub-market. While we will focus on investment opportunities in our target markets, we may make opportunistic acquisitions of Class A industrial properties or industrial properties in primary markets when we believe we can achieve attractive risk-adjusted returns.
We also intend to pursue joint venture arrangements with institutional partners which could provide management fee income as well as residual profit-sharing income. Such joint ventures may involve investing in industrial assets that would be characterized as opportunistic or value-add investments. These may involve development or re-development strategies that may require significant up-front capital expenditures, lengthy lease-up periods and result in inconsistent cash flows. As such, these properties’ risk profiles and return metrics would likely differ from the non-joint venture properties that we target for acquisition.
Following this offering, we believe we will have a competitive advantage in sourcing attractive acquisitions because the competition for our target assets is primarily from local investors who are not likely to have ready access to debt or equity capital. In addition, our umbrella partnership real estate investment trust, or UPREIT, structure may enable us to acquire industrial properties on a non-cash basis in a tax efficient manner through the issuance of OP units as consideration for the transaction. We will also continue to develop our large existing network of relationships with real estate and financial intermediaries. These individuals and companies give us access to significant deal flow—both those broadly marketed and those exposed through only limited marketing. These properties will be acquired primarily from third-party owners of existing leased buildings and secondarily from owner-occupiers through sale-leaseback transactions.
Growth Strategies
We seek to maximize our cash flows through proactive asset management. Our asset management team actively manages our properties in an effort to maintain high retention rates, lease vacant space, manage operating expenses and maintain our properties to an appropriate standard. In doing so, we have developed strong tenant relationships. We intend to leverage those relationships and market knowledge to increase renewals, properly prepare tenants for rent increases, obtain early notification of departures to provide longer re-leasing periods and work with tenants to properly maintain the quality and attractiveness of our properties. Our asset management team also collaborates with our internal credit function to actively monitor the credit profile of each of our tenants and prospective tenants on an ongoing basis.
Our asset management team functions include strategic planning and decision-making, centralized leasing activities and management of third-party leasing companies. Our asset management/credit team oversees property management activities relating to our properties which include controlling capital expenditures and expenses that are not reimbursable by tenants, making regular property inspections, overseeing rent collections and cost control and planning and budgeting activities. Tenant relations matters, including monitoring of tenant compliance with their property maintenance obligations and other lease provisions, will be handled by in-house personnel for most of our properties.
3
Financing Strategy
We intend to maintain a flexible and growth-oriented capital structure. We intend to use the net proceeds from this offering along with additional secured and unsecured indebtedness to acquire industrial properties. See “Use of Proceeds.” Our additional indebtedness may include arrangements such as revolving credit facility or term loan. We believe that we will have the ability to leverage newly-acquired properties up to a 65% debt-to-value ratio, though our long-term target debt-to-value ratio is less than 50%. We also anticipate using OP units to acquire properties from existing owners interested in tax-deferred transactions.
Investment Criteria
We believe that our market knowledge, operations systems and internal processes allow us to efficiently analyze the risks associated with an asset’s ability to produce cash flow going forward. We blend fundamental real estate analysis with corporate credit analysis to make a probabilistic assessment of cash flows that will be realized in future periods. We also use data-driven and event-driven analytics and primary research to identify and pursue emerging investment opportunities. See “Business—Our Investment and Growth Strategies—Investment Criteria.”
Our investment strategy focuses on Class B industrial properties in secondary markets for the following reasons:
| • | Class B industrial properties generally require less capital expenditures than both Class A industrial properties and other commercial property types; | |
| • | investment yields for Class B industrial properties are often greater than investment yields on both Class A industrial properties and other commercial property types; | |
| • | Class B industrial tenants tend to retain their current space more frequently than Class A industrial tenants; | |
| • | Class B industrial properties tend to have higher current returns and lower volatility than Class A industrial properties; | |
| • | we believe there is less competition for Class B industrial properties from institutional real estate buyers; our typical competitors are local investors who often do not have ready access to debt or equity capital; | |
| • | the Class B industrial real estate market is highly fragmented and complex, which we believe make it difficult for less-experienced or less-focused investors to access comparable opportunities on a consistent basis; | |
| • | we believe that there is a limited new supply of Class B industrial space in our target markets; | |
| • | secondary markets generally have less occupancy and rental rate volatility than primary markets; | |
| • | Class B properties and secondary markets are typically “cycle agnostic”; i.e., less prone to overall real estate cycle fluctuations; | |
| • | we believe secondary markets generally have more growth potential at a lower cost basis than primary markets; and | |
| • | we believe that the demand for e-commerce-related properties, or e-fulfillment facilities, will continue to grow and play a significant role in our investing strategy. |
Market Overview
Market Opportunity
A key component of our business strategy is to tap into forecasted U.S. economic growth by investing in industrial real estate that we believe will benefit from rental growth and increased tenant demand. We believe that in some cases there has already been significant growth and capitalization rate compression in primary markets in the Class A industrial sector, but that there still exists an opportunity to take advantage of capitalization rate compression, favorable pricing, limited supply and competition in secondary growth markets and in Class B properties. While we will focus on the acquisition of Class B industrial properties in secondary markets, we may also make opportunistic acquisitions of Class A industrial properties and industrial properties in primary markets.
Our acquisition pipeline focuses on a select group of target markets, including, among others, Atlanta, Chicago, Cincinnati, Columbus and Memphis, which we believe possess certain characteristics that we believe are beneficial to industrial real estate investment. These characteristic include, but are not limited to, employment growth, recent and forecasted rent growth, a shortage of industrial development, and falling vacancy rates. We believe that these characteristics will allow us to increase rental rates, increase occupancy and drive value. For a more detailed overview of these markets, refer to the “Market Overview” section of this prospectus.
4
Industrial Real Estate Fundamentals
According to CB Richard Ellis, or CBRE, industrial real estate demand going into 2017 is strong. In many of our target markets vacancy rates are steadily dropping, construction is starting to slowly pick up and rent growth remains healthy. New construction has lagged leasing demand for 25 consecutive quarters. We believe that while construction starts continue to remain limited and economic demand drivers continue to power absorption, industrial fundamentals will continue to strengthen. We believe that, as a result of the lack of new construction and overall demand for industrial properties in many U.S. markets, vacancy rates will continue to fall until rent growth increases to a point where developers can justify undergoing more speculative projects.
Accelerating U.S. Economic Growth
According to forecasts by the United States Congressional Budget Office, or the CBO, inflation-adjusted U.S. GDP grew by 1.6% in 2016 and is expected to grow 2.3% in 2017, 1.9% in 2018, and 1.7% in 2019. The CBO expects that these increases in U.S. GDP will spur businesses to maintain and or grow hiring rates, which will continue to push down the unemployment rate and raise the rate of participation in the labor force. In particular, the CBO projects that the unemployment rate will maintain a range of 4.5% to 5.0% over the next 11 years. Overall, the CBO anticipates that over the next decade, inflation-adjusted U.S. GDP will increase at an average annual pace of 1.9%. We expect that increased employment will lead to increased consumer spending, further enhancing the demand for warehouse properties, particularly in an e-commerce retail environment.
Industrial Trade
Industrial trade is one of the most important drivers of industrial real estate demand as import and export volume greatly determine the amount of space that is needed in order to store goods. Since the recession of 2008 - 2010, exports have been one of the key drivers of the recovery in trade, with export levels up now more than 20.1% from pre-recession levels. While import rates have not grown as quickly as export rates since the recession, import rates (excluding oil) have risen 6.4% over pre-recession levels, which have resulted in further increased demand for industrial real estate space. We believe that this recovery to import and export rates should continue during 2017 and beyond, which should help drive demand for industrial space.
Manufacturing and Production
We believe that manufacturing and production is another key component of industrial real estate performance as the level of goods that are manufactured and produced has a positive correlation with the amount of space needed to store such goods. The productivity of U.S. mines and factories, as measured by the industrial production index, picked up pace in 2013 and has maintained its momentum to date. Due in large part to the surge in domestic energy production, the U.S. is enjoying lower energy costs, which, combined with more competitive labor costs, should allow industrial production to continue to expand in 2017.
In 2015, the U.S. industrial capacity utilization rate stood just above its historical average, with some sectors running well above their long-run averages. We believe that this suggests that more investment in industrial capacity will be needed for industrial production to continue growing The CBO is forecasting that business investment will grow by 5.0% in 2017 and grow on average around 2.2% the following three years. Likewise, CBO also forecasts total output to grow closer to 2.0% per year rather than the 1.4% increase realized between 2008 and 2016.
Consumer Consumption
Consumer consumption, which accounts for two-thirds of U.S. GDP, declined during the recession, as high unemployment and stagnating wages forced people to cut back on non-essential spending. However, since 2009, real consumer spending has grown at an annual rate of 2.3%.
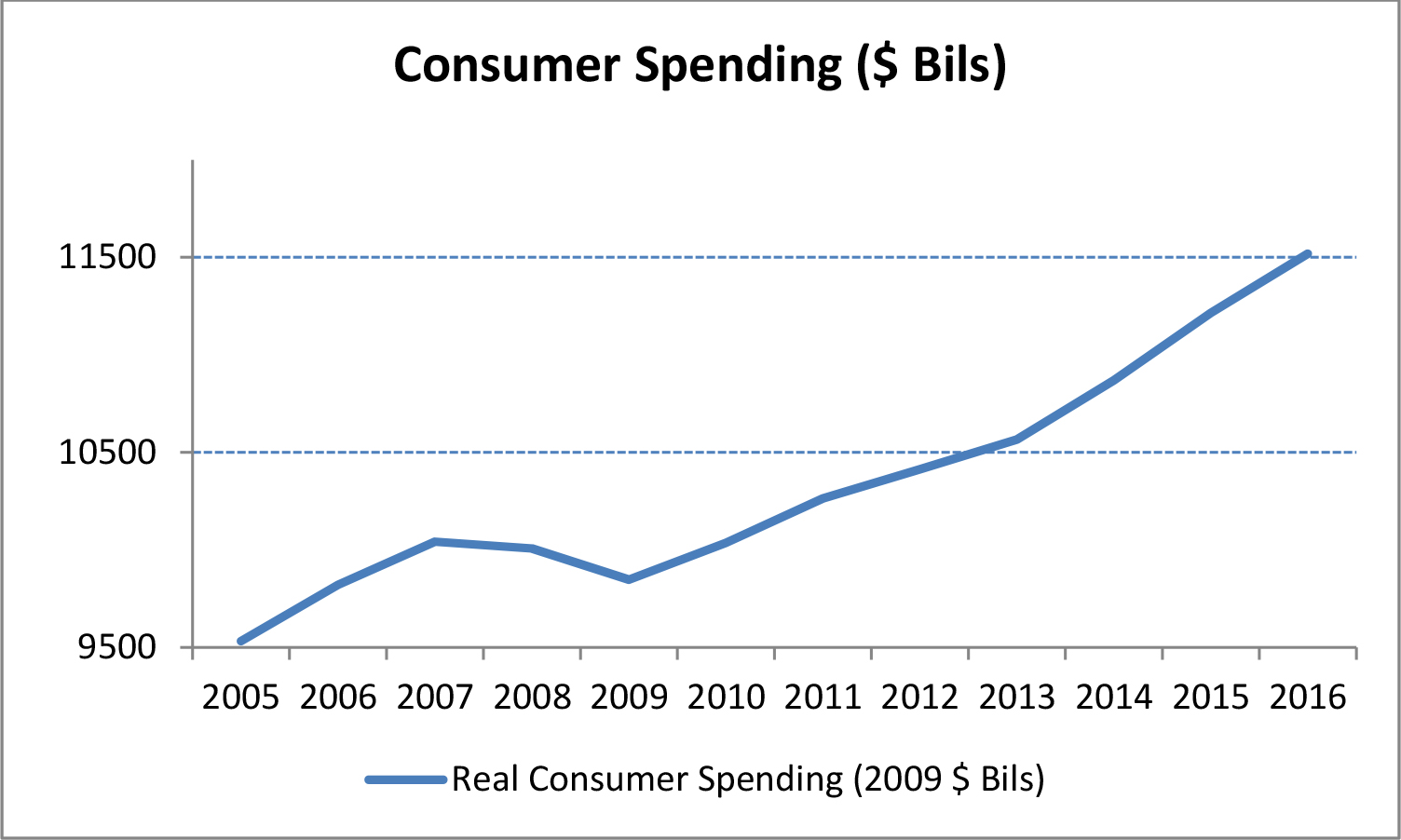 |
| Figure 3 (Source: US Department of Commerce — Bureau of Economic Analysis) |
5
Industrial Real Estate Fundamentals
Overview
According to CBRE, industrial real estate demand going into 2017 is strong. In many of our target markets vacancy rates are steadily dropping, construction is starting to slowly pick up and rent growth remains healthy. New construction has lagged leasing demand for 25 consecutive quarters. We believe that while construction starts continue to remain limited and economic demand drivers continue to power absorption, industrial fundamentals will continue to strengthen. We believe that, as a result of the lack of new construction and overall demand for industrial properties in many U.S. markets, vacancy rates will continue to fall until rent growth increases to a point where developers can justify undergoing more speculative projects. The following graph illustrates this on an historical basis.
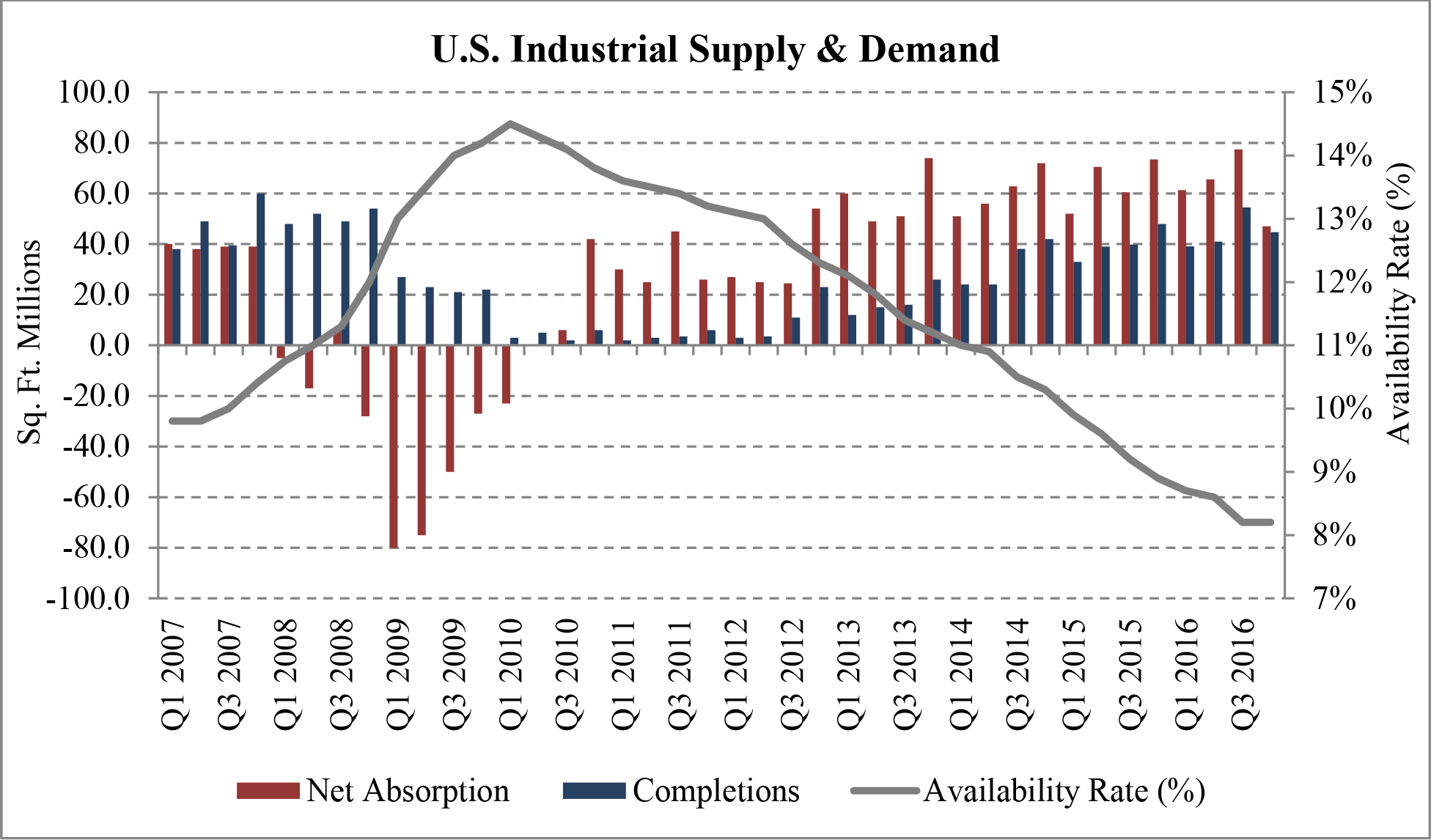 |
| Figure 4 (Source: CBRE) |
Limited new construction and growing demand for industrial properties will cause vacancy rates to fall and rental rates to rise as confirmed by REIS, Inc.’s, or REIS, data and projections on occupancy and effective rental forecasts for both the 6.4 billion square foot warehouse/distribution and 1.2 billion square foot U.S. Flex/R&D markets, which, as illustrated in the two graphs below, show an increase in effective rents since 2011 and a declining vacancy rate through 2020.
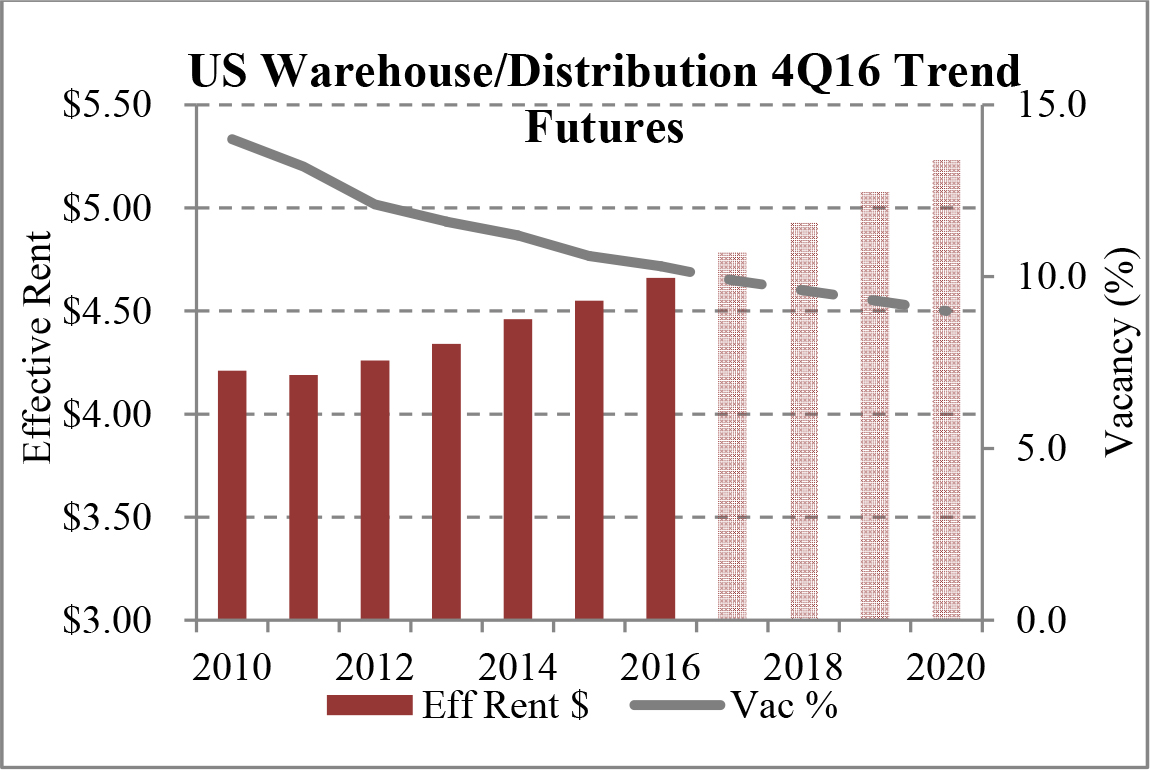 |
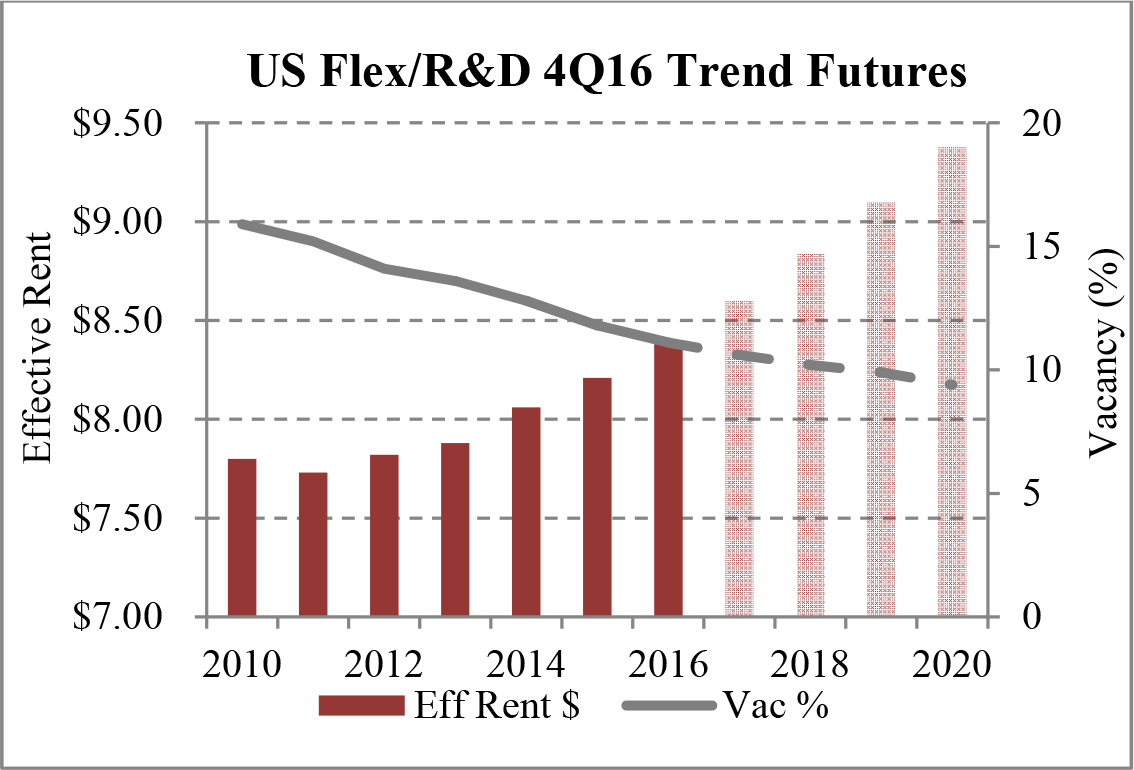 |
| Figure 5 (Source: REIS) | Figure 6 (Source: REIS) |
In the longer term, industrial real estate fundamentals are expected to continue to be strong, as the sector is uniquely positioned to benefit from current economic trends, including increased trade growth, inventory rebuilding, and increased industrial output. Additionally, developing trends point to a strong near-to medium-term outlook for the sector. For example, the growth of big-box warehouses serving large online retailers close to population centers is forecasted to gain popularity, which we believe could potentially influence smaller e-retailers to do the same.
6
Increased e-commerce has a positive impact on warehouse demand, as it tends to transfer retail tenants to warehouses. According to CBRE, U.S. e-commerce sales now comprise 8% of all US retail sales, up from 5.8% in 2013 and 1.5% in 2003. With massive increase in online sales over the past 15 years, e-commerce companies have had to make major investments in infrastructure and facilities to keep pace with demand. This is expected to continue, as online sales keep growing with traditional brick and mortar retailers employing multi-channel sale strategies. Additionally, this emergence of e-commerce and the growth of internet retailers and wholesalers are expanding the universe of tenants seeking industrial space in our target markets, which should drive demand and rent growth into the future.
Manufacturing is also likely to play an increased role in the industrial sector’s recovery. With energy prices and labor costs down, we believe that the fundamentals support a sustained resurgence in domestic manufacturing. Lack of supply may be a hurdle for continued demand growth, as some markets are already reporting shortages of space in certain asset types.
The Company Portfolio
As of the date of this prospectus, we have a minority interest in and operate 20 industrial buildings with an aggregate of approximately 4.0 million square feet of rentable space that as of March 31, 2017 was 98.4% occupied. Upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, we will own 100% of the interest in each of the 20 properties listed below. The following table provides certain information with respect to the Company Portfolio as of March 31, 2017.
| Metro | Address | Property Type | Year Built/
Renovated (1) | Square Footage | Occupancy | Annualized
Rent (2) | Percent
of Total Annualized Rent | Annualized
Rent/Square Foot (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 3940 Stern Avenue | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1987 | 146,798 | 100 | % | $ | 623,891 | 4.4 | % | $ | 4.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 1875 Holmes Road | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1989 | 134,415 | 100 | % | $ | 641,706 | 4.6 | % | $ | 4.77 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 1355 Holmes Road | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1975/1998 | 82,456 | 100 | % | $ | 387,477 | 2.8 | % | $ | 4.70 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 2401 Commerce Drive | Warehouse/Flex | 1994/2009 | 78,574 | 100 | % | $ | 584,663 | 4.2 | % | $ | 7.44 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 189 Seegers Road | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1972 | 25,000 | 100 | % | $ | 162,365 | 1.2 | % | $ | 6.49 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 11351 W. 183rd Street | Warehouse/ Distribution | 2000 | 18,768 | 100 | % | $ | 186,889 | 1.3 | % | $ | 9.96 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cincinnati, OH | Mostellar Distribution Center I & II | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1959 | 358,386 | 100 | % | $ | 1,044,049 | 7.4 | % | $ | 2.91 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cincinnati, OH | 4115 Thunderbird Lane | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1991 | 70,000 | 100 | % | $ | 234,500 | 1.7 | % | $ | 3.35 | ||||||||||||||||
| Florence, KY | 7585 Empire Drive | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1973 | 148,415 | 100 | % | $ | 412,785 | 2.9 | % | $ | 2.78 | ||||||||||||||||
| Columbus, OH | 3500 Southwest Boulevard | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1992 | 527,127 | 100 | % | $ | 1,782,634 | 12.7 | % | $ | 3.38 | ||||||||||||||||
| Columbus, OH | 3100 Creekside Parkway | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1999 | 340,000 | 100 | % | $ | 1,003,000 | 7.1 | % | $ | 2.95 | ||||||||||||||||
| Columbus, OH | 8288 Green Meadows Dr. | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1988 | 300,000 | 100 | % | $ | 906,000 | 6.4 | % | $ | 3.02 | ||||||||||||||||
| Columbus, OH | 8273 Green Meadows Dr. | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1996/2007 | 77,271 | 100 | % | $ | 355,765 | 2.5 | % | $ | 4.60 | ||||||||||||||||
| Columbus, OH | 7001 American Pkwy | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1986/2007 & 2012 | 54,100 | 100 | % | $ | 175,824 | 1.2 | % | $ | 3.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| Memphis, TN | 6005, 6045 & 6075 Shelby Dr. | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1989 | 202,303 | 69.3 | % | $ | 424,078 | 3.0 | % | $ | 3.03 | ||||||||||||||||
| Jackson, TN | 210 American Dr. | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1967/1981 & 2013 | 638,400 | 100 | % | $ | 1,404,480 | 10.0 | % | $ | 2.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| Atlanta, GA | 32 Dart Road | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1988/2014 | 194,800 | 100 | % | $ | 516,228 | 3.7 | % | $ | 2.65 | ||||||||||||||||
| Portland, ME | 56 Milliken Road | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1966,
1995, 2005 & 2013 | 200,625 | 100 | % | $ | 1,036,449 | 7.4 | % | $ | 5.17 | ||||||||||||||||
| Marlton, NJ | 4 East Stow Road | Warehouse/Distribution | 1986 | 156,279 | 100 | % | $ | 834,900 | 5.9 | % | $ | 5.34 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cleveland, OH | 1755 Enterprise Parkway | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1979/2005 | 255,570 | 100 | % | $ | 1,354,762 | 9.6 | % | $ | 5.30 | ||||||||||||||||
| Industrial Properties -- Total/Weighted Average | 4,009,287 | 98.4 | % | $ | 14,072,447 | 100.0 | % | $ | 3.57 | |||||||||||||||||||
_______________
| (1) | Renovation means significant upgrades, alterations or additions to building areas, interiors, exteriors and/or systems. |
| (2) | Annualized base rent is calculated by multiplying (i) rental payments (defined as cash rents before abatements) for the month ended March 31, 2017 by (ii) 12. On March 31, 2017, there were no rental abatements or concessions in effect that would impact cash rent. |
| (3) | Calculated by multiplying (i) rental payments (defined as cash rents before abatements) for the month ended March 31, 2017, by (ii) 12, and then dividing by leased square feet for such property as of March 31, 2017. |
Acquisition Pipeline
Our executive management and acquisition teams maintain a deep, broad network of relationships among key market participants, including property brokers, lenders, owners and tenants. We believe these relationships and our research-driven origination methods provide us access to off-market and lightly marketed acquisition opportunities, many of which may not be available to our competitors. Furthermore, we believe that a significant portion of the approximately 15.4 billion square feet of industrial space in the U.S. falls within our target investment criteria and that there will be ample supply of attractive acquisition opportunities in the future.
In the normal course of our business, we regularly evaluate the market for industrial properties to identify potential acquisition targets. As of the date of this prospectus, we are evaluating approximately $350 million of potential acquisitions in our target markets that we have identified as warranting further investment consideration after an initial review. We do not have any relationship with the sellers of the properties we are evaluating. As of the date of this prospectus, we have neither entered into any letters of intent or purchase agreements with respect to any potential acquisitions, nor have we begun a comprehensive due diligence review with respect to any of these properties. Accordingly, we do not believe that the acquisition of any of the properties under evaluation is probable as of the date of this prospectus.
7
Torchlight Transactions
Redemption of Preferred Interests in Joint Venture
We and Torchlight are party to a joint venture agreement with respect to Plymouth Industrial 20, dated as of October 17, 2016. Each of the properties in the Company Portfolio is owned by Plymouth Industrial 20, in which we currently own a 0.5% interest and Torchlight owns a 99.5% interest, or the Preferred Interests. We are required to redeem the Preferred Interests on or before June 16, 2017, for $25.0 million, which will be paid by a combination of $20.0 million in cash with a portion of the net proceeds from this offering and 263,158 shares of our common stock to be issued in a private placement concurrently with the closing of this offering, which shares will be registered for resale following the first anniversary of the closing of this offering. The shares issuable upon exercise of the warrants will be registered for resale following the first anniversary of the closing of this offering. See “Use of Proceeds” and “Structure of Our Company—Torchlight Transactions.” In the event we do not make the required payment by June 16, 2017, Torchlight has the right to acquire our ownership in Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC for $1.
Termination of Participation Right
As partial consideration for making the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan (as defined below), Plymouth Industrial 20, the borrower under the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan, granted Torchlight, in its capacity as lender, a profit participation in the form of the right to receive 25% of net income and capital proceeds generated by the Company Portfolio following debt service payments and associated costs, or the TL Participation. Pursuant to the Letter Agreement between Torchlight and us, dated as of March 3, 2017, or the Letter Agreement, we have the right to terminate the TL Participation in consideration for the private issuance of warrants to Torchlight to acquire 250,000 shares of our common stock, which we expect to issue concurrently with the closing of this offering. See “Description of Capital Stock—Warrants”.
We refer to the transactions described above collectively as the “Torchlight Transactions.” See “Structure of Our Company—Torchlight Transactions.”
Stockholders Agreement with Torchlight
Immediately upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, we intend to enter into a stockholders agreement with Torchlight, or the Stockholders Agreement, in order to establish various arrangements and restrictions with respect to governance of our company and certain rights that will be granted to the Torchlight in connection with the Torchlight Transactions while Torchlight maintains beneficial ownership of at least 2.5% of our common stock. These rights and restrictions will include a board nomination right and certain customary registration and preemptive rights. We will also be prohibited from issuing preferred stock until Torchlight falls below the ownership threshold described above. See “Management—Torchlight Stockholders Agreement.”
Existing Debt Structure
AIG Loan
On October 17, 2016, certain indirect subsidiaries of our operating partnership entered into a senior secured loan agreement with investment entities managed by AIG Asset Management, or the AIG Loan Agreement, which provides for a loan, or the AIG Loan, of $120 million, bearing interest at 4.08% per annum, and a seven-year term. As of March 31, 2017, there was $120 million outstanding under the AIG Loan Agreement. The AIG Loan Agreement provides for monthly payments of interest only for the first three years of the term and thereafter monthly principal and interest payments based on a 27-year amortization period. Our operating partnership used the net proceeds of the AIG Loan to partially repay the outstanding principal and accrued interest under our then-existing senior secured loan agreement. We are currently in technical violation of the net worth covenant in the AIG loan agreement, which we believe was the result of a drafting error. On May 3, 2017, we entered into an agreement with AIG pursuant to which AIG has agreed to waive this default from October 17, 2016 up to and including June 30, 2017. We believe that we will be in compliance with all covenants under the AIG Loan Agreement upon the closing of this offering.
The borrowings under the AIG Loan Agreement are secured by first lien mortgages on all of the properties in the Company Portfolio. The obligations under the AIG Loan Agreement are also guaranteed by our company and each of our operating partnership’s wholly-owned subsidiaries.
Torchlight Mezzanine Loan
On October 17, 2016, Plymouth Industrial 20 entered into a mezzanine loan agreement, or the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan Agreement, with Torchlight, which provides for a loan of $30 million, or the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan. The Torchlight Mezzanine Loan has a seven-year term and bears interest at 15% per annum, of which 7% percent is paid currently during the first four years of the term and 10% is paid for the remainder of the term. The Torchlight Mezzanine Loan requires Plymouth Industrial 20 to pay a repayment premium equal to the difference between (x) the sum of 150% of the principal being repaid (excluding accrued interest) and (y) the sum of the actual principal amount being repaid and current and accrued interest paid through the date of repayment. This repayment feature operates as a prepayment feature since the difference will be zero at maturity. The borrowings under the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan are secured by, among other things, pledges of the equity interest in Plymouth Industrial 20 and each of its property-owning subsidiaries. The proceeds of the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan were used to partially repay the outstanding principal and accrued interest under our then-existing senior secured loan agreement.
8
Summary Risk Factors
An investment in our common stock involves material risks. You should consider carefully the risks described below and under “Risk Factors” before purchasing shares of our common stock in this offering:
| • | The Company Portfolio is concentrated in the industrial real estate sector, and our business would be materially and adversely affected by an economic downturn in that sector. | |
| • | The Company Portfolio is geographically concentrated in seven states, which causes us to be especially susceptible to adverse developments in those markets. | |
| • | The Company Portfolio is comprised almost entirely of Class B industrial properties in secondary markets, which subjects us to risk associated with concentrating the Company Portfolio on such assets. | |
| • | We are subject to risks associated with single-tenant leases, and the default by one or more tenants could materially and adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition. | |
| • | We are subject to risks related to tenant concentration, which could materially adversely affect our cash flows, results of operations and financial condition. | |
| • | We may be unable to renew leases, lease vacant space or re-lease space as leases expire. | |
| • | We may be unable to identify and complete acquisitions of properties that meet our investment criteria, which may have a material adverse effect on our growth prospects. | |
| • | We may be unable to source “off-market” or “lightly-marketed” deal flows in the future, which may have a material adverse effect on our growth. | |
| • | Our success depends on key personnel whose continued service is not guaranteed, and the departure of one or more of our key personnel could adversely affect our ability to manage our business and to implement our growth strategies, or could create a negative perception in the capital markets. | |
| • | Our charter and bylaws, the partnership agreement of our operating partnership and Maryland law contain provisions that may delay, defer or prevent a change of control transaction. | |
| • | Failure to maintain our qualification as a REIT would have significant adverse consequences to us and the per share trading price of our common stock. | |
| • | We may be unable to make distributions at expected levels, and we may be required to borrow funds to make distributions. | |
| • | The number of shares of our common stock available for future issuance or sale could adversely affect the trading price of our common stock. |
Structure and Formation of Our Company
Our Company
We were formed as a Maryland corporation in March 2011 and previously conducted business as Plymouth Opportunity REIT, Inc. We conduct our business through an UPREIT structure in which our properties are owned by our operating partnership directly or through subsidiaries, as described below under “—Our Operating Partnership.” We are the sole general partner of our operating partnership and, upon completion of this offering and the redemption of the Preferred Interests, we will directly or indirectly own 100% of the OP units in our operating partnership and its subsidiaries. Our board of directors oversees our business and affairs.
Our Operating Partnership
Our operating partnership was formed as a Delaware limited partnership in March 2011. Substantially all of our assets are held by, and our operations are conducted through, our operating partnership. We will contribute the net proceeds from this offering to our operating partnership in exchange for OP units. Our interest in our operating partnership will generally entitle us to share in cash distributions from, and in the profits and losses of, our operating partnership in proportion to our percentage ownership. As the sole general partner of our operating partnership, we will generally have the exclusive power under the partnership agreement to manage and conduct its business and affairs, subject to certain limited approval and voting rights of the limited partners, which are described more fully below in “Description of the Partnership Agreement of Plymouth Industrial OP, LP.”
9
Corporate Structure
The chart below reflects our organizational structure immediately following completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions.
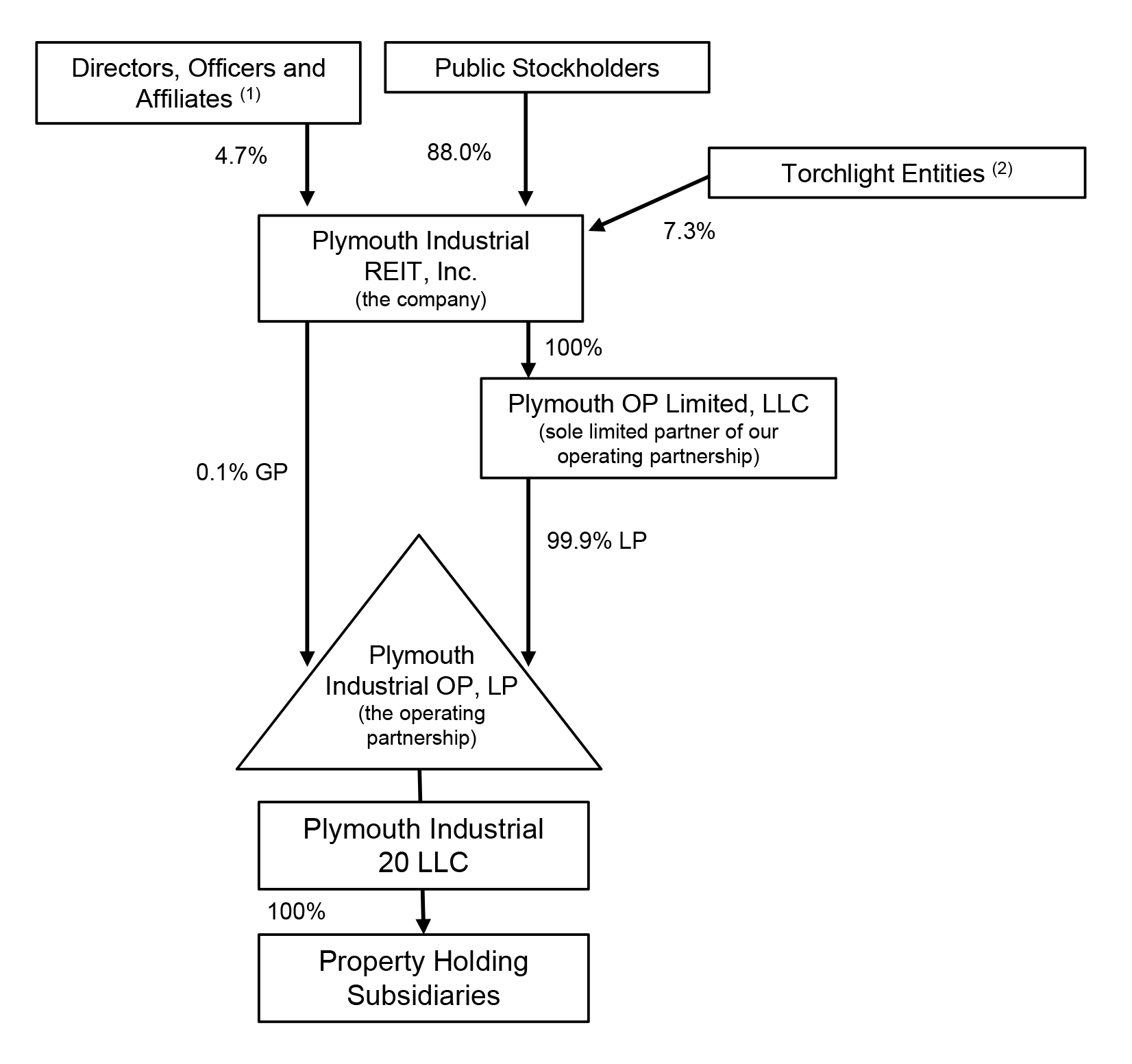
________________
| (1) | Reflects (a) an aggregate of 115,790 restricted shares of common stock to be granted to our executive officers and, (b) an aggregate of 15,789 restricted shares of common stock to be granted to our independent directors, in each case, concurrently with the completion of this offering. | |
| (2) | Reflects an aggregate of 263,158 shares of our common stock to be issued to DOF IV Plymouth PM, LLC in the Torchlight Transactions, and excludes warrants exercisable for 250,000 shares of common stock to be issued to DOF IV REIT Holdings, LLC in the Torchlight Transactions. |
Conflicts of Interest
Each of our executive officers entered into an employment agreement with us in April 2017. See “Executive Compensation—Executive Compensation Arrangements.” We may choose not to enforce, or to enforce less vigorously, our rights under these agreements because of our desire to maintain our ongoing relationships with members of our senior management, with possible negative impact on stockholders. Moreover, these agreements were not negotiated at arm’s length and certain of our executive officers had the ability to influence the types and level of benefits that they will receive from us under these agreements.
Conflicts of interest may exist or could arise in the future as a result of the relationships between us and our affiliates, on the one hand, and our operating partnership or any partner thereof, on the other. Our directors and officers have duties to our company under Maryland law in connection with their management of our company. At the same time, we, as the general partner of our operating partnership, have fiduciary duties and obligations to our operating partnership and its limited partners under Maryland law and the partnership agreement of our operating partnership in connection with the management of our operating partnership. Our fiduciary duties and obligations as the general partner of our operating partnership may come into conflict with the duties of our directors and officers to our company. We have adopted policies that are designed to eliminate or minimize certain potential conflicts of interests, and the partnership agreement of our operating partnership provides that, in the event of a conflict between the interests of us or our stockholders and the interests of our operating partnership or any of its limited partners, we may give priority to the separate interests of our company or our stockholders, including with respect to tax consequences to limited partners, assignees or our stockholders. See “Policies With Respect to Certain Activities—Conflict of Interest Policy” and “Description of the Partnership Agreement of Plymouth Industrial OP, LP.”
10
Tax Status
We elected to be taxed as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2012 and we believe that our organization and method of operation enable us to meet the requirements for qualification and taxation as a REIT. To maintain REIT qualification, we must meet a number of organizational and operational requirements, including a requirement that we annually distribute at least 90% of our REIT taxable income (determined without regard to the deduction for dividends paid and any net capital gain) to our stockholders. As a REIT, we generally will not be subject to federal income tax on our taxable income we currently distribute to our stockholders. If we fail to qualify as a REIT in any taxable year, we will be subject to federal income tax at regular corporate rates. Even if we qualify for taxation as a REIT, we may be subject to some federal, state and local taxes on our income or property. In addition, the income of any taxable REIT subsidiary that we own will be subject to taxation at regular corporate rates. See “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations.”
Distribution Policy
We made quarterly distributions in shares of our common stock beginning with the fiscal quarter ended September 30, 2012 through the fiscal quarter ended March 31, 2014. Following completion of this offering, we intend to make regular quarterly cash distributions to holders of shares of our common stock. Any future distributions we make will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend upon our earnings and financial condition, maintenance of our REIT qualification, applicable restrictions contained in the Maryland General Corporation Law, or the MGCL, and such other factors as our board may determine in its sole discretion. We anticipate that our estimated cash available for distribution will exceed the annual distribution requirements applicable to REITs. However, under some circumstances, we may be required to pay distributions in excess of cash available for distribution in order to meet these distribution requirements and may need to use the proceeds from future equity and debt offerings, sell assets or borrow funds to make some distributions. We have no intention to use the net proceeds of this offering to make distributions nor do we intend to make distributions using shares of common stock. We cannot assure you that our distribution policy will not change in the future. See “Distribution Policy.”
Restrictions on Ownership
Due to limitations on the concentration of ownership of REIT stock imposed by the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, our charter generally prohibits any person from actually, beneficially or constructively owning more than 9.8% in value or number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of the outstanding shares of any class or series of our capital stock. Our charter permits our board of directors, in its sole and absolute discretion, to exempt a person, prospectively or retroactively, from one or both of the ownership limits if, among other conditions, the person’s ownership of our stock in excess of the ownership limits would not cause us to fail to qualify as a REIT. Our board of directors may waive the ownership limit with respect to a particular person if it: (i) determines that such ownership will not cause any individual’s beneficial ownership of shares of our stock to violate the ownership limit and that any exemption from the ownership limit will not jeopardize our status as a REIT and (ii) determines that such stockholder does not and will not own, actually or constructively, an interest in a tenant of ours (or a tenant of any entity whose operations are attributed in whole or in part to us) that would cause us to own, actually or constructively, more than a 9.8% interest (as set forth in Section 856(d)(2)(B) of the Code) in such tenant or that any such ownership would not cause us to fail to qualify as a REIT under the Code.
Emerging Growth Company
We are an “emerging growth company,” as defined in the JOBS Act. For as long as we continue to be an emerging growth company, we may take advantage of exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies, including not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and shareholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. Although these exemptions will be available to us, they will not have a material impact on our public reporting and disclosure.
We could be an emerging growth company for up to five years, although circumstances could cause us to lose that status earlier. We will remain an “emerging growth company” until the earliest to occur of (i) the last day of the fiscal year during which our total annual revenues equal or exceed $1.0 billion (subject to adjustment for inflation), (ii) the last day of the fiscal year ending December 31, 2017, (iii) the date on which we have, during the previous three-year period, issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt, or (iv) the date on which we are deemed a “large accelerated filer” under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act.
Under the JOBS Act, emerging growth companies can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(13) of the Securities Act for complying with new or revised accounting standards. However, we are choosing to “opt out” of such extended transition period and, as a result, we will comply with any such new or revised accounting standards on the relevant dates on which adoption of such standards is required for non-emerging growth companies. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that our decision to opt out of the extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards is irrevocable.
Our Corporate Information
Our principal executive offices are located at 260 Franklin Street, 6th Floor, Boston, Massachusetts 02110. Our telephone number is (617) 340-3814. Our website is www.plymouthreit.com. The information found on, or otherwise accessible through, our website is not incorporated into, and does not form a part of, this prospectus or any other report or document we file with or furnish to you.
11
The Offering
| Common stock offered by us | 2,900,000 shares of common stock (plus up to an additional 435,000 shares of common stock that we may issue and sell upon the exercise of the underwriters’ over-allotment option). | |
| Common stock to be issued to the Torchlight Entities(1) | 263,158 shares of common stock | |
| Common stock to be outstanding after completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions(2) | 3,626,702 shares of common stock | |
| Use of proceeds | We estimate that the net proceeds (after deducting the underwriting discount and commissions and offering expenses payable by us) we will receive from the sale of shares of our common stock in this offering will be approximately $50.1 million (or approximately $57.8 million if the underwriters exercise their over-allotment option in full). We will contribute the net proceeds we receive from this offering to our operating partnership in exchange for OP units. | |
| We expect our operating partnership will use approximately $20.0 million of the net proceeds from this offering to redeem the Preferred Interests. Our operating partnership is expected to use the remaining net proceeds to acquire and manage additional industrial properties and for general corporate purposes. | ||
| Prior to the full deployment of the net proceeds as described above, we intend to invest the undeployed net proceeds in interest-bearing short-term investment grade securities or money-market accounts that are consistent with our intention to qualify as a REIT, including, for example, government and government agency certificates, certificates of deposit and interest-bearing bank deposits. We expect that these initial investments will provide a lower net return than we expect to receive from investments in industrial properties. If the underwriters exercise their over-allotment option in full, we expect to use the additional approximately $7.7 million of net proceeds to acquire additional properties or for general corporate purposes. See “Use of Proceeds.” | ||
| Risk Factors | Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully read and consider the information set forth under the heading “Risk Factors” beginning on page 16 and the other information included in this prospectus before investing in our common stock. | |
| NYSE MKT symbol | “PLYM” |
_____________________
| (1) | Represents shares of our common stock to be issued to the Torchlight Entities upon the completion of this offering, but excludes the 250,000 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of the warrants to be issued to the Torchlight Entities in connection with the Torchlight Transactions. |
| (2) | Includes (a) 2,900,000 shares of our common stock to be issued in this offering, (b) 263,158 shares of our common stock to be issued to the Torchlight Entities in connection with the Torchlight Transactions, (c) an aggregate of 15,789 restricted shares of common stock to be granted to our independent directors concurrently with the completion of this offering and (d) an aggregate of 115,790 restricted shares of common stock to be granted to our executive officers concurrently with the completion of this offering. Excludes (a) 435,000 shares of our common stock issuable upon the exercise of the underwriter’s over-allotment option in full, (b) 243,421 shares of our common stock available for future issuance under our 2014 Incentive Award Plan, and (c) 250,000 shares of our common stock issuable upon the exercise of the warrants to be issued to the Torchlight Entities in connection with the Torchlight Transactions. |
12
Summary Selected Financial Information
You should read the following summary financial and operating data in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operation,” our unaudited pro forma consolidated financial statements and related notes and the historical consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in the prospectus.
The unaudited pro forma consolidated balance sheet data is presented as if this offering and the Torchlight Transactions had occurred on March 31, 2017, and the unaudited pro forma statements of operations and other data for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and the year ended December 31, 2016 is presented as if this offering and the Torchlight Transactions had occurred on January 1, 2016. The pro forma consolidated financial information is not necessarily indicative of what our actual financial condition would have been as of March 31, 2017 or what our actual results of operations would have been assuming this offering had been completed as of January 1, 2016, nor does it purport to represent our future financial position or results of operations.
The summary unaudited historical condensed consolidated balance sheet information on March 31, 2017 and 2016 and the statement of operations data for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and March 31, 2016 have been derived from our financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The summary historical consolidated balance sheet information as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the historical consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 on pages 13 and 14 have been derived from the company’s consolidated financial statements, which were audited by Marcum LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm, and are included elsewhere in this prospectus.
| ($ in thousands) | As of March 31, | As of December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pro Forma | Historical | Historical | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Rental property, net of accumulated depreciation | $ | 121,207 | $ | 121,207 | $ | 128,170 | $ | 123,059 | $ | 129,714 | ||||||||||
| Investment in real estate joint venture | — | — | 2,968 | — | 2,987 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and other assets | 36,719 | 6,626 | 2,819 | 12,154 | 2,577 | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred lease intangibles, net | 9,610 | 9,610 | 13,560 | 10,533 | 14,773 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets | 167,536 | 137,443 | 147,517 | 145,746 | 150,051 | |||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities | 4,870 | 4,870 | 5,870 | 5,352 | 4,268 | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred lease intangibles, net | 1,278 | 1,278 | 1,806 | 1,405 | 1,941 | |||||||||||||||
| Senior secured debt, net | 116,258 | 116,258 | 199,500 | 116,053 | 196,800 | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred interest | 207 | 207 | 15,696 | 207 | 8,081 | |||||||||||||||
| Mezzanine debt to investor, net | 29,292 | 29,292 | — | 29,262 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Redeemable preferred member interest | — | 25,000 | — | 31,043 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities | 151,905 | 176,905 | 222,872 | 183,322 | 211,090 | |||||||||||||||
| Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. stockholders’ equity (deficit) | 15,631 | (98,467 | ) | (75,335 | ) | (98,026 | ) | (61,039 | ) | |||||||||||
| Non-controlling interest | — | 59,005 | — | 60,450 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Total equity (deficit) | $ | 15,631 | $ | (39,462 | ) | $ | (75,335 | ) | $ | (37,576 | ) | $ | (61,039 | ) | ||||||
13
| (In thousands) | Three Months Ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rental revenue | $ | 4,938 | $ | 4,938 | $ | 4,808 | $ | 19,658 | $ | 19,658 | $ | 19,290 | ||||||||||||
| Equity investment income (loss) | 1 | 1 | 30 | 230 | 230 | (85 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total revenues | 4,939 | 4,939 | 4,838 | 19,888 | 19,888 | 19,205 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Property | 1,408 | 1,408 | 1,412 | 5,927 | 5,927 | 5,751 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative | 886 | 724 | 911 | 4,392 | 3,742 | 4,688 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition costs | — | — | 19 | — | — | 1,061 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Offering costs | — | — | — | — | — | 938 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses | 5,066 | 4,904 | 5,370 | 21,993 | 21,343 | 24,574 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) | (127 | ) | 35 | (532 | ) | (2,105 | ) | (1,455 | ) | (5,369 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gain on disposition of equity investment | — | — | — | 2,846 | 2,846 | 1,380 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (2,603 | ) | (2,941 | ) | (13,784 | ) | (40,189 | ) | (40,679 | ) | (44,676 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Total other income (expense) | (2,603 | ) | (2,941 | ) | (13,784 | ) | (37,343 | ) | (37,833 | ) | (43,296 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net (loss) | (2,730 | ) | (2,906 | ) | (14,316 | ) | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest | — | (2,465 | ) | — | — | (2,301 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Net loss attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. common stockholders | $ | (2,730 | ) | $ | (441 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (36,987 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
14
| (In thousands) | Three Months Ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total in service Properties | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||
| NOI: (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,730 | ) | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
| General and administrative | 886 | 724 | 911 | 4,392 | 3,742 | 4,688 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition expense | — | — | 19 | — | — | 1,061 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 2,603 | 2,941 | 13,784 | 40,189 | 40,679 | 44,676 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Offering costs | — | — | — | — | — | 938 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other (income) expense | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | (30 | ) | (3,076 | ) | (3,076 | ) | (1,295 | ) | ||||||||||||
| NOI | $ | 3,530 | $ | 3,530 | $ | 3,396 | $ | 13,731 | $ | 13,731 | $ | 13,539 | ||||||||||||
| EBITDA: (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,730 | ) | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 2,603 | 2,941 | 13,784 | 40,189 | 40,679 | 44,676 | ||||||||||||||||||
| EBITDA | $ | 2,645 | $ | 2,807 | $ | 2,496 | $ | 12,415 | $ | 13,065 | $ | 8,147 | ||||||||||||
| FFO: (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,730 | ) | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gain on disposition of equity investment | — | — | — | (2,846 | ) | (2,846 | ) | (1,380 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Adjustment for unconsolidated joint ventures | — | — | — | 452 | 452 | 1,363 | ||||||||||||||||||
| FFO | $ | 42 | $ | (134 | ) | $ | (11,288 | ) | $ | (30,168 | ) | $ | (30,008 | ) | $ | (36,546 | ) | |||||||
| AFFO: (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FFO | $ | 42 | $ | (134 | ) | $ | (11,288 | ) | $ | (30,168 | ) | $ | (30,008 | ) | $ | (36,546 | ) | |||||||
| Amortization of above or accretion of below market lease rents | (83 | ) | (83 | ) | (88 | ) | (355 | ) | (355 | ) | (351 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Acquisition costs | — | — | 19 | — | — | 1,061 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Offering Costs | — | — | — | — | — | 938 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 162 | — | — | 650 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Distributions | — | — | 49 | 337 | 337 | 2,030 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Straight line rent | (45 | ) | (45 | ) | (75 | ) | (287 | ) | (287 | ) | (404 | ) | ||||||||||||
| AFFO | $ | 76 | $ | (262 | ) | $ | (11,383 | ) | $ | (29,823 | ) | $ | (30,313 | ) | $ | (33,272 | ) | |||||||
____________________
| (1) | For definitions and reconciliations of net income to NOI, EBITDA, FFO and AFFO, as well as a statement disclosing the reasons why our management believes that NOI, EBITDA, FFO and AFFO provide useful information to investors as to the financial performance of our company, and, to the extent material, any additional purposes for which our management uses NOI, EBITDA, FFO and AFFO, see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Non-GAAP Financial Measures.” |
15
RISK FACTORS
An investment in our common stock involves risks. In addition to other information in this prospectus, you should carefully consider the following risks before investing in our common stock. The occurrence of any of the following risks could materially and adversely affect our business, prospects, financial condition, results of operations and our ability to make cash distributions to our stockholders, which could cause you to lose all or a significant portion of your investment in our common stock. Some statements in this prospectus, including statements in the following risk factors, constitute forward-looking statements. See “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.”
Risks Related to Our Business and Operations
The Company Portfolio is concentrated in the industrial real estate sector, and our business would be adversely affected by an economic downturn in that sector.
Our assets are comprised entirely of industrial facilities, including warehouse/distribution facilities, light manufacturing facilities and flex/office facilities. This concentration may expose us to the risk of economic downturns in the industrial real estate sector to a greater extent than if our properties were more diversified across other sectors of the real estate industry. In particular, an economic downturn affecting the market for industrial properties could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, cash flows, financial condition and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
The Company Portfolio is geographically concentrated in seven states, which causes us to be especially susceptible to adverse developments in those markets.
In addition to general, regional, national and international economic conditions, our operating performance is impacted by the economic conditions of the specific geographic markets in which we have concentrations of properties. The Company Portfolio includes holdings in the following states (which will account for the percentage of our total annualized rent indicated) as of March 31, 2017: Ohio (48.7%); Illinois (18.4%); Tennessee (13.0%); Maine (7.4%); New Jersey (5.9%); Georgia (3.7%) and Kentucky (2.9%). This geographic concentration could adversely affect our operating performance if conditions become less favorable in any of the states or regions in which we have a concentration of properties. We cannot assure you that any of our target markets will grow or that underlying real estate fundamentals will be favorable to owners and operators of industrial properties. Our operations may also be affected if competing properties are built in our target markets. Any adverse economic or real estate developments in our target markets, or any decrease in demand for industrial space resulting from the regulatory environment, business climate or energy or fiscal problems, could materially and adversely impact our financial condition, results of operations, cash flow, our ability to satisfy our debt service obligations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
The Company Portfolio is comprised almost entirely of Class B industrial properties in secondary markets, which subjects us to risks associated with concentrating the Company Portfolio on such assets.
The Company Portfolio is comprised of almost entirely Class B industrial properties in secondary markets. While we believe that Class B industrial properties in secondary markets have shown positive trends, we cannot give any assurance that these trends will continue. Any developments or circumstances that adversely affect the value of Class B industrial properties generally could have a more significant adverse impact on us than if the Company Portfolio was diversified by asset type, which could materially and adversely impact our financial condition, results of operations and ability to make distributions to our stockholders.
Our business strategy depends on achieving revenue growth from anticipated increases in demand for Class B industrial space in our target markets; accordingly, any delay or a weaker than anticipated economic recovery could materially and adversely affect us and our growth prospects.
Our business strategy depends on achieving revenue growth from anticipated near-term growth in demand for Class B industrial space in our target markets as a result of improving demographic trends and supply and demand fundamentals. As a result, any delay or a weaker than anticipated economic recovery, particularly in our target markets, could materially and adversely affect us and our growth prospects. Furthermore, even if economic conditions generally improve, we cannot provide any assurances that demand for Class B industrial space will increase from current levels. If demand does not increase in the near future, or if demand weakens, our future results of operations and our growth prospects could also be materially and adversely affected.
16
We may not be aware of characteristics or deficiencies involving any one or all of the properties that we acquire in the future which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Newly acquired properties may have characteristics or deficiencies unknown to us that could affect their valuation or revenue potential and such properties may not ultimately perform to our expectations. We cannot assure you that the operating performance of any newly acquired properties will not decline under our management. Any characteristics or deficiencies in any newly acquired that adversely affect the value of the properties or their revenue-generation potential could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
We are subject to risks associated with single-tenant leases, and the default by one or more tenants could materially and adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
We are subject to the risk that the default, financial distress or bankruptcy of a single tenant could cause interruptions in the receipt of rental revenue and/or result in a vacancy, which is likely to result in the complete reduction in the operating cash flows generated by the property leased to that tenant and may decrease the value of that property. In addition, a majority of our leases generally require the tenant to pay all or substantially all of the operating expenses normally associated with the ownership of the property, such as utilities, real estate taxes, insurance and routine maintenance. Following a vacancy at a single-tenant property, we will be responsible for all of the operating costs at such property until it can be re-let, if at all.
We are subject to risks related to tenant concentration, which could materially adversely affect our cash flows, results of operations and financial condition.
As of March 31, 2017, one of our tenants comprised approximately 12.7% of our total annualized rent and our top three tenants collectively comprised approximately 29.8% of our total annualized rent. As a result, our financial performance will be dependent, in large part, on the revenues generated from these significant tenants and, in turn, the financial condition of these tenants. In the event that a tenant occupying a significant portion of one or more of our properties or whose rental income represents a significant portion of the rental revenue at our properties were to experience financial weakness or file bankruptcy, it could have a material adverse effect on our cash flows, results of operations and financial condition.
We may be unable to renew leases, lease vacant space or re-lease space as leases expire.
Leases representing 18.3%, 7.3% and 22.8% of the rentable square footage of the industrial properties in the Company Portfolio will expire in 2017, 2018 and 2019, respectively. We cannot assure you that our leases will be renewed or that our properties will be re-leased at rental rates equal to or above the current average rental rates or that we will not offer substantial rent abatements, tenant improvements, early termination rights or below-market renewal options to attract new tenants or retain existing tenants. If the rental rates for our properties decrease, or if our existing tenants do not renew their leases or we do not re-lease a significant portion of our available space and space for which leases will expire, our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock could be adversely affected.
Certain of our properties are subject to tenant rights of first refusal and options to repurchase, which could inhibit our ability to sell or retain such properties
Our tenants at 8288 Green Meadows Drive, 3500 Southwest Blvd. and 3100 Creekside Parkway each have rights of first refusal to purchase the property before we can sell any these properties to a third party. The existence of such rights of first refusal could limit third-party offers for such properties, inhibit our ability to sell a property or adversely affect the timing of any sale of any such property and affect our ability to obtain the highest price for any sale of such property.
Our tenant at 1875 Holmes Rd. has an option to repurchase the property at fair market value at the end of the lease term on October 31, 2019. The existence of the repurchase right could inhibit our ability to retain the 1875 Holmes Rd. property upon the expiration of the current lease.
We may be unable to identify and complete acquisitions of properties that meet our investment criteria, which may have a material adverse effect on our growth prospects.
Our primary investment strategy involves the acquisition of Class B industrial properties predominantly in secondary markets. These activities require us to identify suitable acquisition candidates or investment opportunities that meet our investment criteria and are compatible with our growth strategies. We may be unable to acquire properties identified as potential acquisition opportunities. Our ability to acquire properties on favorable terms, or at all, may expose us to the following significant risks:
| • | we may incur significant costs and divert management attention in connection with evaluating and negotiating potential acquisitions, including ones that we are subsequently unable to complete; | |
| • | even if we enter into agreements for the acquisition of properties, these agreements are subject to conditions to closing, which we may be unable to satisfy; and | |
| • | we may be unable to finance any given acquisition on favorable terms or at all. |
If we are unable to finance property acquisitions or acquire properties on favorable terms, or at all, our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock could be adversely affected. In addition, failure to identify or complete acquisitions of suitable properties could limit our growth.
17
Our acquisition activities may pose risks that could harm our business.
As a result of our future acquisitions, we may be required to incur debt and expenditures and issue additional common stock or OP units to pay for the acquired properties. These acquisitions may dilute our stockholders’ ownership interests, delay or prevent our profitability and may also expose us to risks such as:
| • | the possibility that we may not be able to successfully integrate any future acquisitions into the Company Portfolio; | |
| • | the possibility that senior management may be required to spend considerable time negotiating agreements and integrating acquired properties, diverting their attention from our other objectives; | |
| • | the possibility that we may overpay for a property; | |
| • | the possible loss or reduction in value of acquired properties; and | |
| • | the possibility of pre-existing undisclosed liabilities regarding acquired properties, including environmental or asbestos liability, for which our insurance may be insufficient or for which we may be unable to secure insurance coverage. |
We cannot assure you that the price for any future acquisitions will be similar to prior acquisitions. If our revenue does not keep pace with these potential acquisition and expansion costs, we may incur net losses. There is no assurance that we will successfully overcome these risks or other problems encountered with acquisitions.
We may obtain limited or no warranties when we purchase a property, which increases the risk that we may lose invested capital in or rental income from such property.
The seller of a property will often sell such property in its “as is” condition on a “where is” basis and “with all faults,” without any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular use or purpose. In addition, purchase agreements may contain only limited warranties, representations and indemnifications that will only survive for a limited period after the closing. Also, many sellers of real estate are single-purpose entities without any other significant assets. The purchase of properties with limited warranties or from undercapitalized sellers increases the risk that we may lose some or all of our invested capital in the property as well as the loss of rental income from such property.
We expect to have significant indebtedness outstanding following this offering, which may expose us to the risk of default under our debt obligations.
Upon completion of this offering, we anticipate that our total consolidated indebtedness will consist of approximately $150 million of indebtedness, which consists of expected borrowings under the AIG Loan and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan. We may incur significant additional debt to finance future acquisition and development activities.
Payments of principal and interest on borrowings may leave us with insufficient cash resources to operate our properties or to pay the dividends currently contemplated or necessary to maintain our REIT qualification. Our level of debt and the limitations imposed on us by our debt agreements could have significant adverse consequences, including the following:
| • | our cash flow may be insufficient to meet our required principal and interest payments; | |
| • | we may be unable to borrow additional funds as needed or on favorable terms, which could, among other things, adversely affect our ability to meet operational needs; | |
| • | we may be unable to refinance our indebtedness at maturity or the refinancing terms may be less favorable than the terms of our original indebtedness; | |
| • | we may be forced to dispose of one or more of our properties, possibly on unfavorable terms or in violation of certain covenants to which we may be subject; | |
| • | we may violate restrictive covenants in our loan documents, which would entitle the lenders to accelerate our debt obligations; and | |
| • | our default under any loan with cross default provisions could result in a default on other indebtedness. |
If any one of these events were to occur, our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock could be materially adversely affected. Furthermore, foreclosures could create taxable income without accompanying cash proceeds, which could hinder our ability to meet the REIT distribution requirements imposed by the Code. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Existing Indebtedness.”
18
We face significant competition for acquisitions of real properties, which may reduce the number of acquisition opportunities available to us and increase the costs of these acquisitions.
The current market for acquisitions of industrial properties in our target markets continues to be extremely competitive. This competition may increase the demand for our target properties and, therefore, reduce the number of suitable acquisition opportunities available to us and increase the prices paid for such acquisition properties. We also face significant competition for attractive acquisition opportunities from an indeterminate number of investors, including publicly traded and privately held REITs, private equity investors and institutional investment funds, some of which have greater financial resources than we do, a greater ability to borrow funds to acquire properties and the ability to accept more risk than we can prudently manage, including risks with respect to the geographic proximity of investments and the payment of higher acquisition prices. This competition will increase if investments in real estate become more attractive relative to other forms of investment. Competition for investments may reduce the number of suitable investment opportunities available to us and may have the effect of increasing prices paid for such acquisition properties and/or reducing the rents we can charge and, as a result, adversely affecting our operating results.
We may be unable to source “off-market” or “lightly-marketed” deal flow in the future, which may have a material adverse effect on our growth.
A key component of our investment strategy is to acquire additional industrial real estate assets. We seek to acquire properties before they are widely marketed by real estate brokers. Properties that are acquired in off-market or lightly-marketed transactions are typically more attractive to us as a purchaser because of the absence of a formal sales process, which could lead to higher prices. If we do not have access to off-market or lightly-marketed deal flow in the future, our ability to locate and acquire additional properties in our target markets at attractive prices could be materially adversely affected.
Our future acquisitions may not yield the returns we expect.
Our future acquisitions and our ability to successfully operate the properties we acquire in such acquisitions may be exposed to the following significant risks:
| • | even if we are able to acquire a desired property, competition from other potential acquirers may significantly increase the purchase price; | |
| • | we may acquire properties that are not accretive to our results upon acquisition, and we may not successfully manage and lease those properties to meet our expectations; | |
| • | our cash flow may be insufficient to meet our required principal and interest payments; | |
| • | we may spend more than budgeted amounts to make necessary improvements or renovations to acquired properties; | |
| • | we may be unable to quickly and efficiently integrate new acquisitions, particularly acquisitions of portfolios of properties, into our existing operations, and as a result our results of operations and financial condition could be adversely affected; | |
| • | market conditions may result in higher than expected vacancy rates and lower than expected rental rates; and | |
| • | we may acquire properties subject to liabilities and without any recourse, or with only limited recourse, with respect to unknown liabilities such as liabilities for clean-up of undisclosed environmental contamination, claims by tenants, vendors or other persons dealing with the former owners of the properties, liabilities incurred in the ordinary course of business and claims for indemnification by general partners, directors, officers and others indemnified by the former owners of the properties. |
If we cannot operate acquired properties to meet our financial expectations, our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock could be adversely affected.
19
High mortgage rates and/or unavailability of mortgage debt may make it difficult for us to finance or refinance properties, which could reduce the number of properties we can acquire, our net income and the amount of cash distributions we can make.
If mortgage debt is unavailable to us in the future at reasonable rates, we may not be able to finance the purchase of additional properties or refinance our properties on favorable terms or at all. If interest rates are higher when we refinance our properties, our income could be reduced. If any of these events occur, our cash flow could be reduced. This, in turn, could reduce cash available for distribution to our stockholders and materially and adversely affect our ability to raise more capital by issuing additional equity securities or by borrowing more money.
The AIG Loan and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan, and some of our future financing arrangements are expected to, involve balloon payment obligations, which may adversely affect our financial condition and our ability to make distributions.
Both the AIG Loan and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan require, and some of our future financing arrangements are expected to, require us to make a lump-sum or “balloon” payment at maturity. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Existing Indebtedness.” Our ability to satisfy a balloon payment at maturity is uncertain and may depend upon our ability to obtain additional financing or our ability to sell property securing such financing. At the time the balloon payment is due, we may or may not be able to refinance the existing financing on terms as favorable as the original loan or sell the property at a price sufficient to satisfy the balloon payment. The effect of a refinancing or sale could affect the rate of return to stockholders and the projected time of disposition of our assets. In addition, payments of principal and interest made to service our debts may leave us with insufficient cash to pay the distributions that we are required to pay to maintain our qualification as a REIT.
The AIG Loan and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan contain, and future indebtedness we incur may contain, various covenants, and the failure to comply with those covenants could materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
The AIG Loan and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan contain, and any future indebtedness we incur, including debt assumed pursuant to property acquisitions, may contain, certain covenants, which, among other things, restrict our activities, including, as applicable, our ability to sell the underlying property without the consent of the holder of such indebtedness, to repay or defease such indebtedness or to engage in mergers or consolidations that result in a change in control of our company. We may also be subject to financial and operating covenants. Failure to comply with any of these covenants would likely result in a default under the applicable indebtedness that would permit the acceleration of amounts due thereunder and under other indebtedness and foreclosure of properties, if any, serving as collateral therefor.
The AIG Loan and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan are secured by the Company Portfolio and the equity of Plymouth Industrial 20, respectively, so a default under either of these loan documents could result in a loss of the Company Portfolio.
The AIG Loan is secured by a first lien mortgage on each of the properties in the Company Portfolio. A default under the AIG Loan could result in the foreclosure on all, or a material portion, of the Company Portfolio, which could leave us with insufficient cash to make debt service payments on the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan and to make distributions to our stockholders. In addition, the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan is secured by a pledge of our equity interests in Plymouth Industrial 20, which is the sole member of each of the owners of the Company Portfolio. As a result, a default under the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan could result in the loss of all of our equity in Plymouth Industrial 20, resulting in the loss of all cash flow from the Company Portfolio.
The AIG Loan and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan restrict our ability to engage in some business activities, which could put us at a competitive disadvantage and materially adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
The AIG Loan and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan contain customary negative covenants and other financial and operating covenants that, among other things:
| • | restrict our ability to incur additional indebtedness; | |
| • | restrict our ability to dispose of properties; | |
| • | restrict our ability to make certain investments; | |
| • | restrict our ability to enter into material agreements; | |
| • | limit our ability to make capital expenditures; |
20
| • | require us to maintain a specified amount of capital in Plymouth Industrial 20; | |
| • | restrict our ability to merge with another company; | |
| • | restrict our ability to make distributions to stockholders; and | |
| • | require us to maintain financial coverage and leverage ratios. |
These limitations will restrict our ability to engage in some business activities, which could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock. In addition, debt agreements we enter into in the future may contain specific cross-default provisions with respect to specified other indebtedness, giving the lenders the right to declare a default if we are in default under other loans in some circumstances.
Future mortgage and other secured debt obligations expose us to the possibility of foreclosure, which could result in the loss of our investment in a property or group of properties subject to mortgage debt.
Incurring mortgage and other secured debt obligations increases our risk of property losses because defaults on indebtedness secured by properties may result in foreclosure actions initiated by lenders and ultimately our loss of the property securing any loans for which we are in default. Any foreclosure on a mortgaged property or group of properties could adversely affect the overall value of the Company Portfolio. For tax purposes, a foreclosure on any of our properties that is subject to a nonrecourse mortgage loan would be treated as a sale of the property for a purchase price equal to the outstanding balance of the debt secured by the mortgage. If the outstanding balance of the debt secured by the mortgage exceeds our tax basis in the property, we would recognize taxable income on foreclosure, but would not receive any cash proceeds, which could hinder our ability to meet the REIT distribution requirements imposed by the Code.
We may not be able to successfully operate our business or generate sufficient cash flows to make or sustain distributions to our stockholders as a publicly traded company or maintain our qualification as a REIT.
We may not be able to successfully operate our business or implement our operating policies and investment strategy as described in this prospectus. Failure to operate successfully as a listed public company, to develop and implement appropriate control systems and procedures in accordance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act or maintain our qualification as a REIT would have an adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flow and per share trading price of our common stock. See “—Risks Related to Our Status as a REIT—Failure to maintain our qualification as a REIT would have significant adverse consequences to us and the per share trading price of our common stock.” Furthermore, we may not be able to generate sufficient cash flows to pay our operating expenses, service any debt we may incur in the future and make distributions to our stockholders. Our ability to successfully operate our business and implement our operating policies and investment strategy will depend on many factors, including:
| • | the availability of, and our ability to identify, attractive acquisition opportunities consistent with our investment strategy; | |
| • | our ability to contain renovation, maintenance, marketing and other operating costs for our properties; | |
| • | our ability to maintain high occupancy rates and target rent levels; | |
| • | costs that are beyond our control, including title litigation, litigation with tenants, legal compliance, real estate taxes and insurance; interest rate levels and volatility, such as the accessibility of short- and long-term financing on desirable terms; and | |
| • | economic conditions in our target markets as well as the condition of the financial and real estate markets and the economy generally. |
Upon completion of this offering, even though we will be an “emerging growth company” as defined in the JOBS Act and therefore may take advantage of various exemptions to public reporting requirements (see “—We are an ‘emerging growth company,’ and we cannot be certain if the reduced reporting requirements applicable to emerging growth companies will make our common stock less attractive to investors”), we will still be required to implement substantial control systems and procedures in order to maintain our qualification as a REIT, satisfy our periodic and current reporting requirements under applicable SEC regulations and comply with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010, or Dodd Frank, and the NYSE MKT or other relevant listing standards. As a result, we will incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses, particularly after we are no longer an “emerging growth company,” and our management and other personnel will need to devote a substantial amount of time to comply with these rules and regulations and establish the corporate infrastructure and control systems and procedures demanded of a publicly traded REIT. These costs and time commitments could be substantially more than we currently expect.
The Stockholders Agreement will grant Torchlight certain rights that may restrain our ability to take various actions in the future.
Immediately upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, we intend to enter into the Stockholders Agreement with Torchlight in order to establish various arrangements with respect to governance of our company and certain rights that will be granted to the Torchlight in connection with the Torchlight Transactions. Pursuant to the terms of the Stockholders Agreement, within 30 days of the closing of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, and as long as Torchlight maintains beneficial ownership of at least 2.5% of our then outstanding shares of common stock, Torchlight will be entitled to nominate one director to our board of directors. In connection with this board nomination right, the size of our board will be increased to seven directors and the vacancy will be filled by Torchlight’s nominee.
In addition, the Stockholders Agreement will provide that, for so long as Torchlight’s level of beneficial ownership is equal to or greater than 2.5% of our outstanding common stock, we will be prohibited from issuing preferred stock of any class. Torchlight’s rights under the Stockholders Agreement may prohibit us from taking certain actions that would benefit our other stockholders.
21
Under the Stockholders Agreement, Torchlight is also entitled, subject to certain exceptions, to certain customary registration rights, including the requirement that we file a registration statement registering the resale of (1) the 263,158 shares of common stock and (2) the 250,000 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of the warrants issued in the Torchlight Transactions following the first anniversary of the closing of this offering or to participate in future offerings of our common stock. In addition, Torchlight will have a pre-emptive right to participate in future issuances of common stock by the company for so long as Torchlight maintains beneficial ownership of at least 2.5% of our outstanding common stock. These rights may reduce our ability to raise capital through the equity capital markets in the future because we will be required to accommodate sales of our common stock by Torchlight. See “Shares Eligible for Future Sale.”
If Torchlight’s beneficial ownership of our outstanding common stock falls below the percentage threshold set forth above, Torchlight will promptly cause its nominated director to resign from our board of directors and all of the rights set forth above shall be terminated, even if Torchlight subsequently acquires additional shares of our common stock through the exercise of warrants or otherwise. See “Management—Stockholders Agreement with Torchlight.”
We face significant competition in the leasing market, which may decrease or prevent increases of the occupancy and rental rates of our properties.
We compete with numerous developers, owners and operators of real estate, many of whom own properties similar to ours in the same submarkets in which our properties are located. If our competitors offer space at rental rates below current market rates, or below the rental rates we currently charge our tenants, we may lose existing or potential tenants and we may be pressured to reduce our rental rates below those we currently charge or to offer more substantial rent abatements, tenant improvements, early termination rights or below-market renewal options in order to retain tenants when our tenants’ leases expire. As a result, our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the value of, our common stock could be adversely affected.
We may be required to make rent or other concessions and/or significant capital expenditures to improve our properties in order to retain and attract tenants, causing our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock to be adversely affected.
In order to attract and retain tenants, we may be required to make rent or other concessions to tenants, accommodate requests for renovations, build-to-suit remodeling and other improvements or provide additional services to our tenants. Additionally, when a tenant at one of our properties does not renew its lease or otherwise vacates its space, it is likely that, in order to attract one or more new tenants, we will be required to expend funds for improvements in the vacated space. As a result, we may have to make significant capital or other expenditures in order to retain tenants whose leases expire and to attract new tenants in sufficient numbers. Additionally, we may need to raise capital to make such expenditures. If we are unable to do so or if capital is otherwise unavailable, we may be unable to make the required expenditures. This could result in non-renewals by tenants upon expiration of their leases, which could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
A substantial majority of the leases in the Company Portfolio are with tenants who have non-investment grade credit ratings, which may result in our leasing to tenants that are more likely to default in their obligations to us than an entity with an investment grade credit rating.
A substantial majority of the leases in the Company Portfolio are with tenants who have non-investment grade credit ratings. The ability of a non-investment grade tenant to meet its obligations to us cannot be considered as well assured as that of an investment grade tenant. All of our tenants may face exposure to adverse business or economic conditions which could lead to an inability to meet their obligations to us. However, non-investment grade tenants may not have the financial capacity or liquidity to adapt to these conditions or may have less diversified businesses, which may exacerbate the effects of adverse conditions on their businesses. Moreover, the fact that so many of our tenants are not investment grade may cause investors or lenders to view our cash flows as less stable, which may increase our cost of capital, limit our financing options or adversely affect the trading price of our common stock.
The actual rents we receive for the Company Portfolio may be less than our asking rents, and we may experience lease roll down from time to time.
As a result of various factors, including competitive pricing pressure in our submarkets, adverse conditions in our target markets, a general economic downturn and a decline in the desirability of our properties compared to other properties in our submarkets, we may be unable to realize the asking rents for properties in the Company Portfolio. In addition, the degree of discrepancy between our asking rents and the actual rents we are able to obtain may vary both from property to property and among different leased spaces within a single property. If we are unable to obtain rental rates comparable to our asking rents for the properties in the Company Portfolio, our ability to generate cash flow growth will be negatively impacted. In addition, depending on fluctuations in asking rental rates at any given time, from time to time rental rates for expiring leases in the Company Portfolio may be higher than starting rental rates for new leases.
We may acquire properties or portfolios of properties through tax-deferred contribution transactions, which could result in stockholder dilution and limit our ability to sell such assets.
In the future, we may acquire properties or portfolios of properties through tax-deferred contribution transactions in exchange for partnership interests in our operating partnership, which may result in stockholder dilution. This acquisition structure may have the effect of, among other things, reducing the amount of tax depreciation we are able to deduct over the tax life of the acquired properties, and may require that we agree to protect the contributors’ ability to defer recognition of taxable gain through restrictions on our ability to dispose of the acquired properties and/or the allocation of partnership debt to the contributors to maintain their tax bases. These restrictions limit our ability to sell an asset at a time, or on terms, that would be favorable absent such restrictions.
22
Any real estate development and re-development activities are subject to risks particular to development and re-development.
We may engage in development and redevelopment activities with respect to certain of our properties. To the extent that we do so, we will be subject to the following risks associated with such development and redevelopment activities:
| • | unsuccessful development or redevelopment opportunities could result in direct expenses to us; | |
| • | construction or redevelopment costs of a project may exceed original estimates, possibly making the project less profitable than originally estimated, or unprofitable; | |
| • | time required to complete the construction or redevelopment of a project or to lease up the completed project may be greater than originally anticipated, thereby adversely affecting our cash flow and liquidity; | |
| • | contractor and subcontractor disputes, strikes, labor disputes or supply disruptions; | |
| • | failure to achieve expected occupancy and/or rent levels within the projected time frame, if at all; | |
| • | delays with respect to obtaining or the inability to obtain necessary zoning, occupancy, land use and other governmental permits, and changes in zoning and land use laws; | |
| • | occupancy rates and rents of a completed project may not be sufficient to make the project profitable; | |
| • | our ability to dispose of properties developed or redeveloped with the intent to sell could be impacted by the ability of prospective buyers to obtain financing given the current state of the credit markets; and | |
| • | the availability and pricing of financing to fund our development activities on favorable terms or at all. |
These risks could result in substantial unanticipated delays or expenses and, under certain circumstances, could prevent completion of development or redevelopment activities once undertaken, any of which could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
Our success depends on key personnel whose continued service is not guaranteed, and the departure of one or more of our key personnel could adversely affect our ability to manage our business and to implement our growth strategies, or could create a negative perception in the capital markets.
Our continued success and our ability to manage anticipated future growth depend, in large part, upon the efforts of key personnel, particularly Messrs. Witherell and White, who have extensive market knowledge and relationships and exercise substantial influence over our operational, financing, acquisition and disposition activity.
Our ability to retain our senior management, particularly Messrs. Witherell and White, or to attract suitable replacements should any member of our senior management leave, is dependent on the competitive nature of the employment market. We have not obtained and do not expect to obtain key man life insurance on any of our key personnel. The loss of services of one or more members of our senior management team, or our inability to attract and retain highly qualified personnel, could adversely affect our business, diminish our investment opportunities and weaken our relationships with lenders, business partners, existing and prospective tenants and industry participants. Further, the loss of a member of our senior management team could be negatively perceived in the capital markets. Any of these developments could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the value of, our common stock.
Potential losses, including from adverse weather conditions and natural disasters, may not be covered by insurance.
We will carry commercial property, liability and terrorism coverage on all the properties in the Company Portfolio under a blanket insurance policy, in addition to other coverages that may be appropriate for certain of our properties. We will select policy specifications and insured limits that we believe to be appropriate and adequate given the relative risk of loss, the cost of the coverage and industry practice. Some of our policies will be insured subject to limitations involving large deductibles or co-payments and policy limits that may not be sufficient to cover losses, which could affect certain of our properties that are located in areas particularly susceptible to natural disasters. In addition, we may discontinue terrorism or other insurance on some or all of our properties in the future if the cost of premiums for any such policies exceeds, in our judgment, the value of the coverage discounted for the risk of loss. We will not carry insurance for certain types of extraordinary losses, such as loss from riots, war, earthquakes and wildfires because such coverage may not be available or is cost prohibitive or available at a disproportionately high cost. As a result, we may incur significant costs in the event of loss from riots, war, earthquakes, wildfires and other uninsured losses.
23
If we or one or more of our tenants experiences a loss that is uninsured or that exceeds policy limits, we could lose the capital invested in the damaged properties as well as the anticipated future cash flows from those properties. In addition, if the damaged properties are subject to recourse indebtedness, we would continue to be liable for the indebtedness, even if these properties were irreparably damaged. Furthermore, we may not be able to obtain adequate insurance coverage at reasonable costs in the future as the costs associated with property and casualty renewals may be higher than anticipated.
We may not be able to rebuild the Company Portfolio to its existing specifications if we experience a substantial or comprehensive loss of such properties.
In the event that we experience a substantial or comprehensive loss of one of our properties, we may not be able to rebuild such property to its existing specifications. Further, reconstruction or improvement of such a property would likely require significant upgrades to meet zoning and building code requirements. Environmental and legal restrictions could also restrict the rebuilding of our properties.
Existing conditions at some of our properties may expose us to liability related to environmental matters.
Independent environmental consultants conducted a Phase I or similar environmental site assessment of our properties at the time of their acquisition or in connection with subsequent financings. Such Phase I or similar environmental site assessments are limited in scope and may not include or identify all potential environmental liabilities or risks associated with the relevant properties. We have not obtained and do not intend to obtain new or updated Phase I or similar environmental site assessments in connection with this offering, which may expose us to liability related to unknown or unanticipated environmental matters. Unless required by applicable laws or regulations, we may not further investigate, remedy or ameliorate the liabilities disclosed in the existing Phase I or similar environmental site assessments and this failure may expose us to liability in the future.
We may be unable to sell a property if or when we decide to do so.
We expect to hold the various real properties until such time as we decide that a sale or other disposition is appropriate. Our ability to dispose of properties on advantageous terms depends on factors beyond our control, including competition from other sellers and the availability of attractive financing for potential buyers of our properties. We cannot predict the various market conditions affecting the industrial real estate market which will exist at any particular time in the future. Due to the uncertainty of market conditions which may affect the future disposition of our properties, we cannot assure you that we will be able to sell our properties at a profit in the future, which could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the value of, our common stock.
Furthermore, we may be required to expend funds to correct defects or to make improvements before a property can be sold. We cannot assure you that we will have funds available to correct such defects or to make such improvements.
Joint venture investments could be adversely affected by our lack of sole decision-making authority, our reliance on co-venturers’ financial condition and disputes between us and our co-venturers.
We may co-invest in the future with third parties through partnerships, joint ventures or other entities, acquiring non-controlling interests in or sharing responsibility for managing the affairs of a property, partnership, joint venture or other entity. In such event, we would not be in a position to exercise sole decision-making authority regarding the property, partnership, joint venture or other entity. Investments in partnerships, joint ventures or other entities may, under certain circumstances, involve risks not present were a third party not involved, including the possibility that partners or co-venturers might become bankrupt or fail to fund their share of required capital contributions. Partners or co-venturers may have economic or other business interests or goals which are inconsistent with our business interests or goals, and may be in a position to take actions contrary to our policies or objectives, and they may have competing interests in our markets that could create conflict of interest issues. Such investments may also have the potential risk of impasses on decisions, such as a sale, because neither we nor the partner or co-venturer would have full control over the partnership or joint venture. In addition, prior consent of our joint venture partners may be required for a sale or transfer to a third party of our interests in the joint venture, which would restrict our ability to dispose of our interest in the joint venture. If we become a limited partner or non-managing member in any partnership or limited liability company and such entity takes or expects to take actions that could jeopardize our company’s status as a REIT or require us to pay tax, we may be forced to dispose of our interest in such entity. Disputes between us and partners or co-venturers may result in litigation or arbitration that would increase our expenses and prevent our officers and/or directors from focusing their time and effort on our business. Consequently, actions by or disputes with partners or co-venturers might result in subjecting properties owned by the partnership or joint venture to additional risk. In addition, we may in certain circumstances be liable for the actions of our third-party partners or co-venturers. Our joint ventures may be subject to debt and, in the current volatile credit market, the refinancing of such debt may require equity capital calls.
24
If we fail to implement and maintain an effective system of integrated internal controls, or to remediate the material weaknesses we have identified in our internal control over financial reporting and disclosure controls and procedures, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results.
As a publicly traded company, we will be required to comply with the applicable provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which requires, among other things, that we establish and maintain effective internal controls and procedures for financial reporting and effective disclosure controls and procedures for making required filings with the SEC. Effective internal and disclosure controls are necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports and effectively prevent fraud and to operate successfully as a public company. If we cannot provide reliable financial reports or prevent fraud, our reputation and operating results would be harmed.
The process for designing and implementing an effective system of integrated internal controls is a continuous effort that requires significant resources and devotion of time, and material weaknesses in our internal controls also may result in certain deficiencies in our disclosure controls and procedures. As part of the ongoing monitoring of internal controls required of publicly traded companies, and in connection with management’s evaluation of our internal control over financial reporting and disclosure controls and procedures as of March 31, 2017, we identified material weaknesses in our internal controls and our disclosure controls and procedures. In particular, we identified as a material weakness that we did not have a sufficient number of adequately trained technical accounting and external reporting personnel to support stand-alone external financial reporting under SEC requirements. Although we have developed and are in the process of implementing a remediation plan for the identified material weaknesses, we can provide no assurances that our remediation plan will adequately remediate the identified material weakness. The Company continues to evaluate what additional policies and procedures may be necessary, how to most effectively communicate the policies and procedures to its personnel and how to improve our financial reporting system. We expect that work on the plan to remediate the identified weaknesses will continue throughout 2017, as financial resources permit.
There is no assurance that we will be successful in remediating the identified deficiencies in our internal controls or that we will be successful in remediating any additional deficiencies that may arise in the future. If the remedial measures we are implementing are insufficient to address any of the identified material weaknesses or are not implemented effectively, or additional deficiencies arise in the future, material misstatements in our interim or annual financial statements may occur in the future. Among other things, any unremediated material weaknesses could result in material post-closing adjustments in future financial statements. In addition, as an “emerging growth company,” our independent registered public accounting firm will not be required to formally attest to the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting until the date we are no longer an “emerging growth company,” which may be up until December 31, 2017.
Any failure to maintain effective controls or timely effect any necessary improvement of our internal and disclosure controls could harm operating results or cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations, which could adversely affect our ability to remain listed with the NYSE MKT. Ineffective internal and disclosure controls could also cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information, which would likely have a negative effect on the per share trading price of our common stock.
Our growth depends on external sources of capital that are outside of our control and may not be available to us on commercially reasonable terms or at all.
In order to maintain our qualification as a REIT, we are required under the Code, among other things, to distribute annually at least 90% of our REIT taxable income, determined without regard to the dividends paid deduction and excluding any net capital gain. In addition, we will be subject to income tax at regular corporate rates to the extent that we distribute less than 100% of our REIT taxable income, including any net capital gains. Because of these distribution requirements, we may not be able to fund future capital needs, including any necessary acquisition financing, from operating cash flow. Consequently, we intend to rely on third-party sources to fund our capital needs. We may not be able to obtain such financing on favorable terms or at all and any additional debt we incur will increase our leverage and likelihood of default. Our access to third-party sources of capital depends, in part, on:
| • | general market conditions; | |
| • | the market’s perception of our growth potential; | |
| • | our current debt levels; | |
| • | our current and expected future earnings; | |
| • | our cash flow and cash distributions; and | |
| • | the market price per share of our common stock. |
25
In recent years, the capital markets have been subject to significant disruptions. If we cannot obtain capital from third-party sources, we may not be able to acquire or develop properties when strategic opportunities exist, meet the capital and operating needs of the Company Portfolio, satisfy our debt service obligations or make the cash distributions to our stockholders necessary to maintain our qualification as a REIT.
We are an “emerging growth company,” and we cannot be certain if the reduced reporting requirements applicable to emerging growth companies will make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an “emerging growth company” as defined in the JOBS Act. We will remain an “emerging growth company until the earliest to occur of:
| • | the last day of the fiscal year during which our total annual revenue equals or exceeds $1 billion (subject to adjustment for inflation); | |
| • | the last day of the fiscal year ending December 31, 2017; | |
| • | the date on which we have, during the previous three-year period, issued more than $1 billion in non-convertible debt; or | |
| • | the date on which we are deemed to be a “large accelerated filer” under the Exchange Act. |
We may take advantage of exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies, including but not limited to, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. We cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive because we may rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our per share trading price may be adversely affected and more volatile.
Risks Related to the Real Estate Industry
Our performance and value are subject to risks associated with real estate assets and the real estate industry.
Our ability to pay expected dividends to our stockholders depends on our ability to generate revenues in excess of expenses, scheduled principal payments on debt and capital expenditure requirements. Events and conditions generally applicable to owners and operators of real property that are beyond our control may decrease cash available for distribution and the value of our properties. These events include many of the risks set forth above under “—Risks Related to Our Business and Operations,” as well as the following:
| • | local oversupply or reduction in demand for industrial space; | ||
| • | adverse changes in financial conditions of buyers, sellers and tenants of properties; | ||
| • | vacancies or our inability to rent space on favorable terms, including possible market pressures to offer tenants rent abatements, tenant improvements, early termination rights or below-market renewal options, and the need to periodically repair, renovate and re-lease space; | ||
| • | increased operating costs, including insurance premiums, utilities, real estate taxes and state and local taxes; | ||
| • | civil unrest, acts of war, terrorist attacks and natural disasters, including earthquakes, floods and wildfires, which may result in uninsured or underinsured losses; | ||
| • | decreases in the underlying value of our real estate; changing submarket demographics; and | ||
| • | changing traffic patterns. | ||
In addition, periods of economic downturn or recession, rising interest rates or declining demand for real estate, or the public perception that any of these events may occur, could result in a general decline in rents or an increased incidence of defaults under existing leases, which would adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
26
Illiquidity of real estate investments could significantly impede our ability to respond to adverse changes in the performance of our properties and harm our financial condition.
The real estate investments made, and to be made, by us are relatively difficult to sell quickly. As a result, our ability to promptly sell one or more properties in the Company Portfolio in response to changing economic, financial and investment conditions is limited. Return of capital and realization of gains, if any, from an investment generally will occur upon disposition or refinancing of the underlying property. We may be unable to realize our investment objectives by sale, other disposition or refinancing at attractive prices within any given period of time or may otherwise be unable to complete any exit strategy. Our ability to dispose of one or more properties within a specific time period is subject to the possible weakness in or even the lack of an established market for a property, changes in the financial condition or prospects of prospective purchasers, changes in national or international economic conditions, and changes in laws, regulations or fiscal policies of jurisdictions in which the property is located.
In addition, the Code imposes restrictions on a REIT’s ability to dispose of properties that are not applicable to other types of real estate companies. In particular, the tax laws applicable to REITs effectively require that we hold our properties for investment, rather than primarily for sale in the ordinary course of business, which may cause us to forego or defer sales of properties that otherwise would be in our best interest. Therefore, we may not be able to vary the Company Portfolio in response to economic or other conditions promptly or on favorable terms, which may adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
Declining real estate valuations and impairment charges could materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
We intend to review the carrying value of our properties when circumstances, such as adverse market conditions, indicate a potential impairment may exist. We intend to base our review on an estimate of the future cash flows (excluding interest charges) expected to result from the property’s use and eventual disposition on an undiscounted basis. We intend to consider factors such as future operating income, trends and prospects, as well as the effects of leasing demand, competition and other factors. If our evaluation indicates that we may be unable to recover the carrying value of a real estate investment, an impairment loss will be recorded to the extent that the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value of the property.
Impairment losses have a direct impact on our operating results because recording an impairment loss results in an immediate negative adjustment to our operating results. The evaluation of anticipated cash flows is highly subjective and is based in part on assumptions regarding future occupancy, rental rates and capital requirements that could differ materially from actual results in future periods. A worsening real estate market may cause us to reevaluate the assumptions used in our impairment analysis. Impairment charges could materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
Adverse economic conditions and the dislocation in the credit markets could materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
Ongoing challenging economic conditions have negatively impacted the lending and capital markets, particularly for real estate. The capital markets have experienced significant adverse conditions in recent years, including a substantial reduction in the availability of, and access to, capital. The risk premium demanded by lenders has increased markedly, as they are demanding greater compensation for risk, and underwriting standards have been tightened. In addition, failures and consolidations of certain financial institutions have decreased the number of potential lenders, resulting in reduced lending sources available to the market. These conditions may limit the amount of indebtedness we are able to obtain and our ability to refinance our indebtedness, and may impede our ability to develop new properties and to replace construction financing with permanent financing, which could result in our having to sell properties at inopportune times and on unfavorable terms. If these conditions continue, our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock could be materially adversely affected.
The lack of availability of debt financing may require us to rely more heavily on additional equity issuances, which may be dilutive to our current stockholders, or on less efficient forms of debt financing. Additionally, the limited amount of financing currently available may reduce the value of our properties and limit our ability to borrow against such properties, which could materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
Acquired properties may be located in new markets where we may face risks associated with investing in an unfamiliar market.
We have acquired, and may continue to acquire, properties in markets that are new to us. When we acquire properties located in new markets, we may face risks associated with a lack of market knowledge or understanding of the local economy, forging new business relationships in the area and unfamiliarity with local government and permitting procedures.
27
We may choose not to distribute the proceeds of any sales of real estate to our stockholders, which may reduce the amount of our cash distributions to stockholders.
We may choose not to distribute any proceeds from the sale of real estate investments to our stockholders. Instead, we may elect to use such proceeds to:
| • | acquire additional real estate investments; | ||
| • | repay debt; | ||
| • | buy out interests of any partners in any joint venture in which we are a party; | ||
| • | create working capital reserves; or | ||
| • | make repairs, maintenance, tenant improvements or other capital improvements or expenditures on our other properties. | ||
Any decision to retain or invest the proceeds of any sales, rather than distribute such proceeds to our stockholders may reduce the amount of cash distributions you receive on your common stock.
Uninsured losses relating to real property may adversely affect your returns.
We attempt to ensure that all of our properties are adequately insured to cover casualty losses. However, there are certain losses, including losses from floods, earthquakes, wildfires, acts of war, acts of terrorism or riots, that are not generally insured against or that are not generally fully insured against because it is not deemed economically feasible or prudent to do so. In addition, changes in the cost or availability of insurance could expose us to uninsured casualty losses. In the event that any of our properties incurs a casualty loss that is not fully covered by insurance, the value of our assets will be reduced by the amount of any such uninsured loss, and we could experience a significant loss of capital invested and potential revenue in these properties and could potentially remain obligated under any recourse debt associated with the property. Moreover, we, as the general partner of our operating partnership, generally will be liable for all of our operating partnership’s unsatisfied recourse obligations, including any obligations incurred by our operating partnership as the general partner of joint ventures. Any such losses could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock. In addition, we may have no source of funding to repair or reconstruct the damaged property, and we cannot assure you that any such sources of funding will be available to us for such purposes in the future. We evaluate our insurance coverage annually in light of current industry practice through an analysis prepared by outside consultants.
Our property taxes could increase due to property tax rate changes or reassessment, which could adversely impact our cash flows.
Even if we maintain our qualification as a REIT for federal income tax purposes, we will be required to pay some state and local taxes on our properties. The real property taxes on our properties may increase as property tax rates change or as our properties are assessed or reassessed by taxing authorities. The amount of property taxes we pay in the future may increase substantially from what we have paid in the past. If the property taxes we pay increase, our cash flow would be adversely impacted to the extent that we are not reimbursed by tenants for those taxes, and our ability to pay any expected dividends to our stockholders could be adversely affected.
We could incur significant costs related to government regulation and litigation over environmental matters.
Under various federal, state and local laws and regulations relating to the environment, as a current or former owner or operator of real property, we may be liable for costs and damages resulting from the presence or discharge of hazardous or toxic substances, waste or petroleum products at, on, in, under or migrating to or from such property, including costs to investigate, clean up such contamination and liability for harm to natural resources. Such laws often impose liability without regard to whether the owner or operator knew of, or was responsible for, the presence of such contamination, and the liability may be joint and several. These liabilities could be substantial and the cost of any required remediation, removal, fines or other costs could exceed the value of the property and/or our aggregate assets. In addition, the presence of contamination or the failure to remediate contamination at our properties may expose us to third-party liability for costs of remediation and/or personal, property, or natural resources damage or materially adversely affect our ability to sell, lease or develop our properties or to borrow using the properties as collateral. In addition, environmental laws may create liens on contaminated sites in favor of the government for damages and costs it incurs to address such contamination. Moreover, if contamination is discovered on our properties, environmental laws may impose restrictions on the manner in which property may be used or businesses may be operated, and these restrictions may require substantial expenditures.
28
Some of the properties in the Company Portfolio have been or may be impacted by contamination arising from current or prior uses of the property, or adjacent properties, for commercial or industrial purposes. Such contamination may arise from spills of petroleum or hazardous substances or releases from tanks used to store such materials.
From time to time, we may acquire properties with known adverse environmental conditions where we believe that the environmental liabilities associated with these conditions are quantifiable and that the acquisition will yield a superior risk-adjusted return. We usually perform a Phase I environmental site assessment at any property we are considering acquiring. In connection with certain financing transactions our lenders have commissioned independent environmental consultants to conduct Phase I environmental site assessments on the properties in the Company Portfolio. However, we have not always received copies of the Phase I environmental site assessment reports commissioned by our lenders and, as such, may not be aware of all potential or existing environmental contamination liabilities at the properties in the Company Portfolio. In addition, Phase I environmental site assessments are limited in scope and do not involve sampling of soil, soil vapor, or groundwater, and these assessments may not include or identify all potential environmental liabilities or risks associated with the property. Even where subsurface investigation is performed, it can be very difficult to ascertain the full extent of environmental contamination or the costs that are likely to flow from such contamination. We cannot assure you that the Phase I environmental site assessment or other environmental studies identified all potential environmental liabilities, or that we will not face significant remediation costs or other environmental contamination that makes it difficult to sell any affected properties. Also, we have not always implemented actions recommended by these assessments, and recommended investigation and remediation of known or suspected contamination has not always been performed. As a result, we could potentially incur material liability for these issues, which could adversely impact our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
Environmental laws also govern the presence, maintenance and removal of asbestos-containing building materials, or ACBM, and may impose fines and penalties for failure to comply with these requirements. Such laws require that owners or operators of buildings containing ACBM (and employers in such buildings) properly manage and maintain the asbestos, adequately notify or train those who may come into contact with asbestos, and undertake special precautions, including removal or other abatement, if asbestos would be disturbed during renovation or demolition of a building. In addition, the presence of ACBM in our properties may expose us to third-party liability (e.g., liability for personal injury associated with exposure to asbestos).
In addition, the properties in the Company Portfolio also are subject to various federal, state and local environmental and health and safety requirements, such as state and local fire requirements. Moreover, some of our tenants routinely handle and use hazardous or regulated substances and wastes as part of their operations at our properties, which are subject to regulation. Such environmental and health and safety laws and regulations could subject us or our tenants to liability resulting from these activities. Environmental liabilities could affect a tenant’s ability to make rental payments to us. In addition, changes in laws could increase the potential liability for noncompliance. This may result in significant unanticipated expenditures or may otherwise materially and adversely affect our operations, or those of our tenants, which could in turn have an adverse effect on us.
We cannot assure you that costs or liabilities incurred as a result of environmental issues will not affect our ability to make distributions to you or that such costs or other remedial measures will not have an adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock. If we do incur material environmental liabilities in the future, we may face significant remediation costs, and we may find it difficult to sell any affected properties.
Our properties may contain or develop harmful mold or suffer from other air quality issues, which could lead to liability for adverse health effects and costs of remediation.
When excessive moisture accumulates in buildings or on building materials, mold growth may occur, particularly if the moisture problem remains undiscovered or is not addressed over a period of time. Some molds may produce airborne toxins or irritants. Indoor air quality issues can also stem from inadequate ventilation, chemical contamination from indoor or outdoor sources, and other biological contaminants such as pollen, viruses and bacteria. Indoor exposure to airborne toxins or irritants above certain levels can be alleged to cause a variety of adverse health effects and symptoms, including allergic or other reactions. As a result, the presence of significant mold or other airborne contaminants at any of our properties could require us to undertake a costly remediation program to contain or remove the mold or other airborne contaminants from the affected property or increase indoor ventilation. In addition, the presence of significant mold or other airborne contaminants could expose us to liability from our tenants, employees of our tenants or others if property damage or personal injury is alleged to have occurred.
29
We may incur significant costs complying with various federal, state and local laws, regulations and covenants that are applicable to our properties.
The properties in the Company Portfolio are subject to various covenants and federal, state and local laws and regulatory requirements, including permitting and licensing requirements. Local regulations, including municipal or local ordinances and zoning restrictions may restrict our use of our properties and may require us to obtain approval from local officials or restrict our use of our properties and may require us to obtain approval from local officials of community standards organizations at any time with respect to our properties, including prior to acquiring a property or when undertaking renovations of any of the Company Portfolio. Among other things, these restrictions may relate to fire and safety, seismic or hazardous material abatement requirements. There can be no assurance that existing laws and regulatory policies will not adversely affect us or the timing or cost of any future acquisitions or renovations, or that additional regulations will not be adopted that increase such delays or result in additional costs. Our growth strategy may be adversely affected by our ability to obtain permits, licenses and zoning relief. Our failure to obtain such permits, licenses and zoning relief or to comply with applicable laws could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
In addition, federal and state laws and regulations, including laws such as the Americans with Disabilities Act, or ADA, and the Fair Housing Amendment Act of 1988, or FHAA, impose further restrictions on our properties and operations. Under the ADA and the FHAA, all public accommodations must meet federal requirements related to access and use by disabled persons. Some of our properties may currently be in non-compliance with the ADA or the FHAA. If one or more of the properties in the Company Portfolio is not in compliance with the ADA, the FHAA or any other regulatory requirements, we may be required to incur additional costs to bring the property into compliance, including the removal of access barriers, and we might incur governmental fines or the award of damages to private litigants. In addition, we do not know whether existing requirements will change or whether future requirements will require us to make significant unanticipated expenditures that will adversely impact our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
Risks Related to Our Organizational Structure
Conflicts of interest may exist or could arise in the future between the interests of our stockholders and the interests of holders of OP units, which may impede business decisions that could benefit our stockholders.
Conflicts of interest may exist or could arise in the future as a result of the relationships between us and our affiliates, on the one hand, and our operating partnership or any partner thereof, on the other. Our directors and officers have duties to our company under Maryland law in connection with their management of our company. At the same time, we, as the general partner of our operating partnership, have fiduciary duties and obligations to our operating partnership and its limited partners under Maryland law and the partnership agreement of our operating partnership in connection with the management of our operating partnership. Our fiduciary duties and obligations as the general partner of our operating partnership may come into conflict with the duties of our directors and officers to our company.
Under Delaware law, a general partner of a Delaware limited partnership has fiduciary duties of loyalty and care to the partnership and its partners and must discharge its duties and exercise its rights as general partner under the partnership agreement or Delaware law consistent with the obligation of good faith and fair dealing. The partnership agreement provides that, in the event of a conflict between the interests of our operating partnership or any partner, on the one hand, and the separate interests of our company or our stockholders, on the other hand, we, in our capacity as the general partner of our operating partnership, may give priority to the separate interests of our company or our stockholders (including with respect to tax consequences to limited partners, assignees or our stockholders), and, in the event of such a conflict, any action or failure to act on our part or on the part of our directors that gives priority to the separate interests of our company or our stockholders that does not result in a violation of the contract rights of the limited partners of our operating partnership under its partnership agreement does not violate the duty of loyalty or any other duty that we, in our capacity as the general partner of our operating partnership, owe to our operating partnership and its partners or violate the obligation of good faith and fair dealing.
30
Additionally, the partnership agreement provides that we generally will not be liable to our operating partnership or any partner for any action or omission taken in our capacity as general partner, for the debts or liabilities of our operating partnership or for the obligations of the operating partnership under the partnership agreement, except for liability for our fraud, willful misconduct or gross negligence, pursuant to any express indemnity we may give to our operating partnership or in connection with a redemption as described in “Description of the Partnership Agreement of Plymouth Industrial OP, LP—Exchange Rights.” Our operating partnership must indemnify us, our directors and officers, officers of our operating partnership and our designees from and against any and all claims that relate to the operations of our operating partnership, unless (1) an act or omission of the person was material to the matter giving rise to the action and either was committed in bad faith or was the result of active and deliberate dishonesty, (2) the person actually received an improper personal benefit in violation or breach of the partnership agreement or (3) in the case of a criminal proceeding, the indemnified person had reasonable cause to believe that the act or omission was unlawful. Our operating partnership must also pay or reimburse the reasonable expenses of any such person in advance of a final disposition of the proceeding upon its receipt of a written affirmation of the person’s good faith belief that the standard of conduct necessary for indemnification has been met and a written undertaking to repay any amounts paid or advanced if it is ultimately determined that the person did not meet the standard of conduct for indemnification. Our operating partnership is not required to indemnify or advance funds to any person with respect to any action initiated by the person seeking indemnification without our approval (except for any proceeding brought to enforce such person’s right to indemnification under the partnership agreement) or if the person is found to be liable to our operating partnership on any portion of any claim in the action.
Our charter and bylaws, the partnership agreement of our operating partnership and Maryland law contain provisions that may delay, defer or prevent a change of control transaction.
Our charter contains certain ownership limits with respect to our stock. Our charter authorizes our board of directors to take such actions as it determines are advisable, in its sole and absolute discretion, to preserve our qualification as a REIT. Our charter also prohibits the actual, beneficial or constructive ownership by any person of more than 9.8% in value or number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of the outstanding shares of any class or series of our capital stock, in each case excluding any shares that are not treated as outstanding for federal income tax purposes. Our board of directors, in its sole and absolute discretion, may exempt a person, prospectively or retroactively, from these ownership limits if certain conditions are satisfied. The restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock may:
| • | discourage a tender offer or other transactions or a change in management or of control that might involve a premium price for our common stock or that our stockholders otherwise believe to be in their best interests; or | |
| • | result in the transfer of shares acquired in excess of the restrictions to a trust for the benefit of a charitable beneficiary and, as a result, the forfeiture by the acquirer of the benefits of owning the additional shares. |
We could increase the number of authorized shares of stock, classify and reclassify unissued stock and issue stock without stockholder approval. Our board of directors, without stockholder approval, has the power under our charter to amend our charter to increase the aggregate number of shares of stock or the number of shares of stock of any class or series that we are authorized to issue, to authorize us to issue authorized but unissued shares of our common stock or preferred stock and to classify or reclassify any unissued shares of our common stock or preferred stock into one or more classes or series of stock and set the terms of such newly classified or reclassified shares. See “Description of Stock—Power to Increase or Decrease Authorized Shares of Common Stock and Issue Additional Shares of Common and Preferred Stock.” As a result, we may issue classes or series of common stock or preferred stock with preferences, powers and rights, voting or otherwise, that are senior to, or otherwise conflict with, the rights of holders of our common stock. Although our board of directors has no such intention at the present time, it could establish a class or series of preferred stock that could, depending on the terms of such series, delay, defer or prevent a transaction or a change of control that might involve a premium price for our common stock or that our stockholders otherwise believe to be in their best interest.
Certain provisions of Maryland law could inhibit changes in control, which may discourage third parties from conducting a tender offer or seeking other change of control transactions that could involve a premium price for our common stock or that our stockholders otherwise believe to be in their best interest. Certain provisions of the MGCL may have the effect of inhibiting a third party from making a proposal to acquire us or of impeding a change of control under circumstances that otherwise could provide the holders of shares of our common stock with the opportunity to realize a premium over the then-prevailing market price of such shares, including:
| • | “business combination” provisions that, subject to certain exceptions, prohibit certain business combinations between us and an “interested stockholder” (defined generally as any person who beneficially owns 10% or more of the voting power of our shares or an affiliate thereof or an affiliate or associate of ours who was the beneficial owner, directly or indirectly, of 10% or more of the voting power of our then outstanding voting stock at any time within the two-year period; and |
31
| • | “control share” provisions that provide that holders of “control shares” of our company (defined as shares that, when aggregated with other shares controlled by the stockholder, entitle the stockholder to exercise voting power in the election of directors within one of three increasing ranges) acquired in a “control share acquisition” (defined as the direct or indirect acquisition of ownership or control of the voting power of issued and outstanding “control shares,” subject to certain exceptions) have no voting rights with respect to their control shares, except to the extent approved by our stockholders by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of all the votes entitled to be cast on the matter, excluding all interested shares. |
As permitted by the MGCL, our bylaws provide that we will not be subject to the control share provisions of the MGCL and our board of directors has, by resolution, exempted us from the business combination between us and any other person. However, we cannot assure you that our board of directors will not revise the bylaws or such resolution in order to be subject to such business combination and control share provisions in the future. Notwithstanding the foregoing, an alteration or repeal of the board resolution exempting such business combinations will not have any effect on any business combinations that have been consummated or upon any agreements existing at the time of such modification or repeal.
Certain provisions of the MGCL permit the board of directors of a Maryland corporation with at least three independent directors and a class of stock registered under the Exchange Act without stockholder approval and regardless of what is currently provided in its charter or bylaws, to implement certain corporate governance provisions, some of which (for example, a classified board) are not currently applicable to us. These provisions may have the effect of limiting or precluding a third party from making an unsolicited acquisition proposal for our company or of delaying, deferring or preventing a change in control under circumstances that otherwise could provide the holders of shares of our stock with the opportunity to realize a premium over the then current market price.
Certain provisions in the partnership agreement of our operating partnership may delay or prevent unsolicited acquisitions of us. Provisions of the partnership agreement of our operating partnership may delay or make more difficult unsolicited acquisitions of us or changes of our control. These provisions could discourage third parties from making proposals involving an unsolicited acquisition of us or change of our control, although some stockholders or limited partners might consider such proposals, if made, desirable. These provisions include, among others:
| • | redemption rights of qualifying parties; | |
| • | a requirement that we may not be removed as the general partner of our operating partnership without our consent; | |
| • | transfer restrictions on OP units; | |
| • | our ability, as general partner, in some cases, to amend the partnership agreement and to cause our operating partnership to issue additional partnership interests with terms that could delay, defer or prevent a merger or other change of control of us or our operating partnership without the consent of our stockholders or the limited partners; and | |
| • | the right of the limited partners to consent to certain transfers of our general partnership interest (whether by sale, disposition, statutory merger or consolidation, liquidation or otherwise). |
Our charter and bylaws, the partnership agreement of our operating partnership and Maryland law also contain other provisions that may delay, defer or prevent a transaction or a change of control that might involve a premium price for our common stock or that our stockholders otherwise believe to be in their best interest. See “Description of the Partnership Agreement of Plymouth Industrial OP, LP—Transferability of Interests,” “Material Provisions of Maryland Law and of Our Charter and Bylaws—Removal of Directors,” “—Control Share Acquisitions” and “—Advance Notice of Director Nominations and New Business.”
Our board of directors may change our investment and financing policies without stockholder approval and we may become more highly leveraged, which may increase our risk of default under our debt obligations.
Our investment and financing policies are exclusively determined by our board of directors. Accordingly, our stockholders do not control these policies. Further, our charter and bylaws do not limit the amount or percentage of indebtedness, funded or otherwise, that we may incur. Our board of directors may alter or eliminate our current policy on borrowing at any time without stockholder approval. If this policy changed, we could become more highly leveraged which could result in an increase in our debt service. Higher leverage also increases the risk of default on our obligations. In addition, a change in our investment policies, including the manner in which we allocate our resources across the Company Portfolio or the types of assets in which we seek to invest, may increase our exposure to interest rate risk, real estate market fluctuations and liquidity risk. Changes to our policies with regard to the foregoing could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
32
Our rights and the rights of our stockholders to take action against our directors and officers are limited.
As permitted by Maryland law, our charter eliminates the liability of our directors and officers to us and our stockholders for money damages, except for liability resulting from:
| • | actual receipt of an improper benefit or profit in money, property or services; or | |
| • | active and deliberate dishonesty by the director or officer that was established by a final judgment and was material to the cause of action adjudicated. |
In addition, our charter authorizes us to obligate our company, and our bylaws require us, to indemnify our directors and officers for actions taken by them in those and certain other capacities to the maximum extent permitted by Maryland law in effect from time to time. Generally, Maryland law permits a Maryland corporation to indemnify its present and former directors and officers except in instances where the person seeking indemnification acted in bad faith or with active and deliberate dishonesty, actually received an improper personal benefit in money, property or services or, in the case of a criminal proceeding, had reasonable cause to believe that his or her actions were unlawful. Under Maryland law, a Maryland corporation also may not indemnify a director or officer in a suit by or on behalf of the corporation in which the director or officer was adjudged liable to the corporation or for a judgment of liability on the basis that a personal benefit was improperly received. A court may order indemnification if it determines that the director or officer is fairly and reasonably entitled to indemnification, even though the director or officer did not meet the prescribed standard of conduct; however, indemnification for an adverse judgment in a suit by us or on our behalf, or for a judgment of liability on the basis that personal benefit was improperly received, is limited to expenses. As a result, we and our stockholders may have more limited rights against our directors and officers than might otherwise exist. Accordingly, in the event that actions taken in good faith by any of our directors or officers impede the performance of our company, your ability to recover damages from such director or officer will be limited. See “Material Provisions of Maryland law and of Our Charter and Bylaws—Indemnification and Limitation of Directors’ and Officers’ Liability.”
We are a holding company with no direct operations and, as such, we will rely on funds received from our operating partnership to pay liabilities, and the interests of our stockholders will be structurally subordinated to all liabilities and obligations of our operating partnership and its subsidiaries.
We are a holding company and will conduct substantially all of our operations through our operating partnership. We do not have, apart from an interest in our operating partnership, any independent operations. As a result, we will rely on distributions from our operating partnership to pay any dividends we might declare on shares of our common stock. We will also rely on distributions from our operating partnership to meet any of our obligations, including any tax liability on taxable income allocated to us from our operating partnership. In addition, because we are a holding company, your claims as stockholders will be structurally subordinated to all existing and future liabilities and obligations (whether or not for borrowed money) of our operating partnership and its subsidiaries. Therefore, in the event of our bankruptcy, liquidation or reorganization, our assets and those of our operating partnership and its subsidiaries will be available to satisfy the claims of our stockholders only after all of our and our operating partnership’s and its subsidiaries’ liabilities and obligations have been paid in full.
Our operating partnership may issue additional OP units to third parties without the consent of our stockholders, which would reduce our ownership percentage in our operating partnership and would have a dilutive effect on the amount of distributions made to us by our operating partnership and, therefore, the amount of distributions we can make to our stockholders.
After giving effect to this offering, we will own 100% of the outstanding OP units and we may, in connection with our acquisition of properties or otherwise, cause our operating partnership to issue additional OP units to third parties. Such issuances would reduce our ownership percentage in our operating partnership and affect the amount of distributions made to us by our operating partnership and, therefore, the amount of distributions we can make to our stockholders. Because you will not directly own OP units, you will not have any voting rights with respect to any such issuances or other partnership level activities of our operating partnership.
33
Risks Related to Our Status as a REIT
Failure to maintain our qualification as a REIT would have significant adverse consequences to us and the per share trading price of our common stock.
We have elected to be taxed as a REIT for federal income tax purposes commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2012 and have operated in a manner that we believe will allow us to maintain our qualification as a REIT. We cannot assure you that we will remain qualified as a REIT in the future. If we lose our REIT qualification, we will face serious tax consequences that would substantially reduce the funds available for distribution to you for each of the years involved because:
| • | we would not be allowed a deduction for distributions to stockholders in computing our taxable income and would be subject to federal income tax at regular corporate rates; | |
| • | we also could be subject to the federal alternative minimum tax and possibly increased state and local taxes; and | |
| • | unless we are entitled to relief under applicable statutory provisions, we could not elect to be taxed as a REIT for four taxable years following the year during which we were disqualified. |
Any such corporate tax liability could be substantial and would reduce our cash available for, among other things, our operations and distributions to stockholders. In addition, if we fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT, we will not be required to make distributions to our stockholders. As a result of all these factors, our failure to maintain our qualification as a REIT also could impair our ability to expand our business and raise capital, and could materially and adversely affect the per share trading price of our common stock.
Qualification as a REIT involves the application of highly technical and complex Code provisions for which there are only limited judicial and administrative interpretations. The complexity of these provisions and of the applicable Treasury regulations that have been promulgated under the Code, or the Treasury regulations, is greater in the case of a REIT that, like us, holds its assets through a partnership. The determination of various factual matters and circumstances not entirely within our control may affect our ability to qualify as a REIT. In order to maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must satisfy a number of requirements, including requirements regarding the ownership of our stock, requirements regarding the composition of our assets and a requirement that at least 95% of our gross income in any year must be derived from qualifying sources, such as “rents from real property.” Also, we must make distributions to stockholders aggregating annually at least 90% of our REIT taxable income, determined without regard to the dividends paid deduction and excluding net capital gains and losses. In addition, legislation, new regulations, administrative interpretations or court decisions may materially adversely affect our investors, our ability to maintain our qualification as a REIT for federal income tax purposes or the desirability of an investment in a REIT relative to other investments.
Even if we maintain our qualification as a REIT for federal income tax purposes, we may be subject to some federal, state and local income, property and excise taxes on our income or property and, in certain cases, a 100% penalty tax, in the event we sell property as a dealer. In addition, any taxable REIT subsidiaries that we own will be subject to tax as regular C corporations in the jurisdictions in which they operate.
If our operating partnership failed to qualify as a partnership or a disregarded entity for federal income tax purposes, we would cease to qualify as a REIT and suffer other adverse consequences.
We believe that our operating partnership will be treated as a partnership or a disregarded entity for federal income tax purposes. As a disregarded entity, our operating partnership will not be subject to federal income tax on its income. Rather, its income will be attributed to us as the sole owner for federal income tax purposes of the operating partnership. During periods in which our operating partnership has limited partners other than Plymouth OP Limited, LLC, the operating partnership will be treated as a partnership for federal income tax purposes. As a partnership, our operating partnership would not be subject to federal income tax on its income. Instead, each of its partners would be allocated, and may be required to pay tax with respect to, its share of our operating partnership’s income. We cannot assure you, however, that the Internal Revenue Service, or the IRS will not challenge the status of our operating partnership or any other subsidiary partnership in which we own an interest as a partnership for federal income tax purposes, or that a court would not sustain such a challenge. If the IRS were successful in treating our operating partnership or any such other subsidiary partnership as an entity taxable as a corporation for federal income tax purposes, we would fail to meet the gross income tests and certain of the asset tests applicable to REITs and, accordingly, we would likely cease to maintain our qualification as a REIT. Also, if our operating partnership or any subsidiary partnerships were treated as entities taxable as corporations, such entities could become subject to federal and state corporate income tax, which would reduce significantly the amount of cash available for debt service and for distribution to its partners, including us.
34
Our taxable REIT subsidiaries will be subject to federal income tax, and we will be required to pay a 100% penalty tax on certain income or deductions if our transactions with our taxable REIT subsidiaries are not conducted on arm’s length terms.
We will own an interest in one or more taxable REIT subsidiaries, and may acquire securities in additional taxable REIT subsidiaries in the future. A taxable REIT subsidiary is a corporation other than a REIT in which a REIT directly or indirectly holds stock, and that has made a joint election with such REIT to be treated as a taxable REIT subsidiary. If a taxable REIT subsidiary owns more than 35% of the total voting power or value of the outstanding securities of another corporation, such other corporation will also be treated as a taxable REIT subsidiary. Other than some activities relating to lodging and health care facilities, a taxable REIT subsidiary may generally engage in any business, including the provision of customary or non-customary services to tenants of its parent REIT. A taxable REIT subsidiary is subject to federal income tax as a regular C corporation. In addition, a 100% excise tax will be imposed on certain transactions between a taxable REIT subsidiary and its parent REIT that are not conducted on an arm’s length basis.
To maintain our REIT qualification, we may be forced to borrow funds during unfavorable market conditions.
To maintain our qualification as a REIT, we generally must distribute to our stockholders at least 90% of our REIT taxable income each year, determined without regard to the dividends paid deduction and excluding net capital gains, and we will be subject to regular corporate income taxes to the extent that we distribute less than 100% of our REIT taxable income each year. In addition, we will be subject to a 4% nondeductible excise tax on the amount, if any, by which distributions paid by us in any calendar year are less than the sum of 85% of our ordinary income, 95% of our capital gain net income and 100% of our undistributed income from prior years. Accordingly, we may not be able to retain sufficient cash flow from operations to meet our debt service requirements and repay our debt. Therefore, we may need to raise additional capital for these purposes, and we cannot assure you that a sufficient amount of capital will be available to us on favorable terms, or at all, when needed, which would materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock. Further, in order to maintain our REIT qualification and avoid the payment of income and excise taxes, we may need to borrow funds to meet the REIT distribution requirements even if the then prevailing market conditions are not favorable for these borrowings. These borrowing needs could result from, among other things, differences in timing between the actual receipt of cash and inclusion of income for federal income tax purposes, or the effect of non-deductible capital expenditures, the creation of reserves or required debt or amortization payments. These sources, however, may not be available on favorable terms or at all. Our access to third-party sources of capital depends on a number of factors, including the market’s perception of our growth potential, our current debt levels, the per share trading price of our common stock, and our current and potential future earnings. We cannot assure you that we will have access to such capital on favorable terms at the desired times, or at all, which may cause us to curtail our investment activities and/or to dispose of assets at inopportune times, and could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
Dividends payable by REITs do not qualify for the reduced tax rates available for some dividends.
The maximum tax rate applicable to “qualified dividend income” payable to U.S. stockholders that are individuals, trusts and estates is 20%. Dividends payable by REITs, however, generally are not eligible for the reduced rates. Although these rules do not adversely affect the taxation of REITs or dividends payable by REITs, investors who are individuals, trusts and estates may perceive investments in REITs to be relatively less attractive than investments in the stocks of non-REIT corporations that pay dividends, which could adversely affect the value of the shares of REITs, including the per share trading price of our common stock.
The tax imposed on REITs engaging in “prohibited transactions” may limit our ability to engage in transactions which would be treated as sales for federal income tax purposes.
A REIT’s net income from prohibited transactions is subject to a 100% penalty tax. In general, prohibited transactions are sales or other dispositions of property, other than foreclosure property, held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business. Although we do not intend to hold any properties that would be characterized as held for sale to customers in the ordinary course of our business, unless a sale or disposition qualifies under certain statutory safe harbors, such characterization is a factual determination and no guarantee can be given that the IRS would agree with our characterization of our properties or that we will always be able to make use of the available safe harbors.
35
Complying with REIT requirements may affect our profitability and may force us to liquidate or forgo otherwise attractive investments.
To maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must continually satisfy tests concerning, among other things, the nature and diversification of our assets, the sources of our income and the amounts we distribute to our stockholders. We may be required to liquidate or forgo otherwise attractive investments in order to satisfy the asset and income tests or to qualify under certain statutory relief provisions. We also may be required to make distributions to stockholders at disadvantageous times or when we do not have funds readily available for distribution. As a result, having to comply with the distribution requirement could cause us to: (1) sell assets in adverse market conditions; (2) borrow on unfavorable terms; or (3) distribute amounts that would otherwise be invested in future acquisitions, capital expenditures or repayment of debt. Accordingly, satisfying the REIT requirements could have an adverse effect on our business results, profitability and ability to execute our business plan. Moreover, if we are compelled to liquidate our investments to meet any of these asset, income or distribution tests, or to repay obligations to our lenders, we may be unable to comply with one or more of the requirements applicable to REITs or may be subject to a 100% tax on any resulting gain if such sales constitute prohibited transactions.
Changes to the U.S. federal income tax laws, including the enactment of certain proposed tax reform measures, could have an adverse impact on our business and financial results.
Numerous changes to the U.S. federal income tax laws are proposed regularly. Moreover, legislative and regulatory changes may be more likely in the 115th Congress because the Presidency and such Congress will be controlled by the same political party and significant reform of the Code has been described publicly as a legislative priority. Additionally, the REIT rules are constantly under review by persons involved in the legislative process and by the IRS and the U.S. Treasury Department, which may result in revisions to regulations and interpretations in addition to statutory changes. If enacted, certain such changes could have an adverse impact on our business and financial results. For example, certain proposals set forth in Trump administration and House Republican tax plans could reduce the relative competitive advantage of operating as a REIT unless accompanied by responsive changes to the REIT rules. These proposals include: the lowering of income tax rates on individuals and corporations, which could ease the burden of double taxation on corporate dividends and make the single level of taxation on REIT distributions relatively less attractive; allowing the expensing of capital expenditures, which could have a similar impact and also could result in the bunching of taxable income and required distributions for REITs; and further limiting or eliminating the deductibility of interest expense, which could disrupt the real estate market and could increase the amount of REIT taxable income that must be distributed as dividends to shareholders.
We cannot predict whether, when or to what extent new U.S. federal tax laws, regulations, interpretations or rulings will be issued, nor is the long-term impact of proposed tax reforms on the real estate investment industry or REITs clear. Prospective investors are urged to consult their tax advisors regarding the effect of potential changes to the U.S. federal tax laws on an investment in our shares.
Risks Related to our Common Stock and this Offering
There has been no public market for our common stock prior to this offering and an active trading market for our common stock may not develop following this offering.
Prior to this offering, there has not been any public market for our common stock, and there can be no assurance that an active trading market will develop or be sustained or that shares of our common stock will be resold at or above the public offering price. Our common stock has been approved for listing, subject to official notice of issuance, on the NYSE MKT under the symbol “PLYM.” The public offering price of our common stock has been determined by agreement among us and the underwriters, but there can be no assurance that our common stock will not trade below the public offering price following the completion of this offering. See “Underwriting.” The per share trading price of our common stock could be substantially affected by general market conditions, including the extent to which a secondary market develops for our common stock following the completion of this offering, the extent of institutional investor interest in us, the general reputation of REITs and the attractiveness of their equity securities in comparison to other equity securities (including securities issued by other real estate-based companies), our financial performance and general stock and bond market conditions.
We may be unable to make distributions at expected levels, and we may be required to borrow funds to make distributions.
We may be unable to pay our estimated annual distribution to stockholders out of cash available for distribution. Because our estimated annual distribution for the 12 months ending March 31, 2018 exceeds our pro forma cash available for distribution, if our operating cash flow does not increase we may have to fund distributions from borrowings under our anticipated credit facility or other loans, selling certain of our assets or using a portion of the net proceeds we receive from this offering, declare taxable distributions or reduce the amount of such distributions. See “Distribution Policy.” If cash available for distribution generated by our assets is less than our current estimate, or if such cash available for distribution decreases in future periods from expected levels, our inability to make the expected distributions could result in a decrease in the market price of our common stock. In the event the underwriters’ over-allotment option is exercised, pending investment of the proceeds therefrom, our ability to pay such distributions out of cash from our operations may be further materially adversely affected. Our ability to make distributions may also be limited by the terms of debt agreements we may enter into in the future.
All distributions will be made at the discretion of our board of directors and will be based upon, among other factors, our earnings and financial condition, maintenance of REIT qualification, the applicable restrictions contained in the MGCL and such other factors as our board may determine in its sole discretion. We may not be able to make distributions in the future. In addition, some of our distributions may include a return of capital. If we decide to make distributions in excess of our current and accumulated earnings and profits, such distributions would generally be considered a return of capital for federal income tax purposes to the extent of the holder’s adjusted tax basis in its shares, and thereafter as gain on a sale or exchange of such shares. See “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations—U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations for Holders of Our Common Stock.” If we borrow to fund distributions, our future interest costs would increase, thereby reducing our earnings and cash available for distribution from what they otherwise would have been.
36
You will experience immediate and material dilution in connection with the purchase of our common stock in this offering.
As of March 31, 2017, our aggregate historical consolidated net tangible book value was approximately $(47.8) million, or $(143.97) per share of common stock. As a result, the pro forma net tangible book value per share of common stock after the completion of this offering will be less than the initial public offering price. The purchasers of our common stock offered hereby will experience immediate and substantial dilution of $16.99 per share of common stock in the pro forma net tangible book value per share of our common stock, based on the offering price set forth on the front cover of this prospectus. See “Dilution” for additional information.
The market price and trading volume of our common stock may be volatile following this offering.
Even if an active trading market develops for our common stock, the per share trading price of our common stock may be volatile. In addition, the trading volume in our common stock may fluctuate and cause significant price variations to occur. If the per share trading price of our common stock declines significantly, you may be unable to resell your shares at or above the public offering price. We cannot assure you that the per share trading price of our common stock will not fluctuate or decline significantly in the future.
Some of the factors that could negatively affect our share price or result in fluctuations in the price or trading volume of our common stock include:
| • | actual or anticipated variations in our quarterly operating results or dividends; | |
| • | changes in our funds from operations or earnings estimates; | |
| • | publication of research reports about us or the real estate industry; | |
| • | increases in market interest rates that lead purchasers of our shares to demand a higher yield; | |
| • | changes in market valuations of similar companies; | |
| • | adverse market reaction to any additional debt we incur in the future; | |
| • | additions or departures of key management personnel; | |
| • | actions by institutional stockholders; | |
| • | speculation in the press or investment community; | |
| • | the realization of any of the other risk factors presented in this prospectus; | |
| • | the extent of investor interest in our securities; | |
| • | the general reputation of REITs and the attractiveness of our equity securities in comparison to other equity securities, including securities issued by other real estate-based companies; | |
| • | our underlying asset value; | |
| • | investor confidence in the stock and bond markets, generally; | |
| • | changes in tax laws; | |
| • | future equity issuances; | |
| • | failure to meet earnings estimates; | |
| • | failure to maintain our qualification as a REIT; | |
| • | changes in our credit ratings; and | |
| • | general market and economic conditions. |
In the past, securities class action litigation has often been instituted against companies following periods of volatility in the price of their common stock. This type of litigation could result in substantial costs and divert our management’s attention and resources, which could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to pay distributions on, and the per share trading price of, our common stock.
Market interest rates may have an effect on the per share trading price of our common stock.
One of the factors that will influence the price of our common stock will be the dividend yield on the common stock (as a percentage of the price of our common stock) relative to market interest rates. An increase in market interest rates, which are currently at low levels relative to historical rates, may lead prospective purchasers of our common stock to expect a higher dividend yield and higher interest rates would likely increase our borrowing costs and potentially decrease funds available for distribution. Thus, higher market interest rates could cause the market price of our common stock to decrease.
37
The number of shares of our common stock available for future issuance or sale could adversely affect the per share trading price of our common stock.
We are offering 2,900,000 shares of our common stock as described in this prospectus. Upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, we will have outstanding approximately 3,626,702 shares of our common stock. Of these shares, the 2,900,000 shares sold in this offering will be freely tradable, except for any shares purchased in this offering by our affiliates, as that term is defined by Rule 144 under the Securities Act. Upon completion of this offering, our directors and management and their affiliates will beneficially own 169,790 shares or approximately 4.7% of our common stock (or 4.2% if the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares is exercised in full). In connection with this offering, we have entered into a lock-up agreement that prevents us from offering additional common stock until 180 days after the date of this prospectus, as described in “Underwriting.” Our executive officers and directors may sell the shares of our common stock that they own or are granted in connection with the offering at any time following the expiration of the lock-up period for such shares, which expires 180 days after the date of this prospectus for our executive officers and directors, or earlier with the prior written consent of D.A. Davidson & Co. These lock-up provisions, at any time and without notice, may be waived by D.A. Davidson & Co. If the restrictions under the lock-up agreements are waived, our common stock may become available for resale into the market, subject to applicable law, which could reduce the per share trading price for our common stock.
In connection with the Torchlight Transactions, upon completion of this offering, we are privately issuing shares and warrants exercisable for shares of common stock to the Torchlight Entities. See “Structure of Our Company—Torchlight Transactions.” Following the completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, the Torchlight Entities, which have agreed to a lock-up for a period of 180 days following the date of this prospectus, will own 263,158 shares or 7.3% of our common stock (excluding shares issuable upon the exercise of warrants). In addition, pursuant to the Stockholders Agreement, we intend to grant certain customary registration rights and preemptive rights with respect to future offerings of our common stock. Sales of our common stock by Torchlight, or the perception that such sales could occur in the future, could have a material adverse effect on the market price of our common stock. If Torchlight sells all or a substantial portion of their shares, it could have a material adverse impact on the market price of our common stock.
From time to time we also intend to issue additional shares of common stock or OP units, which, at our option, may be redeemed for shares of our common stock, in connection with the acquisition of investments, as compensation or otherwise, and we may grant additional registration rights in connection with such issuances. See “Shares Eligible for Future Sale.”
We cannot predict whether future issuances or sales of shares of our common stock or the availability of shares for resale in the open market will decrease the per share trading price per share of our common stock. The per share trading price of our common stock may decline significantly when the restrictions on resale by certain of our stockholders lapse.
The issuance of substantial numbers of shares of our common stock in the public market, or upon exchange of OP units, or the perception that such issuances might occur could adversely affect the per share trading price of the shares of our common stock.
The exercise of the underwriters’ over-allotment option, the exchange of OP units for common stock or the vesting of any stock awards granted to certain directors, executive officers and other employees under our 2014 Incentive Award Plan, the issuance of our common stock or OP units in connection with future property, portfolio or business acquisitions and other issuances of our common stock could have an adverse effect on the per share trading price of our common stock, and the authorization of grants of awards covering OP units or shares of our common stock under our 2014 Incentive Award Plan, may adversely affect the terms upon which we may be able to obtain additional capital through the sale of equity securities. In addition, future issuances of shares of our common stock may be dilutive to existing stockholders.
Future offerings of debt securities, which would be senior to our common stock upon liquidation, and/or preferred equity securities which may be senior to our common stock for purposes of dividend distributions or upon liquidation, may adversely affect the per share trading price of our common stock.
In the future, we may attempt to increase our capital resources by making additional offerings of debt or equity securities (or causing our operating partnership to issue debt or equity securities), including medium-term notes, senior or subordinated notes and classes or series of preferred stock. Upon liquidation, holders of our debt securities and shares of preferred stock and lenders with respect to other borrowings will be entitled to receive our available assets prior to distribution to the holders of our common stock. Additionally, any convertible or exchangeable securities that we issue in the future may have rights, preferences and privileges more favorable than those of our common stock and may result in dilution to owners of our common stock. Holders of our common stock are not entitled to preemptive rights or other protections against dilution. Our preferred stock, if issued, could have a preference on liquidating distributions or a preference on dividend payments that could limit our ability pay dividends to the holders of our common stock. Because our decision to issue securities in any future offering will depend on market conditions and other factors beyond our control, we cannot predict or estimate the amount, timing or nature of our future offerings. Thus, our stockholders bear the risk of our future offerings.
38
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
We make statements in this prospectus that are forward-looking statements, which are usually identified by the use of words such as “anticipates,” “believes,” “estimates,” “expects,” “intends,” “may,” “plans” “projects,” “seeks,” “should,” “will,” and variations of such words or similar expressions. Our forward-looking statements reflect our current views about our plans, intentions, expectations, strategies and prospects, which are based on the information currently available to us and on assumptions we have made. Although we believe that our plans, intentions, expectations, strategies and prospects as reflected in or suggested by our forward-looking statements are reasonable, we can give no assurance that our plans, intentions, expectations, strategies or prospects will be attained or achieved and you should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. Furthermore, actual results may differ materially from those described in the forward-looking statements and may be affected by a variety of risks and factors including, without limitation:
| • | the factors included in this prospectus, including those set forth under the headings “Prospectus Summary,” “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and “Business;” | |
| • | the competitive environment in which we operate; | |
| • | real estate risks, including fluctuations in real estate values and the general economic climate in local markets and competition for tenants in such markets; | |
| • | decreased rental rates or increasing vacancy rates; | |
| • | potential defaults on or non-renewal of leases by tenants; | |
| • | potential bankruptcy or insolvency of tenants; | |
| • | acquisition risks, including failure of such acquisitions to perform in accordance with projections; | |
| • | the timing of acquisitions and dispositions; | |
| • | potential natural disasters such as earthquakes, wildfires or floods; | |
| • | national, international, regional and local economic conditions; | |
| • | the general level of interest rates; | |
| • | potential changes in the law or governmental regulations that affect us and interpretations of those laws and regulations, including changes in real estate and zoning or REIT tax laws, and potential increases in real property tax rates; | |
| • | financing risks, including the risks that our cash flows from operations may be insufficient to meet required payments of principal and interest and we may be unable to refinance our existing debt upon maturity or obtain new financing on attractive terms or at all; | |
| • | lack of or insufficient amounts of insurance; | |
| • | our ability to maintain our qualification as a REIT; | |
| • | litigation, including costs associated with prosecuting or defending claims and any adverse outcomes; and | |
| • | possible environmental liabilities, including costs, fines or penalties that may be incurred due to necessary remediation of contamination of properties presently owned or previously owned by us. |
Any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it is made. New risks and uncertainties arise over time, and it is not possible for us to predict those events or how they may affect us. Except as required by law, we are not obligated to, and do not intend to, update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Market data and industry forecasts and projections used in this prospectus have been obtained from REIS or other independent industry sources. Forecasts, projections and other forward-looking information obtained from REIS or other sources are subject to similar qualifications and uncertainties as other forward-looking statements in this prospectus.
39
USE OF PROCEEDS
We estimate that the net proceeds we will receive from the sale of shares of our common stock in this offering will be approximately $50.1 million (or approximately $57.8 million if the underwriters exercise their over-allotment option in full) after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
We will contribute the net proceeds we receive from this offering, including any net proceeds from the exercise of the over-allotment option, to our operating partnership in exchange for OP units.
We expect our operating partnership will use approximately $20.0 million of the net proceeds from this offering to redeem the Preferred Interests. Our operating partnership is expected to use the remaining net proceeds to acquire and manage additional industrial properties and for general corporate purposes.
Prior to the full deployment of the net proceeds as described above, we intend to invest the undeployed net proceeds in interest-bearing short-term investment grade securities or money-market accounts that are consistent with our intention to maintain our qualification as a REIT, including, for example, government and government agency certificates, certificates of deposit and interest-bearing bank deposits. We expect that these initial investments will provide a lower net return than we expect to receive from investments in industrial properties.
40
DISTRIBUTION POLICY
In order to maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must distribute to our stockholders, on an annual basis, at least 90% of our REIT taxable income, determined without regard to the deduction for dividends paid and excluding net capital gains. In addition, we will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at regular corporate rates to the extent that we distribute less than 100% of our net taxable income (including net capital gains) and will be subject to a 4% nondeductible excise tax on the amount by which our distributions in any calendar year are less than a minimum amount specified under U.S. federal income tax laws. We intend to distribute our net income to our stockholders in a manner intended to satisfy the REIT 90% distribution requirement and to avoid U.S. federal income tax liability on our income and the 4% nondeductible excise tax. We anticipate that our estimated cash available for distribution will exceed the annual distribution requirements applicable to REITs. However, under some circumstances, we may be required to use cash reserves, incur debt or liquidate assets at rates or times that we regard as unfavorable or make a taxable distribution of our shares in order to satisfy the REIT 90% distribution requirement and to avoid U.S. federal income tax and the 4% nondeductible excise tax in that year. For more information, see “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations.”
To satisfy the requirements to qualify as a REIT, and to avoid paying tax on our income, we intend to pay regular quarterly cash dividends of all or substantially all of our REIT taxable income (excluding net capital gains) to holders of our common stock. We intend to pay a pro rata dividend with respect to the period commencing on the completion of this offering and ending on June 30, 2017, based on $0.356 per share for a full quarter. On an annualized basis, this would be $1.425 per share, or an annual dividend rate of approximately 7.5% based on the offering price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus. We intend to maintain our initial distribution rate for the 12-month period following completion of this offering unless our results of operations or other factors differ materially from the assumptions used in our estimate. We estimate that this initial annual dividend rate would have represented approximately 106.9% of estimated cash available for distribution, as adjusted, to holders of our common stock for the trailing 12-month period ended March 31, 2017. We do not intend to reduce the expected dividend per share if the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares is exercised; however, this could require us to borrow funds to pay dividends or to use the net proceeds from this offering to pay dividends. Our intended initial annual distribution rate has been established based on our estimate of cash available for distribution, as adjusted, for the trailing 12-month period ended March 31, 2017, which we have calculated based on adjustments to our pro forma net income for the trailing 12-month period ended March 31, 2017 (after giving effect to this offering and the completion of the Torchlight Transactions). This estimate was based on our pro forma operating results and does not take into account our business and growth strategies, nor does it take into account any unanticipated expenditures we may have to make or any financings for such expenditures. In estimating our cash available for distribution, as adjusted, for the trailing 12-month period ended March 31, 2017, we have made certain assumptions as reflected in the pro forma financial statements, footnotes and the table below.
Our estimate of cash available for distribution, as adjusted, does not include the effect of any changes in our working capital or the amount of cash to be used for investing activities for acquisition and other activities, nor does it include any revenue derived from acquisition activities utilizing the net proceeds from this offering. Any such investing and/or financing activities may have a material effect on our available cash balances. Because we have made the assumptions set forth herein in estimating cash available for distribution, as adjusted, we do not intend this estimate to be a projection or forecast of our actual results of operations, EBITDA, FFO, liquidity or financial condition and have estimated cash available for distribution, as adjusted, for the sole purpose of determining our estimated initial annual distribution. Our estimated cash available for distribution, as adjusted, should not be considered as an alternative to cash flow from operating activities (computed in accordance with GAAP) or as an indicator of our liquidity or our ability to make distributions. In addition, the methodology upon which we made the adjustments described below is not necessarily intended to be a basis for determining future distributions.
We believe that our estimate of cash available for distribution, as adjusted, constitutes a reasonable basis for setting the initial distribution rate. However, we cannot assure you that our estimate will prove accurate, and actual distributions may, therefore, be significantly different than the initial distribution rate. Our actual results of operations will be affected by a number of factors, including the revenue received from our properties, our property operating expenses, interest expense and unanticipated capital expenditures.
We cannot assure you that our estimated distributions will be made or sustained or that our board of directors will not change our distribution policy in the future. Any future distributions will be at the sole discretion of our board of directors, and their form, timing and amount, if any, will depend upon a number of factors, including the revenue we received from our properties, our operating expenses, interest expense, the ability of our lessees to meet their obligations and unanticipated expenditures, our debt service requirements, our capital expenditures, prohibitions and other limitations under our financing arrangements, our REIT taxable income, the annual REIT distribution requirements, applicable law and such other factors as our board of directors deems relevant. To the extent that our cash available for distribution is less than 90% of our REIT taxable income, we may consider various means to cover any such shortfall, including borrowing under our anticipated credit facility or other loans, selling certain of our assets or using a portion of the net proceeds we receive from this offering or future offerings of equity, equity-related or debt securities or declaring taxable share dividends.
41
These calculations do not assume any changes to our operations or any acquisitions or dispositions (or any transaction and pursuit costs related thereto) other than estimated recurring capital expenditures and estimated changes in general and administrative expenses, which would affect our cash flows, or change in our outstanding common stock. We cannot assure you that our actual results will be as indicated in the calculations below.
Estimated Cash Available for Distribution, as Adjusted
| ($ in thousands) | ||||
| Pro Forma net income (loss) for the 12 Months ended December 31, 2016 | $ | (39.448 | ) | |
| Less: Pro forma net (income) loss for the three months ended March 31, 2016 | 14,478 | |||
| Add: Pro forma net income (loss) for the three months ended March 31, 2017 | (2,730 | ) | ||
| Pro forma net income for the 12 months ended March 31, 2017 | (27,700 | ) | ||
| Add: Real estate depreciation and amortization | 7,533 | |||
| Add: Amortization intangibles | 3,885 | |||
| Add: Stock based compensation | 650 | |||
| Less: Estimated improvements, leasing commissions and capital expenditures(1) | (2,005 | ) | ||
| Less: Amortization of above/below market rent | (350 | ) | ||
| Less: Straight line rent | (316 | ) | ||
| Add: Deferred/Accrued interest-non cash | 21,741 | |||
| Add: Amortization of deferred financing costs | 349 | |||
| Add: Adjustment for general and administrative costs(2) | 1,045 | |||
| Estimated cash flow available for distribution | $ | 4,832 | ||
| Estimated annual distribution to stockholders(3) | $ | 5,168 | ||
| Distribution ratio based on estimated cash available for distribution to common stockholders(4)(5) | 106.9% | |||
_______________
| (1) | Estimated improvements, leasing commissions and capital expenditures are estimated to be approximately $2,005,000, or $0.50 per square foot, which represents the amount we are required to pay into escrow annually to cover such expenses pursuant to the AIG Loan Agreement, which has been in effect since October 17, 2016. |
| (2) | Estimated additional general and administrative costs consist of legal and accounting (based upon estimates provided by our external legal and accounting professionals and management’s previous experience in managing a public REIT), insurance, travel, rent and other costs (based on proposed arrangements and anticipated activity). We have estimated a level of continuing general and administrative costs required to manage the company as a public company and to operate the Company Portfolio, including, but not limited to, salaries, board of directors fees and expenses, director’s and officer’s insurance, Sarbanes-Oxley Act compliance costs, and legal, audit and tax fees. This amount is lower than incurred previously due to professional fees related to our debt refinancing. |
| (3) | Represents the aggregate amount per share of the intended annual distribution multiplied by the shares of common stock that will be outstanding upon completion of this offering, the issuance of 131,579 shares of common stock to our executive officers and directors upon the closing of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions. Excludes shares of common stock that may be issued by us upon exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares. |
| (4) | If the underwriters’ option to purchase up to an additional 435,000 shares of common stock from us, our initial annual distribution would increase by approximately $620 and our payout ratio would increase to 119.8% assuming no investment of the additional proceeds. |
| (5) | Because our estimated annual distribution for the 12 months ending March 31, 2018 exceeds our pro forma cash available for distribution, if our operating cash flow does not increase we may have to fund distributions from borrowings under our anticipated credit facility or other loans, selling certain of our assets or using a portion of the net proceeds we receive from this offering, declare taxable distributions or reduce such distributions. |
42
CAPITALIZATION
The following table sets forth as of March 31, 2017:
| • | the actual capitalization of the company; and | |
| • | our pro forma capitalization, which gives effect to (i) the sale of 2,900,000 shares of common stock in this offering based on the offering price set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, net of the underwriting discounts and estimated organizational and offering expenses payable by us, (ii) the completion of the Torchlight Transactions and (iii) the grant of 131,579 restricted shares of our common stock to our executive officers and independent directors upon the closing of this offering. |
This table should be read in conjunction with “Use of Proceeds,” “Selected Financial Information,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the historical audited financial statements and the unaudited pro forma financial information and related notes appearing elsewhere in this prospectus.
| ($ in thousands) | As of March 31, 2017 | |||||||
| Historical | Pro Forma | |||||||
| (Unaudited) | ||||||||
| Debt: | ||||||||
| Senior secured debt, net | $ | 116,258 | $ | 116,258 | ||||
| Deferred interest | 207 | 207 | ||||||
| Mezzanine debt to investor, net | 29,292 | 29,292 | ||||||
| Redeemable preferred member interest | 25,000 | — | ||||||
| Total debt | $ | 170,757 | $ | 145,757 | ||||
| Deficit | ||||||||
| Preferred Stock $0.01 par value, 100,000,000 shares authorized, none issued and outstanding, historical and 100,000,000 shares authorized, none issued and outstanding, pro forma | — | — | ||||||
| Common stock $0.01 par value, 900,000,000 shares authorized, 331,965 shares issued and outstanding, historical, 900,000,000 shares authorized, 3,626,702 shares issued and outstanding, pro forma(1) | $ | 3 | $ | 35 | ||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 12,477 | 126,543 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (110,947 | ) | (110,947 | ) | ||||
| Non-controlling interest | 59,005 | — | ||||||
| Total Deficit | $ | (39,462 | ) | $ | 15,631 | |||
______________________
| (1) | Pro forma common stock outstanding includes (a) 2,900,000 shares of our common stock to be issued in this offering, (b) 263,158 shares of our common stock to be issued to Torchlight in connection with the Torchlight Transactions, (c) an aggregate of 115,790 restricted shares of our common stock to be granted to our executive officers concurrently with the completion of this offering and (d) an aggregate of 15,789 restricted shares of our common stock to be granted to our independent directors concurrently with the completion of this offering, but excludes (i) 435,000 shares of our common stock issuable upon the exercise of the underwriters’ over-allotment option in full, (ii) 243,421 shares of our common stock available for future issuance under our 2014 Incentive Award Plan, and (iii) up to 250,000 shares of our common stock that may be issued upon the exercise of the warrants to be issued to Torchlight in connection with the Torchlight Transactions. |
43
DILUTION
If you invest in our common stock in this offering, your ownership interest will be diluted immediately to the extent of the difference between the offering price per share of our common stock and the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share of our common stock immediately after this offering.
Our historical net tangible book value (deficit) as of March 31, 2017 was $(47.8) million, or $(143.97) per share of common stock. Our historical net tangible book value (deficit) is the amount of our total tangible assets less our total liabilities. Historical net tangible book value per share is our historical net tangible book value (deficit) divided by the number of shares of common stock outstanding as of March 31, 2017.
Our pro forma net tangible book value as of March 31, 2017 was $(42.8) million, or $(71.91) per share of common stock. Pro forma net tangible book value represents the amount of our total tangible assets less total liabilities, after giving effect to the issuance of 263,158 shares upon partial redemption of the Preferred Interests in the Torchlight Transactions. Pro forma net tangible book value per share represents our pro forma net tangible book value divided by the total number of shares outstanding as of March 31, 2017, after giving effect to the issuance of 263,158 shares of common stock upon partial redemption of the Preferred Interests in Torchlight Transactions, but excluding the 250,000 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of the warrants.
After giving effect to (i) the sale of 2,900,000 shares of common stock in this offering, (ii) the issuance of 131,579 shares of common stock to our executive officers and independent directors upon the closing of this offering and (iii) the issuance of 263,158 shares of common stock concurrently with the closing of this offering upon partial redemption of the Preferred Interests in the Torchlight Transactions and after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us, our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value as of March 31, 2017 would have been approximately $7.3 million, or $2.01 per share. This represents an immediate increase to pro forma net book value of $73.92 per share and an increase to historical net tangible book value of $145.99 per share to existing stockholders and an immediate dilution of $16.99 per share to new investors purchasing common stock in this offering at the initial public offering price. Dilution per share to new investors is determined by subtracting pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share after this offering from the assumed initial public offering price per share paid by new investors. The following table illustrates this dilution on a per share basis:
| Assumed initial public offering price per share | $ | 19.00 | ||||||
| Historical net tangible book value (deficit) per share as of March 31, 2017 | $ | (143.97 | ) | |||||
| Increase per share attributable to the issuance of 263,158 shares upon partial redemption of the Preferred Interests | 72.06 | |||||||
| Pro forma net tangible book value per share as of March 31, 2017 | (71.91 | ) | ||||||
| Increase in pro forma net tangible book value per share attributable to new investors purchasing shares in this offering | 73.92 | |||||||
| Pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share after this offering | 2.01 | |||||||
| Dilution per share to new investors purchasing shares in this offering | $ | 16.99 |
If the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares in full, our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value after this offering would be approximately $15.0 million, or $3.69 per share, representing an immediate increase to pro forma as adjusted net book value per share of $1.68 and to historical net tangible book value per share of $147.66 to existing stockholders and immediate dilution of $15.31 in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share to new investors purchasing common stock in this offering.
44
The following table summarizes, on a pro forma as adjusted basis described above, the number of shares of our common stock, the total consideration and the average price per share (i) paid to us by existing stockholders, (ii) to be paid by new investors purchasing shares of common stock in this offering, before deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us and (iii) to be paid by Torchlight upon the exercise of the warrants.
| Shares Purchased | Total Consideration | Average Price | ||||||||||||||||||
| Number | Percent | Amount | Percent | Per Share | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted shares of common stock to be issued to executive officers and independent directors | 131,579 | 3.4% | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Existing stockholders | 331,965 | 8.6% | $ | 11,581 | 15.0% | $ | 34.89 | |||||||||||||
| New investors(1) | 3,163,158 | 81.6% | $ | 60,100 | 77.6% | $ | 19.00 | |||||||||||||
| Shares that may be issued upon exercise of warrants issued to Torchlight | 250,000 | 6.4% | $ | 5,750 | 7.4% | $ | 23.00 | |||||||||||||
| Total | 3,876,702 | 100.0% | $ | 77,431 | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||
_____________________
| (1) | Includes 263,158 shares to be issued in the Torchlight Transactions. |
The table above assumes no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares in this offering. If the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares is exercised in full, the number of shares of our common stock held by existing stockholders would be reduced to 7.7% of the total number of shares of our common stock outstanding after this offering, and the number of shares of common stock held by new investors participating in the offering would be increased to 83.5% of the total number of shares of our common stock outstanding after this offering.
The above discussion and table exclude 243,421 shares of our common stock that will become available for future issuance under our 2014 Incentive Award Plan as described in “Executive Compensation—2014 Incentive Award Plan.”
In addition, we may choose to raise additional capital due to market conditions or strategic considerations even if we believe we have sufficient funds for our current or future operating plans. To the extent that additional capital is raised through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the issuance of these securities may result in further dilution to our stockholders.
45
SELECTED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The following table sets forth selected financial and operating data on (i) a historical basis and (ii) a pro forma basis for our company.
You should read the following summary financial and operating data in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” our unaudited pro forma consolidated financial statements and related notes, and our historical consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in the prospectus.
The unaudited pro forma consolidated balance sheet data as of March 31, 2017 is presented as if this offering and the Torchlight Transactions had occurred on March 31, 2017, and the unaudited pro forma statements of operations and other data for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and the year ended December 31, 2016 is presented as if this offering and the Torchlight Transactions had occurred on the first day of the period. The pro forma financial information is not necessarily indicative of what our actual financial condition would have been as of March 31, 2017 or what our actual results of operations would have been assuming this offering and the Torchlight Transactions had been completed as of January 1, 2016 or 2017, or December 31, 2016 nor does it purport to represent our future financial position or results of operations.
The summary unaudited historical condensed consolidated balance sheet information on March 31, 2017 and the statement of operations data for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and March 31, 2016 have been derived from our financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The selected historical consolidated balance sheet information as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the historical consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 on pages 46 and 47 have been derived from the company’s consolidated financial statements, which were audited by Marcum LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm, and are included elsewhere in this prospectus.
| (In thousands) | As of March 31, | As of December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Rental Property | $ | 139,123 | $ | 139,123 | $ | 138,553 | $ | 139,086 | $ | 138,236 | ||||||||||
| Less Accumulated Depreciation | (17,916 | ) | (17,916 | ) | (10,383 | ) | (16,027 | ) | (8,522 | ) | ||||||||||
| Real estate properties, net | 121,207 | 121,207 | 128,170 | 123,059 | 129,714 | |||||||||||||||
| Investments in real estate joint ventures | — | 2,968 | — | 2,987 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cash | 31,244 | 1,151 | 925 | 941 | 698 | |||||||||||||||
| Restricted cash | 771 | 771 | 750 | 6,353 | 757 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash escrows/ reserves | 3,103 | 3,103 | — | 2,907 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred lease intangibles, net | 9,610 | 9,610 | 13,560 | 10,533 | 14,773 | |||||||||||||||
| Other assets | 1,601 | 1,601 | 1,144 | 1,953 | 1,122 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 167,536 | $ | 137,443 | $ | 147,517 | $ | 145,746 | $ | 150,051 | ||||||||||
| Liabilities and stockholders' equity | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior debt, net | $ | 116,258 | $ | 116,258 | $ | 199,500 | $ | 116,053 | $ | 196,800 | ||||||||||
| Mezzanine debt to investor, net | 29,292 | 29,292 | — | 29,262 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred interest | 207 | 207 | 15,696 | 207 | 8,081 | |||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities | 4,870 | 4,870 | 5,870 | 5,352 | 4,268 | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred lease intangibles, net | 1,278 | 1,278 | 1,806 | 1,405 | 1,941 | |||||||||||||||
| Redeemable Preferred member interest | — | 25,000 | — | 31,043 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Liabilities | $ | 151,905 | $ | 176,905 | $ | 222,872 | $ | 183,322 | $ | 211,090 | ||||||||||
| Stockholders' equity (deficit): | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred stock, $0.01 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; none issued and outstanding | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock, $0.01 par value: 900,000,000 shares authorized; 331,965 shares issued and outstanding. Pro forma issued and outstanding 3,626,702 | 35 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Additional paid in capital | 126,543 | 12,477 | 12,477 | 12,477 | 12,477 | |||||||||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (110,947 | ) | (110,947 | ) | (87,835 | ) | (110,506 | ) | (73,519 | ) | ||||||||||
| Total Plymouth Industrial REIT stockholders' equity (deficit) | 15,631 | (98,467 | ) | (75,355 | ) | (98,026 | ) | (61,039 | ) | |||||||||||
| Non-controlling interest | $ | — | $ | 59,005 | $ | — | $ | 60,450 | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Total equity (deficit) | 15,631 | (39,462 | ) | (75,355 | ) | (37,576 | ) | (61,039 | ) | |||||||||||
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 167,536 | $ | 137,443 | $ | 147,517 | $ | 145,746 | $ | 150,051 | ||||||||||
46
| (In thousands) | Three Months Ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rental revenue | $ | 4,938 | $ | 4,938 | $ | 4,808 | $ | 19,658 | $ | 19,658 | $ | 19,290 | ||||||||||||
| Equity investment income (loss) | 1 | 1 | 30 | 230 | 230 | (85 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total revenues | 4,939 | 4,939 | 4,838 | 19,888 | 19,888 | 19,205 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Property | 1,408 | 1,408 | 1,412 | 5,927 | 5,927 | 5,751 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative | 886 | 724 | 911 | 4,392 | 3,742 | 4,688 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition costs | — | — | 19 | — | — | 1,061 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Offering costs | — | — | — | — | — | 938 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses | 5,066 | 4,904 | 5,370 | 21,993 | 21,343 | 24,574 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) | (127 | ) | 35 | (532 | ) | (2,105 | ) | (1,455 | ) | (5,369 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gain on disposition of equity investment | — | — | — | 2,846 | 2,846 | 1,380 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (2,603 | ) | (2,941 | ) | (13,784 | ) | (40,189 | ) | (40,679 | ) | (44,676 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Total other income (expense) | (2,603 | ) | (2,941 | ) | (13,784 | ) | (37,343 | ) | (37,833 | ) | (43,296 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net (loss) | (2,730 | ) | (2,906 | ) | (14,316 | ) | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest | — | (2,465 | ) | — | — | (2,301 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Net loss attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. common stockholders | $ | (2,730 | ) | $ | (441 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (36,987 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
47
| (In thousands) | Three Months Ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total in service Properties | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||
| NOI: (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,730 | ) | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
| General and administrative | 886 | 724 | 911 | 4,392 | 3,742 | 4,688 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition expense | — | — | 19 | — | — | 1,061 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 2,603 | 2,941 | 13,784 | 40,189 | 40,679 | 44,676 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Offering costs | — | — | — | — | — | 938 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other (income) expense | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | (30 | ) | (3,076 | ) | (3,076 | ) | (1,295 | ) | ||||||||||||
| NOI | $ | 3,530 | $ | 3,530 | $ | 3,396 | $ | 13,731 | $ | 13,731 | $ | 13,539 | ||||||||||||
| EBITDA: (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,730 | ) | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 2,603 | 2,941 | 13,784 | 40,189 | 40,679 | 44,676 | ||||||||||||||||||
| EBITDA | $ | 2,645 | $ | 2,807 | $ | 2,496 | $ | 12,415 | $ | 13,065 | $ | 8,147 | ||||||||||||
| FFO: (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,730 | ) | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gain on disposition of equity investment | — | — | — | (2,846 | ) | (2,846 | ) | (1,380 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Adjustment for unconsolidated joint ventures | — | — | — | 452 | 452 | 1,363 | ||||||||||||||||||
| FFO | $ | 42 | $ | (134 | ) | $ | (11,288 | ) | $ | (30,168 | ) | $ | (30,008 | ) | $ | (36,546 | ) | |||||||
| AFFO: (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FFO | $ | 42 | $ | (134 | ) | $ | (11,288 | ) | $ | (30,168 | ) | $ | (30,008 | ) | $ | (36,546 | ) | |||||||
| Amortization of above or accretion of below market lease rents | (83 | ) | (83 | ) | (88 | ) | (355 | ) | (355 | ) | (351 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Acquisition costs | — | — | 19 | — | — | 1,061 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Offering Costs | — | — | — | — | — | 938 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 162 | — | — | 650 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Distributions | — | — | 49 | 337 | 337 | 2,030 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Straight line rent | (45 | ) | (45 | ) | (75 | ) | (287 | ) | (287 | ) | (404 | ) | ||||||||||||
| AFFO | $ | 76 | $ | (262 | ) | $ | (11,383 | ) | $ | (29,823 | ) | $ | (30,313 | ) | $ | (33,272 | ) | |||||||
_____________________
| (1) | For definitions and reconciliations of net income to NOI, EBITDA, FFO and AFFO, as well as a statement disclosing the reasons why our management believes that NOI, EBITDA, FFO and AFFO provide useful information to investors as to the financial performance of our company, and, to the extent material, any additional purposes for which our management uses NOI, EBITDA, FFO and AFFO, see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Non-GAAP Financial Measures.” |
48
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
OF FINANCIAL
CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Our actual results could differ materially from those expressed or implied in forward-looking statements for many reasons, including the risks described in “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus. You should read the following discussion together with the “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and the pro forma and consolidated historical financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus.
The following discussion and analysis is based on, and should be read in conjunction with, our unaudited financial statement and notes thereto as of March 31, 2017 and audited historical financial statements and related notes thereto as of and for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015. We also present in this prospectus pro forma financial information for our company reflecting the Company Portfolio, on a consolidated basis after giving effect to this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, as of and for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and for the year ended December 31, 2016. These effects are reflected in the unaudited pro forma consolidated financial statements located elsewhere in this prospectus.
Overview
We are a full service, vertically integrated, self-administered and self-managed REIT focused on the acquisition, ownership and management of single- and multi-tenant Class B industrial properties, including distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties. The Company Portfolio consists of 20 industrial buildings located in seven states with an aggregate of approximately 4.0 million rentable square feet leased to 37 different tenants.
Our strategy is to invest in single- and multi-tenant Class B industrial properties located primarily in secondary markets across the U.S.; however, we may make opportunistic acquisitions of Class A industrial properties or industrial properties located in primary markets. We seek to generate attractive risk-adjusted returns for our stockholders through a combination of dividends and capital appreciation.
Factors That May Influence Future Results of Operations
Business and Strategy
Our core investment strategy is to acquire primarily Class B industrial properties predominantly in secondary markets across the U.S. We expect to acquire these properties through third-party purchases and structured sale-leasebacks where we believe we can achieve high initial yields and strong ongoing cash-on-cash returns. In addition, we may make opportunistic acquisitions of Class A industrial properties or industrial properties in primary markets that offer similar return characteristics.
Our target markets are comprised primarily of secondary markets because we believe these markets tend to have less occupancy and rental rate volatility and less buyer competition relative to primary markets. We also believe that the systematic aggregation of such properties will result in a diversified portfolio that will produce sustainable risk-adjusted returns. Future results of operations may be affected, either positively or negatively, by our ability to effectively execute this strategy.
We also intend to pursue joint venture arrangements with institutional partners which could provide management fee income as well as residual profit-sharing income. Such joint ventures may involve investing in industrial assets that would be characterized as opportunistic or value-add investments. These may involve development or re-development strategies that may require significant up-front capital expenditures, lengthy lease-up periods and result in inconsistent cash flows. As such, these properties’ risk profiles and return metrics would likely differ from the non-joint venture properties that we target for acquisition.
Rental Revenue and Tenant Recoveries
We receive income primarily from rental revenue from our properties. The amount of rental revenue generated by the Company Portfolio depends principally on the occupancy levels and lease rates at our properties, our ability to lease currently available space and space that becomes available as a result of lease expirations and on the rental rates at our properties.
Occupancy Rates. As of March 31, 2017, the Company Portfolio was approximately 98.4% occupied. Our occupancy rate is impacted by general market conditions in the geographic areas in which our properties are located and the financial condition of tenants in our target markets.
Rental Rates. We believe that rental rates for Class B industrial properties in our markets are recovering from the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent economic recession, and accordingly we expect increases in lease rates upon renewal of upcoming lease expirations as market conditions continue to improve. Additional detailed market information is set out elsewhere in this prospectus. See “Market Overview.”
49
Future economic downturns affecting our markets could impair our ability to renew or re-lease space, and adverse developments that affect the ability of our tenants to fulfill their lease obligations, such as tenant bankruptcies, could adversely affect our ability to maintain or increase occupancy or rental rates at our properties. Adverse developments or trends in one or more of these factors could adversely affect our rental revenue in future periods.
Scheduled Lease Expirations
Our ability to re-lease space subject to expiring leases will impact our results of operations and will be affected by economic and competitive conditions in the markets in which we operate and by the desirability of our individual properties. In the year ending December 31, 2017 through the year ending December 31, 2019, an aggregate of 51.2% of the annualized base rent leases in the Company Portfolio are scheduled to expire, which we believe will provide us an opportunity to adjust below market rates as market conditions continue to improve.
We have historically been able to quickly and efficiently lease vacant space in the Company Portfolio. During 2015, 2016 and the first quarter of 2017, leases for space totaling 471,948 square feet (13.1% of the Company Portfolio) either was subject to renewal or expired. Of this amount, 432,456 square feet (91.6% of this space) was either renewed or leased to new tenants. At March 31, 2017, the vacancy rate of the Company Portfolio was 1.6%.
| Address | Metro | Status | Tenant | Start
Date |
Square
Feet Expired |
Square
Feet Leased/ Renewed |
Portfolio
Vacancy |
Portfolio
Percent Vacant |
| 12/31/2014 | 22,701 | 0.6% | ||||||
| 7585 Empire Drive | Cincinnati | Expired | Best Sanitizers | 5/31/2015 | 58,050 | 80,751 | 2.0% | |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | Expired | JAS Forwarding | 6/30/2015 | 21,153 | 101,904 | 2.5% | |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | New | Dollar Tree | 7/15/2015 | 21,153 | 80,751 | 2.0% | |
| 6005 E Shelby | Memphis | Expired | Selecta Switch | 7/31/2015 | 41,040 | 121,791 | 3.0% | |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | Expired | Bestway Delivery | 7/31/2015 | 13,680 | 135,471 | 3.4% | |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | Expired | JAS Forwarding | 7/31/2015 | 20,400 | 155,871 | 3.9% | |
| 8273 Green Meadows | Columbus | Renewal | Re-Source USA | 8/1/2015 | 19,328 | 19,328 | 155,871 | 3.9% |
| 7585 Empire Drive | Cincinnati | New | Groneck Transportation | 8/1/2015 | 58,050 | 97,821 | 2.4% | |
| 6005 E Shelby | Memphis | New | Libra Resources | 8/4/2015 | 6,840 | 90,981 | 2.3% | |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | New | In House Logistics | 9/1/2015 | 13,680 | 77,301 | 1.9% | |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | New | Dollar Tree | 9/1/2015 | 20,400 | 56,901 | 1.4% | |
| 6005 E Shelby | Memphis | Expired | Libra Resources | 12/31/2015 | 6,840 | 63,741 | 1.6% | |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | Expired | Dollar Tree | 12/31/2015 | 21,153 | 84,894 | 2.1% | |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | Renewal | Dollar Tree | 1/1/2016 | 20,400 | 20,400 | 84,894 | 2.1% |
| 1755 Enterprise | Cleveland | Renewal | Technoform | 3/1/2016 | 53,970 | 53,970 | 84,894 | 2.1% |
| 4115 Thunderbird | Cincinnati | Renewal | Worldpac | 4/1/2016 | 70,000 | 70,000 | 84,894 | 2.1% |
| 6005 E Shelby | Memphis | New | Impact Innovations | 6/9/2016 | 41,040 | 43,854 | 1.1% | |
| 6005 E Shelby | Memphis | Renewal | Libra Resources | 8/1/2016 | 13,680 | 13,680 | 43,854 | 1.1% |
| 8273 Green Meadows | Columbus | New | Signcaster Corporation | 11/1/2016 | 19,473 | 24,381 | 0.6% | |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | New | Impact Innovations | 9/13/2016 | 21,153 | 3,228 | 0.1% | |
| 6005 E Shelby | Memphis | Expired | Impact Innovations | 11/30/2016 | 41,040 | 44,268 | 1.1% | |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | Expired | Impact Innovations | 11/30/2016 | 21,153 | 65,421 | 1.6% | |
| 6045 E Shelby | Memphis | Renewal | RR Donnelly | 10/30/2016 | 11,352 | 11,352 | 65,421 | 1.6% |
| 6075 E Shelby | Memphis | Renewal | Dollar Tree | 1/1/2017 | 20,400 | 20,400 | 65,421 | 1.6% |
| 2401 Commerce | Chicago | Renewal | VW Credit | 1/1/2017 | 18,309 | 18,309 | 65,421 | 1.6% |
| 4 East Stow Rd | Philadelphia | New | Telissa R. Lindsey | 2/18/2017 | 3,228 | 62,193 | 1.6% | |
| 471,948 | 432,456 |
During 2015, 2016 and the first quarter of 2017, we negotiated 14 leases with durations in excess of six months encompassing 383,310 square feet (excludes three properties consisting of an aggregate of 49,146 square feet, for which the lease terms did not exceed six months). Renewed leases made up 59.3% of the square footage covered by the 14 leases, and the rent under the renewed leases increased an average of 3.3% over the prior leases. Leases to new tenants comprised the other 40.7% of the square footage covered by the 14 leases, and the rent under the new leases increase an average of 28.1% over the prior leases. The rental rates under the all leases entered into in 2015, 2016 and the first quarter of 2017, increased by an average of 10.3% over the rates of the prior leases.
50
The table below reflects certain data about our new and renewed leases with terms of greater than six months executed in 2015, 2016 and the first quarter of 2017.
| Year | Type | Square
Footage |
% of Total Square Footage |
Expiring Rent |
New Rent |
% Change |
Tenant
Improvements $/SF/YR |
Lease Commissions $/SF/YR |
| 2015 | Renewals | 19,328 | 17.3% | $ 4.50 | $ 4.50 | 0.0% | $ 0.03 | $ 0.08 |
| New Leases | 92,130 | 82.7% | $ 2.60 | $ 2.65 | 1.8% | $ 0.04 | $ 0.16 | |
| Total | 111,458 | 100.0% | $ 2.93 | $ 2.97 | 1.3% | $ 0.04 | $ 0.15 | |
| 2016 | Renewals | 169,402 | 73.7% | $ 3.69 | $ 3.83 | 3.8% | $ 0.29 | $ 0.13 |
| New Leases | 60,513 | 26.3% | $ 1.90 | $ 2.98 | 57.1% | $ 0.34 | $ 0.26 | |
| Total | 229,915 | 100.0% | $ 3.22 | $ 3.61 | 12.1% | $ 0.31 | $ 0.16 | |
| 2017 | Renewals | 38,709 | 92.3% | $ 4.57 | $ 4.70 | 2.8% | $ 0.44 | $ 0.30 |
| New Leases | 3,228 | 7.7% | — | $ 9.29 | NA | $ 0.55 | $ 0.68 | |
| Total | 41,937 | 100.0% | $ 3.37 | $ 5.91 | 75.3% | $ 0.47 | $ 0.40 | |
| Total | Renewals | 227,439 | 59.3% | $ 3.91 | $ 4.04 | 3.3% | $ 0.30 | $ 0.15 |
| New Leases | 155,871 | 40.7% | $ 2.27 | $ 2.92 | 28.1% | $ 0.17 | $ 0.21 | |
| Total | 383,310 | 100.0% | $ 3.25 | $ 3.58 | 10.3% | $ 0.24 | $ 0.18 |
Conditions in Our Markets
The Company Portfolio is located primarily in various secondary markets in the Eastern half of the U.S. positive or negative changes in economic or other conditions, adverse weather conditions and natural disasters in these markets are likely to affect our overall performance.
Rental Expenses
Our rental expenses generally consist of utilities, real estate taxes, insurance and site repair and maintenance costs. For the majority of the Company Portfolio, rental expenses are controlled, in part, by either the triple net provisions or modified gross lease expense reimbursement provisions in tenant leases. However, the terms of our tenant leases vary and in some instances the leases may provide that we are responsible for certain rental expenses. Accordingly, our overall financial results will be impacted by the extent to which we are able to pass-through rental expenses to our tenants.
General and Administrative Expenses
Following the completion of this offering, we expect to incur increased general and administrative expenses, including legal, accounting and other expenses related to corporate governance, public reporting and compliance with various provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. In addition, we anticipate that our staffing levels will increase slightly from nine employees as of the date of this prospectus to between 10 and 12 employees during the 12 to 24 months following the closing of this offering and, as a result, our general and administrative expenses will increase further.
Critical Accounting Policies
Our discussion and analysis of our company’s historical financial condition and results of operations are based upon its consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. The preparation of these financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions in certain circumstances that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amount of revenue and expenses in the reporting period. Actual amounts may differ from these estimates and assumptions.
We believe our most critical accounting policies are the regular evaluation of whether the value of a real estate asset has been impaired and accounting for joint ventures. Each of these items involves estimates that require management to make judgments that are subjective in nature. We rely on our experience, we collect historical data and current market data, and we analyze these assumptions in order to arrive at what we believe to be reasonable estimates. Under different conditions or assumptions, materially different amounts could be reported related to the accounting policies described below. In addition, application of these accounting policies involves the exercise of judgments on the use of assumptions as to future uncertainties and, as a result, actual results could materially differ from these estimates.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Management makes significant estimates regarding impairments. These estimates and assumptions are based on management’s best estimates and judgment. Management evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis using historical experience and other factors, including the current economic environment. The current economic environment has increased the degree of uncertainty inherent in these estimates and assumptions. Management adjusts such estimates when facts and circumstances dictate. As future events and their effects cannot be determined with precision, actual results could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
51
Going Concern
In accordance with ASU 2014-15, Presentation of Financial Statements – Going Concern (“ASU 2014-15”), we have evaluated our ability to continue as a going concern. At March 31, 2017, we had an accumulated deficit of $110,947,000 and had limited amounts of liquidity evidenced by the cash position of $1,151,000 as of March 31, 2017. We continue to maintain arrangements with certain vendors to limit future expenses related to certain professional services. Our ability to meet our working capital needs, redeem the Preferred Interests and make required payments under the AIG Loan and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan is dependent on our ability to issue additional equity or secure additional debt financing. These conditions raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern within one year after the date the accompanying consolidated financial statements were issued.
We expect that, upon completion of this offering, we will have sufficient capital to meet our working capital needs. There can be no assurance, however, that upon completion of this offering, that additional debt or other forms of capital will be available on terms acceptable to us, or at all.
Our consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a basis which assumes that we will continue as a going concern and which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities and commitments in the ordinary course of business. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Cash
We maintain our cash in bank deposit accounts, which at times may exceed federally insured limits. As of March 31, 2017, we had not realized any losses in such cash accounts and believe that we are not exposed to any significant risk of loss.
Income Taxes
We elected to be taxed as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2012 and we believe that our organization and method of operation enable us to continue to meet the requirements for qualification and taxation as a REIT. We had no taxable income prior to electing REIT status. To maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must meet certain organizational and operational requirements, including a requirement to distribute at least 90% of our annual REIT taxable income to stockholders (which is computed without regard to the dividends-paid deduction or net capital gain and which does not necessarily equal net income as calculated in accordance with GAAP). As a REIT, we generally will not be subject to federal income tax on income that we distribute as dividends to our stockholders. If we fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT in any tax year, we will be subject to federal income tax on our taxable income at regular corporate income tax rates and generally will not be permitted to qualify for treatment as a REIT for federal income tax purposes for the four taxable years following the year during which qualification is lost, unless we are able to obtain relief under certain statutory provisions. Such an event could materially and adversely affect our net income and net cash available for distribution to stockholders.
Investments in Real Estate
We generally acquire individual properties, and, in some instances, a portfolio of properties. When we acquire individual operating properties with the intention to hold the investment for the long-term, we allocate the purchase price to the various components of the acquisition based upon the fair value of each component. The components typically include land, building, debt, intangible assets related to above and below market leases, value of costs to obtain tenants, and other assumed assets and liabilities. We consider Level 3 inputs such as the replacement cost of such assets, appraisals, property condition reports, comparable market rental data and other related information in determining the fair value of the tangible assets. The recorded fair value of intangible lease assets or liabilities includes Level 3 inputs including the value associated with leasing commissions, legal and other costs, as well as the estimated period necessary to lease such property and lease commencement. An intangible asset or liability resulting from in-place leases that are above or below the market rental rates are valued based upon our estimates of prevailing market rates for similar leases. Intangible lease assets or liabilities are amortized over the estimated, reasonably assured lease term of the remaining in-place leases as an adjustment to “Rental revenues” or “Real estate related depreciation and amortization” depending on the nature of the intangible. The difference between the fair value and the face value of debt assumed in connection with an acquisition is recorded as a premium or discount and amortized to “Interest expense” over the life of the debt assumed. The valuation of assumed liabilities is based on our estimate of the current market rates for similar liabilities in effect at the acquisition date.
In an acquisition of multiple properties, we must also allocate the purchase price among the properties. The allocation of the purchase price is based on our assessment of estimated fair value and often is based upon the expected future cash flows of the property and various characteristics of the markets where the property is located. The fair value may also include an enterprise value premium that we estimate a third party would be willing to pay for a portfolio of properties. The initial allocation of the purchase price is based on management’s preliminary assessment, which may differ when final information becomes available. Subsequent adjustments made to the initial purchase price allocation are made within the allocation period, which typically does not exceed one year.
52
Capitalization of Costs and Depreciation and Amortization
We capitalize costs incurred in developing, renovating, rehabilitating and improving real estate assets as part of the investment basis. Costs incurred in making repairs and maintaining real estate assets are expensed as incurred. During the land development and construction periods, we capitalize interest costs, insurance, real estate taxes and certain general and administrative costs of the personnel performing development, renovations and rehabilitation if such costs are incremental and identifiable to a specific activity to get the asset ready for its intended use. Capitalized costs are included in the investment basis of real estate assets. We also capitalize costs incurred to successfully originate a lease that result directly from, and are essential to, the acquisition of that lease. Leasing costs that meet the requirements for capitalization are presented as a component of other assets.
Real estate, including land, building and land improvements, tenant improvements, and furniture, fixtures and equipment, leasing costs and intangible lease assets and liabilities are stated at historical cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization, unless circumstances indicate that the cost cannot be recovered, in which case, the carrying value of the property is reduced to estimated fair value as discussed below in our policy with regards to impairment of long-lived assets. We estimate the depreciable portion of our real estate assets and related useful lives in order to record depreciation expense. Our ability to estimate the depreciable portions of our real estate assets and useful lives is critical to the determination of the appropriate amount of depreciation and amortization expense recorded and the carrying value of the underlying assets. Any change to the assets to be depreciated and the estimated depreciable lives of these assets would have an impact on the depreciation expense recognized.
As discussed above in investments in real estate, in connection with property acquisitions, we may acquire leases with rental rates above or below the market rental rates. Such differences are recorded as an intangible lease asset or liability and amortized to “Rental revenues” over the reasonably assured term of the related leases. The unamortized balances of these assets and liabilities associated with the early termination of leases are fully amortized to their respective revenue line items in our consolidated financial statements over the shorter of the expected life of such assets and liabilities or the remaining lease term.
Our estimate of the useful life of our assets is evaluated upon acquisition and when circumstances indicate a change in the useful life, which requires significant judgment regarding the economic obsolescence of tangible and intangible assets.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
We assess the carrying values of our respective long-lived assets, including goodwill, whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amounts of these assets may not be fully recoverable.
Recoverability of real estate assets is measured by comparison of the carrying amount of the asset to the estimated future undiscounted cash flows. In order to review our real estate assets for recoverability, we consider current market conditions, as well as our intent with respect to holding or disposing of the asset. Our intent with regard to the underlying assets might change as market conditions change, as well as other factors, especially in the current global economic environment. Fair value is determined through various valuation techniques, including discounted cash flow models, applying a capitalization rate to estimated net operating income of a property and quoted market values and third-party appraisals, where considered necessary. The use of projected future cash flows is based on assumptions that are consistent with our estimates of future expectations and the strategic plan we use to manage our underlying business. If our analysis indicates that the carrying value of the real estate asset is not recoverable on an undiscounted cash flow basis, we recognize an impairment charge for the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the current estimated fair value of the real estate property.
Assumptions and estimates used in the recoverability analyses for future cash flows, discount rates and capitalization rates are complex and subjective. Changes in economic and operating conditions or our intent with regard to our investment that occurs subsequent to our impairment analyses could impact these assumptions and result in future impairment of our real estate properties.
53
Valuation of Receivables
We are subject to tenant defaults and bankruptcies that could affect the collection of outstanding receivables. In order to mitigate these risks, we perform credit reviews and analyses on prospective tenants before significant leases are executed and on existing tenants before properties are acquired. We specifically analyze aged receivables, customer credit-worthiness, historical bad debts and current economic trends when evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts. As a result of our periodic analysis, we maintain an allowance for estimated losses that may result from the inability of our tenants to make required payments. This estimate requires significant judgment related to the lessees’ ability to fulfill their obligations under the leases. If a tenant is insolvent or files for bankruptcy protection and fails to make contractual payments beyond any allowance, we may recognize additional bad debt expense in future periods equal to the net outstanding balances, which include amounts recognized as straight-line revenue not realizable until future periods.
Consolidation
We consolidate all entities that are wholly owned and those in which we own less than 100% but control, as well as any variable interest entities in which we are the primary beneficiary. We evaluate our ability to control an entity and whether the entity is a variable interest entity and we are the primary beneficiary through consideration of the substantive terms of the arrangement to identify which enterprise has the power to direct the activities of a variable interest entity that most significantly impacts the entity’s economic performance and the obligation to absorb losses of the entity or the right to receive benefits from the entity. Investments in entities in which we do not control but over which we have the ability to exercise significant influence over operating and financial policies are presented under the equity method. Investments in entities that we do not control and over which we do not exercise significant influence are carried at the lower of cost or fair value, as appropriate. Our ability to correctly assess our influence and/or control over an entity affects the presentation of these investments in our consolidated financial statements.
Historical Results of Operations
Three Months Ended March 31, 2017 Compared to March 31, 2016
A discussion of operations for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016 is presented below ($ in thousands).
| Three Months Ended March 31, | ||||||||
| Historical Consolidated | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| (Unaudited) | ||||||||
| Rental revenue | $ | 4,938 | $ | 4,808 | ||||
| Other income | 1 | 30 | ||||||
| Total revenues | 4,939 | 4,838 | ||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||
| Property | 1,408 | 1,412 | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 3,028 | ||||||
| General and administrative | 724 | 911 | ||||||
| Acquisition costs | — | 19 | ||||||
| Offering costs | — | — | ||||||
| Total operating expenses | 4,904 | 5,370 | ||||||
| Operating income (loss) | 35 | (532 | ) | |||||
| Other income (expense): | ||||||||
| Gain on disposition of equity investment | — | — | ||||||
| Interest expense | (2,941 | ) | (13,784 | ) | ||||
| Total other income (expense) | (2,941 | ) | (13,784 | ) | ||||
| Net (loss) | (2,906 | ) | (14,316 | ) | ||||
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest | (2,465 | ) | — | |||||
| Net loss attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. common stockholders | $ | (441 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | ||
Rental Revenue: Rental revenue increased by approximately $130 to $4,938 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 as compared to $4,808 for the three months ended March 31, 2016. The increase was primarily related to increased base rent of $94 and increased real estate taxes and utilities reimbursement of $42.
Other Income: Other income decreased by approximately $29 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 compared to the three months ended March 31, 2016. The decrease is primarily due to the sale of the property held in our final investment in joint ventures in the fourth quarter of 2016.
Property Expenses: Property expenses remained substantially consistent at approximately $1,408 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 as compared to $1,412 for the three months ended March 31, 2016.
54
Depreciation and Amortization: Depreciation and amortization expense decreased by approximately $256 to approximately $2,772 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 as compared to $3,028 for the three months ended March 31, 2016, primarily due to the lower amortization of deferred lease intangibles of approximately $283 to $884 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 from $1,167 for the three months ended March 31, 2016.
General and Administrative: General and administrative expenses decreased approximately $187 to $724 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 as compared to $911 for the three months ended March 31, 2016. The decrease is attributable primarily to reduce compensation costs of $112, directors’ fees of $61, and insurance expense of $59 offset by increases in professional fees of $81.
Acquisition Expenses: There were no acquisition expenses incurred during the three months ended March 31, 2017 as compared to $19 for the three months ended March 31, 2016. Acquisition expenses included costs for acquisitions we decide not to pursue.
Interest Expense: Interest expense decreased by approximately $10,843 to $2,941 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 as compared to $13,784 for the three months ended March 31, 2016 due to the refinancing of the Company’s debt through the AIG Loan, the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan and the Preferred Interests and extinguishment of our prior senior loan. The components of interest expense for the three months ended March 31, 2017 consisted of interest on senior secured debt of $1,225, mezzanine debt of $1,125, preferred members interest return of $338 and amortization of deferred financing cost and fees of $253. For more information about our 2016 refinancing transactions, see Note 6 to the unaudited consolidated financial statements for the three months ended March 31, 2017 included elsewhere in this prospectus.
| Three Months Ended March 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Accrued interest payments | $ | 541 | $ | 4,360 | ||||
| Accretion of Senior Loan discount | — | 419 | ||||||
| Make Whole payment at maturity (accretion) | — | 171 | ||||||
| Accretion of financing fees | 253 | — | ||||||
| Default interest | — | 7,444 | ||||||
| Total accretion of interest and deferred interest | $ | 794 | $ | 12,394 | ||||
| Cash interest paid | 2,147 | 1,390 | ||||||
| Total interest expense | $ | 2,941 | $ | 13,784 | ||||
Other Income: There was no other income for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016.
55
Year Ended December 31, 2016 Compared to December 31, 2015
A discussion of operations for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 is presented below ($ in thousands).
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| Historical Consolidated | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Rental revenue | $ | 19,658 | $ | 19,290 | ||||
| Equity investment income (loss) | 230 | (85 | ) | |||||
| Total revenues | 19,888 | 19,205 | ||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||
| Property | 5,927 | 5,751 | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||
| General and administrative | 3,742 | 4,688 | ||||||
| Acquisition costs | — | 1,061 | ||||||
| Offering costs | — | 938 | ||||||
| Total operating expenses | 21,343 | 24,574 | ||||||
| Operating income (loss) | (1,455 | ) | (5,369 | ) | ||||
| Other income (expense): | ||||||||
| Gain on disposition of equity investment | 2,846 | 1,380 | ||||||
| Interest expense | (40,679 | ) | (44,676 | ) | ||||
| Total other income (expense) | (37,833 | ) | (43,296 | ) | ||||
| Net (loss) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest | (2,301 | ) | — | |||||
| Net loss attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. common stockholders | $ | (36,987 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||
Rental Revenue: Rental revenue increased by approximately $368 to approximately $19,658 for the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $19,290 for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase was primarily from base rent increases of $155 and reimbursement of expenses totaling $333 including increased real estate taxes of $105 and utilities of $70 offset by decreased straight line rent of $120.
Equity Investment Income (Loss): Equity income on our investment in joint venture increased approximately $315 in 2016 to $230 as compared to a loss of $85 in 2015 as a result of increased rental revenue at the property level.
Property Expenses: Property expenses increased by approximately $176 to approximately $5,927 for the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $5,751 for the year ended December 31, 2015 primarily due to real estate taxes of $145 and utilities of $65 offset by $34 of other variable expenses.
Depreciation and Amortization: Depreciation and amortization expense decreased by approximately $462 to approximately $11,674 for the year ended December 31, 2016 from $12,136 for the year ended December 31, 2015, due primarily to $478 of lower amortization of deferred lease intangibles to $4,126 for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $4,604 for the year ended December 31, 2015.
General and Administrative: General and administrative expenses decreased approximately $946 to $3,742 for the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $4,688 for the year ended December 31, 2015. The decrease is attributable primarily to reduced professional fees of $1,001, and directors’ fees of $420, offset by increases in compensation and related expense of $221 and Company insurance expense of $284.
Acquisition Expenses: There were no acquisition expenses incurred in 2016. Acquisition expenses were approximately $1,061 for the year ended December 31, 2015. Acquisition expenses include costs for acquisitions we decide not to pursue.
Interest Expense: Interest expense decreased by approximately $3,997 to $40,679 for the year ended December 31, 2016 from $44,676 for the year ended December 31, 2015 due to the refinancing of our debt through the AIG Loan, the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan and the Preferred Interests and extinguishment of our prior senior loan. The schedule below sets out the components of the interest expense for the years ended December 31 2016 and 2015. For more information about our 2016 refinancing transactions, see Note 6 to our consolidated audited financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2016 included elsewhere in this prospectus.
56
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Accrued Interest Payments | $ | 14,428 | $ | 10,295 | ||||
| Accretion of Prior Senior Loan Discount | 419 | 12,877 | ||||||
| Make Whole Payment at Maturity (Accretion) | — | 6,429 | ||||||
| Accretion of Financing Fees | 113 | 2,927 | ||||||
| Default Interest | 18,730 | — | ||||||
| Total accretion of interest and deferred interest | 33,690 | 32,528 | ||||||
| Cash Interest Paid | 6,989 | 12,148 | ||||||
| Total interest expense | $ | 40,679 | $ | 44,676 | ||||
Other Income: Other income represents amounts received in excess of our basis for an equity investment in real estate and the investment liquidated in 2016 and 2015. In 2016, we recognized gain of $2,846 on the disposition of the property held in the joint venture compared to the gain from disposition in 2015 of $1,380.
For an understanding of our expected results of operations following the completion of this offering and the redemption of the Preferred Interests, please refer to our pro forma financial data and related notes thereto included elsewhere in this prospectus. The unaudited pro forma consolidated financial statements are not necessarily indicative of what our actual financial position and results of operations would have been as of the date or for the periods indicated, nor do they purport to represent our future financial position or results of operations.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We believe that this offering will improve the financial position of the Company through changes in our capital structure. Upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions as described in “Use of Proceeds”, we expect to have approximately $49.8 million of cash available for future acquisitions and to meet operational needs of the company. Our ability to meet our working capital needs, redeem the Preferred Interests and make required payments under the AIG Loan and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan is dependent on our ability to complete this offering or secure additional debt financing. These conditions raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern within one year after the date the consolidated financial statements were issued.
We intend to make reserve allocations as necessary to aid our objective of preserving capital for our investors by supporting the maintenance and viability of properties we acquire in the future. If reserves and any other available income become insufficient to cover our operating expenses and liabilities, it may be necessary to obtain additional funds by borrowing, refinancing properties or liquidating our investments.
Our short-term liquidity requirements consist primarily of funds to pay for operating expenses and other expenditures directly associated with our properties, including:
| · | property expenses that are not borne by our tenants under our leases; |
| · | interest expense on outstanding indebtedness; |
| · | general and administrative expenses; and |
| · | capital expenditures for tenant improvements and leasing commissions. |
In addition, we will require funds for future dividends expected to be paid to our common stockholders following completion of this offering.
We intend to satisfy our short-term liquidity requirements through our existing cash, cash flow from operating activities and the proceeds of this offering.
Our long-term liquidity needs consist primarily of funds necessary to pay for acquisitions, recurring and non-recurring capital expenditures and scheduled debt maturities. We intend to satisfy our long-term liquidity needs through cash flow from operations, long-term secured and unsecured borrowings, future issuances of equity and debt securities, property dispositions and joint venture transactions, and, in connection with acquisitions of additional properties, the issuance of OP units.
Contractual Commitments—Historical
The following table sets forth our principal obligations and commitments as of March 31, 2017:
Future Minimum Rents
($ in thousands)
| Corporate Office | 2017 | $ | 162 | |||||
| 2018 | $ | 221 | ||||||
| 2019 | $ | 225 | ||||||
| 2020 | $ | 57 |
In addition to the pro forma contractual obligations set forth in the table above, we have entered into employment agreements with certain of our executive officers. The material terms of the agreements are described under “Executive Compensation—Executive Compensation Arrangements.” We also enter into contracts for maintenance and other services at certain properties from time to time.
57
Existing Indebtedness
AIG Loan
On October 17, 2016, certain indirect subsidiaries of our operating partnership entered into a senior secured loan agreement with investment entities managed by AIG Asset Management, or the AIG Loan Agreement, which provides for a loan of $120 million, or the AIG Loan, bearing interest at 4.08% per annum, and a seven-year term. As of March 31, 2017, there was $120 million outstanding under the AIG Loan Agreement. The AIG Loan Agreement provides for monthly payments of interest only for the first three years of the term and thereafter monthly principal and interest payments based on a 27-year amortization period. Our operating partnership used the net proceeds of the AIG Loan to partially repay the outstanding principal and accrued interest under our then-existing senior secured loan agreement. We are currently in technical violation of the net worth covenant in the AIG loan agreement, which we believe was the result of a drafting error. On May 3, 2017, we entered into an agreement with AIG pursuant to which AIG has agreed to waive this default from October 17, 2016 up to and including June 30, 2017. We believe that we will be in compliance with all covenants under the AIG Loan Agreement upon the closing of this offering.
The borrowings under the AIG Loan Agreement are secured by first lien mortgages on all of the properties in the Company Portfolio. The obligations under the AIG Loan Agreement are also guaranteed by our company and each of our operating partnership’s wholly-owned subsidiaries.
Torchlight Mezzanine Loan
On October 17, 2016, Plymouth Industrial 20 entered into a mezzanine loan agreement, or the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan Agreement, with Torchlight, which provides for a loan of $30 million, or the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan, and a seven-year term. The Torchlight Mezzanine Loan bears interest at 15% per annum, of which 7% percent is paid currently during the first four years of the term and 10% is paid for the remainder of the term. The Torchlight Mezzanine Loan requires Plymouth Industrial 20 to pay a repayment premium equal to the difference between (x) the sum of 150% of the principal being repaid (excluding accrued interest) and (y) the sum of the actual principal amount being repaid and current and accrued interest paid through the date of repayment. This repayment feature operates as a prepayment feature since the difference will be zero at maturity. The borrowings under the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan are secured by, among other things, pledges of the equity interest in Plymouth Industrial 20 and each of its property-owning subsidiaries. The proceeds of the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan were used to partially repay the outstanding principal and accrued interest under our then-existing senior secured loan agreement.
Redeemable Preferred Member Interests
On October 17, 2016, and in connection with its refinancing of the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan, the Company issued Torchlight a 99.5% redeemable preferred member interest, or the Preferred Interests, in Plymouth Industrial 20 in exchange for $30.5 million. The Preferred Interest is mandatorily redeemable at its redemption price, as defined below, by the Company on January 17, 2017. In the event we default under the Preferred Interests, the interests held by us transfers automatically to Torchlight for payment of one dollar. The redemption price of the Preferred Interests is the amount of Torchlight’s unreturned capital contributions ($30.5 million at March 31, 2017), a preferred return equal to a cumulative annual return of 7%, plus any additional preferred return, compounded monthly on an amount equal to the unreturned capital contributions until the date that such amount is returned to Torchlight, all accrued but unpaid priority preferred returns on Torchlight’s priority additional capital contributions equal to a cumulative annual return of 20%, compounded monthly, on an amount equal to (a) each dollar of Torchlight’s priority additional capital contributions until the date that such amount is returned to Torchlight and all other sums advanced and costs and expenses (including legal fees) incurred by Torchlight in connection with such redemption. There had been no priority additional capital contributions made to Torchlight at December 31, 2016. The carrying value of the Preferred Interest amounted to $31.0 million, including $0.5 million of preferential returns, at December 31, 2016. All amounts are current liabilities at March 31, 2017. Torchlight has agreed, (i) to extend the redemption date of the Preferred Interests from January 17, 2017 to June 16, 2017; (ii) to fix the balance of the Preferred Interests at $25.0 million; and (iii) that the Preferred Interests will bear no interest or be entitled to any additional preferential returns. Of the amount due, we will pay Torchlight $20.0 million in cash and issue 263,158 shares of common stock upon the completion of this offering. Restricted cash in the amount of $5.6 million, which was included on the consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2016, had been applied to the amount due under the Preferred Interest in February 2017. In the event we do not make the required payment by June 16, 2017, Torchlight has the right to acquire our ownership in Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC for $1.
58
In addition, pursuant to the Letter Agreement, we have the right to terminate the TL Participation in consideration for the private issuance of warrants to Torchlight to acquire 250,000 shares of our common stock, which we expect to issue concurrently with the closing of this offering.
In summary, our cash flows for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016 and for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
| ($ in thousands) | Three Months Ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 644 | $ | 436 | $ | 220 | $ | (4,351 | ) | |||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | $ | (434 | ) | $ | (209 | ) | $ | (1,632 | ) | $ | 1,620 | |||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,655 | $ | (1,545 | ) | |||||||
Operating Activities: Net cash provided by operating activities during the three months ended March 31, 2017 increased approximately $208 compared to the three months ended March 31, 2016 primarily due to reduced general and administrative expense. Net cash provided by operating activities was approximately $220 during the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to net cash used of $4,351 in operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2015 due primarily to a decreased amount of interest paid of $5,159 from 2015 to 2016 due to the lack of liquidity in 2016 partially offset by increases in prepaid expenses and cash held in escrow.
Investing Activities: Net cash used in investing activities during the three months ended March 31, 2017 increased approximately $225 compared to the three months ended March 31, 2016 primarily due to increased cash held in escrow of $398 offset by reduced real estate improvements of $222. Net cash used in investing activities in 2016 amounted to $1,632 due primarily to an increase in cash held in escrow during 2016. Net cash provided by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2015 was due primarily to funds provided from the disposition of the investment in real estate joint ventures.
Financing Activities: For the year ended December 31, 2016, the Company refinanced senior debt by borrowing $116,102 from AIG, net of $3,898 of debt issuance costs and repaid Torchlight $114,447. For the year ended December 31, 2015, we incurred debt issuance costs related to the respective Senior Loan maturity date extensions of $1,095 and offering costs of $450.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no off-balance sheet arrangements.
Interest Rate Risk
ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging (formerly known as SFAS No. 133, Accounting for Derivative Instruments and hedging Activities, as amended by SFAS No. 138, Accounting for Certain Derivative Instruments and Certain Hedging Activities), requires us to recognize all derivatives on the balance sheet at fair value. Derivatives that are not hedges must be adjusted to fair value and the changes in fair value must be reflected as income or expense. If the derivative is a hedge, depending on the nature of the hedge, changes in the fair value of derivatives are either offset against the change in fair value of the hedged assets, liabilities, or firm commitments through earnings or recognized in other comprehensive income, which is a component of stockholders equity. The ineffective portion of a derivative’s change in fair value is immediately recognized in earnings.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
In this prospectus, we disclose NOI, EBITDA, FFO and AFFO, each of which meet the definition of “non-GAAP financial measure” set forth in Item 10(e) of Regulation S-K promulgated by the SEC. As a result we are required to include in this prospectus a statement of why management believes that presentation of these measures provides useful information to investors.
None of NOI, EBITDA, FFO or AFFO should be considered as an alternative to net income (determined in accordance with GAAP) as an indication of our performance, and we believe that to understand our performance further NOI, EBITDA, FFO, and AFFO should be compared with our reported net income or net loss and considered in addition to cash flows in accordance with GAAP, as presented in our consolidated financial statements.
The unaudited pro forma consolidated balance sheet data is presented as if this offering and the Torchlight Transactions had occurred on March 31, 2017, and the unaudited pro forma statements of operations and other data for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and the year ended December 31, 2016 are presented as if this offering and the Torchlight Transactions had occurred on January 1, 2017 and January 1, 2016, respectively. The pro forma consolidated financial information is not necessarily indicative of what our actual financial condition would have been as of March 31, 2017 or December 31, 2016 or what our actual results of operations would have been assuming this offering had been completed as of January 1, 2017 or January 1, 2016, nor does it purport to represent our future financial position or results of operations.
59
NOI
We consider net operating income, or NOI, to be an appropriate supplemental measure to net income because it helps both investors and management understand the core operations of our properties. We define NOI as total revenue (including rental revenue, tenant reimbursements, management, leasing and development services revenue and other income) less property-level operating expenses including allocated overhead. NOI excludes depreciation and amortization, general and administrative expenses, impairments, gain/loss on sale of real estate, interest expense, and other non-operating items.
The following is a reconciliation from pro forma and historical reported net loss, the most directly comparable financial measure calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP, to NOI:
| (In thousands) | Three Months Ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro
forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,730 | ) | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
| General and administrative | 886 | 724 | 911 | 4,392 | 3,742 | 4,688 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition expense | — | — | 19 | — | — | 1,061 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 2,603 | 2,941 | 13,784 | 40,189 | 40,679 | 44,676 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Offering costs | — | — | — | — | — | 938 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other (income) expense | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | (30 | ) | (3,076 | ) | (3,076 | ) | (1,295 | ) | ||||||||||||
| NOI | $ | 3,530 | $ | 3,530 | $ | 3,396 | $ | 13,731 | $ | 13,731 | $ | 13,539 | ||||||||||||
EBITDA
We believe that earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, or EBITDA, is helpful to investors as a supplemental measure of our operating performance as a real estate company because it is a direct measure of the actual operating results of our industrial properties. We also use this measure in ratios to compare our performance to that of our industry peers. The following table sets forth a reconciliation of our pro forma and historical EBITDA for the periods presented.
| (In thousands) | Three Months Ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro
forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,730 | ) | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 2,603 | 2,941 | 13,784 | 40,189 | 40,679 | 44,676 | ||||||||||||||||||
| EBITDA | $ | 2,645 | $ | 2,807 | $ | 2,496 | $ | 12,415 | $ | 13,065 | $ | 8,147 | ||||||||||||
FFO
Funds from operations, or FFO, is a non-GAAP financial measure that is widely recognized as a measure of REIT operating performance. We consider FFO to be an appropriate supplemental measure of our operating performance as it is based on a net income analysis of property portfolio performance that excludes non-cash items such as depreciation. The historical accounting convention used for real estate assets requires straight-line depreciation of buildings and improvements, which implies that the value of real estate assets diminishes predictably over time. Since real estate values rise and fall with market conditions, presentations of operating results for a REIT, using historical accounting for depreciation, could be less informative. We define FFO, consistent with the National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts, or NAREIT, definition, as net income, computed in accordance with GAAP, excluding gains (or losses) from sales of property, depreciation and amortization of real estate assets, impairment losses and after adjustments for unconsolidated partnerships and joint ventures. Adjustments for unconsolidated partnerships and joint ventures will be calculated to reflect FFO on the same basis. Other equity REITs may not calculate FFO in accordance with the NAREIT definition as we do, and, accordingly, our FFO may not be comparable to such other REITs’ FFO. FFO should not be used as a measure of our liquidity, and is not indicative of funds available for our cash needs, including our ability to pay dividends.
60
The following table sets forth a reconciliation of our pro forma and historical net loss to FFO for the periods presented:
| (In thousands) | Three Months Ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro
forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2730 | ) | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | $ | (39,448 | ) | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 2,772 | 3,028 | 11,674 | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gain on disposition of equity investment | — | — | — | (2,846 | ) | (2,846 | ) | (1,380 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Adjustment for unconsolidated joint ventures | — | — | — | 452 | 452 | 1,363 | ||||||||||||||||||
| FFO | $ | 42 | $ | (134 | ) | $ | (11,288 | ) | $ | (30,168 | ) | $ | (30,008 | ) | $ | (36,546 | ) | |||||||
AFFO
Adjusted funds from operation, or AFFO, is presented in addition to FFO calculated in accordance the standards set forth by NAREIT. AFFO is defined as FFO, excluding acquisition and transaction related costs as well as certain other costs that we consider to be non-recurring. The purchase of properties, and the corresponding expenses associated with that process, is a key operational feature of our business plan to generate operational income and cash flows in order to make distributions to investors. In evaluating investments in real estate, we differentiate the costs to acquire the investment from the operations derived from the investment. By excluding expensed acquisition and transaction related costs as well as other non-recurring costs, we believe AFFO provides a useful supplemental measure of our operating performance because it provides a consistent comparison of our operating performance across time periods that is comparable for each type of real estate investment and is consistent with management’s analysis of the operating performance of our properties.
AFFO further adjusts FFO for certain other non-cash items, including the amortization or accretion of above or below market rents included in revenues, straight line rent adjustments, impairment losses and non-cash equity compensation. As with FFO, our reported AFFO may not be comparable to other REITs’ AFFO, should not be used as a measure of our liquidity, and is not indicative of our funds available for our cash needs, including our ability to pay dividends.
The following table sets forth a reconciliation of our pro forma and historical FFO to AFFO.
| (In thousands) | Three Months Ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro
forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | Pro
Forma Consolidated | Historical Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| FFO | $ | 42 | $ | (134 | ) | $ | (11,288 | ) | $ | (30,168 | ) | $ | (30,008 | ) | $ | (36,546 | ) | |||||||
| Amortization of above or accretion of below market lease rents | (83 | ) | (83 | ) | (88 | ) | (355 | ) | (355 | ) | (351 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Acquisition costs | — | — | 19 | — | — | 1,061 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Offering Costs | — | — | — | — | — | 938 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 162 | — | — | 650 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Distributions | — | — | 49 | 337 | 337 | 2,030 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Straight line rent | (45 | ) | (45 | ) | (75 | ) | (287 | ) | (287 | ) | (404 | ) | ||||||||||||
| AFFO | $ | 76 | $ | (262 | ) | $ | (11,383 | ) | $ | (29,823 | ) | $ | (30,313 | ) | $ | (33,272 | ) | |||||||
Inflation
The majority of our leases are either triple net or provide for tenant reimbursement for costs related to real estate taxes and operating expenses. In addition, most of the leases provide for fixed rent increases. We believe that inflationary increases may be at least partially offset by the contractual rent increases and tenant payment of taxes and expenses described above. We do not believe that inflation has had a material impact on our historical financial position or results of operations.
61
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) (“ASU 2014-09”), which supersedes all existing revenue recognition requirements, including most industry-specific guidance. The new standard requires a company to recognize revenue when it transfers goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration that the company expects to receive for those goods or services. The new standard will be effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017. Earlier application is permitted only for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim reporting periods within that reporting period. We are in the process of evaluating the impact of this pronouncement on its consolidation financial statements.
In August 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-15, Presentation of Financial Statements – Going Concern (“ASU 2014-15”), which requires a company to evaluate the existence of conditions or events that raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern within one year of the issuance date of its financial statements. The standard is effective for interim and annual periods ending after December 15, 2016 with early adoption permitted. We have evaluated the impact of ASU 2014-15 and have included the appropriate disclosures in the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
In February 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-02, Consolidation (Topic 810) (“ASU 2015-02”), to address financial reporting considerations for the evaluation as to the requirement to consolidate certain legal entities. ASU 2015-02 is effective for fiscal years and for interim periods within those fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2015. We have evaluated the impact of ASU 2015-02 and has concluded that it has no effect on the consolidated financial statements.
In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-01, Financial Instruments – Overall: Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities. ASU 2016-01 requires equity investments (except those accounted for under the equity method of accounting, or those that result in consolidation of the investee) to be measured at fair value with changes in fair value recognized in net income, requires public business entities to use the exit price notion when measuring the fair value of financial instruments for disclosure purposes, requires separate presentation of financial assets and financial liabilities by measurement category and form of financial asset, and eliminates the requirement for public business entities to disclose the method(s) and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair value that is required to be disclosed for financial instruments measured at amortized cost. ASU 2016-01 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early application is permitted. We are currently assessing the potential impact that the adoption of ASU 2016-01 will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases (“ASU 2016-02”), which requires a lessee to recognize assets and liabilities on the balance sheet for operating leases and changes many key definitions, including the definition of a lease. The update includes a short-term lease exception for leases with a term of 12 months or less, in which a lessee can make an accounting policy election not to recognize lease assets and lease liabilities. For lessees, the recognition, measurement, and presentation of expenses and cash flows arising from a lease have not significantly changed from previous U.S. GAAP. Lessees and lessors are required to recognize and measure leases at the beginning of the earliest period presented using a modified retrospective approach. The modified retrospective approach includes a number of optional practical expedients that entities may elect to apply as well as transition guidance specific to nonstandard leasing transactions. ASU 2016-02 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within those fiscal years. We are currently evaluating the potential impact that the adoption of ASU 2016-02 may have on its consolidated financial statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09, Stock Compensation – Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting, (“ASU 2016-09”), which simplifies several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment transactions, including the income tax consequences, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, classification on the statement of cash flows and policy elections on the impact for forfeitures. ASU 2016-09 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016 and interim periods within those annual periods. We are in the process of evaluating the impact of ASU 2016-09 on its financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash (“ASU 2016-18”). The ASU requires an entity to explain the changes in the total of cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash, and restricted cash equivalents on the statement of cash flows and to provide a reconciliation of the totals in that statement to the related captions in the balance sheet when the cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash, and restricted cash equivalents are presented in more than one line item on the balance sheet. This ASU is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2017, and is required to be adopted using a retrospective approach, with early adoption permitted. We are currently evaluating the potential impact that the adoption of ASU 2016-18 may have on its consolidated financial statements.
Other accounting standards that have been issued or proposed by the FASB or other standards-setting bodies that do not require adoption until a future date are not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements upon adoption.
62
Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an “emerging growth company” can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act for complying with new or revised accounting standards. However, we are choosing to “opt out” of such extended transition period and, as a result, we will comply with any such new or revised accounting standards on the relevant dates on which adoption of such standards is required for non-emerging growth companies.
Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that our decision to opt out of the extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards is irrevocable.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure About Market Risk
Our future income, cash flows and fair values relevant to financial instruments are dependent upon prevailing market interest rates. Market risk refers to the risk of loss from adverse changes in market prices and interest rates. In the future, we may use derivative financial instruments to manage, or hedge, interest rate risks related to our borrowings, primarily through interest rate swaps.
An interest rate swap is a contractual agreement entered into by two counterparties under which each agrees to make periodic payments to the other for an agreed period of time based on a notional amount of principal. Under the most common form of interest rate swap, known from our perspective as a floating-to-fixed interest rate swap, a series of floating, or variable, rate payments on a notional amount of principal is exchanged for a series of fixed interest rate payments on such notional amount.
No assurance can be given that any future hedging activities by us will have the desired beneficial effect on our results of operations or financial condition.
63
MARKET OVERVIEW
Market Opportunity
A key component of our business strategy is to tap into forecasted U.S. economic growth by investing in industrial real estate that we believe will benefit from rental growth and increased tenant demand. We believe that in some cases there has already been significant growth and capitalization rate compression in primary markets in the Class A industrial sector, but that there still exists an opportunity to take advantage of capitalization rate compression, favorable pricing, limited supply and competition in secondary growth markets and in Class B properties. While we will focus on the acquisition of Class B industrial properties in secondary markets, we may also make opportunistic acquisitions of Class A industrial properties and industrial properties in primary markets.
Our acquisition pipeline focuses on a select group of target markets, including, among others, Atlanta, Chicago, Cincinnati, Columbus and Memphis, which we believe possess certain characteristics that we believe are beneficial to industrial real estate investment. These characteristic include, but are not limited to, employment growth, recent and forecasted rent growth, a shortage of industrial development, and falling vacancy rates. We believe that these characteristics will allow us to increase rental rates, increase occupancy and drive value.
U.S. Economic Trends
We believe that growth in U.S. gross domestic product, or U.S. GDP, is a key driver of performance for industrial real estate. Coupled with solid industry fundamentals and limited new supply of suitable industrial real estate in our target markets, we believe that current market conditions make investments in Class B industrial real estate in secondary markets particularly attractive.
U.S. Economic Outlook Through 2027
According to forecasts by the CBO, inflation-adjusted U.S. GDP grew by 1.8% in 2016 and is expected to grow 2.3% in 2017, 1.9% in 2018, and 1.7% in 2019. The CBO expects that these increases in U.S. GDP will spur businesses to maintain and or grow hiring rates, which will continue to push down the unemployment rate and raise the rate of participation in the labor force. In particular, the CBO projects that the unemployment rate will maintain a range of 4.5% to 5.0% over the next 11 years. Overall, the CBO anticipates that over the next decade, inflation-adjusted U.S. GDP will increase at an average annual pace of 1.9%. We expect that increased employment will lead to increased consumer spending, further enhancing the demand for warehouse space, particularly in an e-commerce retail environment.
Key Drivers of Industrial Real Estate Market: Trade, Manufacturing/Production, and Consumer Consumption
In addition to our belief in the correlation between U.S. GDP growth and U.S. industrial real estate performance, we believe that industrial real estate fundamentals in our target markets will be favorably impacted by observable macroeconomic factors including increased rates related to international trade, manufacturing /production and consumer consumption. These key factors experienced declines during the recent recession but have experienced positive growth since 2011 and we believe the continued growth related to these three key drivers will increase demand for and enhance the value of U.S. industrial real estate.
64
Industrial Trade
Industrial trade is one of the most important drivers of industrial real estate demand as import and export volume greatly determine the amount of space that is needed in order to store goods. Since the recession of 2008 - 2010, exports have been one of the key drivers of the recovery in trade, with export levels up now more than 20.1% from pre-recession levels as illustrated in the graph below. While import rates have not grown as quickly as export rates since the recession, import rates (excluding oil) have risen 6.4% over pre-recession levels, which have resulted in further increased demand for industrial real estate space. We believe that this recovery to import and export rates should continue during 2017, which should help drive demand for industrial space.
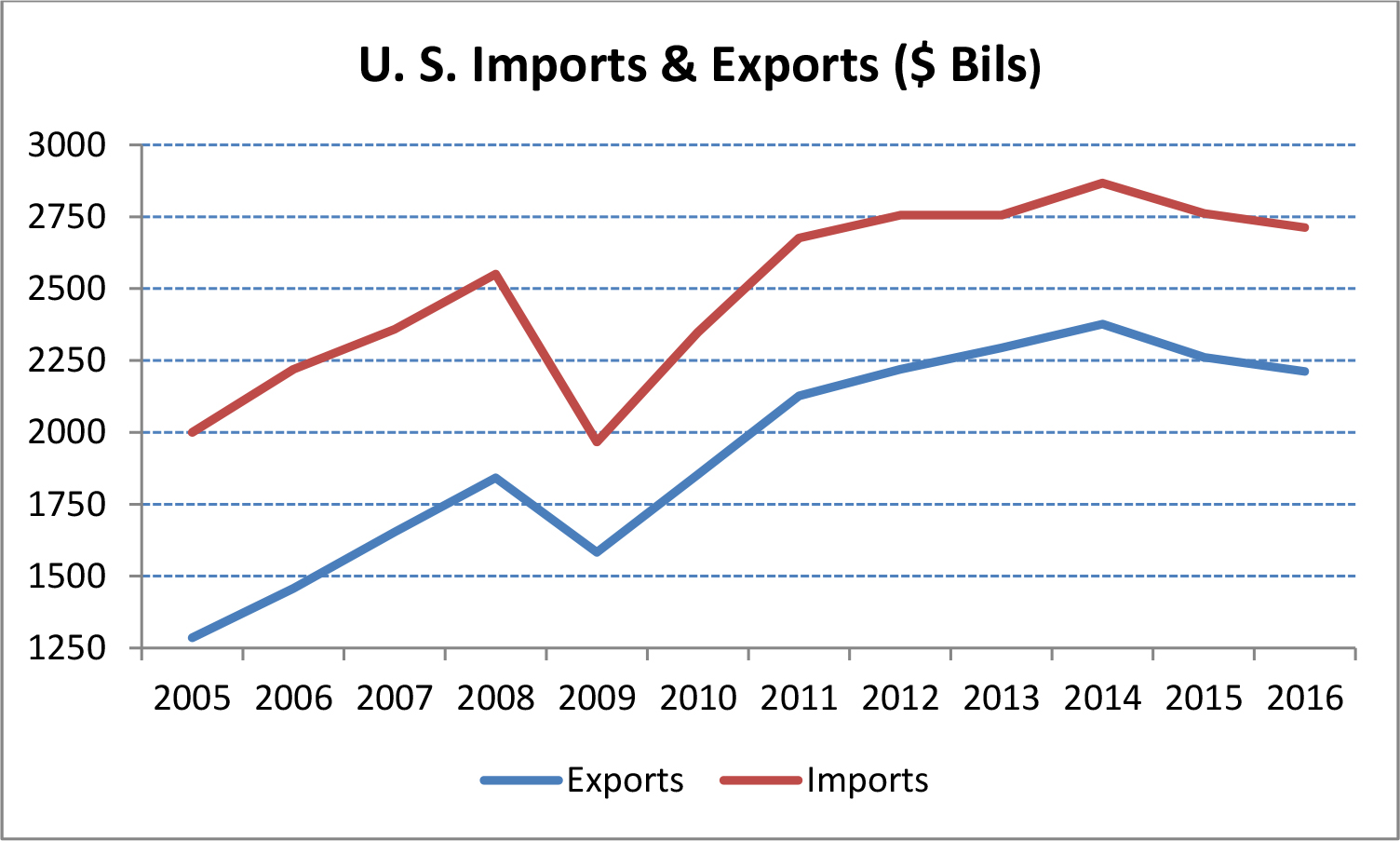 |
| Figure 1 (Source: US Department of Commerce — Bureau of Economic Analysis) |
Manufacturing and Production
We believe that manufacturing and production are key components of industrial real estate performance as the level of goods that are manufactured and produced has a positive correlation with the amount of space needed to store such goods. The productivity of U.S. mines and factories, as measured by the industrial production index, picked up pace in 2013 and has maintained its momentum to date. Due in large part to the surge in domestic energy production, the U.S. is enjoying lower energy costs, which, combined with more competitive labor costs, should allow industrial production to continue to expand in 2017.
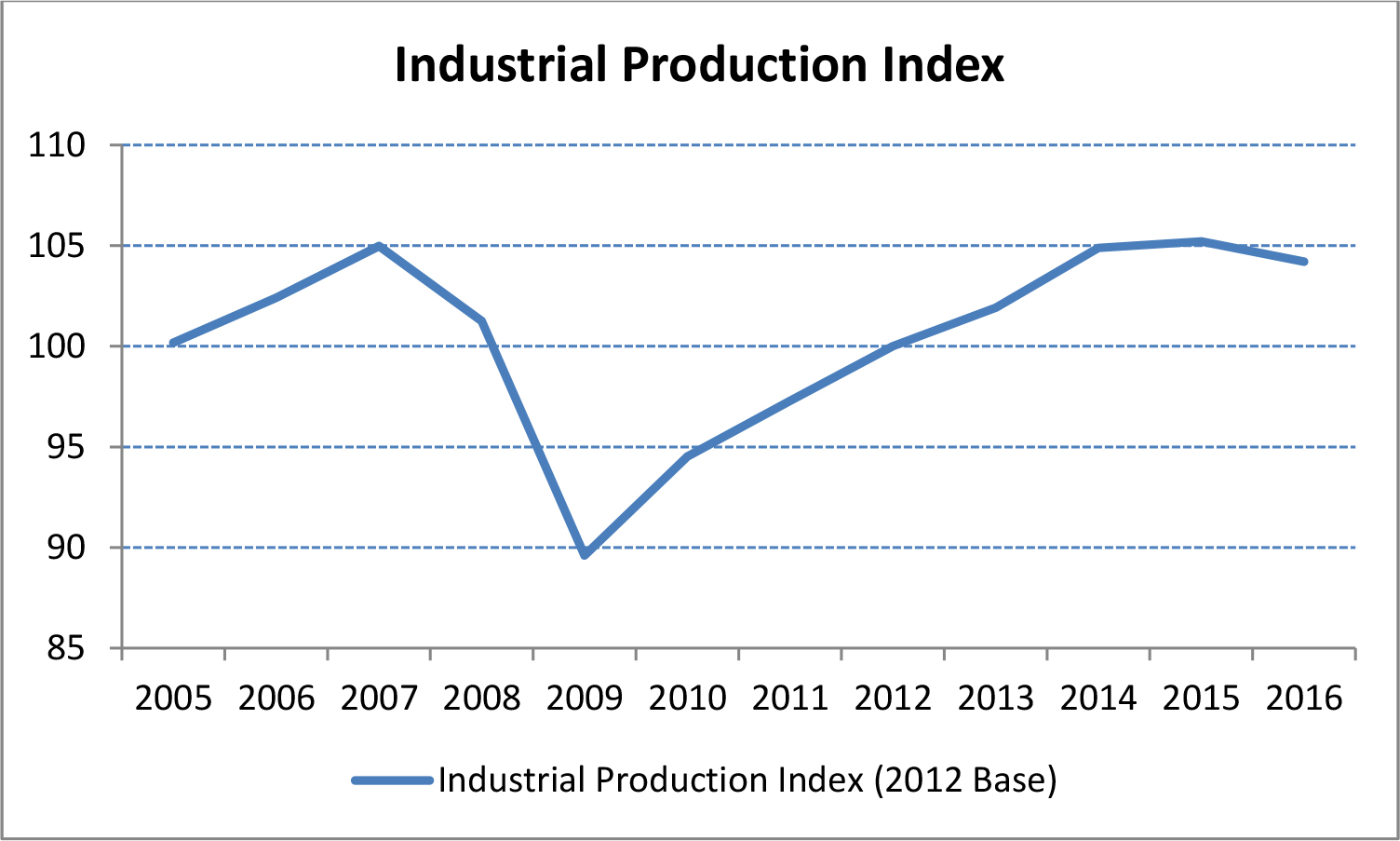 |
| Figure 2 (Source: US Federal Reserve) |
65
In 2015, the U.S. industrial capacity utilization rate stood just above its historical average, with some sectors running well above their long-run averages. We believe that this suggests that more investment in industrial capacity will be needed for industrial production to continue growing The CBO is forecasting that business investment will grow by 5.0% in 2017 and grow on average around 2.2% the following three years. Likewise, the CBO also forecasts total output to grow closer to 2.0% per year rather than the 1.4% increase realized between 2008 and 2016.
Consumer Consumption
Consumer consumption, which accounts for two-thirds of U.S. GDP, declined during the recession, as high unemployment and stagnating wages forced people to cut back on non-essential spending. However, since 2009, real consumer spending has grown at an annual rate of 2.3%.
 |
| Figure 3 (Source: US Department of Commerce — Bureau of Economic Analysis) |
66
Industrial Real Estate Fundamentals
Overview
According to CBRE, industrial real estate demand going into 2017 is strong. In many of our target markets vacancy rates are steadily dropping, construction is starting to slowly pick up and rent growth remains healthy. New construction has lagged leasing demand for 25 consecutive quarters. We believe that while construction starts continue to remain limited and economic demand drivers continue to power absorption, industrial fundamentals will continue to strengthen. We believe that, as a result of the lack of new construction and overall demand for industrial properties in many U.S. markets, vacancy rates will continue to fall until rent growth increases to a point where developers can justify undergoing more speculative projects. The following graph illustrates this on an historical basis.
 |
| Figure 4 (Source: CBRE) |
This belief aligns with REIS’ data and projections on occupancy and effective rental forecasts for both the 6.4 billion square foot warehouse/distribution and 1.2 billion square foot U.S. Flex/R&D markets, which, as illustrated in the two graphs below, show an increase in effective rents since 2011 and a declining vacancy rate through 2020.
 |
 |
| Figure 5 (Source: REIS) | Figure 6 (Source: REIS) |
In the longer term, industrial real estate fundamentals are expected to continue to be strong, as the sector is uniquely positioned to benefit from current economic trends, including increased trade growth, inventory rebuilding, and increased industrial output. Additionally, developing trends point to a strong near-to medium-term outlook for the sector. For example, the growth of big-box warehouses serving large online retailers close to population centers is forecasted to gain popularity, which we believe could potentially influence smaller e-retailers to do the same.
67
Increased e-commerce has a positive impact on warehouse demand, as it tends to transfer retail tenants to warehouses. According to CBRE, U.S. e-commerce sales now comprise 8% of all US retail sales, up from 5.8% in 2013 and 1.5% in 2003. With massive increase in online sales over the past 15 years, e-commerce companies have had to make major investments in infrastructure and facilities to keep pace with demand. This is expected to continue, as online sales keep growing with traditional brick and mortar retailers employing multi-channel sale strategies. Additionally, this emergence of e-commerce and the growth of internet retailers and wholesalers are expanding the universe of tenants seeking industrial space in our target markets, which should drive demand and rent growth into the future.
Manufacturing is also likely to play an increased role in the industrial sector’s recovery. With energy prices and labor costs down, we believe that the fundamentals support a sustained resurgence in domestic manufacturing. Lack of supply may be a hurdle for continued demand growth, as some markets are already reporting shortages of space in certain asset types.
Our Target Markets
The U.S. Industrial real estate market is large and there is significant opportunity for REITs to participate in that market. According to CoStar, the U.S. industrial real estate market is 15.4 billion square feet and it’s estimated to be valued at approximately $1 trillion. Industrial REITs currently only own approximately 8%, or 1.2 billion square feet, of the U.S. industrial real estate market.
The following sections reflect the current market status, based largely on REIS data, of the key markets in which we currently own and where we expect to acquire additional properties in the future. Currently, these markets include Atlanta, Chicago, Cincinnati, Columbus and Memphis.
Atlanta Industrial Market
Overall Market Fundamentals
Atlanta’s long-standing role as a significant center for logistics, along with its centralized location (which is bisected by key transportation corridors) and an international airport have established Atlanta as a leading warehouse/distribution market. These substantial advantages of the Atlanta market have driven prominent firms including Home Depot, Walmart, Williams-Sonoma, and others in their decisions to open facilities in the region. Other large projects, including new warehouses for FedEx and Dollar General, are in progress. Warehouse demand has been exceedingly strong, keeping pace, and then some, with the rising volumes of new supply. Thus, the completion of nearly 9.3 million square feet of new warehouse/distribution space in 2016 met with more than 9.8 million square feet of net absorption. Vacancy only dropped marginally during 2016 but is forecasted to drop over the coming years as new supply slows and move-ins take place.
As seen below in Figure 7, U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) preliminary data for December 2016 put total non-farm employment up 74,217 jobs (2.9%) from 12 months earlier, with the gain over 24 months being 156,5567 jobs (6.2%).
 |
| Figure 7 (Source: US Department of Labor) |
Employment growth is strong and is diversified among a number of industries (professional and business services, transportation, utilities, travel, education and health services). According to REIS, the distribution/warehouse vacancy rate finished 2016 at 12.0% and will fall 0.7 percentage points to 11.3% by year-end 2018. REIS also projects that asking rent growth will accelerate to an annualized average of 3.2% during 2017 and 2018 to reach a level of $4.11 per square foot. Effective rents are forecasted to climb by a more rapid annualized average rate of 3.4%, during the same period, as market conditions begin to allow landlords to reduce the value of concession packages.
68
Atlanta Warehouse/Distribution Market
A summary of key real estate supply and demand market indicators show that during Q4 2016 the Atlanta warehouse/distribution market recorded positive net absorption of 4.2 million square feet which advanced effective rents and pushed the vacancy rate down. As seen in Figure 8 below, the Atlanta metro warehouse/distribution absorption also totaled 9.8 million square feet over the past four quarters. Additionally, the market’s year-end 2016 vacancy rate was 2.1 percentage points lower than the 14.1% average since 2010.
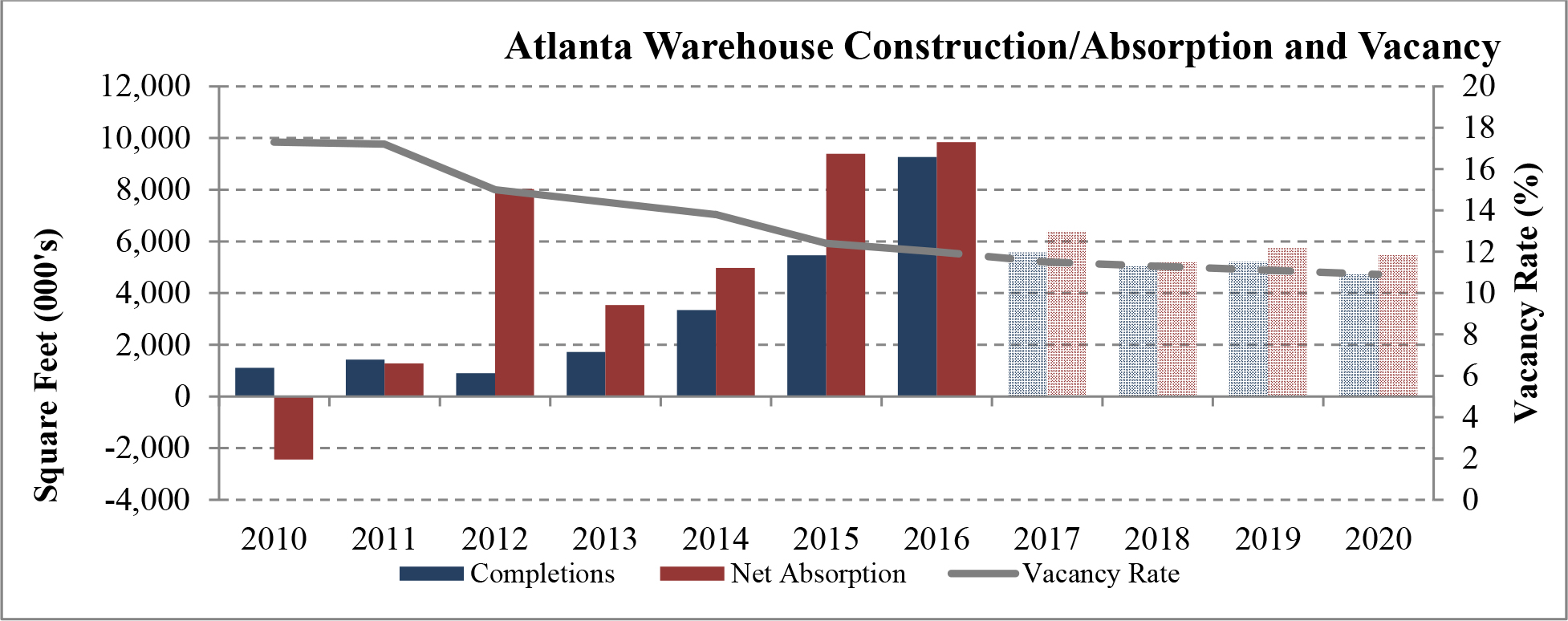 |
| Figure 8 (Source: REIS) |
Also during Q4 2016, effective rents rose by 1.2%, 3.3% for the year, to an average of $3.43. As shown in Figure 9, positive movement in effective rent is slated to continue.
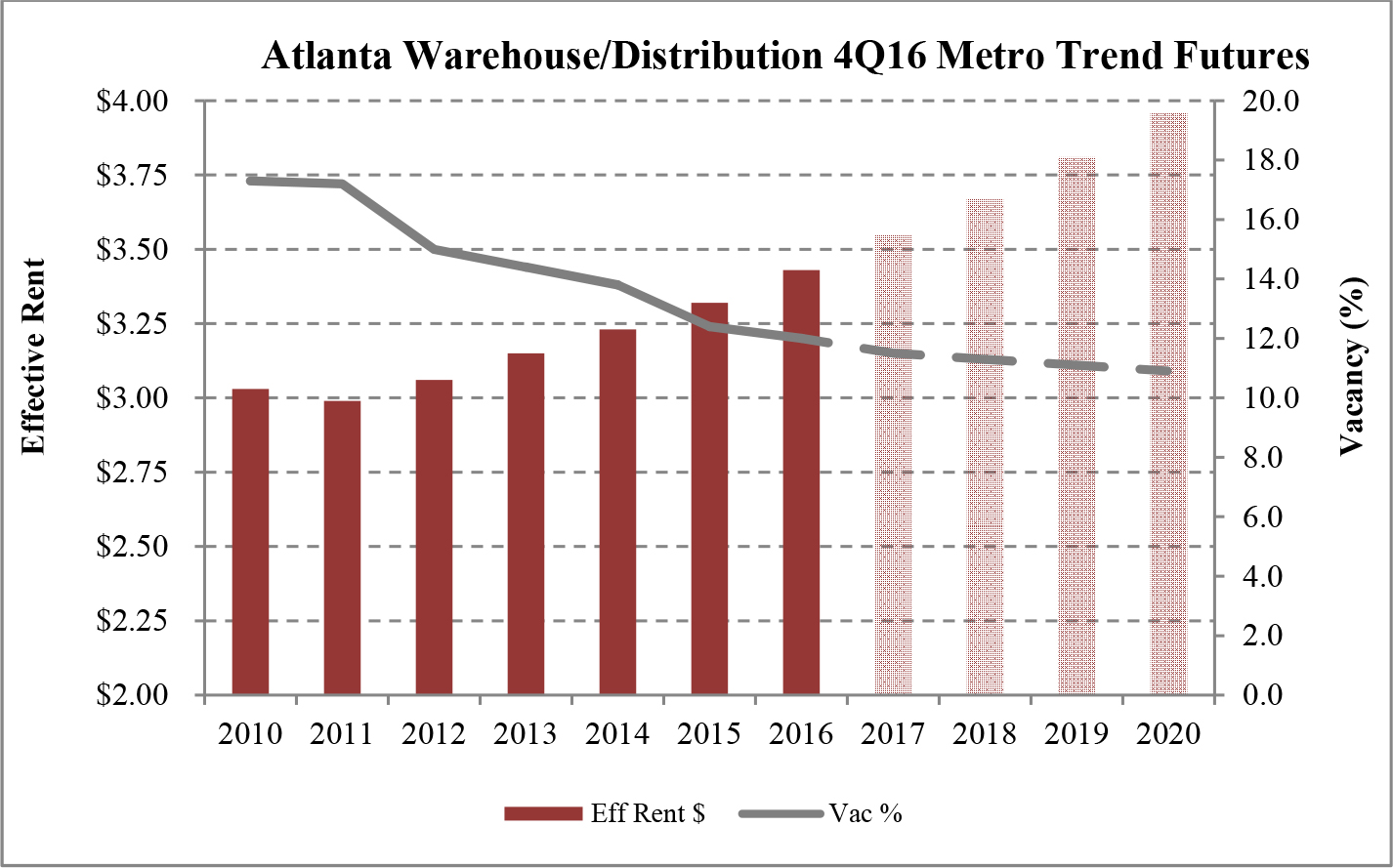 |
| Figure 9 (Source: REIS) |
69
Atlanta Flex/R&D Market
Atlanta’s 50.3 million square foot metro area Flex/R&D sector had a solid year in 2016 with net absorption of 735,000 square feet. Currently there are limited Flex/R&D projects under construction which should help keep net absorption high in the future. As seen in Figures 10 and 11 below, a summary of key real estate supply and demand metrics shows that during 2016 the Atlanta Flex/R&D market recorded increasing effective rents, positive net absorption, and downward movement in the market’s vacancy rate. Effective rents increased by 0.7% during Q4 2016, 2.2% in all of 2016, to an average of $5.47. Additionally, asking rents rose by 0.6% during the Q4 2016 and 2.0% for the year.
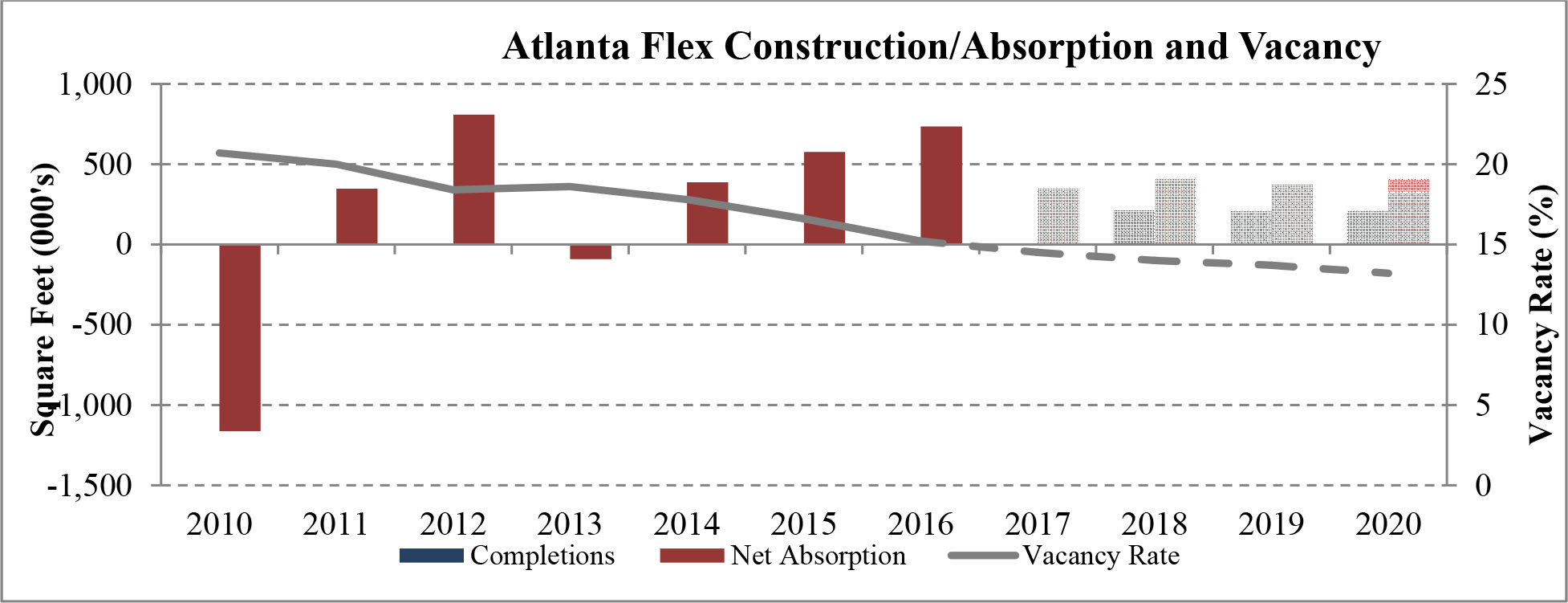 |
| Figure 10 (Source: REIS) |
Atlanta experienced positive net absorption for each of the past three years and is projected to remain that way for the next four years. From a historical perspective, the market’s year ending 2016 vacancy rate is 2.6 percentage points lower than its 17.8% average recorded since 2010.
As per REIS, over the next two years, developers are expected to deliver a total of 212,000 square feet to the Atlanta Flex/R&D market. As mentioned before, employment growth at the Atlanta metro is expected to remain strong, which we believe is enough to facilitate an absorption rate averaging 374,600 square feet per year. This absorption rate exceeds total completions over the two-year period by enough to reduce the market vacancy rate to 14.0% by year end 2018. Thereafter, REIS anticipates that effective rent growth will accelerate to an annualized average of 3.0% during 2017 and 2018 to reach a level of $5.80 per square foot, as is illustrated in Figure 11 below.
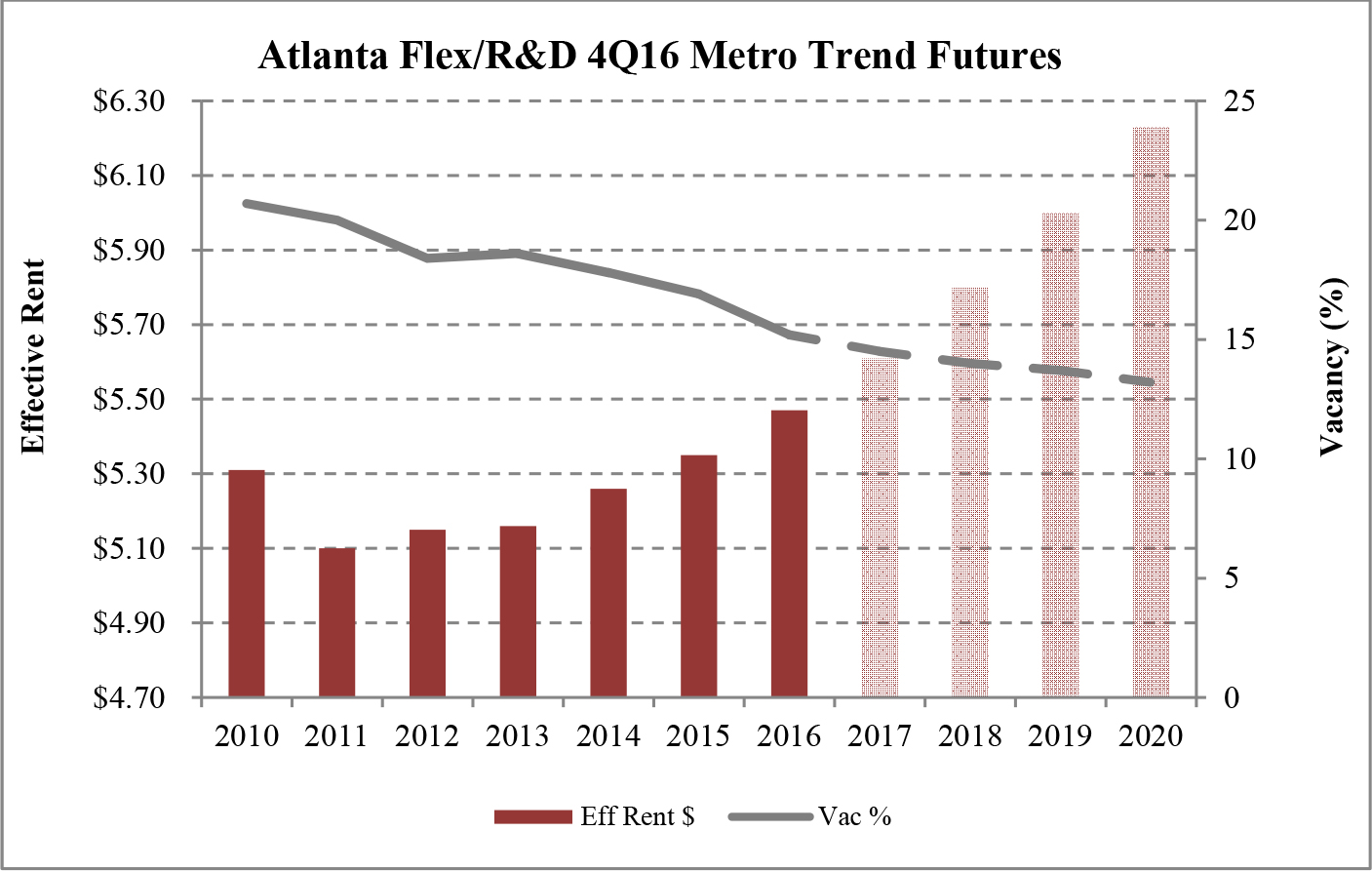 |
| Figure 11 (Source: REIS) |
70
Chicago Industrial Market
Overall Market Fundamentals
The 544 million square foot Chicago warehouse/distribution market continues to surge, with extensive speculative construction, strong demand, and steady rent gains. It is one of the strongest commercial real estate markets in the country. The year-end 2016 warehouse/distribution vacancy rate is 12.1% for Chicago, down from 12.6% in 2015. The rate is down 520 basis points from the 17.3% recorded at the end of 2010 While new supply has slowed the rate of decline slightly, REIS predicts the vacancy rate will continue to trend down to 10.2% by 2020.
The 49.2 million square foot Flex/R&D had an impressive year in 2016 with the vacancy rate dropping to 13.5, down from 15.1% at the end of 2015. This trend should continue with REIS projecting that the vacancy rate will drop to 11.5% by 2020.
As seen below in Figure 12, non-farm employment growth has experienced year over year growth since 2010. While the growth is positive, the growth rate has been slower than other metropolitan areas. However, employment is expected to continue growing through 2018 then level off for a period due to population growth slowing, thus creating an environment where the industrial real estate market should continue to prosper with high rent growth driven by low levels of new supply forecasted.
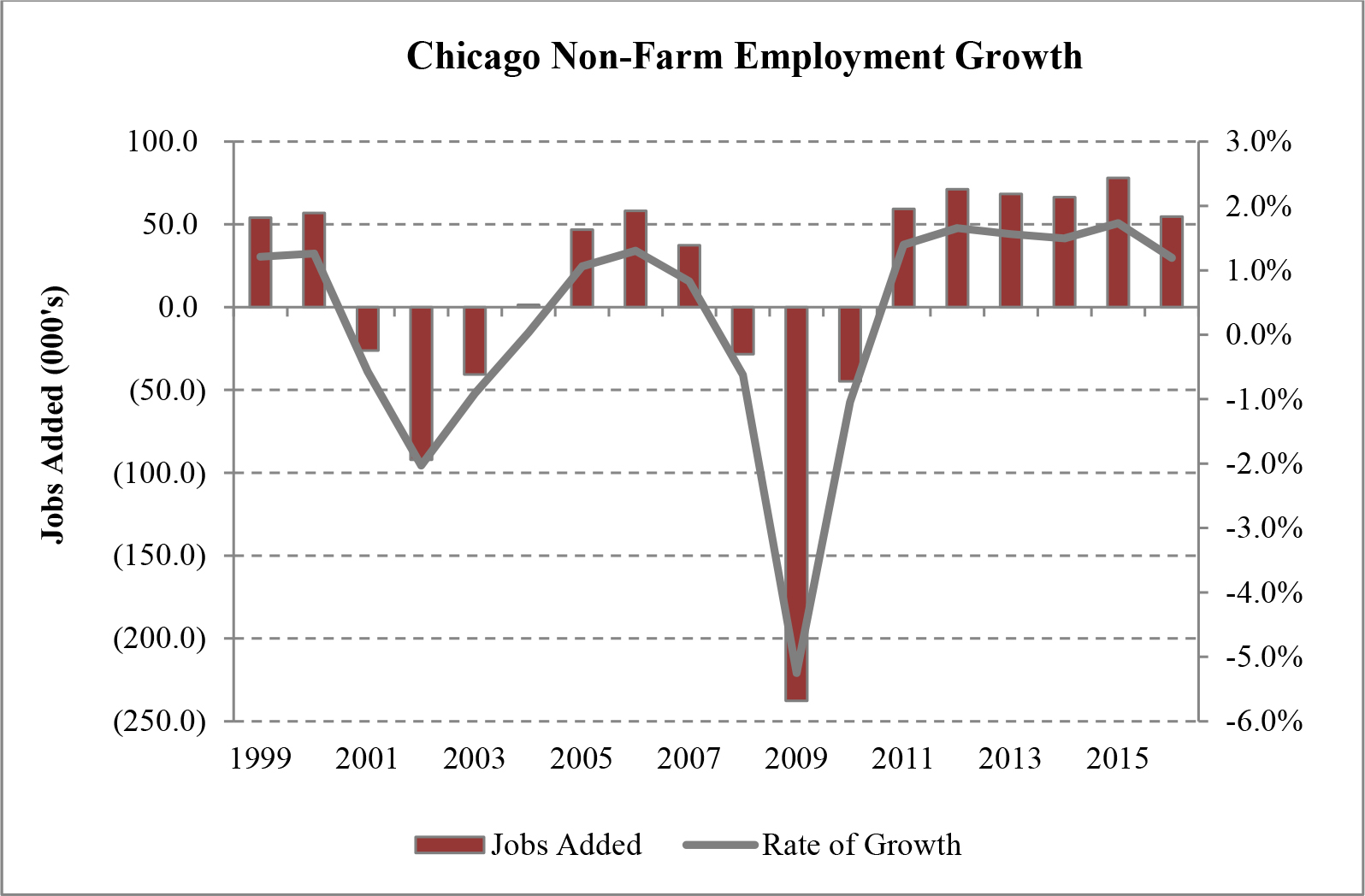 |
| Figure 12 (Source: US Department of Labor) |
71
Chicago Warehouse/Distribution Market
As seen in Figure 13 below, effective rents increased by 2.8% during 2016 to an average of $4.34. REIS predicts that this effective rental growth and vacancy rate decline are going to continue through 2018, which we believe bodes well for our focus on warehouse/distribution product in Chicago.
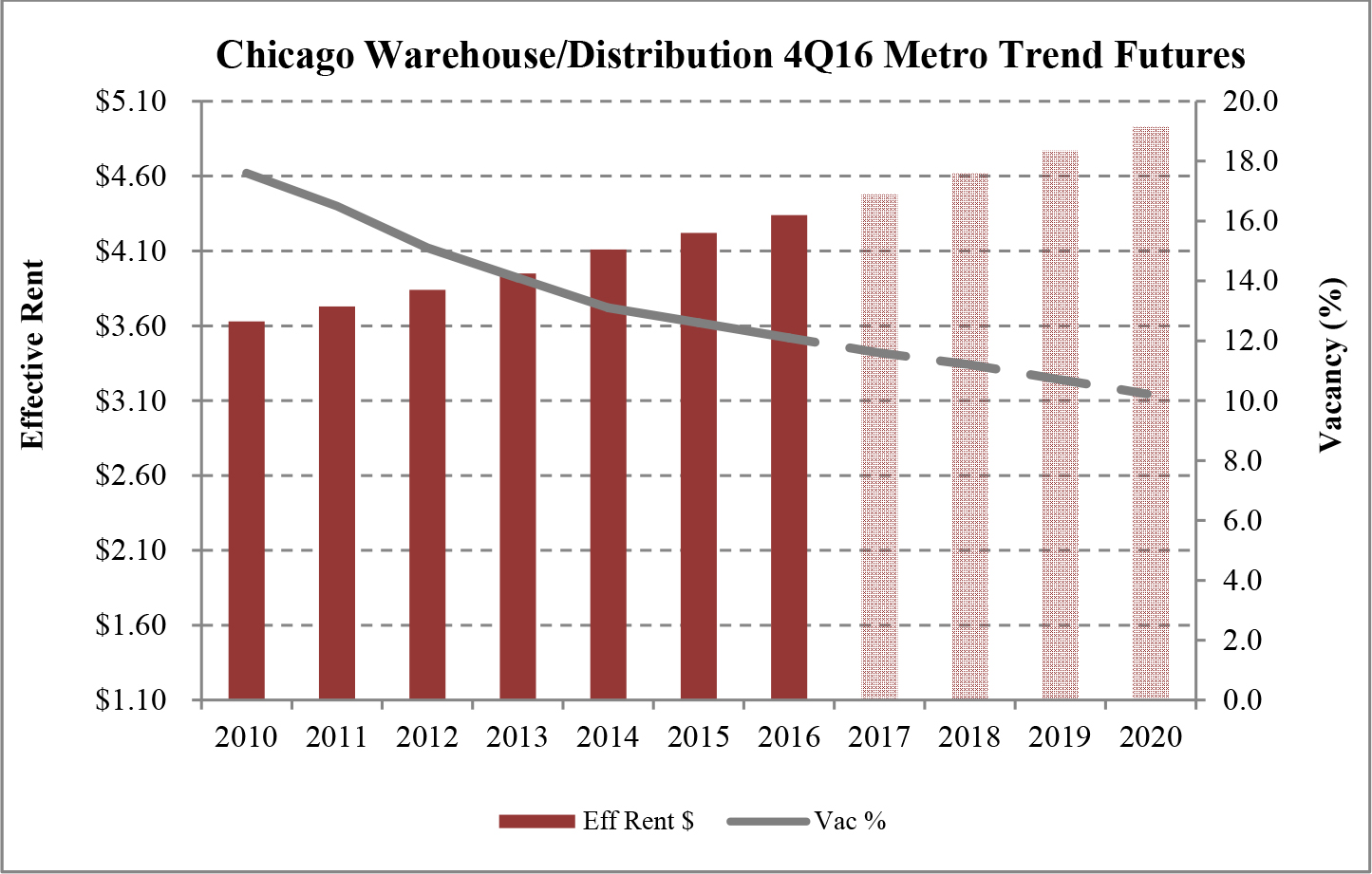 |
| Figure 13 (Source: REIS) |
As is illustrated in Figure 14 below, during 2015 and 2016 developers delivered a total of 19.4 million square feet to the warehouse/distribution market. However, those numbers were not enough to slow net absorption which was a stunning 22.4 million square feet over those two years. The market vacancy rate finished 2016 at 12.1% and is predicted to fall further to 10.2% by 2020. REIS anticipates that asking rent growth will accelerate to an annualized average of 3.2% during 2017 through 2020 to reach a level of $4.93 per square foot. Additionally, they are projecting effective rents to advance by a more rapid annualized average rate as market conditions begin to allow landlords to limit the value of their concession packages. New construction is projected to gradually slow down over the next few years.
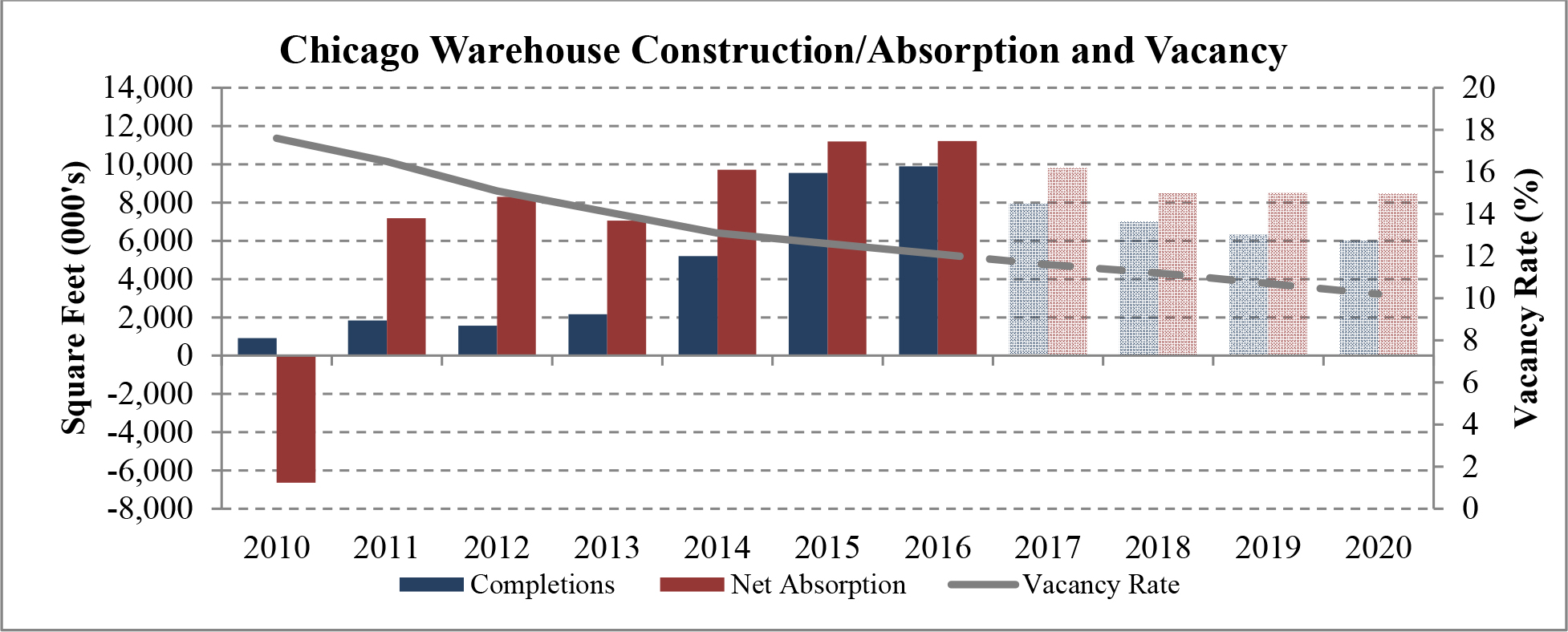 |
| Figure 14 (Source: REIS) |
72
Chicago Flex/R&D Market
Construction in the Chicago Flex/R&D market has been limited over the past six years but net absorption has been positive over the past three years. Flex/R&D vacancy has dropped from a high of 18.9% in 2011 to its current level of 13.5%. Average annual effective rents have begun to increase and are expected to grow at an average annual rate of 3.0% over the next four years to an effective rental rate of $7.72 per square foot in 2020, as shown in Figure 15. Vacancy rates will also continue to decrease over this period which we believe makes the Flex/R&D product in Chicago very attractive at this time.
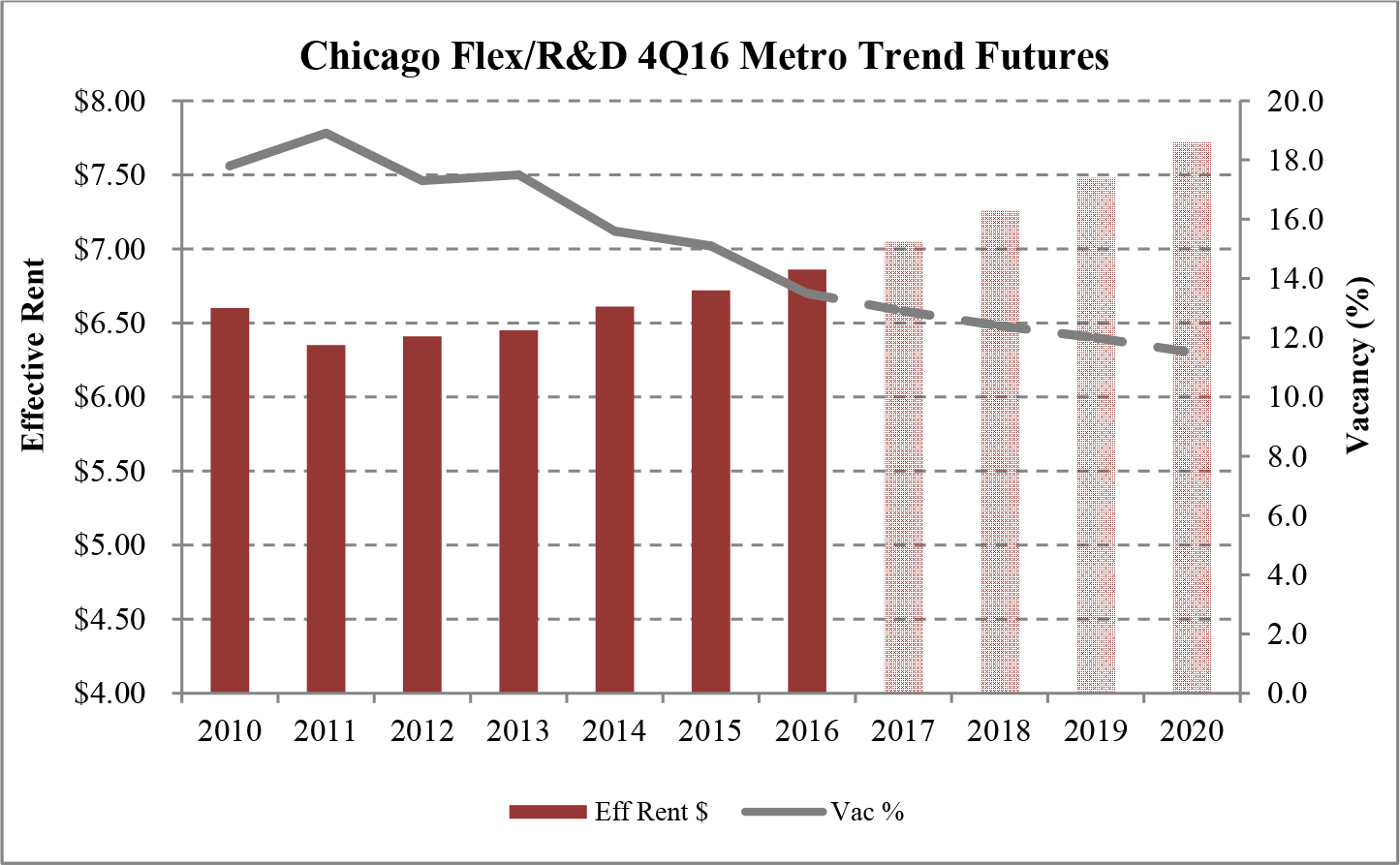 |
| Figure 15 (Source: REIS) |
As illustrated in Figure 16 below, during 2017 through 2020, developers are expected to deliver an average of 320,000 square feet to the Chicago Flex/R&D market. Net Absorption will continue to out-pace construction at 525,000 square feet per year during the same period. The market vacancy rate is forecasted to continue dropping from its 2016 rate of 13.5% to 11.5% by the end of 2020.
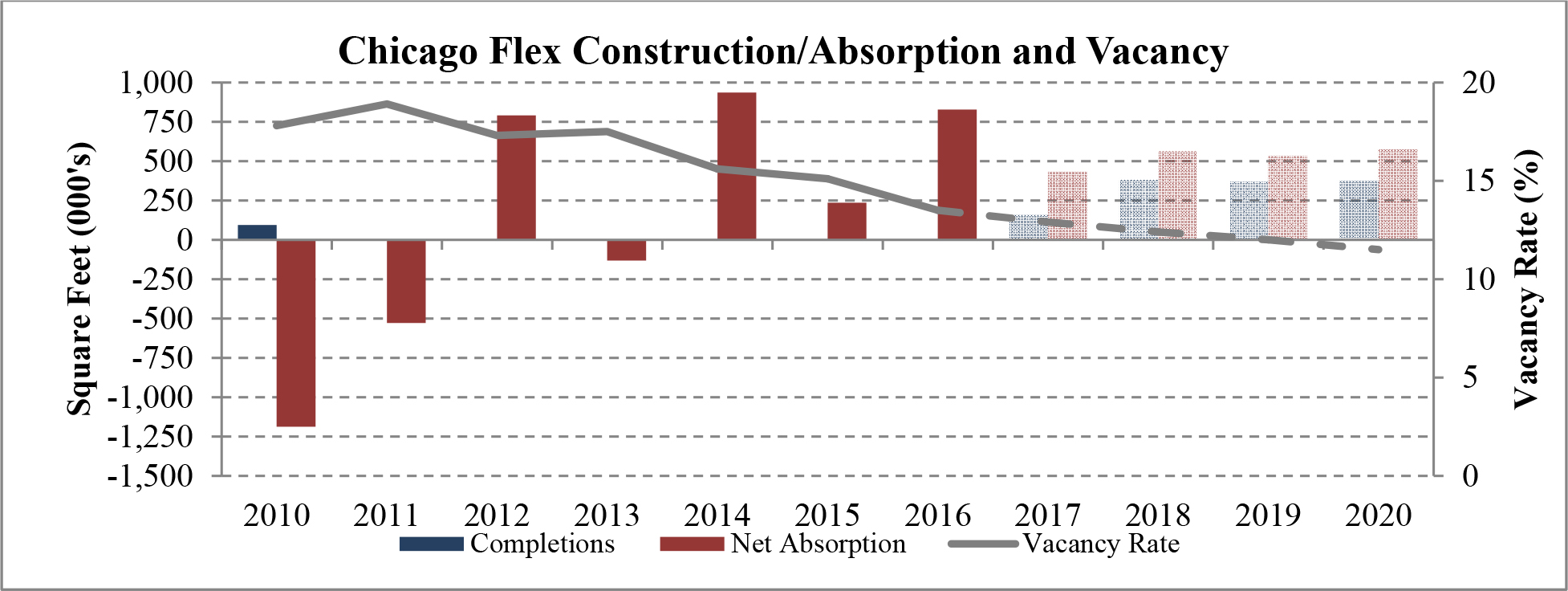 |
| Figure 16 (Source: REIS) |
73
Columbus Industrial Market
Overall Market Fundamentals
During 2016, the U.S. Department of Labor data shows an increase of approximately 20,133 jobs for a 1.9% increase over 2015. While the rate of growth has slowed steadily from the high of 2.8% in 2012, it still remains higher than the national average of 1.4%. As seen below in Figure 17, non-farm employment has grown an average of 23,276 per year over the past six years. The transportation industry, which is a focus in Ohio, remained hot growing at over 3.1% in 2016. Overall employment is projected to bounce back and grow 2.2% in 2017.
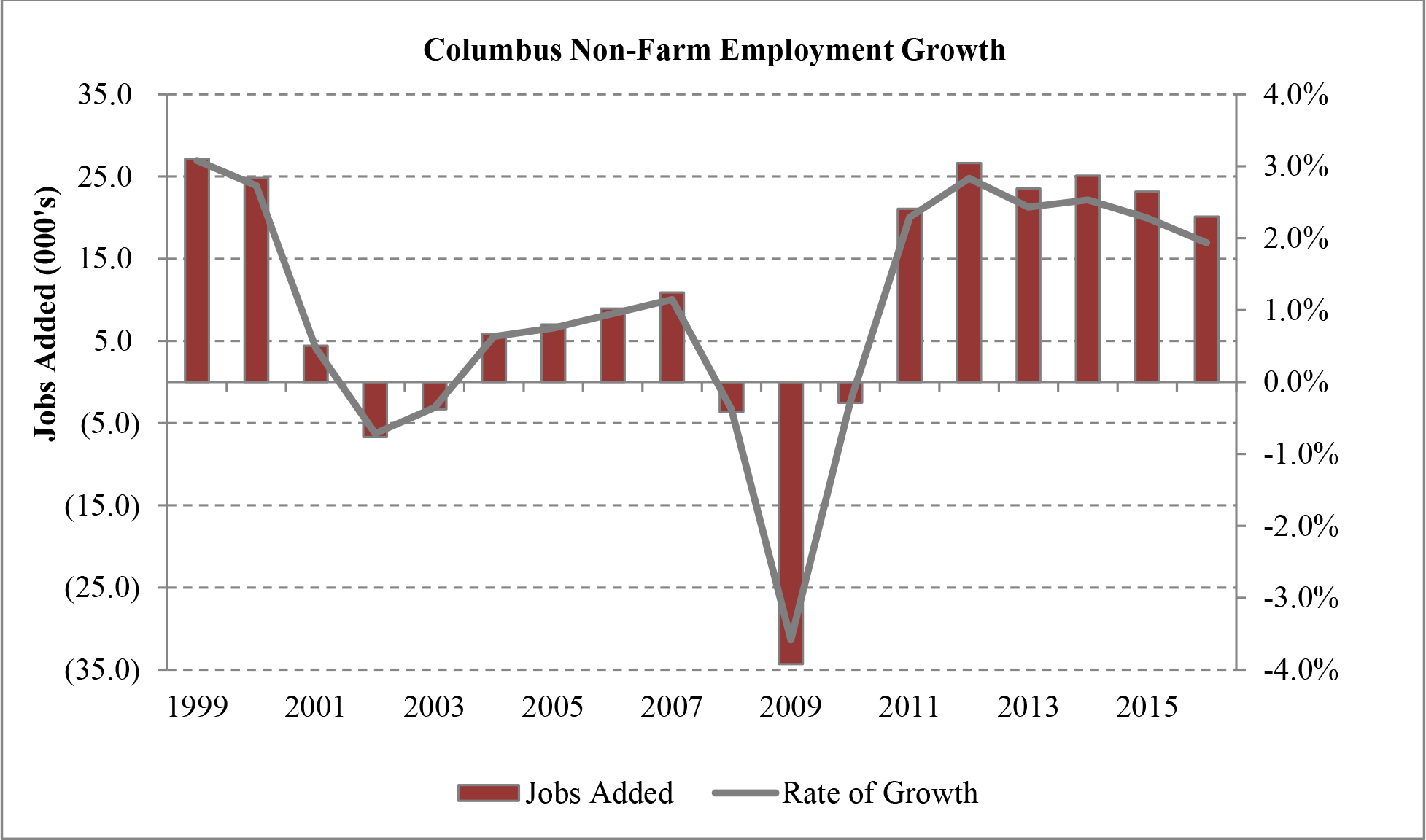 |
| Figure 17 (Source: US Department of Labor) |
Columbus Warehouse/Distribution Market
The Columbus warehouse/distribution market is comprised of 112 million square feet in four geographic concentrations. During 2016, the warehouse/distribution market experienced positive absorption of 1,077,000 square feet, which is slightly below the average of 1,128,000 square feet over the past six years. In a long-term context, the market’s year-end 2016 vacancy rate of 12.8% is 3.3 percentage points lower than the 16.1% vacancy rate during 2010. New construction slowed during 2016 and is expected to remain more subdued during 2017 before picking up again in 2018.
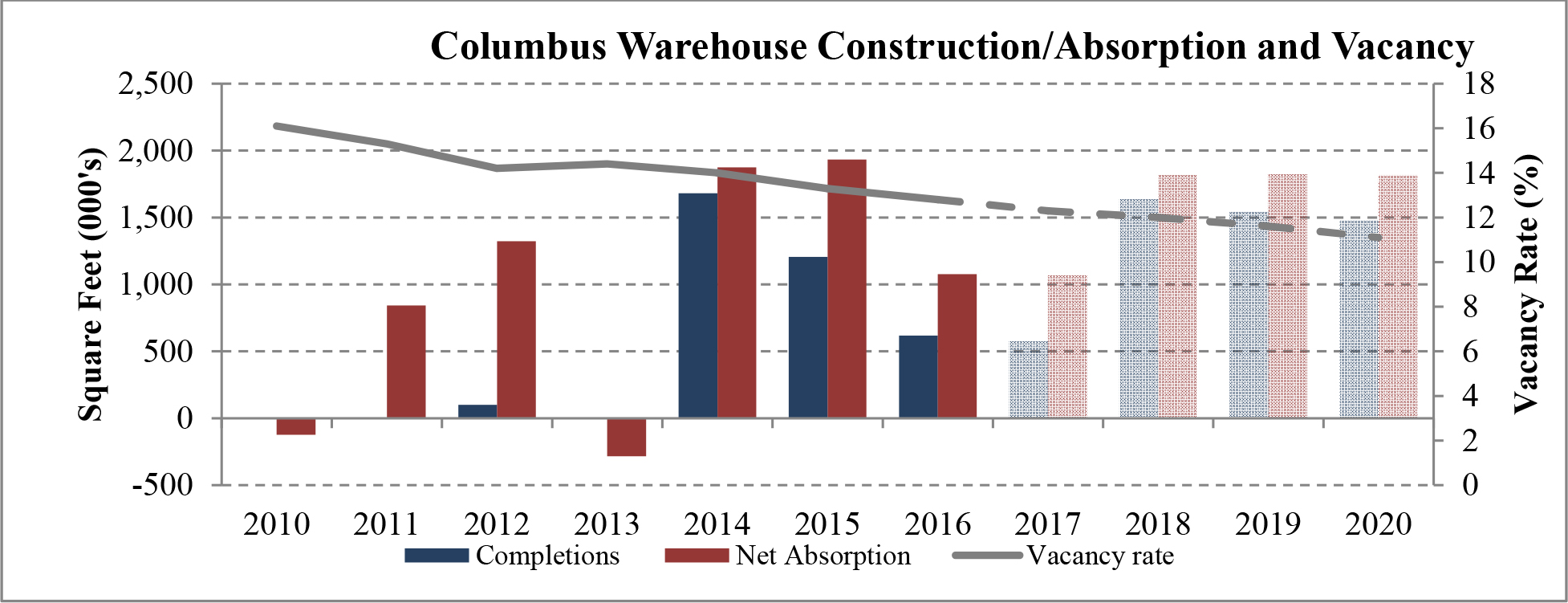 |
| Figure 18 (Source: REIS) |
74
Effective rents were up 1.9% during 2016 at $3.27 per square foot which is 1.2% greater than the average growth over the past six years. Over the next four years effective rents are projected to grow an average of 2.8% annually reaching $3.66 per square foot by 2020.
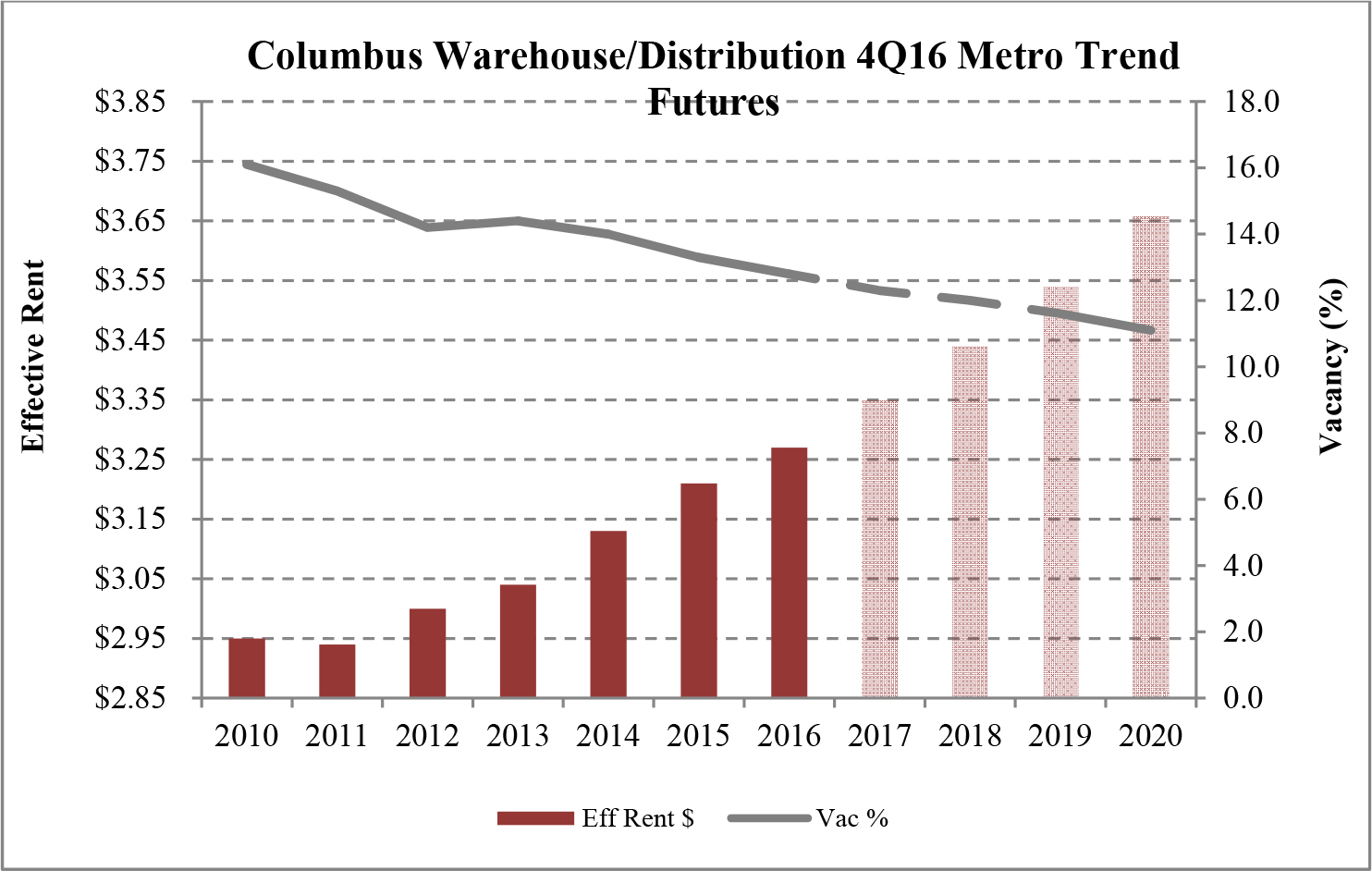 |
| Figure 19 (Source: REIS) |
Columbus Flex/R&D Market
During 2016, Flex and R&D effective rents in Columbus rose by 1.5% to $4.66. As highlighted by REIS in Figure 20 below, this effective rental growth and vacancy rate decline are forecasted to accelerate through 2020, which we believe bodes well for the Flex/R&D product in Columbus. By 2020 vacancy is projected to decrease to 15.5% and effective rents are expected to be $5.21 per square foot. We believe that market conditions will begin to allow landlords to reduce the value of concession packages and allow effective rents to climb more rapidly.
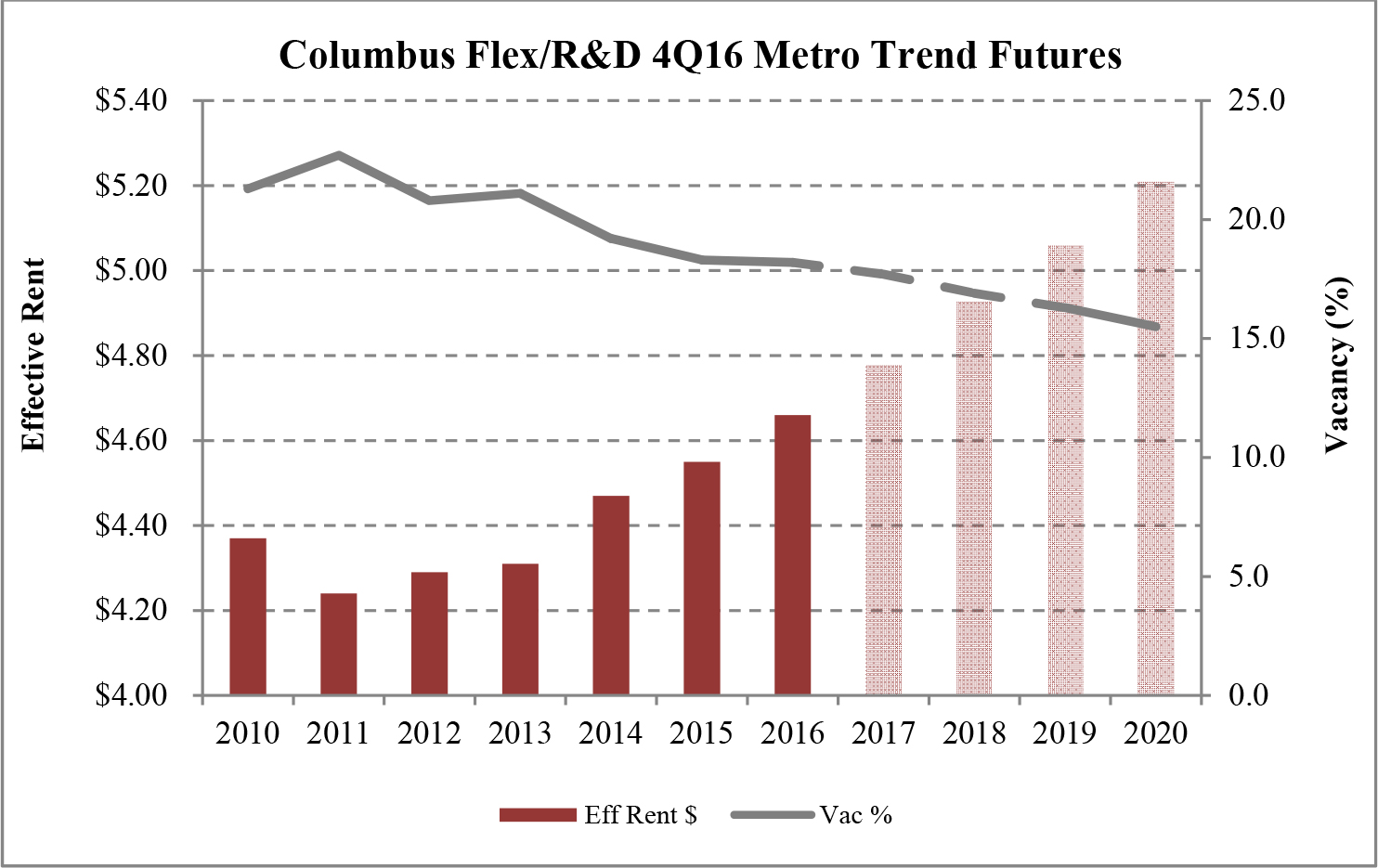 |
| Figure 20 (Source: REIS) |
75
As illustrated in Figure 21 below, Columbus Flex and R&D construction activity has been minimal with modest growth projected at 66,000 square feet to be added on average over the next four years. Net absorption has been steady and will continue to outpace construction over the foreseeable future.
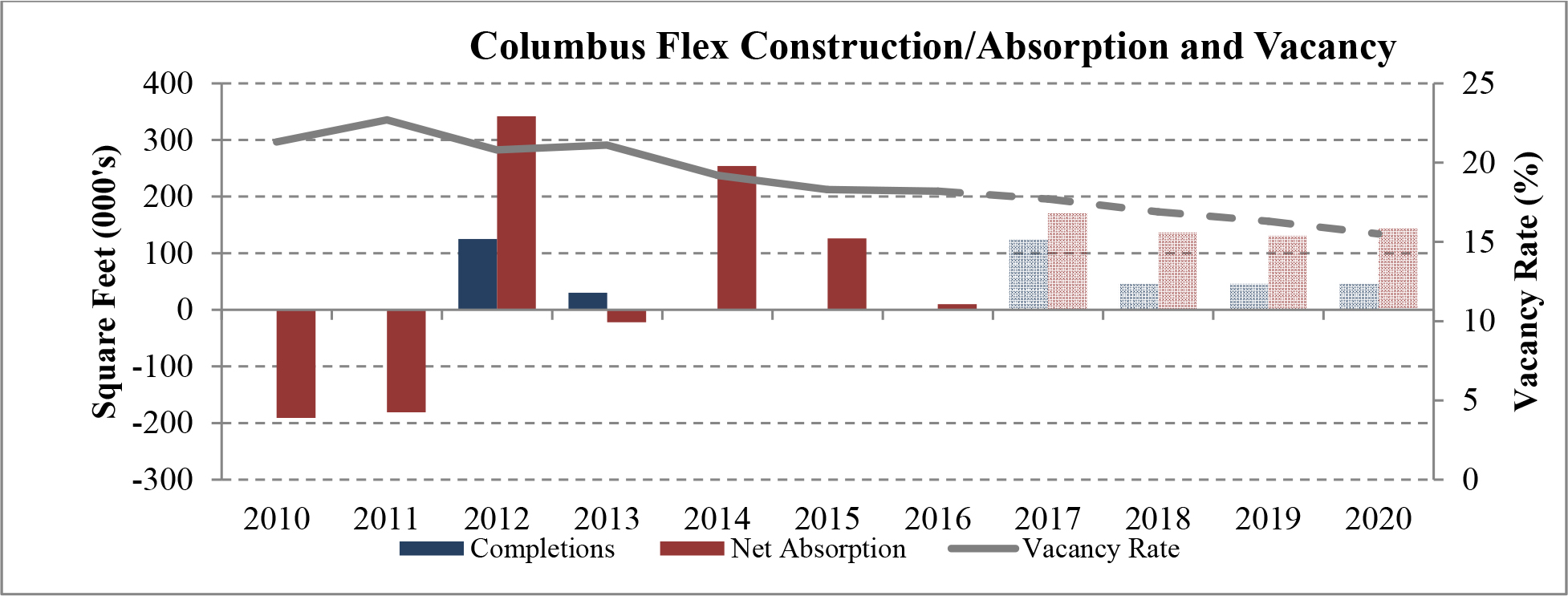 |
| Figure 21 (Source: REIS) |
Memphis Industrial Market
Overall Market Fundamentals
The approximate 111 million square foot Memphis warehouse/distribution market had a solid year in 2016 with 0.9 million square feet of net absorption. However, there was a 40 basis point vacancy rate increase to 14.6%. The vacancy rate increase was driven by the 1.5 million square feet of new space that came online during the year.
With regard to employment overall, the Memphis market has just recovered from the recession, as is seen in Figure 22 below. After having lost jobs in years 2008 through 2010, metro Memphis has now experienced six years of positive job growth, averaging 1.1% per year. There was an increase of job growth in Memphis of 1.3% in 2016 and it is expected to be higher over the next two years before it starts slowing.
 |
| Figure 22 (Source: US Department of Labor) |
76
Memphis Warehouse/Distribution Market Overview
A summary of key real estate supply and demand metrics reveals that during 2016 the Memphis warehouse/distribution market experienced positive net absorption, advancing effective rents, and downward movement in the market’s vacancy rate. During 2016, effective rents increased by 2.1% to an average of $2.43 per square foot and are forecasted to be $2.69 per square foot by 2020. As highlighted by REIS in Figure 23 below, this rental growth and vacancy rate decline are forecasted to continue through 2020, which we believe bodes well for our focus on warehouse/distribution product in Memphis.
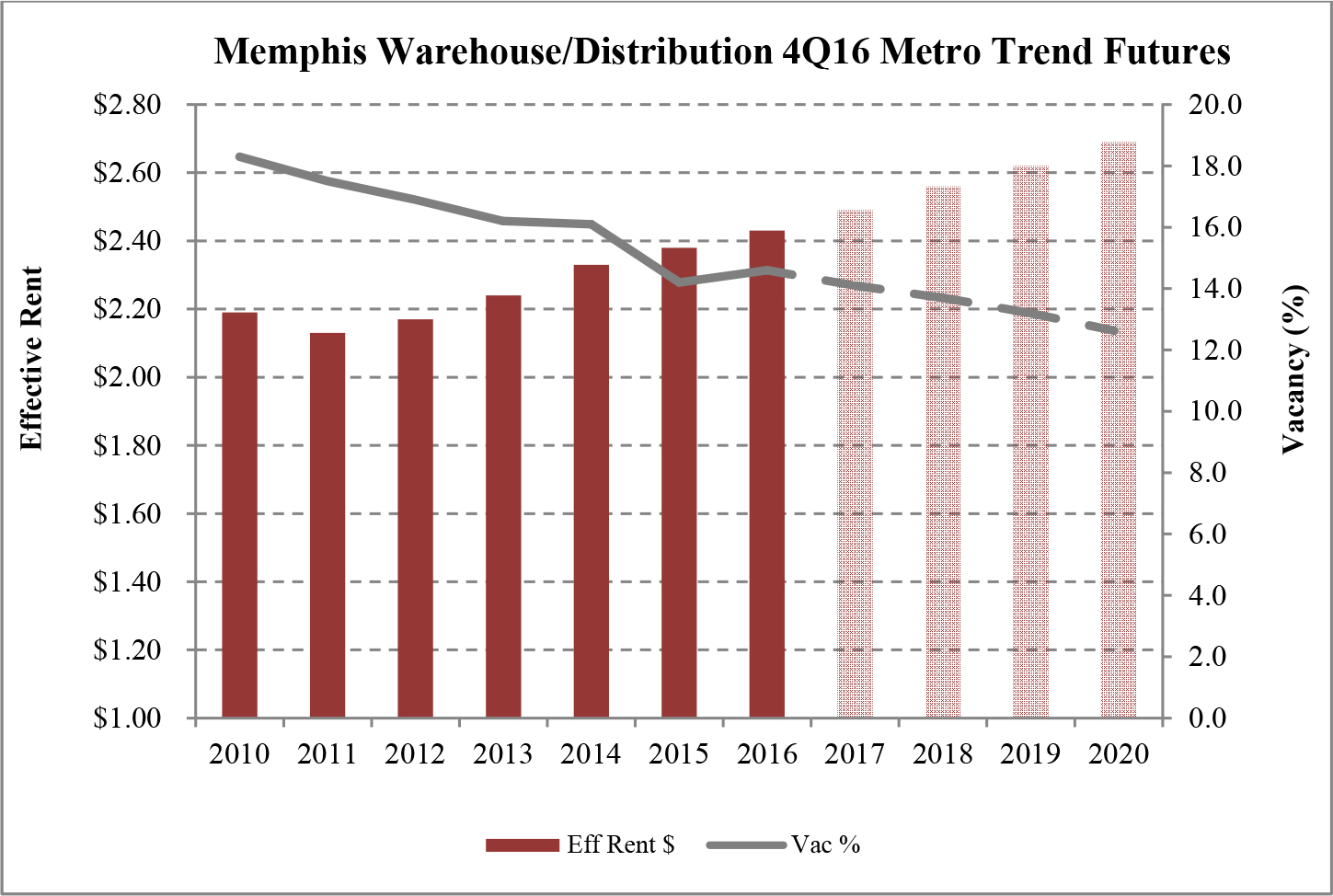 |
| Figure 23 (Source: REIS) |
Leasing activity generated positive 913,000 square feet of absorption during 2016, while over the prior four years, warehouse/distribution absorption averaged a positive 1.6 million square feet. From a historical standpoint, the market’s 2016 vacancy rate of 14.6% is 1.7 percentage points lower than the 16.3% average recorded since 2010.
As is illustrated in Figure 24 below, developers are expected to deliver an average of 1.7 million square feet to the warehouse/distribution market in Memphis over the next four years. However, industrial employment growth at the metro level over the same period is expected to average over 1.0% annually, enough to facilitate an absorption rate averaging 2.0 million square feet per year and drive the vacancy rate down to 12.6% by 2020. REIS projects that effective rent growth will continue at an annualized average rate of 2.6% through 2020. Overall the Memphis warehouse/distribution market is projected to continue its steady improvements.
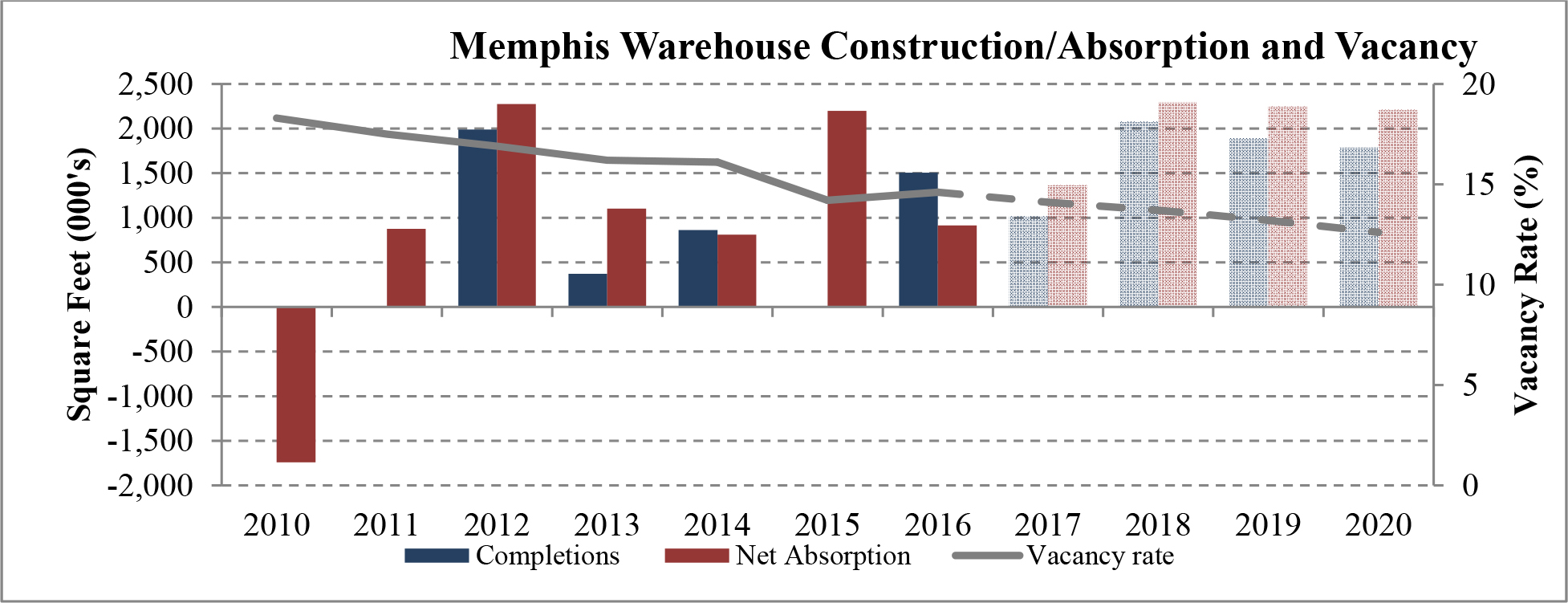 |
| Figure 24 (Source: REIS) |
77
Memphis Flex/R&D Market
A summary of key real estate supply and demand market indicators shows that during 2016 the Memphis Flex/R&D market recorded slightly negative net absorption and a small increase in the market’s vacancy rate but saw increasing effective rents. During 2016, effective rents increased 0.8% to $4.99 per square foot and vacancy increased 0.2 percentage points to 14.4%.
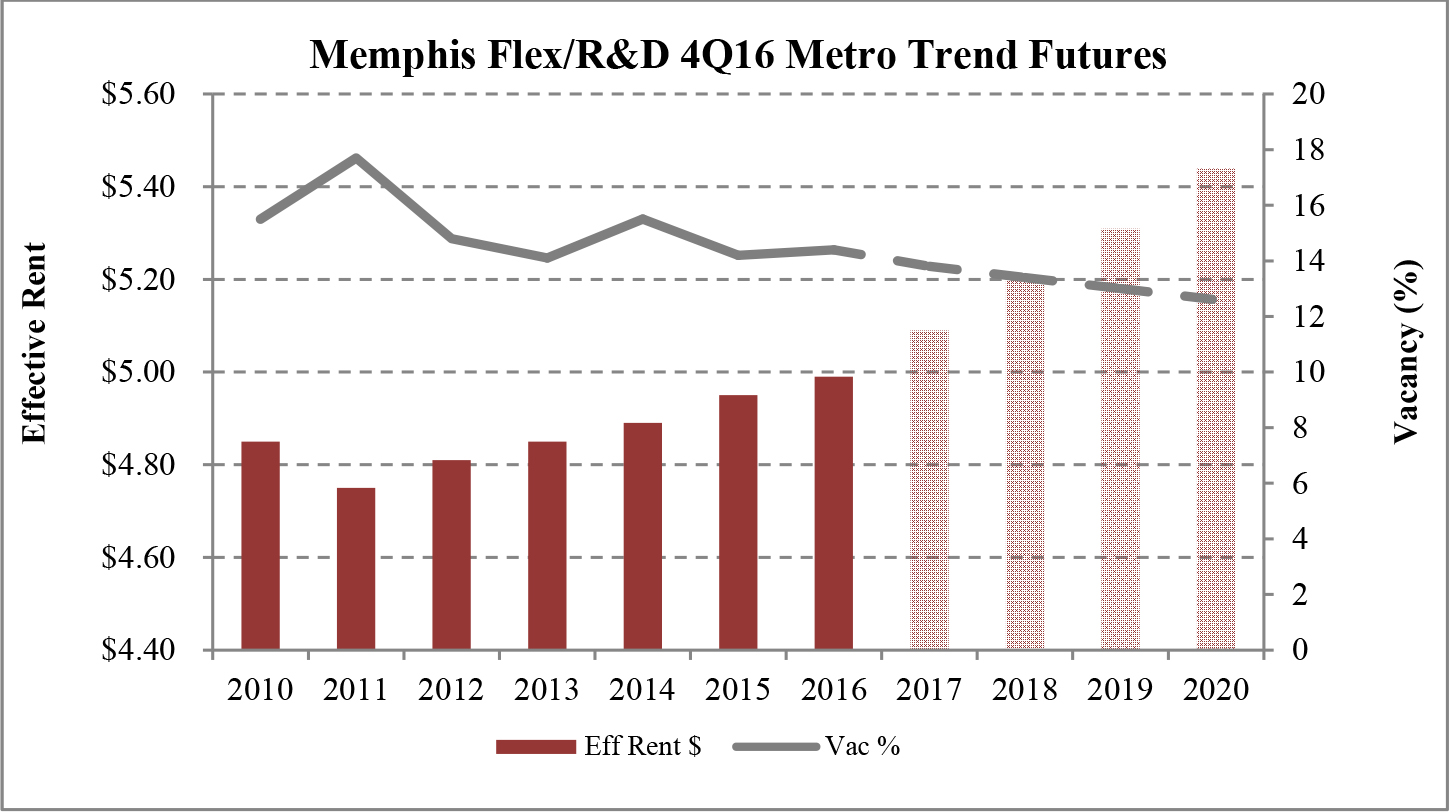 |
| Figure 25 (Source: REIS) |
Leasing activity generated negative 20,000 square feet of absorption during the 2016, while over the prior four years, positive Flex/R&D absorption averaged 83,000 square feet. From a historical standpoint, the market’s 2016 vacancy rate of 14.4% is 0.8 percentage points lower than the 15.2% average recorded since 2010.
As is illustrated in Figure 26 below, developers are expected to deliver a total of 64,000 square feet to the Memphis Flex/R&D market over the next four years. Industrial employment growth at the metro level over the same period is expected to average 1.0% annually, which we believe is enough to facilitate a net positive absorption rate averaging 97,000 square feet per year. REIS projects the market vacancy rate to finish 2020 at 12.6%, down an additional 1.8 percentage points. On an annualized basis effective rents are anticipated to climb an average of 2.2%, ending 2020 at $5.44 per square foot.
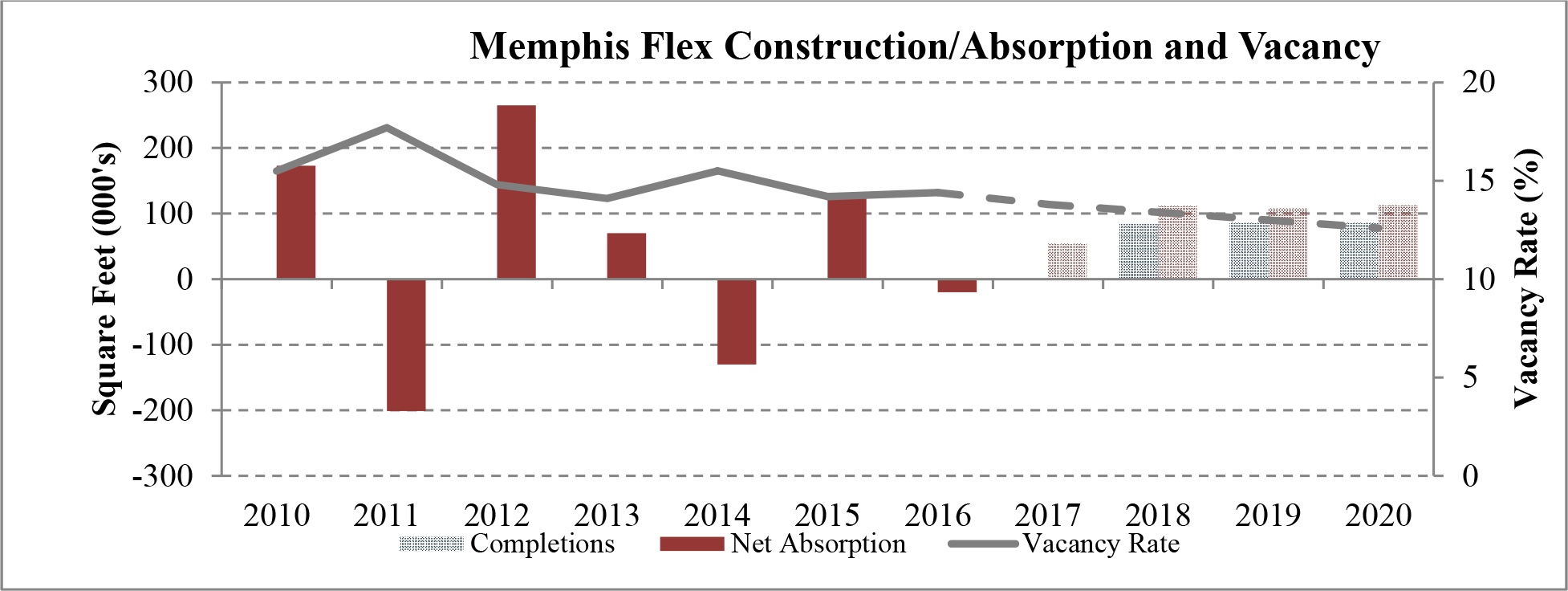 |
| Figure 26 (Source: REIS) |
78
Cincinnati Industrial Market
Overall Market Fundamentals
The Cincinnati warehouse/distribution real estate market saw a slight uptick in vacancy in 2016 even with a net absorption of over 1.7 million square feet. The low vacancy rates and robust jobs market has sparked some speculative construction. However, even with new product the vacancy rate is projected to continue its descent over the next four years. Total employment rose by 21,100 (2.0%) jobs since 2015. This is the fifth year in a row that Cincinnati has seen employment growth of over 2% per annum. It is projected that the employment growth will continue, at around 1.5% over the next few years.
 |
| Figure 27 (Source: REIS) |
Cincinnati Warehouse/Distribution Market
Cincinnati’s warehouse/distribution market finished 2016 with a vacancy rate of 10.8%, up from 10.7% in 2015. Net absorption was a positive 1,742,000 square feet during the year. The solid absorption performance was achieved even with the completion of over 2.0 million newly constructed square feet. REIS projects that an average of 1.1 million square feet of new product will come on line per year over the next four years. Even with this new product, absorption should outpace construction and the vacancy rate should come down to 9.2% by 2020.
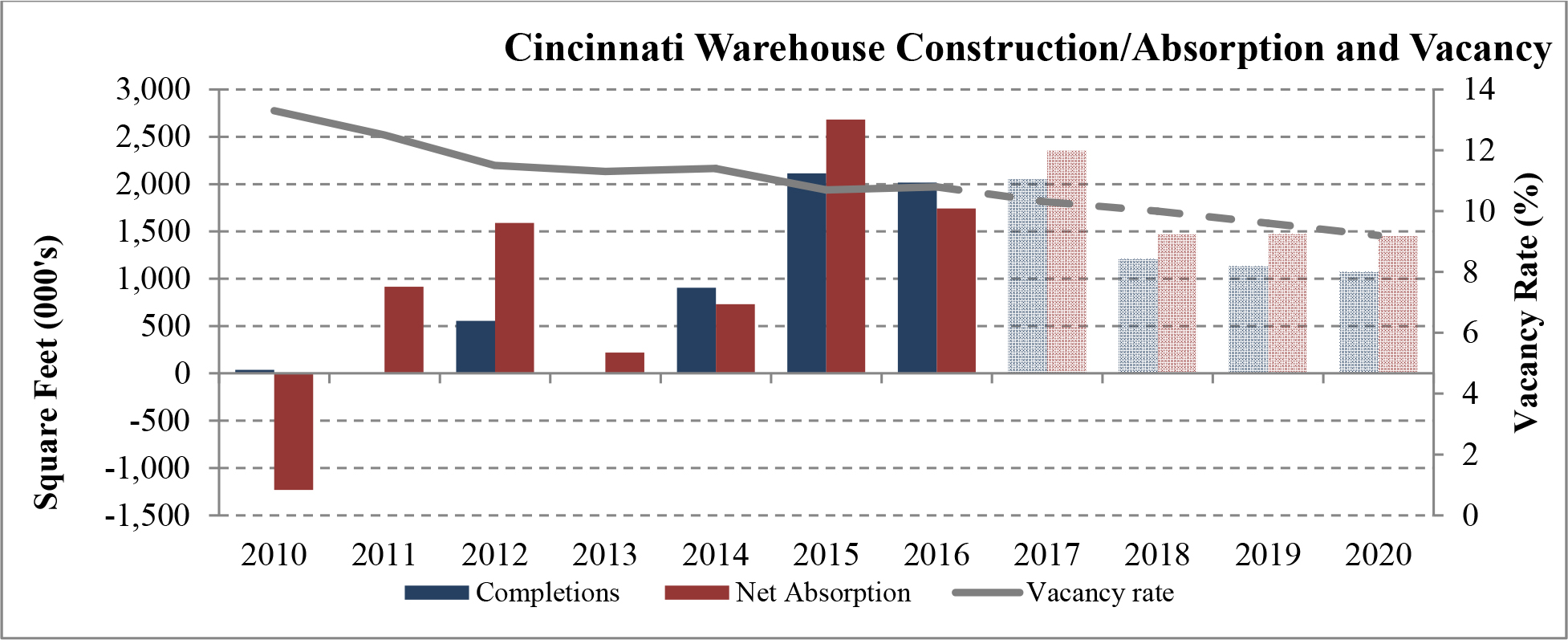 |
| Figure 28 (Source: REIS) |
79
During 2016, effective rents rose 2.0% to $3.09 per square foot. Rents had risen 1.3% on average over the past four years and are projected, by REIS, to grow by 2.4% per annum over the next four years.
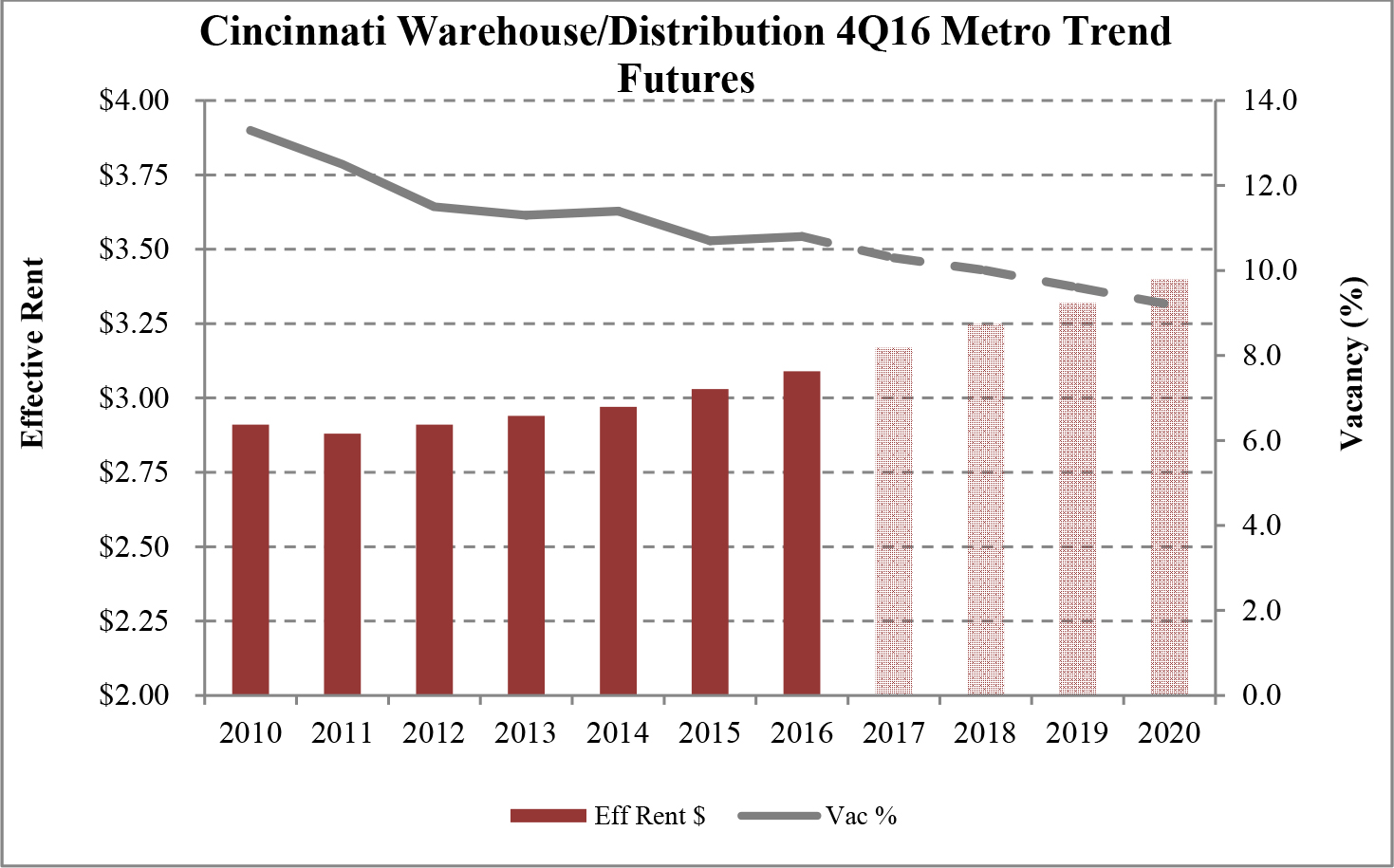 |
| Figure 29 (Source: REIS) |
Cincinnati Flex/R&D Market
For Flex/R&D space, REIS reports 2016 vacancy at 12.3%, slightly up from the prior year’s 11.9%. New construction over the next for years should average 40,000 square feet while net absorption should average 125,000 square feet.
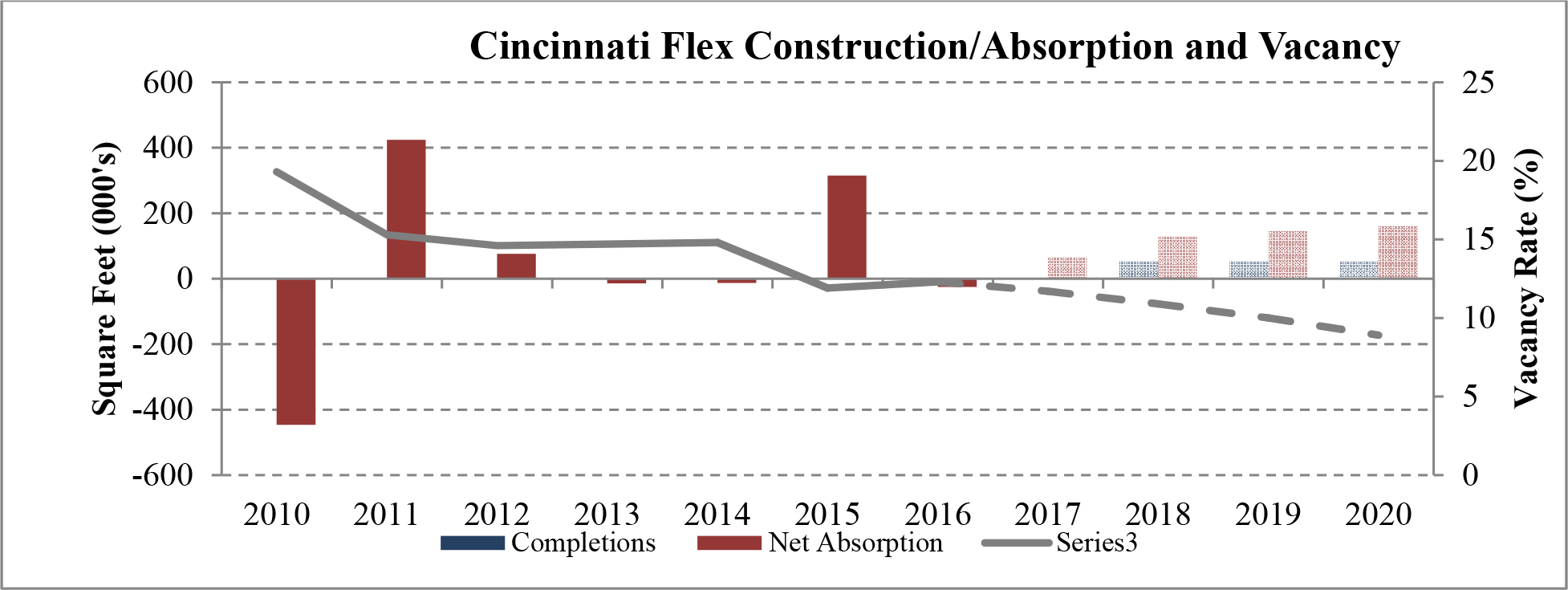 |
| Figure 30 (Source: REIS) |
80
For Flex/R&D space, REIS reports average effective rent increased 1.6% to $5.74 per square foot. Flex/R&D rents are expected to increase an average of 2.4% per annum over the next four years to $6.31 per square foot by 2020.
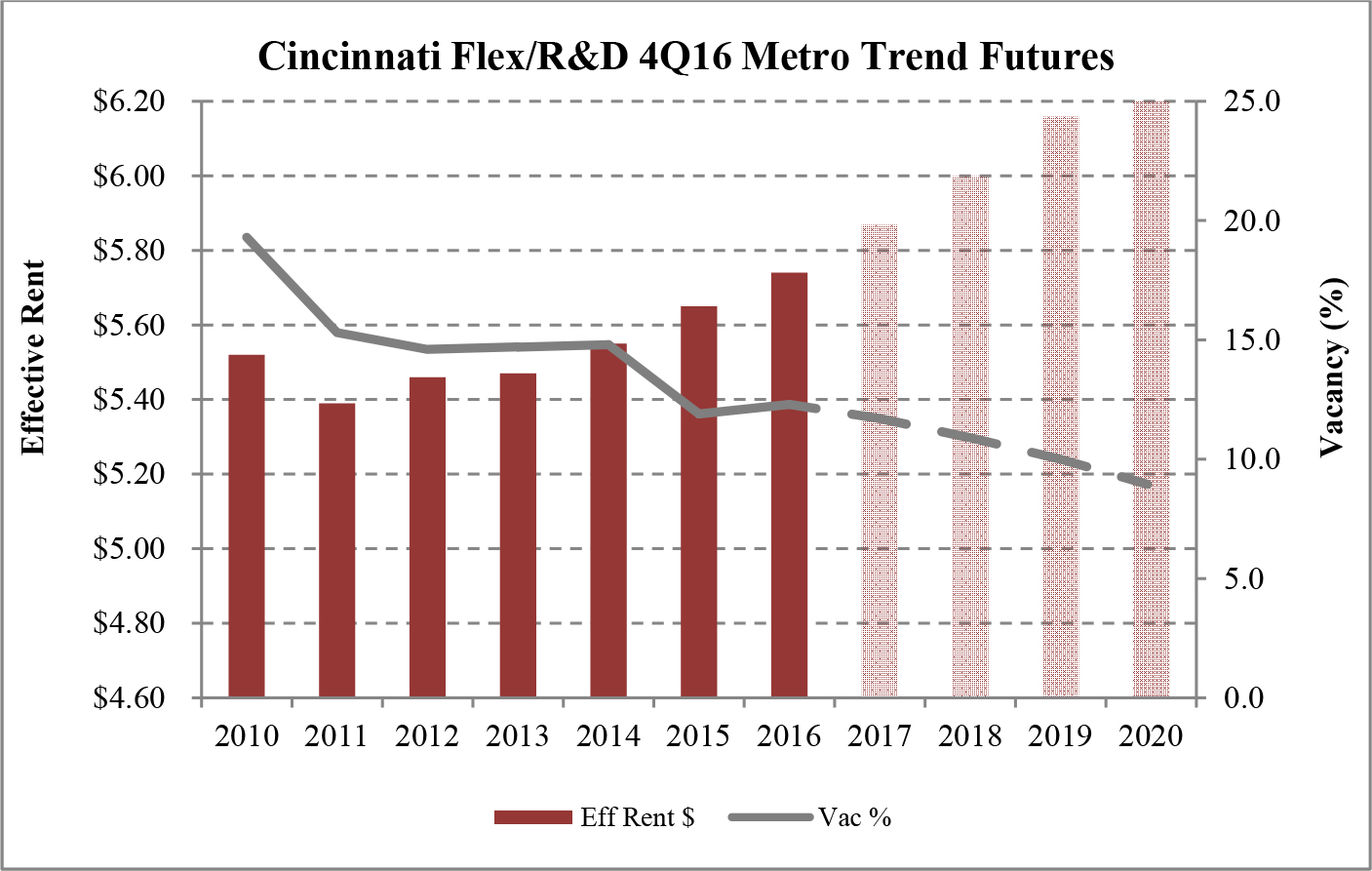 |
| Figure 31 (Source: REIS) |
81
BUSINESS
Overview
We are a full service, vertically integrated, self-administered and self-managed Maryland corporation focused on the acquisition, ownership and management of single- and multi-tenant Class B industrial properties, including distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties, primarily located in secondary and select primary markets across the U.S. For a definition of Class B industrial properties, see “—Our Investment and Growth Strategies—General.” The Company Portfolio, which consists of 20 industrial properties located in seven states, is currently held through Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC, a joint venture with Torchlight in which we own a 0.5% interest. In connection with the completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, we will redeem Torchlight’s interest in Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC, or Plymouth Industrial 20, and will own 100% of the interests in the Company Portfolio. See “—Torchlight Transactions.” As of March 31, 2017, the Company Portfolio was approximately 98.4% leased to 37 different tenants across 17 industry types.
We intend to continue to focus on the acquisition of industrial properties in secondary markets with net rentable square footage ranging between approximately 100 million and 300 million square feet, which we refer to as our target markets. We believe industrial properties in such target markets will provide superior and consistent cash flow returns at generally lower acquisition costs relative to industrial properties in primary markets. Further, we believe there is a greater potential for higher rates of appreciation in the value of industrial properties in our target markets relative to industrial properties in primary markets.
We believe our target markets provide us with opportunities to acquire both stabilized properties generating favorable cash flows, as well as properties where we can enhance returns through value-add renovations and redevelopment. We focus primarily on the following investments:
| • | single-tenant industrial properties where tenants are paying below-market rents with near-term lease expirations that we believe have a high likelihood of renewal at market rents; and | |
| • | multi-tenant industrial properties that we believe would benefit from our value-add management approach to create attractive leasing options for our tenants, and as a result of the presence of smaller tenants, obtain higher per-square-foot rents. |
We believe there are a significant number of attractive acquisition opportunities available to us in our target markets and that the fragmented and complex nature of our target markets generally make it difficult for less-experienced or less-focused investors to access comparable opportunities on a consistent basis. See “Market Overview.”
Our company, which was formerly known as Plymouth Opportunity REIT, Inc., was founded in March 2011 by two of our executive officers, Jeffrey Witherell and Pendleton White, Jr., each of whom has at least 25 years of experience acquiring, owning and operating commercial real estate properties. Specifically, both were members of a team of senior investment executives that was responsible for the acquisition and capital formation of commercial properties for Franklin Street Properties (NYSE: FSP), a REIT based in Boston, MA, from 2000 to 2007, during which time Franklin Street listed its stock on the American Stock Exchange. Following their time at Franklin Street, our founders recognized a growing opportunity in the Class B industrial space, particularly in secondary markets and select primary markets, following the 2008-2010 recession, and founded the company to participate in the cyclical recovery of the U.S. economy. Between March 2011 to April 2014, we prepared for and engaged in a non-listed public offering of our common stock. We used the proceeds from that offering to acquire equity interests in five industrial properties. In 2014, we used the proceeds of a senior secured loan to acquire 100% fee ownership in three of these properties and 100% fee ownership in the remaining 17 properties that comprise the Company Portfolio. In July 2015 and January 2017, we sold our equity interests in the two properties in which we did not have 100% fee ownership.
We believe that our focus on owning and expanding a portfolio of such properties will generate attractive risk-adjusted returns for our stockholders. Specifically, we believe we can achieve attractive and stable cash flow yields relative to yields achievable from Class A industrial properties because average capitalization rates tend to be higher in Class B industrial properties. In addition, we believe Class B industrial properties offer a higher degree of stability in occupancy and rental rates relative to Class A industrial properties. See “Our Investment and Growth Strategies.”
We source our acquisitions primarily through a combination of off-market and lightly marketed transactions, sale lease-backs and related transactions from illiquid owners and short sales and discounted note purchases from financial institutions. We expect to benefit from our management team’s extensive business and personal relationships and research-driven origination methods to generate investment opportunities, many of which may not be available to our competitors. Additionally, rental rates in our target markets have only recently begun to recover from their recessionary lows, and we believe these rates will increase over time.
We elected to be taxed as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2012. As a REIT, we generally are not subject to U.S. federal taxes on our income to the extent we annually distribute at least 90% of our REIT taxable income, determined without regard to the deduction for dividends paid, to our stockholders and otherwise maintain our qualification as a REIT. We are structured as an UPREIT and will own substantially all of our assets and conduct substantially all of our business through our operating partnership. We are the sole general partner and own 100% of the interests in our operating partnership.
82
Competitive Strengths
We believe that our investment strategy and operating model distinguish us from other owners, operators and acquirers of industrial real estate in several important ways, including the following:
High-Quality Portfolio with Strong Fundamentals: Since 2014, we have acquired a portfolio of 20 industrial assets with an aggregate of over four million square feet of rentable space. As of March 31, 2017, the Company Portfolio was 98.4% leased to 37 different tenants across 17 diversified industries, which we believe reduces our exposure to tenant default risk and earnings volatility. We have seen consistent increases in rental rates since the acquisition of the properties comprising the Company Portfolio. Rental rates on new leases signed in 2016 were approximately 57.1% higher than rental rates on prior leases, and rental rates for renewing tenants increased 3.8%. In addition, our tenant retention rate increased from 17.3% in 2015 to 73.7% in 2016. We believe that high occupancy rates across the Company Portfolio, as well as strong rental growth, are indicative of the consistent execution of our business strategy.
Strong Alignment of Interests: We believe the interests of our management team, our board of directors and our stockholders are strongly aligned. We will grant an aggregate of 131,579 restricted shares of common stock to our executive officers and independent directors upon the closing of this offering. In addition, following the completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transaction, the Torchlight Entities will own approximately 7.3% of our common stock (13.2% assuming the full exercise of the warrants to be issued in the Torchlight Transactions). Each of the members of our management team, our board of directors and the Torchlight Entities has entered into a lock-up agreement restricting the direct or indirect sale of such securities for 180 days after the date of this prospectus without the prior written consent of D.A. Davidson & Co.
Strategic Focus on Class B Industrial Properties in Secondary Markets with Stable and Predictable Cash Flows: We focus on Class B distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties rather than Class A industrial or other commercial properties for the following reasons, among others: fewer capital expenditure requirements, generally greater investment yields, overall greater tenant retention, generally higher current returns and lower earnings volatility. We believe the Company Portfolio is, and our future acquisitions will be, attractively positioned to participate in the recovering rental rates in our target markets while providing our stockholders with consistent, stable cash flows.
We intend to continue to focus on the acquisition of industrial properties in our target markets across the U.S. We believe that our target markets have exhibited, or will exhibit in the near future, positive demographic trends (i.e., population growth, decreasing unemployment rates, personal income growth and/or favorable tax climates), scarcity of available industrial space and favorable rental growth projections, which should help create superior long-term risk-adjusted returns. However, we will consider acquisitions in non-target markets that will our overall investment criteria.
Superior Access to Deal Flow: We believe our management team’s extensive personal relationships and research-driven origination methods will provide us access to off-market and lightly marketed acquisition opportunities, many of which may not be available to our competitors. Off-market and lightly marketed transactions are characterized by a lack of a formal marketing process and a lack of widely disseminated marketing materials. Our executive management and acquisition teams maintain a deep, broad network of relationships among key market participants, including property brokers, lenders, owners and tenants, and greater than 50% of the Company Portfolio was sourced in off-market or lightly marketed transactions. We also utilize data-driven and event-driven analytics and primary research to identify and pursue events and circumstances, including financial distress, related to owners, lenders, and tenants that we believe signal emerging investment opportunities that our competitors may not recognize. We believe that our sourcing approach will provide us access to a significant number of attractive investment opportunities.
Experienced Management Team: Each of the three senior members of our executive management team has over 25 years of real estate industry experience, with each member having previous public REIT or public real estate company experience. Led by Mr. Witherell, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Mr. White, our President and Chief Investment Officer, and Mr. Wright, our Chief Financial Officer, our management team has significant experience in acquiring, owning, operating and managing commercial real estate, with a particular emphasis on industrial assets. Throughout their careers, Mr. Witherell and Mr. White have had primary responsibility of overseeing the acquisition, financing, ownership and management of more than ten million square feet of office and industrial properties in our target markets, while over the past 18 years Mr. Wright has served as the Chief Financial Officer of two real estate companies, one of which had approximately $8 billion in assets.
83
Our Investment and Growth Strategies
General
Our primary objective is to generate attractive risk-adjusted returns for our stockholders through dividends and capital appreciation primarily through the acquisition of Class B industrial properties, including distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties. We generally define Class B industrial properties as industrial properties that are typically more than 15 years old, have clear heights between 18 and 26 feet and square footage between 50,000 and 500,000 square feet, with building systems that have adequate capacities to deliver the services currently needed by existing tenants, but may need upgrades for future tenants. In contrast, we define Class A industrial properties as industrial properties that typically are 15 years old or newer, have clear heights in excess of 26 feet and square footage in excess of 200,000 square feet, with energy efficient design characteristics suitable for current and future tenants.
Our investment strategy will also focus on the burgeoning e-commerce industry, acquiring industrial properties that may service tenants’ e-commerce fulfillment needs, or “last mile” deliver requirements. These properties, termed “in-fill” properties are typically located in highly populated areas, new city centers or populous suburban areas.
We target Class B industrial properties, as compared to Class A industrial properties. The distinction between Class A industrial and Class B industrial properties is subjective. However, we consider Class A industrial properties and Class B industrial properties to have the following characteristics:
| • | Class A industrial properties typically possess most of the following characteristics: 15 years old or newer, square footage generally in excess of 300,000 square feet, concrete tilt-up construction, clear height in excess of 26 feet, a ratio of dock doors to floor area that is more than one door per 10,000 square feet and energy efficient design characteristics for current and future tenants. Rents are based on a specified range between the top 20-30% of the industrial rents in the marketplace. | |
| • | Class B industrial properties typically vary from Class A industrial properties in that they have some but not all of the features of the Class A industrial properties. They are typically more than 15 years old, have clear heights between 18 and 26 feet and square footage between 50,000 and 300,000 square feet. Building systems (mechanical, HVAC and utility) have adequate capacities to deliver services currently required by tenants but may need upgrades for future tenants. Rents are typically 30-50% below Class A properties in the marketplace. |
Our definitions of Class A industrial properties and Class B industrial properties may vary from the definitions of these terms used by investors, analysts or other industrial REITs.
In addition, we primarily target secondary markets, as compared to primary markets. The distinction between primary markets and secondary markets is subjective. However, we define primary and secondary markets as follows:
| • | Primary Markets include gateway cities and the following six target metropolitan areas in the U.S., each generally consisting of more than 300 million square feet of industrial space: Los Angeles, San Francisco, New York, Chicago, Washington, DC and Boston. | |
| • | Secondary Markets for our purposes include non-gateway markets, each generally consisting of between 100 million and 300 million square feet of industrial space, including the following metropolitan areas in the U.S.: Atlanta, Austin, Baltimore, Charlotte, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Columbus, Dallas, Detroit, Houston, Indianapolis, Jacksonville, Kansas City, Memphis, Milwaukee, Nashville, Norfolk, Orlando, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, Raleigh/Durham, San Antonio, South Florida, St. Louis and Tampa. |
Our definitions of primary and secondary markets may vary from the definitions of these terms used by investors, analysts and other industrial REITs, could include additional metropolitan statistical areas in addition to those named above and may change over time.
We will focus our acquisition activities on our core property types, which include warehouse/distribution facilities and light manufacturing facilities, because we believe they generate higher tenant retention rates and require lower tenant improvement and re-leasing costs. To a lesser extent, we will focus on flex/office facilities (light assembly and research and development). We define these property types as follows:
| • | Warehouse/Distribution—properties generally 200,000 to 500,000 square feet in size with ceiling heights between 22 feet and 36 feet and used to store and ship various materials and products. | |
| • | Light Manufacturing—properties generally 75,000 to 250,000 square feet in size with ceiling heights between 16 feet and 22 feet and used to manufacture all types of goods and products. |
84
According to CBRE, secondary industrial market areas have, on average, a high degree of fundamental stability in rents and occupancies. Alternatively, although primary markets may offer a substantial amount of depth and ability to re-tenant vacant space, these markets tend to have a higher degree of volatility in occupancy and rent due in large part to a tenant dependence on external trade and distribution flows and these tend to be more volatile than locally-generated demand. Additionally, these primary markets tend to be prone to a higher propensity for speculative construction.
According to a recent study published by CBRE, which examines the availability rates of industrial properties, the majority of industrial tenants are satisfied with their Class B industrial properties. While these Class B industrial properties usually have lower clear height, less cross-docked loading, less technology incorporated into building utilities and overall less functionality than Class A industrial properties, such building characteristics also result in lower building costs which result in lower rents when compared to Class A industrial properties. Thus, Class B industrial properties are priced for the industrial functionality they deliver, which tends to result in high tenant retention rates.
The CBRE study also revealed that older industrial buildings generally have higher occupancy rates than newer buildings. Specifically by decade of construction, buildings built in the 1980s had higher rates of occupancy than those built in the 1990s, with this trend continuing with buildings built in 2000 and thereafter. These statistics seem to refute the common misperception of diminished functionality and desirability of older Class B industrial properties.
Overall, we believe that the aforementioned factors impacting the supply and demand dynamic create a compelling case for the attractiveness and overall cost effectiveness of Class B industrial properties among a variety of tenants. Class B industrial property owners and operators generally benefit from low tenant rollover because of the properties’ locations and sufficient functionality. Tenants tend to benefit from lower rentals rates, while we believe investors can expect stable and predictable cash flows and lower volatility.
We believe that pursuing the following strategies will enable us to achieve our investment objectives.
Investment Strategy
Our primary investment strategy is to acquire Class B industrial properties predominantly in secondary markets across the U.S. We intend to acquire properties that we believe can achieve high initial yields and strong ongoing cash-on-cash returns and that exhibit the potential for increased rental growth in the near future. In addition, we may acquire Class A industrial properties that offer similar attractive return characteristics if the cost bases for such properties are comparable to those of Class B industrial properties in a given market or sub-market.
Our investment strategy also focuses on properties in our target markets that consist of the following tenant profiles:
Multi-Tenant Acquisitions: Our core acquisition strategy is to (1) acquire multi-tenanted industrial properties, and (2) acquire properties currently occupied by a single tenant that have the capacity to efficiently break-up the space and create customized sizes for various tenants. We believe that smaller tenants (ranging typically between 25,000 square feet to 100,000 square feet) will pay more on a per-square-foot basis than a single tenant while reducing the binary risk associated with leasing to single tenants. Further, typically the extra cost we incur to break-up a property (such as demising walls, additional doors, signage) is off-set by the expected increase in rent paid by the individual tenant over the term of the lease. This multi-tenant property strategy also benefits us in acquiring such properties as many of our competitors steer away from smaller-sized properties in favor of pursuing larger and newer (and, in or view, more competitive) Class A single tenant properties where the pricing is typically higher on a price-per-square-foot basis.
Single Tenant Acquisitions: The performance of single-tenant properties tends to be binary in nature: either a tenant is paying rent or the owner is paying the entire carrying cost of the property. We believe that this binary nature frequently causes the market to inefficiently price certain single-tenant assets. In an attempt to avoid this binary risk, potential investors in single-tenant properties often apply a set of rigid decision rules that would force buyers of single-tenant properties to avoid acquisitions where the tenant does not have an investment grade rating or where the remaining primary lease term is less than an arbitrary number such as 10 years. By adhering to such inflexible decision rules, these types of investors may miss attractive opportunities that we can identify and acquire.
We currently own both multi-tenant and single-tenant properties which make up approximately 61% and 39% of the Company Portfolio by square footage, respectively.
We further believe that our method of using and applying the results of our due diligence and our ability to understand and underwrite risk allows us to exploit certain market inefficiencies. We believe the systematic aggregation of individual properties will result in a diversified portfolio that mitigates the risk of any single property and will produce sustainable risk-adjusted returns which are attractive in light of the associated risks. A diversified portfolio with low correlated risk facilitates debt financing and mitigates individual property ownership risk. This, coupled with our intention to maintain relatively low debt levels, should mitigate any potential carrying costs in the event a tenant decides to vacate.
85
We will employ a “bottom-up” set of analyses that evaluates potential acquisitions within the context of the market and submarket in which they are located. Each submarket has its own unique market characteristics that determine the timing and amount of cash flow that can reasonably be expected to be derived from the ownership of real estate asset in that market.
The company also intends to pursue joint venture arrangements with institutional partners which could provide management fee income as well as residual profit-sharing income. Such joint ventures may involve investing in industrial assets that would be characterized as opportunistic or value-add investments. These may involve development or re-development strategies that may require significant up-front capital expenditures, lengthy lease-up periods and result in inconsistent cash flows. As such, these properties’ risk profiles and return metrics would likely differ from the non-joint venture properties that we target for acquisition.
Finally, following this offering, we believe we will have a competitive advantage in sourcing attractive acquisitions because the competition for our target assets is primarily local investors who are not likely to have ready access to debt or equity capital. In addition, our UPREIT structure may enable us to acquire industrial properties on a non-cash basis in a tax efficient manner through the issuance of OP units as consideration for the transaction. We will also continue to develop our large existing network of relationships with real estate and financial intermediaries. These individuals and companies give us access to significant deal flow—both those broadly marketed and those exposed through only limited marketing. These properties will be acquired primarily from third-party owners of existing leased buildings and secondarily from owner-occupiers through sale-leaseback transactions.
Growth Strategies
We will seek to maximize our cash flows through proactive asset management. Our asset management team will be actively managing the Company Portfolio in an effort to maintain high retention rates, lease vacant space, manage operating expenses and maintain our properties to an appropriate standard. In doing so, we will seek to develop strong tenant relationships with all of our tenants and leverage those relationships and market knowledge to increase renewals, properly prepare tenants for rent increases, obtain early notification of departures to provide longer re-leasing periods and work with tenants to properly maintain properties. Our asset management team will collaborate with our internal credit function to actively monitor the credit profile of each of our tenants and prospective tenants on an ongoing basis.
Our asset management team functions include strategic planning and decision-making, centralized leasing activities and management of third-party leasing and property management companies. Our asset management/credit team oversees property management activities relating to our properties which include controlling capital expenditures and expenses that are not reimbursable by tenants, making regular property inspections, overseeing rent collections and cost control and planning and budgeting activities. Tenant relations matters, including monitoring of tenant compliance with their property maintenance obligations and other lease provisions, will be handled by in-house personnel for most of our properties.
A key asset management goal is to cost effectively retain tenants and increase occupancy. Our asset management team strives to maintain an active dialogue with all tenants to identify lease extension opportunities. We intend to typically prepare our renewal or releasing strategy 12 months prior to scheduled lease expiration dates, and also enter into discussions with tenants well in advance of such expiration dates to identify any potential changing tenant requirements. By actively working to retain tenants we will keep occupancy levels high and minimize “down time” and releasing costs.
Additionally, we will seek to stagger lease termination dates in order to minimize the possibility of significant portions of the Company Portfolio becoming vacant at the same time.
In addition to cost effective tenant retention, we intend to actively market space for which tenant renewals are not obtained. We plan to work with national and local brokerage companies to market and lease available properties on advantageous terms. We will track the activity of these brokerage firms and we will position our properties in the market to cost effectively balance occupancy downtime with asking rents and incentives. We aim to increase the cash flow generated by our acquired properties through appropriate rent increase provisions in our leases.
Our asset management team monitors our assets on an ongoing basis through engagement and supervision of local property managers and regular site visits, and keeps apprised on local market conditions through discussions with brokers and principals, as well as by tracking comparable sales and rental data from various reporting services such as CoStar and REIS. By maintaining this knowledge base we are better prepared for discussions with tenants regarding retention terms and be better able to position our properties appropriately when marketing to potential tenants.
Another vital asset management function is our active monitoring of our tenant’s and prospective tenant’s credit profiles. On a continuing basis, our asset management/credit team will monitor the financial data provided by our tenants including quarterly, semi-annual, or annual financial information. We also expect to have access to our tenants’ executive management teams to discuss their historical performance and future expectations. The credit monitoring process involves the review of key news developments, financial statement analysis, credit rating agency data, management discussions, and the exchange of information with the other asset management specialists.
86
Financing Strategy
We intend to maintain a flexible and growth-oriented capital structure. We intend to use the net proceeds from this offering along with additional secured and unsecured indebtedness to acquire industrial properties. See “Use of Proceeds.” Our additional indebtedness may include arrangements such as revolving credit facility or term loan. We believe that we will have the ability to leverage newly-acquired properties up to a 65% debt-to-value ratio, though our long-term target debt-to-value ratio is less than 50%. We also anticipate using OP units to acquire properties from existing owners interested in tax-deferred transactions.
Investment Criteria
We believe that our market knowledge, operations systems and internal processes allow us to efficiently analyze the risks associated with an asset’s ability to produce cash flow going forward. We blend fundamental real estate analysis with corporate credit analysis to make a probabilistic assessment of cash flows that will be realized in future periods. We also utilize data-driven and event-driven analytics and primary research to identify and pursue events and circumstances, including financial distress, related to owners, lenders, and tenants that we believe signal emerging investment opportunities that our competitors may not recognize.
Our investment strategy focuses on Class B industrial properties in secondary markets for the following reasons:
| • | Class B Industrial properties generally require less capital expenditures than both Class A industrial properties and other commercial property types; | |
| • | investment yields for Class B industrial properties are often greater than investment yields on both Class A industrial properties and other commercial property types; | |
| • | Class B industrial tenants tend to retain their current space more frequently than Class A industrial tenants; | |
| • | Class B industrial properties tend to have higher current returns and lower volatility than class A industrial properties; | |
| • | we believe there is less competition for Class B industrial properties from institutional real estate buyers; our typical competitors are local investors who often do not have ready access to debt or equity capital; | |
| • | the Class B industrial properties real estate market is highly fragmented and complex, which we believe make it difficult for less-experienced or less-focused investors to access comparable opportunities on a consistent basis; | |
| • | we believe that there is a limited new supply of Class B industrial properties space in our target markets; | |
| • | secondary markets generally have less occupancy and rental rate volatility than primary markets; | |
| • | Class B properties and secondary markets are typically “cycle agnostic”; i.e., less prone to overall real estate cycle fluctuations; | |
| • | we believe secondary markets, today, generally, have more growth potential at a lower cost basis than primary markets; and | |
| • | we believe that the demand for e-commerce-related properties, or e-fulfillment facilities, will continue to grow and play a significant role in our investing strategy. |
Underwriting Process
For each property we evaluate, our analysis focuses on:
| • | Real Estate. We evaluate the physical real estate within the context of the market (and submarket) in which it is located and the prospect for re-tenanting the building as leases expire by estimating the following: |
| • | market rent for this building in this location; | |
| • | downtime to re-lease and related carrying costs; | |
| • | cost (tenant improvements, leasing commissions and required capital expenditures) to achieve the projected market rent within the projected downtime; and | |
| • | single-tenant or multi-tenant reuse. |
| • | Deal Parameters. We evaluate the tenant and landlord obligations contained within the existing or proposed lease and other transaction documents. |
87
| • | Tenant Credit. We apply fundamental credit analysis to evaluate the tenant’s credit profile by focusing on the tenant’s current and historical financial status, general business plan, operating risks, capital sources and earnings expectations. We also analyze SEC filings, press releases, management calls, rating agency reports and other public information. In the case of a private, non-rated firm, we will obtain financial information from the tenant and calculate common measures of credit strength such as debt-to-EBITDA and coverage ratios. For publicly rated firms, we use the credit information issued by Moody’s Investor Services, Standard & Poor’s, and |
Fitch Ratings. Using this data and publicly available bond default studies of comparable tenant credits, we estimate the probability of future rent loss due to tenant default.
| • | Tenant Retention. We assess the tenant’s use of the property and the degree to which the property is central to the tenant’s ongoing operations, the tenant’s potential cost to relocate, the supply/demand dynamic in the relevant submarket and the availability of suitable alternative properties. We believe tenant retention tends to be greater for properties that are critical to the tenants’ businesses. |
Acquisition Pipeline
Our executive management and acquisition teams maintain a deep, broad network of relationships among key market participants, including property brokers, lenders, owners and tenants. We believe these relationships and our research-driven origination methods will provide us access to off-market and lightly marketed acquisition opportunities, many of which may not be available to our competitors. Furthermore, we believe that a significant portion of the 13.8 billion square feet of industrial space in the U.S. falls within our target investment criteria and that there will be ample supply of attractive acquisition opportunities in the future.
In the normal course of our business, we regularly evaluate the market for industrial properties to identify potential acquisition targets. As of the date of this prospectus, we were evaluating approximately $350 million of potential acquisitions in our target markets that we have identified as warranting further investment consideration after an initial review. We do not have any relationship with the sellers of the properties we are evaluating. As of the date of this prospectus, we have neither entered into any letters of intent or purchase agreements with respect to any potential acquisitions nor have we begun a comprehensive due diligence review with respect to any of these properties. Accordingly, we do not believe that the acquisition of any of the properties under evaluation is probable as of the date of this prospectus.
The Company Portfolio
As of the date of this prospectus, we have a minority interest in and operate 20 industrial buildings, with an aggregate of approximately 4.0 million square feet of rentable space that is currently 98.4% occupied. Upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, we will own 100% of the interest in each of the 20 properties listed below. The following table provides certain information with respect to the Company Portfolio as of March 31, 2017.
| Metro | Address | Property Type | Year Built/
Renovated (1) | Square Footage | Occupancy | Annualized
Rent (2) | Percent
of Total Annualized Rent | Annualized
Rent/Square Foot (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 3940 Stern Avenue | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1987 | 146,798 | 100 | % | $ | 623,891 | 4.4 | % | $ | 4.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 1875 Holmes Road | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1989 | 134,415 | 100 | % | $ | 641,706 | 4.6 | % | $ | 4.77 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 1355 Holmes Road | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1975/1998 | 82,456 | 100 | % | $ | 387,477 | 2.8 | % | $ | 4.70 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 2401 Commerce Drive | Warehouse/Flex | 1994/2009 | 78,574 | 100 | % | $ | 584,665 | 4.2 | % | $ | 7.44 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 189 Seegers Road | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1972 | 25,000 | 100 | % | $ | 162,365 | 1.2 | % | $ | 6.49 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chicago, IL | 11351 W. 183rd Street | Warehouse/ Distribution | 2000 | 18,768 | 100 | % | $ | 186,889 | 1.3 | % | $ | 9.96 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cincinnati, OH | Mostellar Distribution Center I & II | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1959 | 358,386 | 100 | % | $ | 1,044,049 | 7.4 | % | $ | 2.91 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cincinnati, OH | 4115 Thunderbird Lane | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1991 | 70,000 | 100 | % | $ | 234,500 | 1.7 | % | $ | 3.35 | ||||||||||||||||
| Florence, KY | 7585 Empire Drive | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1973 | 148,415 | 100 | % | $ | 412,785 | 2.9 | % | $ | 2.78 | ||||||||||||||||
| Columbus, OH | 3500 Southwest Boulevard | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1992 | 527,127 | 100 | % | $ | 1,782,634 | 12.7 | % | $ | 3.38 | ||||||||||||||||
| Columbus, OH | 3100 Creekside Parkway | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1999 | 340,000 | 100 | % | $ | 1,003,000 | 7.1 | % | $ | 2.95 | ||||||||||||||||
| Columbus, OH | 8288 Green Meadows Dr. | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1988 | 300,000 | 100 | % | $ | 906,000 | 6.4 | % | $ | 3.02 | ||||||||||||||||
| Columbus, OH | 8273 Green Meadows Dr. | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1996/2007 | 77,271 | 100 | % | $ | 355,765 | 2.5 | % | $ | 4.60 | ||||||||||||||||
| Columbus, OH | 7001 American Pkwy | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1986/2007 & 2012 | 54,100 | 100 | % | $ | 175,824 | 1.2 | % | $ | 3.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| Memphis, TN | 6005, 6045 & 6075 Shelby Dr. | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1989 | 202,303 | 69.3 | % | $ | 424,078 | 3.0 | % | $ | 3.03 | ||||||||||||||||
| Jackson, TN | 210 American Dr. | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1967/1981 & 2013 | 638,400 | 100 | % | $ | 1,404,480 | 10.0 | % | $ | 2.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| Atlanta, GA | 32 Dart Road | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1988/2014 | 194,800 | 100 | % | $ | 516,228 | 3.7 | % | $ | 2.65 | ||||||||||||||||
| Portland, ME | 56 Milliken Road | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1966, 1995, 2005 & 2013 | 200,625 | 100 | % | $ | 1,036,449 | 7.4 | % | $ | 5.17 | ||||||||||||||||
| Marlton, NJ | 4 East Stow Road | Warehouse/ Distribution | 1986 | 156,279 | 100 | % | $ | 834,900 | 5.9 | % | $ | 5.34 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cleveland, OH | 1755 Enterprise Parkway | Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 1979/2005 | 255,570 | 100 | % | $ | 1,354,762 | 9.6 | % | $ | 5.30 | ||||||||||||||||
| Industrial Properties -- Total/Weighted Average | 4,009,287 | 98.4 | % | $ | 14,072,447 | 100.0 | % | $ | 3.57 | |||||||||||||||||||
_______________
| (1) | Renovation means significant upgrades, alterations or additions to building areas, interiors, exteriors and/or systems. |
| (2) | Annualized base rent is calculated by multiplying (i) rental payments (defined as cash rents before abatements) for the month ended March 31, 2017 by (ii) 12. On March 31, 2017, there were no rental abatements or concessions in effect that would impact cash rent. |
| (3) | Calculated by multiplying (i) rental payments (defined as cash rents before abatements) for the month ended March 31, 2017, by (ii) 12, and then dividing by leased square feet for such property as of March 31, 2017. |
The tenants at 8288 Green Meadows Dr., 3500 Southwest Blvd. and 3100 Creekside Pkwy. each have a right of first refusal to purchase the property. The tenant at 1875 Holmes Rd. has an option to purchase the property at fair market value at the end of the lease term on October 31, 2019.
88
The two largest properties in the Company Portfolio, each representing 10% or more of our total annualized rent, are Perseus-210 American Drive (the “Perseus Property”) and Pier One-3500 Southwest Boulevard (the “Pier One Property”), consisting of 638,400 and 527,127 square feet, respectively. Additional information regarding these two properties is set forth below.
Perseus-210 American Drive is a 638,400 square foot warehouse and distribution center located in Jackson, Tennessee. The property is 100% leased to Perseus Distribution, the largest third-party book distributor in the United States, which was purchased by Ingram Content Group in 2016. Perseus Distribution has occupied the property since 2006.
| Address | Tenant | Industry | Rentable Square Feet |
Percent
of Rentable Square Feet |
Expiration | Annualized Base Rent/SF |
Annualized Base Rent |
Percent
of Annualized Base Rent |
Lease
Type | |||||||||||||||
| 210 American Drive | Perseus Distribution | Paper & Printing | 638,400 | 100.0% | 5/31/2020 | $ | 2.20 | $ | 1,404,480 | 100.0% | Triple Net | |||||||||||||
Average lease term for the in place lease is 3.2 years as of March 31, 2017.
| Year of Expiration | Number
of Leases Expiring | Total Rentable Square Feet | Percentage
of Rentable Square Feet | Annualized Base Rent | Percentage
of Annualized Base Rent | Annualized Base Rent per Square Foot | ||||||||||||||||||
| Available | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | |||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 1 | 638,400 | 100.0% | $ | 1,404,480 | 100.0% | $ | 2.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2022 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2023 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2024 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2025 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2026 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Thereafter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total/Weighted Average | 1 | 638,400 | 100.0% | $ | 1,404,480 | 100.0% | $ | 2.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| Five Year Occupancy History | ||
| Year-End | Square Feet Occupied | Occupancy % |
| 2012 | 373,600 | 59% |
| 2013 | 638,400 | 100% |
| 2014 | 638,400 | 100% |
| 2015 | 638,400 | 100% |
| 2016 | 638,400 | 100% |
The Perseus Property was purchased in October 2014 and our federal tax basis in this property is estimated to be approximately $13.5 million. The Perseus Property includes a variety of assets, some of which provide a deduction for depreciation over various periods of time and under a variety of methods (e.g., buildings—39 years, tenant improvements—15 years, leasing commissions—over the life of the lease). Other assets, such as land, do not provide a deduction of depreciation. We anticipate the Perseus Property will produce a deduction of approximately $0.3 million annually but the amount is subject to change as assets are added and as assets become fully depreciated.
Pier One-3500 Southwest Boulevard is a 527,127 square foot warehouse and distribution center located in Columbus, Ohio 100% leased to Pier 1 (NYSE: PIR) (“Pier 1”). Pier 1 has occupied the property since it was built in 1992, and uses the property as a main distribution hub for its United States operations. The building has 28 to 32 foot ceiling height and has extensive dock and trailer storage facilities.
| Address | Tenant | Industry | Rentable Square Feet | Percent
of Rentable Square Feet | Expiration | Annualized Base Rent/SF | Annualized Base Rent | Percent
of Annualized Base Rent | Lease Type | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3500 Southwest Boulevard | Pier One | Home Furnishings | 527,127 | 100.0% | 12/31/2017 | $ | 3.38 | $ | 1,782,634 | 100.0% | Triple Net | |||||||||||||||||||
Average lease term for the in place lease is 0.8 year as of March 31, 2017.
| Year of Expiration | Number of Leases Expiring | Total Rentable Square Feet | Percentage of Rentable Square Feet | Annualized Base Rent | Percentage of Annualized Base Rent | Annualized Base Rent per Square Foot | ||||||||||||||||||
| Available | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | |||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 1 | 527,127 | 100.0% | $ | 1,782,634 | 100.0% | $ | 3.38 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2022 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2023 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2024 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2025 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 2026 | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Thereafter | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Total/Weighted Average | 1 | 527,127 | 100.0% | $ | 1,782,634 | 100.0% | $ | 3.38 | ||||||||||||||||
89
| Five Year Occupancy History | ||
| Year-End | Square Feet Occupied | Occupancy % |
| 2012 | 527,127 | 100% |
| 2013 | 527,127 | 100% |
| 2014 | 527,127 | 100% |
| 2015 | 527,127 | 100% |
| 2016 | 527,127 | 100% |
The Pier One Property was purchased in October 2014 and federal tax basis in this property is estimated to be approximately $19.5 million. The Pier One Property includes a variety of assets, some of which provide a deduction for depreciation over various periods of time and under a variety of methods (e.g., buildings—39 years, tenant improvements—15 years, leasing commissions—over the life of the lease). Other assets, such as land, do not provide a deduction of depreciation. We anticipate the Pier One Property will produce a deduction of approximately $0.5 million annually but the amount is subject to change as assets are added and as assets become fully depreciated.
Functionality Diversification
The following tables set forth information relating to functionality diversification by building type based on total square footage and annualized rent as of March 31, 2017.
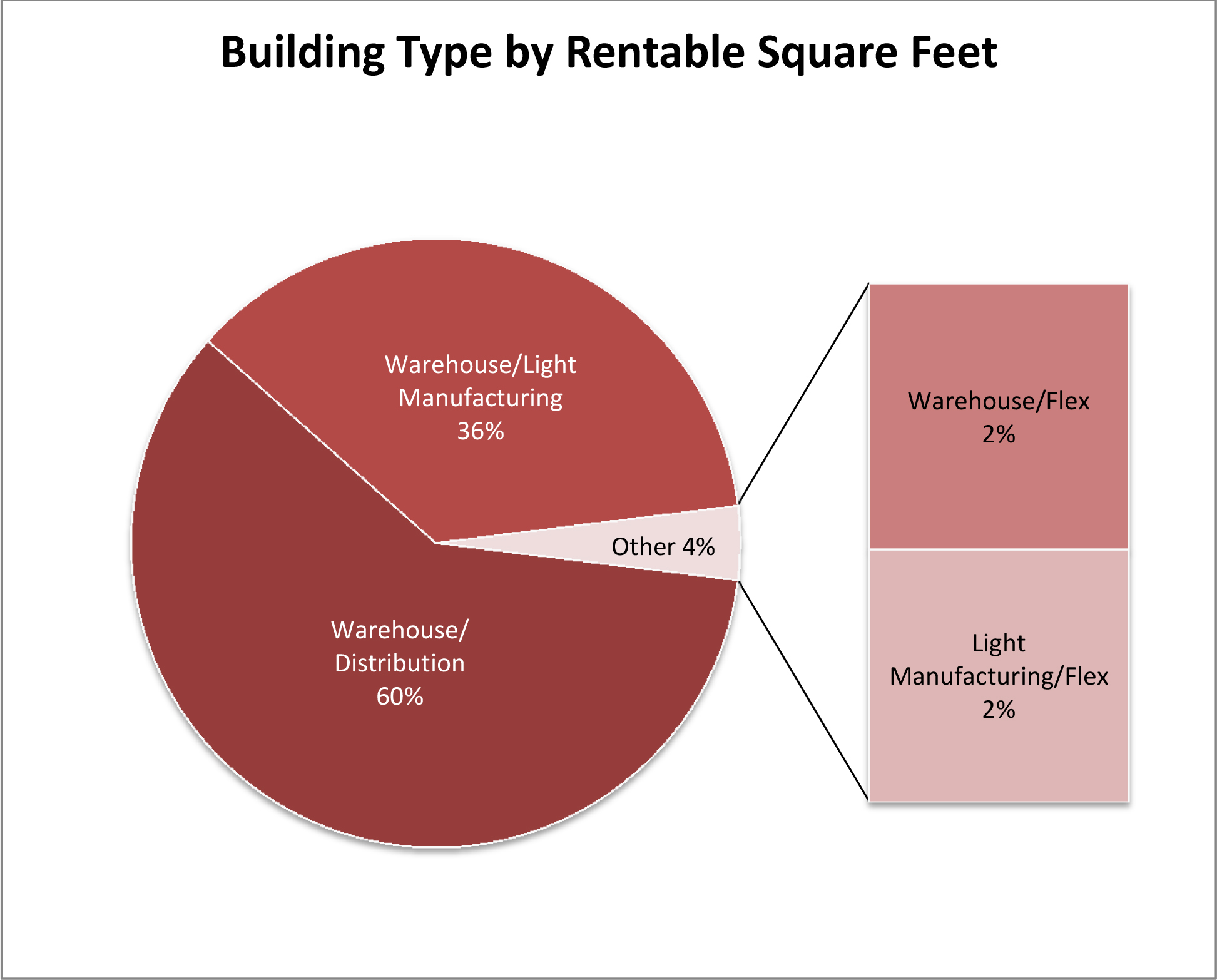 |
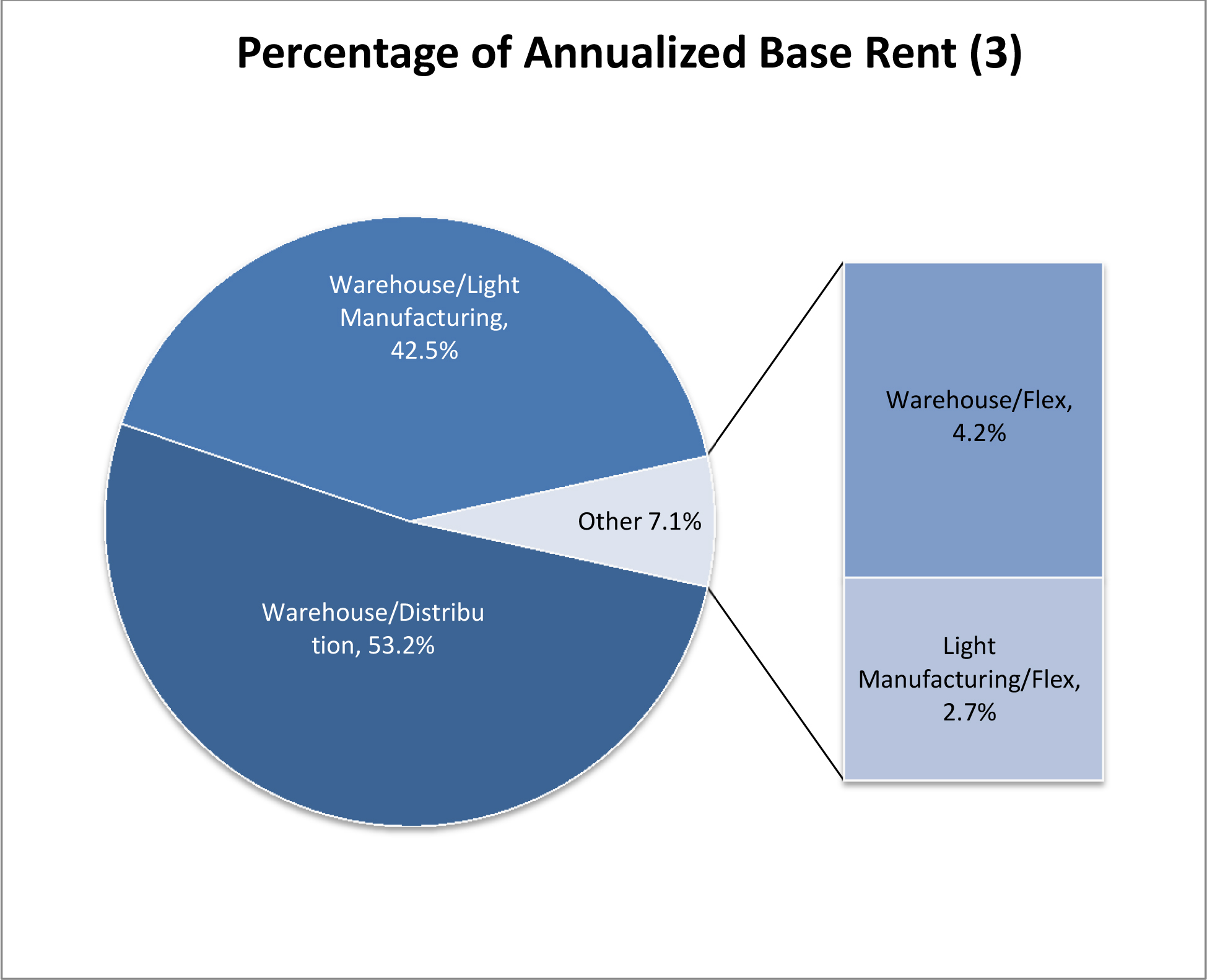 |
| Building Type | Number of Properties | Occupancy(1) | Total Rentable Square Feet | Percentage of Rentable Square Feet | Annualized Base Rent(2) | Percentage of Annualized Base Rent(3) | Annualized Base Rent per Square Foot(4) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Warehouse/Distribution | 10 | 97.3% | 2,391,211 | 59.6% | $ | 7,318,838 | 52.0% | $ | 3.14 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Warehouse/Light Manufacturing | 8 | 100.0% | 1,464,009 | 36.5% | $ | 5,792,236 | 41.2% | $ | 3.96 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Light Manufacturing/Flex | 1 | 100.0% | 78,574 | 2.0% | $ | 584,663 | 4.2% | $ | 7.44 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Warehouse/Flex | 1 | 100.0% | 75,493 | 1.9% | $ | 376,710 | 2.7% | $ | 4.99 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total Company Portfolio | 20 | 98.4% | 4,009,287 | 100.0% | $ | 14,072,447 | 100.0% | $ | 3.57 | |||||||||||||||||||
____________________
| (1) | Calculated as the average occupancy at such properties as of March 31, 2017. |
| (2) | Calculated for each property as the monthly contracted base rent per the terms of the lease(s) at such property, as of March 31, 2017, multiplied by 12 and then aggregated by property type. Excludes billboard and antenna revenue and rent abatements. Total rent abatements with respect to the Company Portfolio for leases in effect as of March 31, 2017 for the 12 months ending March 31, 2018 are $0. Annualized base rent includes rent from triple-net leases, modified triple-net leases and gross leases. See “Business—Lease Overview.” |
| (3) | Calculated for each property type as annualized base rent for such property type divided by total annualized base rent for the Company Portfolio as of March 31, 2017. |
| (4) | Calculated for each property type as annualized base rent for such property type divided by leased square feet for such property type as of March 31, 2017. |
90
Geographic Diversification
The following tables set forth information relating to geographic diversification of the Company Portfolio by state based on total annualized rent as of March 31, 2017.
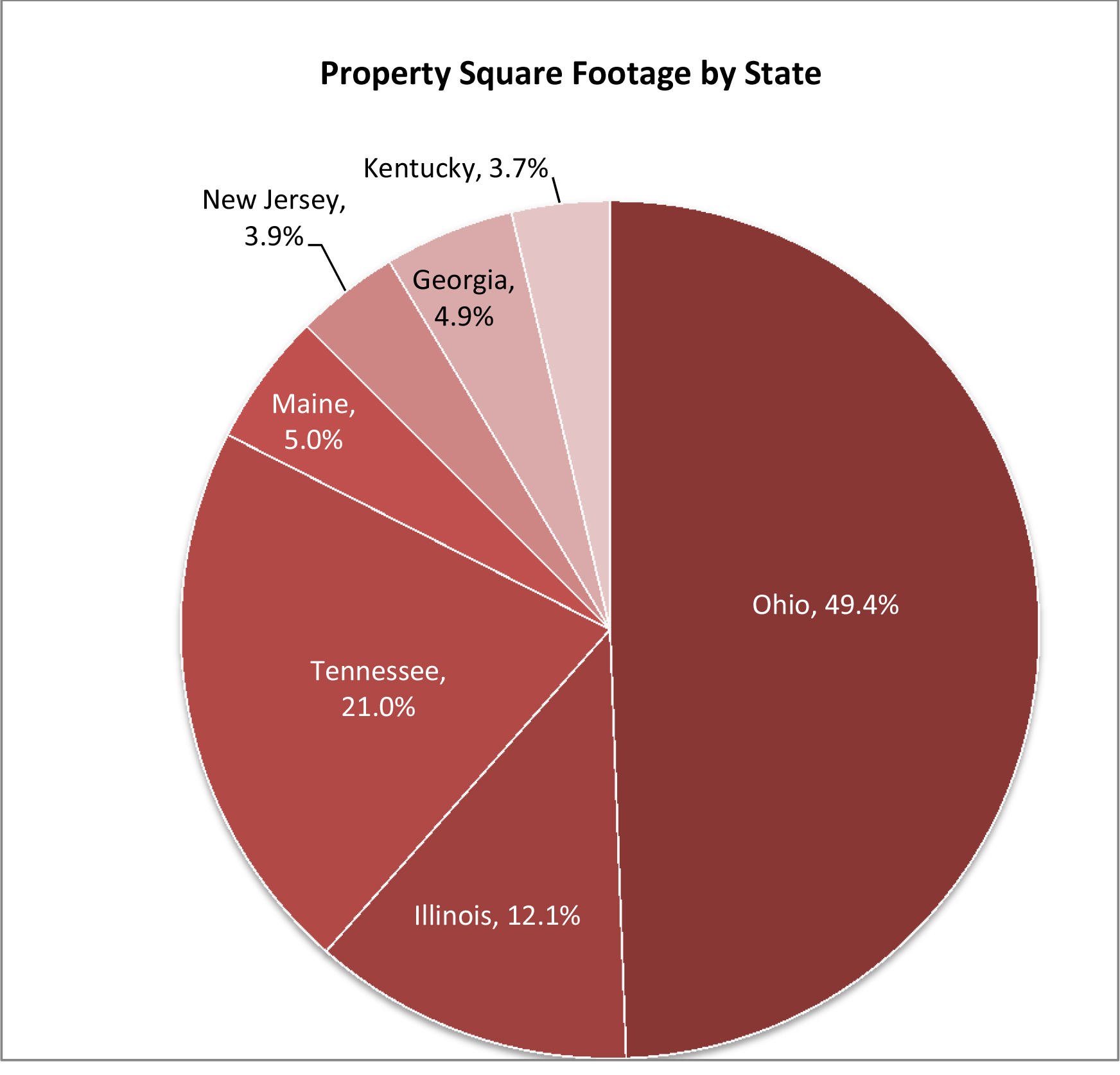 |
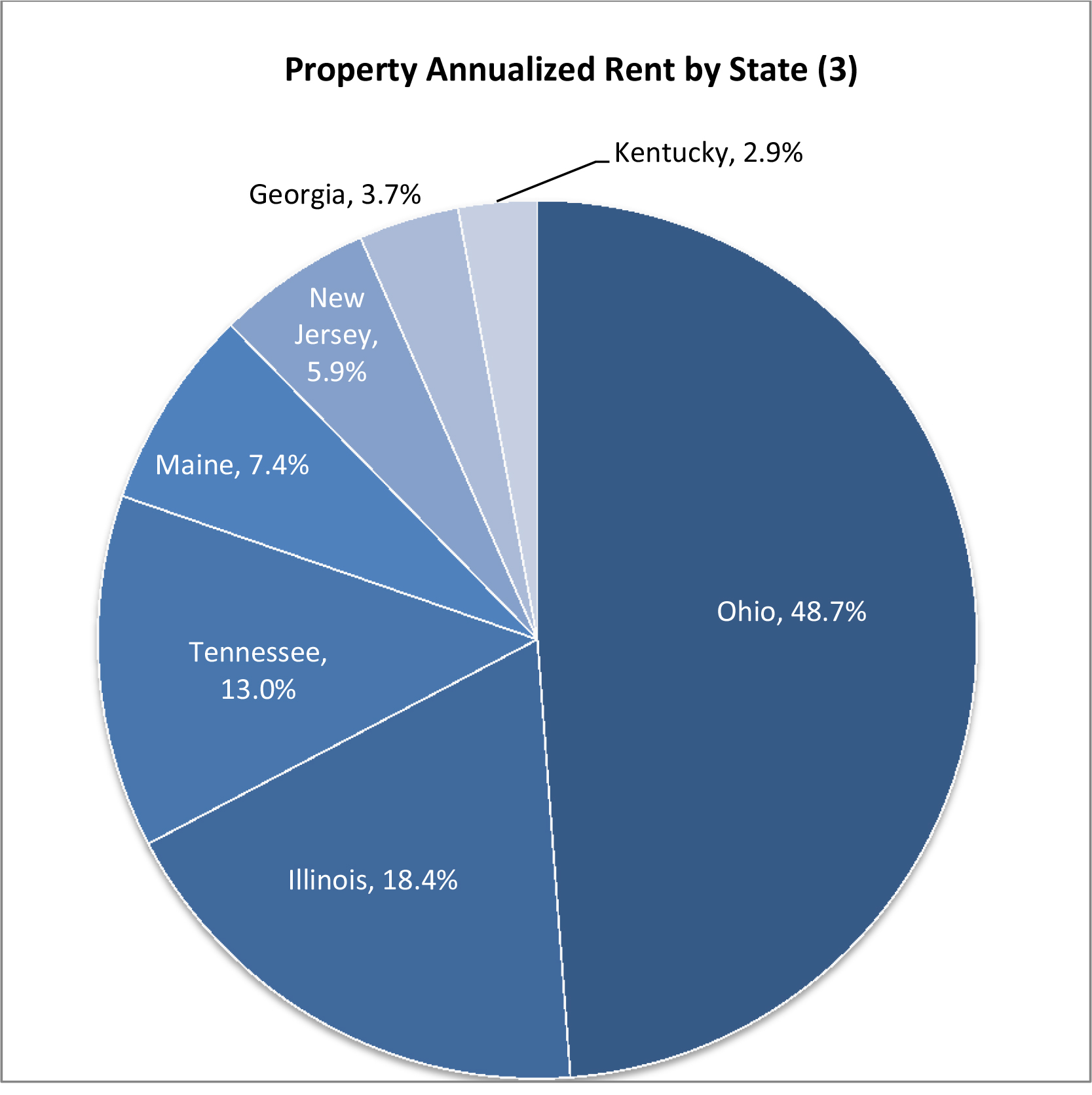 |
| State | Number of Properties | Occupancy(1) | Total Rentable Square Feet | Percentage
of Rentable Square Feet | Annualized Base Rent(2) | Percentage
of Annualized Base Rent(3) | Annualized Base Rent per Square Foot(4) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Ohio | 8 | 100.0% | 1,982,454 | 49.4% | $ | 6,856,533 | 48.7% | $ | 3.46 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Illinois | 6 | 100.0% | 486,011 | 12.1% | $ | 2,586,992 | 18.4% | $ | 5.32 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Tennessee | 2 | 92.6% | 840,703 | 21.0% | $ | 1,828,558 | 13.0% | $ | 2.35 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Maine | 1 | 100.0% | 200,625 | 5.0% | $ | 1,036,448 | 7.4% | $ | 5.17 | |||||||||||||||||||
| New Jersey | 1 | 100.0% | 156,279 | 3.9% | $ | 834,900 | 5.9% | $ | 5.34 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Georgia | 1 | 100.0% | 194,800 | 4.9% | $ | 516,228 | 3.7% | $ | 2.65 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kentucky | 1 | 100.0% | 148,415 | 3.7% | $ | 412,785 | 2.9% | $ | 2.78 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total Company Portfolio | 20 | 98.4% | 4,009,287 | 100.0% | $ | 14,072,447 | 100.0% | $ | 3.57 | |||||||||||||||||||
____________________
| (1) | Calculated as the average occupancy at such properties as of March 31, 2017. |
| (2) | Calculated for each property as monthly contracted base rent per the terms of the lease(s) at such property, as of March 31, 2017, multiplied by 12 and then aggregated by market. Excludes billboard and antenna revenue and rent abatements. Annualized base rent includes rent from triple net leases, modified gross leases and gross leases. See “Business—Lease Overview.” |
| (3) | Calculated as annualized base rent for such market divided by annualized base rent for the Company Portfolio as of March 31, 2017. |
| (4) | Calculated as annualized base rent for such market divided by leased square feet for such market as of March 31, 2017. |
91
Industry Diversification
The following tables set forth information relating to tenant diversification of the Company Portfolio by industry based on total square feet occupied and annualized rent as of March 31, 2017.
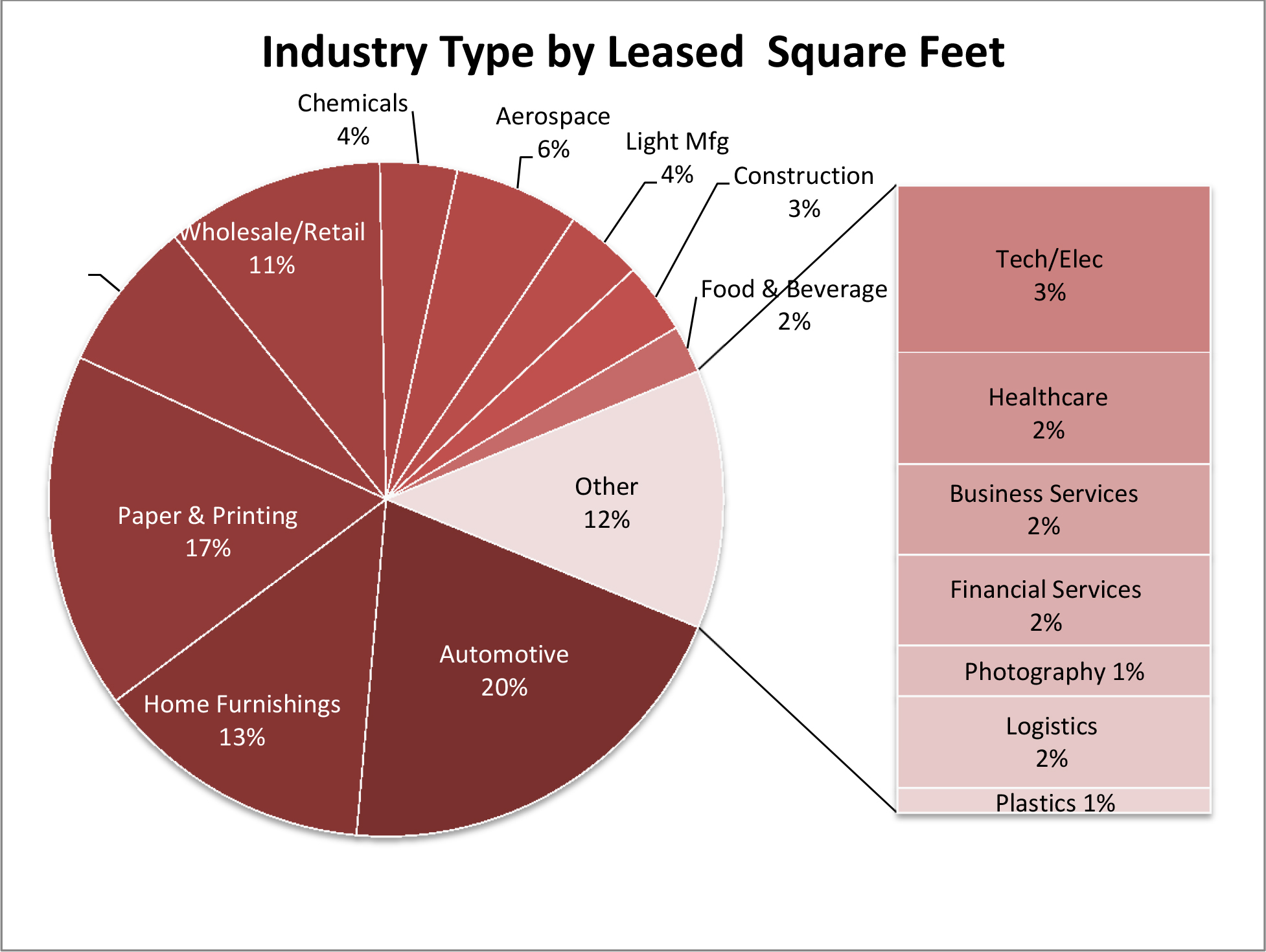 |
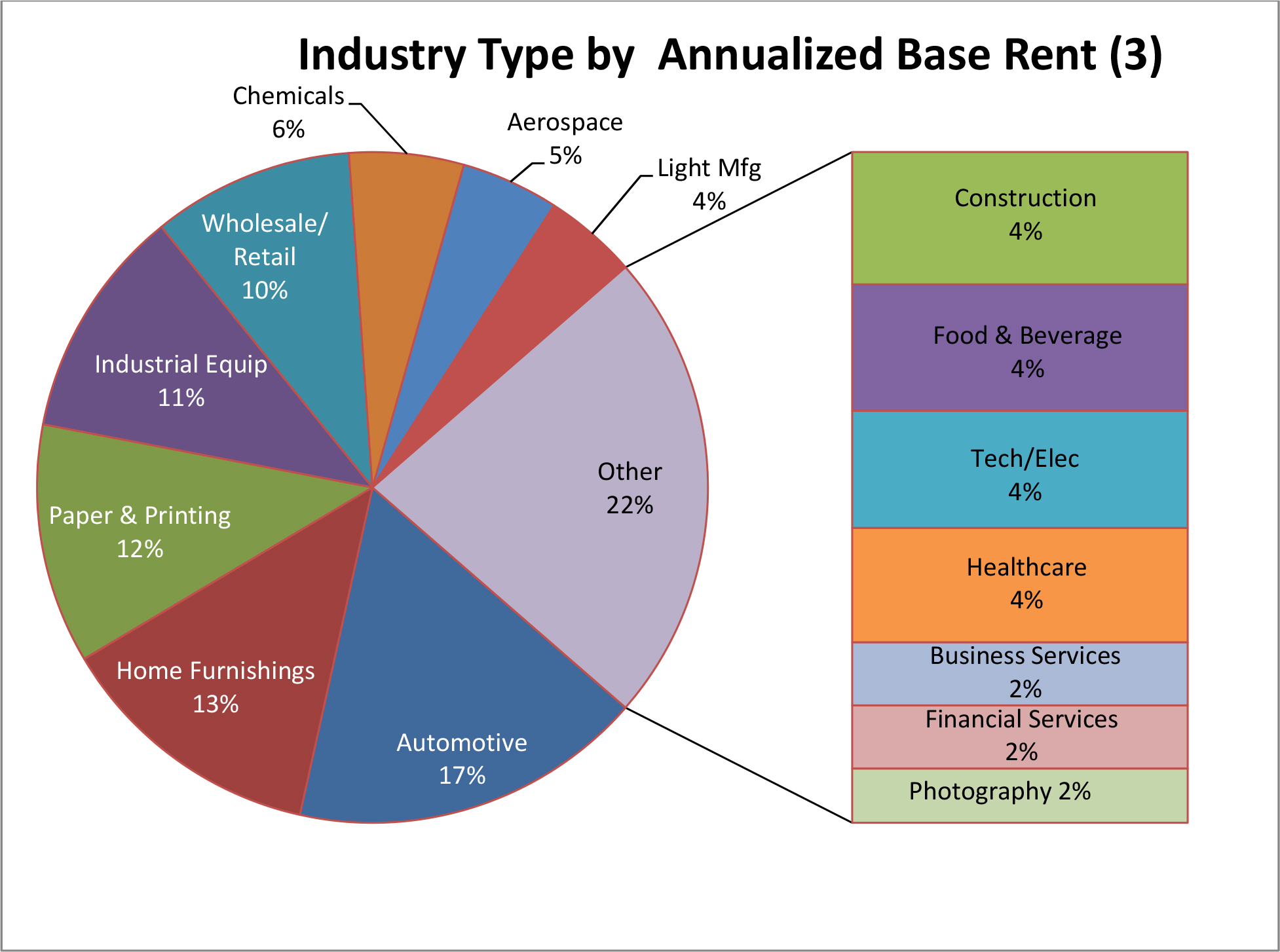 |
| Industry | Number of Leases | Total Leased Square Feet | Percentage of Leased Square Feet | Annualized Base Rent(1) | Percentage of Annualized Base Rent(2) | Annualized Base Rent per Square Foot(3) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Automotive | 6 | 790,826 | 20.2% | $ | 2,343,799 | 16.7% | $ | 2.96 | ||||||||||||||||
| Home Furnishings | 1 | 527,127 | 13.4% | $ | 1,782,634 | 12.7% | $ | 3.38 | ||||||||||||||||
| Paper & Printing | 2 | 676,008 | 17.1% | $ | 1,585,380 | 11.3% | $ | 2.35 | ||||||||||||||||
| Industrial Equipment | 5 | 289,609 | 7.3% | $ | 1,538,380 | 10.8% | $ | 5.24 | ||||||||||||||||
| Wholesale/Retail | 4 | 414,939 | 10.5% | $ | 1,351,316 | 9.6% | $ | 3.26 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chemicals | 1 | 145,939 | 3.7% | $ | 763,280 | 5.4% | $ | 5.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| Aerospace | 1 | 236,405 | 6.0% | $ | 639,682 | 4.5% | $ | 2.71 | ||||||||||||||||
| Light Manufacturing | 1 | 146,798 | 3.7% | $ | 623,891 | 4.4% | $ | 4.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| Construction | 2 | 134,589 | 3.4% | $ | 613,589 | 4.4% | $ | 4.56 | ||||||||||||||||
| Food & Beverage | 1 | 91,036 | 2.3% | $ | 585,225 | 4.2% | $ | 6.43 | ||||||||||||||||
| Tech/Electronics | 2 | 129,593 | 3.3% | $ | 552,534 | 3.9% | $ | 4.26 | ||||||||||||||||
| Healthcare | 2 | 87,645 | 2.2% | $ | 531,800 | 3.8% | $ | 6.07 | ||||||||||||||||
| Business Services | 4 | 72,378 | 1.8% | $ | 330,945 | 2.4% | $ | 4.57 | ||||||||||||||||
| Financial Services | 2 | 72,318 | 1.8% | $ | 297,060 | 2.1% | $ | 4.13 | ||||||||||||||||
| Photography | 1 | 39,950 | 1.0% | $ | 247,290 | 1.8% | $ | 6.19 | ||||||||||||||||
| Logistics | 2 | 71,730 | 1.8% | $ | 197,056 | 1.4% | $ | 2.75 | ||||||||||||||||
| Plastics | 1 | 21,200 | 0.5% | $ | 108,120 | 0.8% | $ | 5.10 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Company Portfolio | 38 | 3,947,094 | 100.0% | $ | 14,072,447 | 100.0% | $ | 3.57 | ||||||||||||||||
____________________
| (1) | Calculated for each lease as the monthly contracted base rent per the terms of such lease, as of March 31, 2017, multiplied by 12 and then aggregated by industry. Excludes billboard and antenna revenue and rent abatements. Annualized base rent includes rent from triple net leases, modified gross leases and gross leases. See “Business—Lease Overview.” |
| (2) | Calculated as annualized base rent for tenants in such industry divided by annualized base rent for the Company Portfolio as of March 31, 2017. |
| (3) | Calculated as annualized base rent for tenants in such industry divided by leased square feet for tenants in such industry as of March 31, 2017. |
92
Tenants
We believe our Company Portfolio has a stable and diversified tenant base. As of March 31, 2017, the Company Portfolio was approximately 98.4% leased to 37 different tenants across 17 industries. The average tenant size is approximately 106,678 square feet, with 50% of tenants occupying less than 54,000 square feet each. The ten largest tenants collectively account for 64.5% of the annualized rent as of March 31, 2017. We intend to continue to maintain a diversified mix of tenants in order to limit our exposure to any single tenant or industry.
The following table sets forth information about the ten largest tenants in our Company Portfolio based on total annualized rent as of March 31, 2017.
Ten Largest Tenants by Annualized Rent
| Tenant | Market | Industry | Number of Leases | Total
Leased Square Feet |
Expiration | Annualized
Base Rent/SF (1) |
Annualized
Base Rent (2) |
Percent
of Total Annualized Rent (3) |
| Pier One | Columbus | Home Furnishings | 1 | 527,127 | 12/31/2017 | $3.38 | $1,782,634 | 12.7% |
| Perseus Distribution | Jackson | Paper & Printing | 1 | 638,400 | 5/31/2020 | $2.20 | $1,404,480 | 10.0% |
| Liquidity Services | Columbus | Wholesale/Retail | 1 | 340,000 | 2/28/2019 | $2.95 | $1,003,000 | 7.1% |
| Volvo Parts North America | Columbus | Automotive | 1 | 300,000 | 10/31/2019 | $3.02 | $906,000 | 6.4% |
| AMTEC Precision Products | Chicago | Industrial Equipment Components | 2 | 174,336 | 10/31/2019, 4/30/2025 | $4.82 | $847,299 | 6.0% |
| Royal Chemical | Cleveland | Chemical | 1 | 145,334 | 3/31/2020 | $5.25 | $763,280 | 5.4% |
| Standard Aero | Cincinnati | Aero Space | 1 | 236,405 | 4/30/2021 | $2.71 | $639,682 | 4.5% |
| Colony Display Systems | Chicago | Light Manufacturing | 1 | 146,798 | 12/31/2017 | $4.25 | $623,891 | 4.4% |
| Barber Foods | Portland | Food & Beverage | 1 | 91,036 | 12/31/2018 | $6.43 | $585,225 | 4.2% |
| American Driveline | Atlanta | Automotive | 1 | 194,800 | 8/31/2024 | $2.65 | $516,228 | 3.7% |
| Ten Largest Tenants by Annualized Rent | 11 | 2,794,236 | $3.25 | $9,071,719 | 64.5% | |||
| All Other | 27 | 1,152,858 | $4.34 | $5,000,728 | 35.5% | |||
| Total Company Portfolio | 38 | 3,947,094 | $3.57 | $14,072,447 | 100.0% | |||
____________________
| (1) | Calculated as annualized base rent for such tenant divided by leased square feet for such tenant as of March 31, 2017. |
| (2) | Calculated for each tenant as the monthly contracted base rent per the terms of such tenant’s lease, as of March 31, 2017, multiplied by 12. Excludes billboard and antenna revenue and rent abatements. Total rent abatements with respect to the Company Portfolio for leases in effect as of March 31, 2017 for the 12 months ending March 31, 2018 are $0. Annualized base rent includes rent from triple net leases, modified triple-net leases and gross leases. See “Business—Lease Overview.” |
| (3) | Calculated as annualized base rent for such tenant divided by annualized base rent for the Company Portfolio as of March 31, 2017. |
Lease Overview
Triple-net lease. In our triple-net leases, the tenant is responsible for all aspects of and costs related to the property and its operation during the lease term. The landlord may have responsibility under the lease to perform or pay for certain capital repairs or replacements to the roof, structure or certain building systems, such as heating and air conditioning and fire suppression. The tenant may have the right to terminate the (ease or abate rent due to a major casualty or condemnation affecting a significant portion of the property or due to the landlord’s failure to perform its obligations under the lease. As of March 31, 2017, there were 32 triple-net leases in the Company Portfolio, representing approximately 82.8% of our total annualized base rent.
Modified triple-net lease. In our modified triple-net leases, the landlord is responsible for some property related expenses during the lease term, but the cost of most of the expenses is passed through to the tenant. The tenant may have the right to terminate the lease or abate rent due to a major casualty or condemnation affecting a significant portion of the property or due to the landlord’s failure to perform its obligations under the lease. As of March 31, 2017, there were four modified triple-net leases in the Company Portfolio, representing approximately 16.4% of our total annualized base rent.
Gross lease. In our gross leases, the landlord is responsible for all aspects of and costs related to the property and its operation during the lease term. The tenant may have the right to terminate the lease or abate rent due to a major casualty or condemnation affecting a significant portion of the property or due to the landlord’s failure to perform its obligations under the lease. As of March 31, 2017, there were two gross leases in the Company Portfolio, representing approximately 0.8% of the annualized base rent.
93
The following table provides information regarding the leases in the Company Portfolio as of March 31, 2017:
| Square Feet | Number of Leases(1) | Total Leased Square Feet | Percentage
of Total Leased Square Feet | Annualized Base Rent(2) | Percentage of Total Annualized Base Rent(3) | Annualized Base Rent per Square Foot(4) | ||||||||||||||||||
| >100,000 | 11 | 2,894,849 | 73.4% | $ | 9,136,493 | 65.0% | $ | 3.16 | ||||||||||||||||
| 50,000 - 99,999 | 9 | 606,897 | 15.4% | $ | 2,713,213 | 19.2% | $ | 4.47 | ||||||||||||||||
| 25,000 - 49,999 | 8 | 285,930 | 7.2% | $ | 1,417,809 | 10.1% | $ | 4.96 | ||||||||||||||||
| <25,000 | 10 | 159,418 | 4.0% | $ | 804,932 | 5.7% | $ | 5.05 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Company Portfolio | 38 | $ | 3,947,094 | 100.0% | $ | 14,072,447 | 100.0% | $ | 3.57 | |||||||||||||||
____________________
| (1) | One tenant has two leases resulting in the number of different tenants to be 37 while there are 38 leases. | |
| (2) | Calculated for each lease as the monthly contracted base rent per the terms of such lease, as of March 31, 2017, multiplied by 12 and then aggregated by square feet. Excludes billboard and antenna revenue and rent abatements. Annualized base rent includes rent from triple net leases, modified triple-net leases and gross leases. See “Business—Lease Overview.” |
| (3) | Calculated as annualized base rent for such leases divided by annualized base rent for the Company Portfolio as of March 31, 2017. |
| (4) | Calculated as annualized base rent for such leases divided by leased square feet for such leases as of March 31, 2017. |
Lease Expirations
As of March 31, 2017, the weighted average in-place remaining lease term of the Company Portfolio was 3.1 years. The following table sets forth a summary schedule of lease expirations for leases in place as of March 31, 2017, plus available space, for each of the ten full and partial calendar years commencing March 31, 2017 and thereafter. The information set forth in the table assumes that tenants exercise no renewal options and no early termination rights.
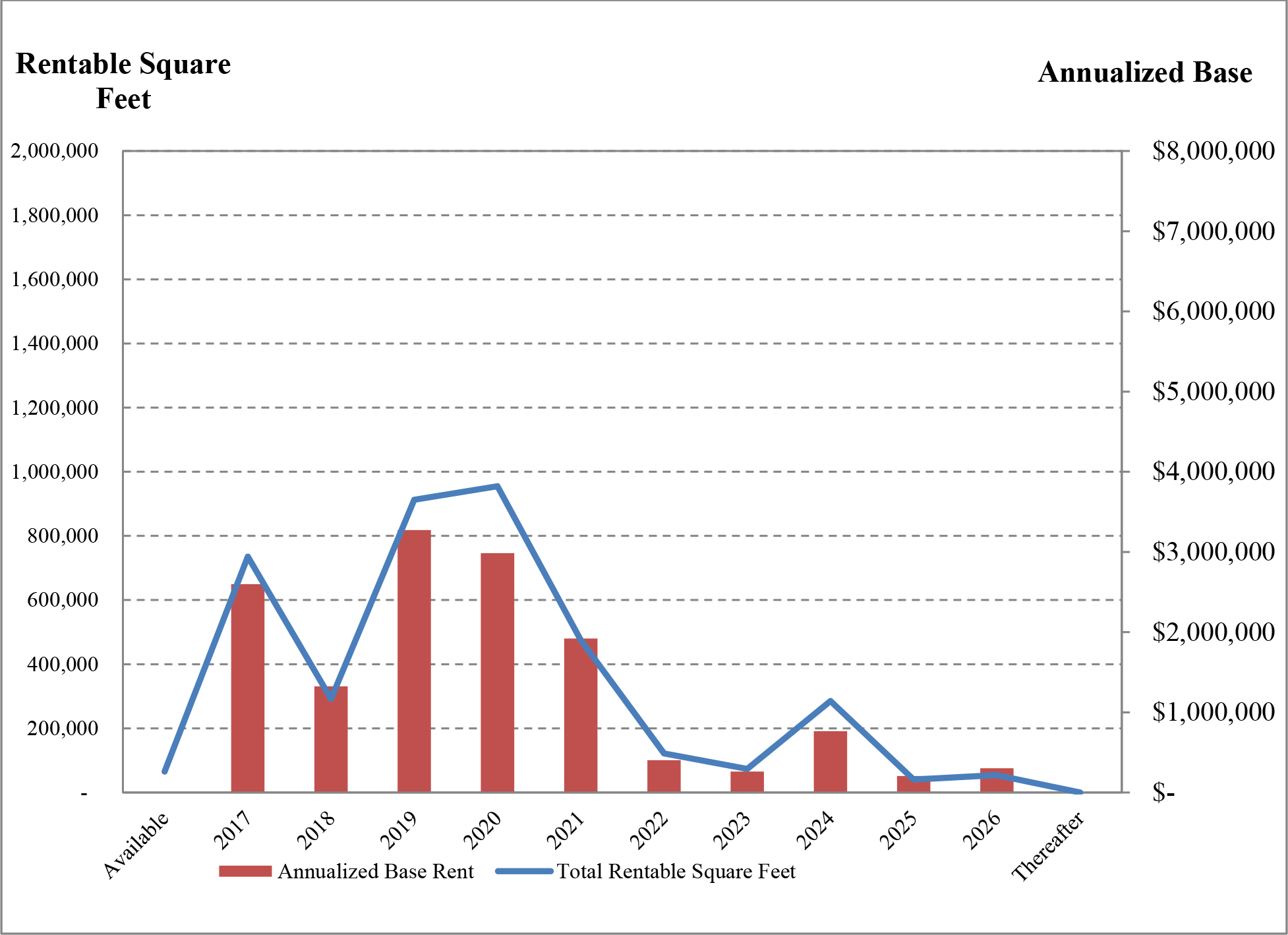 |
| Year of Expiration | Number of Leases Expiring (1) | Total Rentable Square Feet | Percentage of Rentable Square Feet | Annualized Base Rent(2) | Percentage of Annualized Base Rent(3) | Annualized Base Rent per Square Foot(4) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Available | 0 | 62,193 | 1.6% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 5 | 735,385 | 18.3% | $ | 2,598,849 | 18.4% | $ | 3.53 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 7 | 291,978 | 7.3% | $ | 1,326,864 | 9.4% | $ | 4.54 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 6 | 912,516 | 22.9% | $ | 3,270,681 | 23.3% | $ | 3.58 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 6 | 957,854 | 23.9% | $ | 3,017,759 | 21.4% | $ | 3.15 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 7 | 474,751 | 11.8% | $ | 1,920,105 | 13.6% | $ | 4.04 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2022 | 1 | 121,981 | 3.0% | $ | 404,367 | 2.9% | $ | 3.31 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2023 | 2 | 73,573 | 1.8% | $ | 260,726 | 1.9% | $ | 3.54 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2024 | 2 | 285,165 | 7.1% | $ | 764,732 | 5.4% | $ | 2.68 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2025 | 1 | 39,921 | 1.0% | $ | 205,592 | 1.5% | $ | 5.15 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2026 | 1 | 53,970 | 1.3% | $ | 302,772 | 2.2% | $ | 5.61 | ||||||||||||||||
| Thereafter | 0 | — | 0.0% | $ | — | 0.0% | $ | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Company Portfolio | 38 | 4,009,287 | 100.0% | $ | 14,072,447 | 100% | $ | 3.57 | ||||||||||||||||
94
____________________
| (1) | One tenant has two leases resulting in the number of different tenants to be 37 while there are 38 leases. |
| (2) | Calculated as monthly contracted base rent per the terms of such lease, as of March 31, 2017, multiplied by 12. Excludes billboard and antenna revenue and rent abatements. Total rent abatements with respect to the Company Portfolio for leases in effect as of March 31, 2017 for the 12 months ending March 31, 2018 are $0. Annualized base rent includes rent from triple net leases, modified triple-net leases and gross leases. See “Business—Lease Overview.” |
| (3) | Calculated as annualized base rent set forth in this table divided by total annualized base rent for the Company Portfolio as of March 31, 2017. |
| (4) | Calculated as annualized base rent for such leases divided by leased square feet for such leases at each of the properties so impacted by the lease expirations as of March 31, 2017. |
Description of Certain Debt
AIG Loan
On October 17, 2016, certain indirect subsidiaries of our operating partnership entered into a senior secured loan agreement with investment entities managed by AIG Asset Management, or the AIG Loan Agreement, which provides for a loan, or the AIG Loan, of $120 million, bearing interest at 4.08% per annum, and a seven-year term. As of March 31, 2017, there was $120 million outstanding under the AIG Loan Agreement. The AIG Loan Agreement provides for monthly payments of interest only for the first three years of the term and thereafter monthly principal and interest payments based on a 27-year amortization period. Our operating partnership used the net proceeds of the AIG Loan to partially repay the outstanding principal and accrued interest under our then-existing senior secured loan agreement. We are currently in technical violation of the net worth covenant in the AIG loan agreement, which we believe was the result of a drafting error. On May 3, 2017, we entered into an agreement with AIG pursuant to which AIG has agreed to waive this default from October 17, 2016 up to and including June 30, 2017. We believe that we will be in compliance with all covenants under the AIG Loan Agreement upon the closing of this offering.
The borrowings under the AIG Loan Agreement are secured by first lien mortgages on all of the properties in the Company Portfolio. The obligations under the AIG Loan Agreement are also guaranteed by our company and each of our operating partnership’s wholly-owned subsidiaries.
Torchlight Mezzanine Loan
On October 17, 2016, Plymouth Industrial 20 entered into a mezzanine loan agreement, or the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan Agreement, with Torchlight, which provides for a loan of $30 million, or the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan. The Torchlight Mezzanine Loan has a seven-year term and bears interest at 15% per annum, of which 7% percent is paid currently during the first four years of the term and 10% is paid currently for the remainder of the term. The Torchlight Mezzanine Loan requires Plymouth Industrial 20 to pay a repayment premium equal to the difference between (x) the sum of 150% of the principal being repaid (excluding accrued interest) and (y) the sum of the actual principal amount being repaid and current and accrued interest paid through the date of repayment. This repayment feature operates as a prepayment feature since the difference will be zero at maturity. The borrowings under the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan are secured by, among other things, pledges of the equity interest in Plymouth Industrial 20 and each of its property-owning subsidiaries. The proceeds of the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan were used to partially repay the outstanding principal and accrued interest under our then-existing senior secured loan agreement.
The AIG Loan Agreement and the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan Agreement contain customary representations and warranties, as well as affirmative and negative covenants. The negative covenants include restrictions on additional indebtedness, liens, fundamental changes, dispositions, restricted payments, change in nature of business, transactions with affiliates and burdensome agreements. The AIG Loan Agreement is subject to acceleration upon certain specified events of defaults, including breaches of representations or covenants, failure to pay other material indebtedness, failure to pay taxes or a change of control of our company, as defined in the AIG Loan Agreement. As of March 31, 2017, we were in compliance with all covenants under the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan Agreement.
Property Management
We contract with local property management firms or hire internal property managers (when it is economically more efficient) for those properties requiring onsite personnel and oversight. Properties with a single tenant that maintains the exterior of the facility will only be provided an emergency contact. For multi-tenant properties, the designated property manager will directly interface with the tenants and serve as the contact for the day-to-day operations.
Property management compensation will be market specific, ranging from 2%-4% of gross revenue collections. Emergency contact personnel will only be paid a nominal retainer fee unless actually needed. Any construction management services provided for oversight and inspection will also be contracted at market specific rates and will be dependent on total cost and complexity of the project. Typically management agreements will be in effect for one year, with automatic renewals and include a 30- day reciprocal termination notice. When there are vacant suites or near-term expirations, an unrelated listing agent will be contracted with compensation at market rates.
95
Regulation
General
Our properties are subject to various laws, ordinances and regulations, including regulations relating to common areas and fire and safety requirements. We believe that we have the necessary permits and approvals to operate each of our properties.
Americans with Disabilities Act
Our properties must comply with Title III of the Americans with Disabilities Act, or the ADA, to the extent that such properties are “public accommodations” as defined under the ADA. Under the ADA, all public accommodations must meet federal requirements related to access and use by disabled persons. The ADA may require removal of structural barriers to access by persons with disabilities in certain public areas of our properties where such removal is readily achievable. Although we believe that the properties in the Company Portfolio in the aggregate substantially comply with present requirements of the ADA, and we have not received any notice for correction from any regulatory agency, we have not conducted a comprehensive audit or investigation of all of our properties to determine whether we are in compliance and therefore we may own properties that are not in compliance with the ADA.
ADA compliance is dependent upon the tenant’s specific use of the property, and as the use of a property changes or improvements to existing spaces are made, we will take steps to ensure compliance. Noncompliance with the ADA could result in additional costs to attain compliance, imposition of fined by the U.S. government or an award of damages or attorney’s fees to private litigants. The obligation to make readily achievable accommodations is an ongoing one, and we will continue to assess our properties and to make alterations to achieve compliance as necessary.
Environmental Matters
The Company Portfolio is subject to various federal, state and local environmental laws. Under these laws, courts and government agencies have the authority to require us, as owner of a contaminated property, to clean up the property, even if we did not know of or were not responsible for the contamination. These laws also apply to persons who owned a property at the time it became contaminated, and therefore, it is possible we could incur these costs even after we sell some of the properties we acquire. In addition to the costs of cleanup, environmental contamination can affect the value of a property and, therefore, an owner’s ability to borrow using the property as collateral or to sell the property. Under applicable environmental laws, courts and government agencies also have the authority to require that a person who sent waste to a waste disposal facility, such as a landfill or an incinerator, pay for the clean-up of that facility if it becomes contaminated and threatens human health or the environment.
Furthermore, various court decisions have established that third parties may recover damages for injury caused by property contamination. For instance, a person exposed to asbestos at one of our properties may seek to recover damages if he or she suffers injury from the asbestos. Lastly, some of these environmental laws restrict the use of a property or place conditions on various activities. An example would be laws that require a business using chemicals to manage them carefully and to notify local officials that the chemicals are being used.
We could be responsible for any of the costs discussed above. The costs to clean up a contaminated property, to defend against a claim, or to comply with environmental laws could be material and could adversely affect the funds available for distribution to our stockholders. We usually require Phase I or similar environmental assessments by independent environmental consultants at the time of acquisition of a property. We generally expect to continue to obtain a Phase I or similar environmental site assessments by independent environmental consultants on each property prior to acquiring it. However, these environmental assessments may not reveal all environmental costs that might have a material adverse effect on our business, assets, results of operations or liquidity and may not identify all potential environmental liabilities.
We can make no assurances that (1) future laws, ordinances or regulations will not impose material environmental liabilities on us, or (2) the current environmental condition of our properties will not be affected by tenants, the condition of land or operations in the vicinity of our properties (such as releases from underground storage tanks), or by third parties unrelated to us.
96
Insurance
We will carry commercial property, liability and terrorism coverage on all the properties in the Company Portfolio under a blanket insurance policy. Generally, we do not carry insurance for certain types of extraordinary losses, including, but not limited to, losses caused by riots, war, earthquakes and wildfires unless the property is in a higher risk area for those events. Upon completion of this offering, we believe the policy specifications and insured limits will be appropriate and adequate given the relative risk of loss, the cost of the coverage and standard industry practice, however, our insurance coverage may not be sufficient to fully cover all of our losses. In addition, our title insurance policies may not insure for the current aggregate market value of the Company Portfolio, and we do not intend to increase our title insurance coverage as the market value of the Company Portfolio increases. We have not obtained and do not intend to obtain new or additional title insurance in connection with this offering, including any so-called date down endorsements or other modifications to our existing title insurance policies.
Competition
In acquiring our properties, we compete with other public industrial property sector REITs, income oriented non-traded REITs, private real estate fund managers and local real estate investors and developers. The last named group, local real estate investors and developers, historically has represented our dominant competition for acquisition opportunities. Many of these entities have greater resources than us or other competitive advantages. We also face significant competition in leasing available properties to prospective tenants and in re-leasing space to existing tenants.
Employees
As of the date of this prospectus, we employ nine full-time employees. None of our employees are represented by a labor union.
Legal Proceedings
We are not currently a party, as plaintiff or defendant, to any legal proceedings. From time to time, we may become party to various lawsuits, claims and other legal proceedings that arise in the ordinary course of our business. There can be no assurance that these matters that may arise in the future, individually or in the aggregate, will not have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
Our Corporate Information
Our principal executive offices are located at 260 Franklin Street, 6th Floor, Boston, Massachusetts 02110. Our telephone number is (617) 340-3814. Our website is www.plymouthreit.com. The information found on, or otherwise accessible through, our website is not incorporated into, and does not form a part of, this prospectus or any other report or document we file with or furnish to you.
97
MANAGEMENT
Directors and Executive Officers
Upon completion of this offering, our board of directors will consist of six directors, four of whom are “independent” directors with independence being determined in accordance with the listing standards established by the NYSE MKT. Pursuant to the terms of the Stockholders Agreement, within 30 days of the closing of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, and as long as Torchlight maintains beneficial ownership of at least 2.5% of our then outstanding shares of common stock, Torchlight will be entitled to nominate one director to our board of directors. In connection with this board nomination right, the size of our board will be increased to seven directors and the vacancy will be filled by Torchlight’s nominee. See “—Stockholders Agreement with Torchlight.”
All members of our board of directors will serve annual terms. Upon the expiration of their terms at the annual meeting of stockholders in 2017, directors will be elected to serve a term of one year and until their successors are duly elected and qualify. Subject to rights pursuant to any employment agreements, officers serve at the pleasure of our board of directors.
The following sets forth certain information with respect to our directors and executive officers.
| Name* | Age | Positions | ||
| Martin Barber | 72 | Director** | ||
| Philip S. Cottone | 77 | Director**+ | ||
| Richard J. DeAgazio | 72 | Director**+ | ||
| David G. Gaw | 65 | Director**+ | ||
| Jeffrey E. Witherell | 52 | Chairman and Chief Executive Officer | ||
| Pendleton P. White, Jr. | 57 | President, Chief Investment Officer and Director | ||
| Daniel C. Wright | 68 | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
____________________
* The address of each director and executive officer listed is 260 Franklin Street, 6th Floor, Boston, Massachusetts 02110.
** Independent within the meaning of the NYSE MKT listing standards.
+ Will be appointed to the board of directors as of the closing of this offering.
Biographical Summaries of Directors and Executive Officers
Jeffrey E. Witherell
Jeffrey E. Witherell is our Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board and has held these positions since the formation of the company. Mr. Witherell oversees all aspects of our business activities, including the acquisition, management and disposition of assets.
Mr. Witherell has been involved in real estate investment, development and banking activities for over 25 years. He, along with Mr. White, formed Plymouth Industrial REIT in 2011. From April 2008 thru 2011 he was engaged in the formation and operation of Plymouth Group Real Estate and Plymouth Real Estate Capital LLC, a FINRA registered broker/dealer. From April 2000 to March 2008, Mr. Witherell was employed as an investment executive with Franklin Street Properties Corp., a publicly traded REIT, and its subsidiary, FSP Investments LLC. During that time, Mr. Witherell was involved in the acquisition and syndication of 34 separate property investments, structured as single asset REITs, in 12 states, which raised in the aggregate approximately $1.2 billion.
From 1999 to 2000, he was affiliated with IndyMac Bank where he was responsible for closed-loan acquisitions. From 1996 to 1999, Mr. Witherell was COO for GAP LP, a real estate investment firm where he was responsible for the acquisition and subsequent development of several real estate investments in Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, Wyoming and Nova Scotia, Canada. From 1994 to 1996, he founded and served as president of Devonshire Development, Inc., a Massachusetts based real estate development firm, where he was responsible for the acquisition and subsequent development of several real estate ventures. From 1990 to 1994, he was vice president of property management at New Boston Management, Inc., a Boston based real estate management firm. His responsibilities included property management and property disposition services. From 1987 to 1990, he was vice president of development for Kirkwood Development, an Oklahoma City based real estate development firm. His responsibilities included the development and construction of twelve development projects throughout New England. From 1982 to 1987, Mr. Witherell was employed at Dewsnap Engineering, a Boston based civil engineering and land surveying firm, where he was responsible for performing land surveying, permitting, design, and construction management services.
Mr. Witherell graduated from Emmanuel College in Boston with a Bachelor of Science degree in business and is a member of several real estate organizations. He is a board member of AdventCare Inc., a Massachusetts based nonprofit organization that owns and operates skilled nursing facilities.
Mr. Witherell was selected as a director because of his ability to lead our company and his detailed knowledge of our strategic opportunities, challenges, competition, financial position and business.
98
Pendleton P. White, Jr.
Pendleton P. White, Jr. is our President and Chief Investment Officer and one of our directors. He has served in these positions since the formation of the company. Along with Mr. Witherell, Mr. White actively participates in the management of our company and is primarily responsible for the overall investment strategy and acquisition activities.
Mr. White has over 25 years of experience in commercial real estate, serving in numerous capacities including investment banking, property acquisitions and leasing. From November 2008 through March 2011, Mr. White was engaged in the formation of Plymouth Group Real Estate. Prior to that, Mr. White was Executive Vice President and Managing Director at Scanlan Kemper Bard (SKB) from September 2006 through November 2008, where he ran SKB’s East Coast office and managed the funding of SKB Real Estate Investors Fund I. From March 2002 through September 2006, Mr. White was employed as an investment executive with Franklin Street Properties Corp., a publicly traded REIT, and its subsidiary, FSP Investments LLC. During that time, Mr. White was involved in the acquisition and syndication of numerous structured REITs throughout the United States.
From 1997-2001, Mr. White was Principal and Director of North Shore Holdings, a family-owned real estate investment firm. From 1993-1997, Mr. White was Co-Director of Investment Sales at Coldwell Banker Commercial Real Estate Services (now CBRE) and was responsible for overseeing the acquisition and disposition of commercial properties throughout New England. Mr. White also was Vice President at Spaulding & Slye (now Jones Lang LaSalle) from 1991-1993 and Senior Sales Consultant at the Charles E. Smith Companies (now Vornado), in Washington, DC, from 1987-1992 and was responsible for property leasing and investment sale transactions. Mr. White began his career at Coldwell Banker in 1982. Since then he has been involved in over $1 billion of real estate transactions either serving as a broker, investor, consultant or investment banker.
Mr. White received a Bachelor of Science degree from Boston University and is a member of several real estate organizations.
Mr. White was selected as a director because of his extensive knowledge and insight regarding industrial properties and detailed knowledge of our acquisition and operational opportunities and challenges.
Daniel C. Wright
Daniel C. Wright is the Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of our company, and has held those positions since May 2014. He is responsible for the financial performance, compliance and regulatory reporting.
Mr. Wright has over 30 years of significant accounting and financial reporting experience within the real estate industry. Prior to joining Plymouth, he was a principal with Carleton Advisory Group where he was responsible for providing financial and operational expertise to commercial real estate and hospitality investment firms. From 2005 thru 2009, he was the CFO at Pyramid Advisors in Boston where he directed the financial and legal operations across an $8 billion portfolio of properties and 7,600 employees. While at Pyramid he provided leadership and oversight to 9 financial executives and was additionally responsible for the placement of over $1.5 billion of securitized debt. From 1999 to 2005, Mr. Wright was the CFO at Prism Venture Partners where he managed the financial and legal affairs of the company. Assets under management grew from $150 million to over $1 billion in 40 separate investments under his tenure. From 1995 to 1999, he was the CFO for Leggat McCall Properties in Boston, where he responsible for the financial performance of the firm.
From 1982 to 1995, Mr. Wright was affiliated with Sheraton Hotels where he held several successive positions including Internal Audit Director, Director of Strategic Projects and Planning, and Director of Corporate Development. Additionally he was the Senior Vice President and Division Controller of the Pacific Division based in Honolulu, Hawaii, where he managed the financial operations across six countries.
Mr. Wright holds a BSBA from Babson College and a Juris Doctorate from Suffolk University Law School. He is a former CPA, a member of the Massachusetts Bar, the Massachusetts Society of Public Accountants, and the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants.
Martin Barber
Mr. Barber is one of our independent directors, a position he has held since February 2015. Mr. Barber is currently, and has been since 2010, chairman and a director of Moirai Capital Ltd., a property development and investment company based in England. He has also served as a director of Steamroller Restaurants since 1999. From 1991 to 2004 Mr. Barber simultaneously served as chairman of Transeuropean Properties 1 and 2, comprised of European real estate funds managed by the US-based Prudential Insurance Group. In 1974 Mr. Barber founded and assumed responsibility as CEO of Capital & Regional PLC, a British-based real estate investment fund with $5 Billion in assets under management in Great Britain and the United States, which was listed on the London Stock Exchange in 1986. Mr. Barber retired from his responsibilities with Capital & Regional in 2008.
99
In 1994 the United States assets were separated from Capital & Regional, was re-named CenterPoint Properties Trust and was listed on the New York Stock Exchange. CenterPoint was the first Industrial REIT in the USA and Mr. Barber served as its chairman and lead independent trustee until its $3.4 Billion sale in April, 2006. Mr. Barber also currently serves as an independent director for Applied Residential, a provider of creative lease-purchase financing structures for the residential housing industry.
Philip S. Cottone
Mr. Cottone will serve as an independent director of our company upon the closing of this offering. He previously served as one of our independent directors and chairman of the compensation committee from November 2011 until September 2016. He is an attorney by background and is currently, and has been an arbitrator since 1977 as well as a mediator since 1995 for FINRA, the American Arbitration Association, and the Counselors of Real Estate, primarily concentrating in securities, real estate and general commercial matters. He has been certified by the International Mediation Institute at The Hague, and is a member of the American College of Civil Trial Mediators. For six years, through 2015, he was an officer of the governing Council of the ABA Dispute Resolution Section, a member of the Faculty of the Annual Arbitration and Mediation Institutes, and Co-Chair of the Arbitration Institute in 2016 and 2017.
From 2003 to 2008 he was a member of the Board of Government Properties Trust (NYSE – GPT) and Chair of the Nominating and Governance Committee, and from 2004 to 2009 he was a Lead Director of Boston Capital REIT, a public, non-traded REIT.
In 1981 Mr. Cottone co-founded Ascott Investment Corporation, a real estate investment, development and syndication company, and as Chairman and CEO, and founder and President of its NASD broker-dealer, he headed a staff of 65 people in the acquisition, management, capital raising and sale of more than thirty real estate programs in fourteen states. From 1972 to 1981, Mr. Cottone was Senior Real Estate officer and Group Executive of IU International (NYSE – IU), a $2 billion Fortune 100 company, and previously, from 1966 to 1972, he was Manager of Real Estate at the Port of NY Authority, where, among other things, he was responsible for the acquisition of the World Trade Center property in Manhattan.
From 1977 through 1983, and again from 1998 through 2002, he was General Counsel and member of the Executive Committee of the International Right of Way Association, and from 1988 to 1997 he was Trustee and Treasurer of the IRWA Foundation. In 1988 he was national President of RESSI, the Real Estate Securities and Syndication Institute, and in 2004 he was national Chair of The Counselors of Real Estate, both divisions of the National Association of Realtors. From 198 to 1991 he was Governor of the NASD (National Association of Securities Dealers), the predecessor to FINRA, and was Vice Chairman in 1991. He was a member of the National Business conduct Committee of the Board in 1989, and Chair in 1990. For ten years, from 1995 to 2005, he was an adjunct on the faculty of the Real Estate Institute at New York University, teaching a course he wrote in real estate securities.
Mr. Cottone has an A.B. from Columbia College where he was awarded the Burdette Kinne Prize for Humanities, and an L.L.B. from New York University where he received the Administrative Law Prize. Mr. Cottone was selected as a director because of his extensive investment, finance and real estate experience, board service, and corporate governance background.
Richard J. DeAgazio
Richard J. DeAgazio will serve as an independent director of our company upon the closing of this offering. He had previously served as one of our independent directors and chairman of our corporate governance committee from November 2011 until September 2016. Mr. DeAgazio has been the principal of Ironsides Assoc. LLC., a consulting company in marketing and sales in the financial services industry, since he founded the company in June 2007. He is also currently, and has been since 2009, Chairman of the Board of AgileQR, Inc. (DBA 121 Nexus), a supply chain software company and a member of the Board of Directors of Commodore Builders, a construction management firm, also from 2009 to the present. In 2016, Mr. DeAgazio was Chairman of the Advisory Board of Billaway.com, a cloud-based technology platform in the mobile data industry. In 1981, he joined Boston Capital Corp., a diversified real estate and investment banking firm, which, through its various investment funds, owns over $12 billion in real estate assets, as Executive Vice President and Principal. He founded and served as the President of Boston Capital Securities, Inc., a FINRA-registered broker dealer, which is an affiliate of Boston Capital Corp., from 1981 through December 2007. Mr. DeAgazio formerly served on the National Board of Governors of FINRA and served as a member of the National Adjudicatory Council of FINRA. He was the Vice Chairman of FINRA’s District 11, and served as Chairman of the FINRA’s Statutory Disqualification Subcommittee of the National Business Conduct Committee. He also served on the FINRA State Liaison Committee, the Direct Participation Program Committee and as Chairman of the Nominating Committee. He is a founder and past President of the National Real Estate Investment Association. He is past President of the National Real Estate Securities and Syndication Institute and past President of the Real Estate Securities and Syndication Institute (MA Chapter). Prior to joining Boston Capital in 1981, Mr. DeAgazio was the Senior Vice President and Director of the Brokerage Division of Dresdner Securities (USA), Inc., an international investment-banking firm owned by four major European banks, and was a Vice President of Burgess & Leith/Advest. He was member of the Boston Stock Exchange for 42 years. He was on the Board of Directors of Cognistar Corporation and FurnitureFind.com and recently retired from serving as Vice-Chairman of the Board of Trustees of Bunker Hill Community College, the Board of Trustees of Junior Achievement of Massachusetts and the Board of Advisors for the Ron Burton Kid’s Training Village. He is on the Board of Corporators of Northeastern University and also is active on the Boards of numerous not-for-profit organizations. He graduated from Northeastern University. Mr. DeAgazio was selected as a director because of his extensive senior executive officer and board service experience and experience with real estate operations.
100
David G. Gaw
David G. Gaw will serve as an independent director of our company upon the closing of this offering. He previously served as one of our independent directors and chairman of our audit committee from November 2011 until September 2016. Mr. Gaw is currently a real estate project consultant and is managing personal investments. From November 2009 through January 2011, Mr. Gaw served as Chief Financial Officer of Pyramid Hotels and Resorts, a REIT that focused on hospitality properties. From September 2008 through November 2009, Mr. Gaw was engaged in managing his personal investments. From June 2007 to September 2008, he was Chief Financial Officer of Berkshire Development, a private real estate developer that focused on retail development. From April 2001 until June 2007, he served as the Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer of Heritage Property Investment Trust, Inc., a publicly traded REIT listed on the NYSE. Mr. Gaw was serving in those capacities when Heritage Property engaged in its initial public offering. Mr. Gaw served as Senior Vice President of Boston Properties, Inc., a publicly traded REIT listed on the NYSE, from 1982 - 2000, and also served as its Chief Financial Officer beginning at the time of its initial public offering in 1997. Mr. Gaw received a bachelor of science degree and an MBA from Suffolk University. Mr. Gaw was selected as a director because of his extensive experience with financial reporting, accounting and controls and REIT management.
Other Key Employees
James M. Connolly
James M. Connolly is a Senior Vice President/Asset Manager of our company. He has served as the Director of Asset Management since May 2011 and has direct responsibility for overseeing the day to day operating activities of our properties.
Mr. Connolly is an experienced real estate asset management executive with a significant background in property level and portfolio wide operations. From 1998 to May 2011, Mr. Connolly was employed with Nortel Corporation, where he held positions as Global Leader Real Estate Asset Management from 1998 through December 2003, Director of Real Estate Finance from January 2004 through December 2008, Director of Real Estate for Europe, Middle East and Africa from December 2008 through March 2009, and Director of Real Estate Asset Management from April 2009 through May 2011. His responsibilities included asset, property and facilities management functions across Nortel’s global portfolio of office, industrial, and distribution properties. In addition, he managed internal and external personnel on a national and global basis. Prior to Nortel, Mr. Connolly was affiliated with Bay Networks from 1996 to 1998 and Raytheon from 1986 to 1996 where his responsibilities with those companies included facility finance and property administration.
Mr. Connolly holds a BSBA from the University of Massachusetts and an MBA in Real Estate Financial Management from Northeastern University, and is a member of several real estate organizations including NAIOP.
K. Cory Benson
K. Cory Benson is a Senior Vice President/Acquisitions of our company, and has held that position since our formation. He is responsible for property acquisitions and dispositions.
Prior to joining Plymouth, Mr. Benson was the Founder and President of Sinclair Realty Advisors in January 2001. While at Sinclair, he provided real estate management and development services for corporate clients, specializing in facility planning/investment, build-to-suits, sale-leasebacks and property dispositions throughout the United States, Canada and Mexico. Prior to Sinclair, Mr. Benson was the real estate partner at Biltmore Broadcasting from 1998 to January 2001. Prior to that, he served as Vice President of Real Estate for Astrum International from 1989 to 1998 where he was responsible for the administration and management of a 125 property portfolio. From 1981 to 1989, Mr. Benson was a partner at Hall Davidson & Bullfinch Development, a real estate investment firm, where he was responsible for property acquisitions and real estate development.
Mr. Benson has a Bachelor of Science degree from Cornell University and an MBA from Harvard Business School. He is a member of numerous industry organizations, including the Society of Office and Industrial Realtors (SIOR) and Certified Commercial Investment Managers (CCIM).
101
Anne Alger Hayward
Anne Alger Hayward is a Senior Vice President and is the General Counsel of our company and has served in these positions since March 2011. Ms. Hayward is responsible for the overall legal operations and compliance of our company.
Ms. Hayward has over 30 years of experience in the practice of law, specializing in project finance, securities, and real estate transactional matters. She has structured and documented a wide variety of complex commercial transactions and public and private equity and debt securities offerings. Prior to joining Plymouth, from November 2007 through February 2011 she was General Counsel at Shane & Associates, Ltd., a Boston-based privately held real estate development and management company. Prior thereto, from April 2004 to November 2007 she was employed by Atlantic Exchange Company, an I.R.C. Section 1031 exchange accommodator. From 2001 to 2004, Ms. Hayward served as Senior Counsel at Holland & Knight LLP, representing large corporate clients in structuring tax credit transactions and real estate development projects. From 1997 to 2001, Ms. Hayward was senior counsel at BankBoston, NA representing the bank’s asset based financing subsidiary. From 1993 to 1997, Ms. Hayward was Associate General Counsel at American Finance Group, a Boston-based general equipment leasing company. From 1985 to 1993, Ms. Hayward was corporate/securities counsel at CSA Financial Corp., an equipment lease finance company concentrating in high technology assets. From 1976 to 1985 Ms. Hayward was an Associate at Gaston & Snow representing firm corporate and securities industry clients.
Ms. Hayward is a graduate of Skidmore College and New England School of Law. She holds FINRA Series 22 and 63 licenses, is a licensed real estate broker, and is a member of the Massachusetts and Federal District Court Bars.
Corporate Governance Profile
We have structured our corporate governance in a manner we believe closely aligns our interests with those of our stockholders. Notable features of our corporate governance structure include the following:
| • | our board of directors is not classified, instead, each of our directors is subject to re-election annually; | |
| • | of the six persons who will serve on our board of directors upon the closing of this offering, four, or 67%, of our directors satisfy the listing standards for independence of the NYSE MKT and Rule l0A-3 under the Exchange Act; | |
| • | one of our directors qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” as defined by the SEC; | |
| • | we have opted out of the business combination and control share acquisition statutes in the MGCL; and | |
| • | we do not have a stockholder rights plan. |
Our directors stay informed about our business by attending meetings of our board of directors and its committees and through supplemental reports and communications. Our independent directors will meet regularly in executive sessions without the presence of our corporate officers or non-independent directors.
Role of the Board in Risk Oversight
One of the key functions of our board of directors is informed oversight of our risk management process. Our board of directors administers this oversight function directly, with support from its three standing committees, the audit committee, the nominating and corporate governance committee and the compensation committee, each of which addresses risks specific to their respective areas of oversight. In particular, our audit committee has the responsibility to consider and discuss our major financial risk exposures and the steps our management has taken to monitor and control these exposures, including guidelines and policies to govern the process by which risk assessment and management is undertaken. The audit committee also monitors compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, in addition to oversight of the performance of our internal audit function. Our nominating and corporate governance committee monitors the effectiveness of our corporate governance guidelines, including whether they are successful in preventing illegal or improper liability-creating conduct. Our compensation committee assesses and monitors whether any of our compensation policies and programs has the potential to encourage excessive risk-taking.
Board Committees
Our board of directors has established three standing committees: an audit committee, a compensation committee and a nominating and corporate governance committee. The principal functions of each committee are briefly described below. We intend to comply with the listing requirements and other rules and regulations of the NYSE MKT, as amended or modified from time to time, and each of these committees will be comprised exclusively of independent directors. Additionally, our board of directors may from time to time establish certain other committees to facilitate the management of our company.
102
Audit Committee
Upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, our audit committee will consist of Messrs. Barber, DeAgazio and Gaw, with Mr. Gaw serving as chairman. The chairman of our audit committee qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” as that term is defined by the applicable SEC regulations and NYSE MKT corporate governance listing standards. Our board of directors has determined that each of the audit committee members is “financially literate” as that term is defined by the NYSE MKT corporate governance listing standards. We have adopted an audit committee charter, which details the principal functions of the audit committee, including oversight related to:
| • | our accounting and financial reporting processes; | |
| • | the integrity of our consolidated financial statements and financial reporting process; | |
| • | our systems of disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting; | |
| • | our compliance with financial, legal and regulatory requirements; | |
| • | the evaluation of the qualifications, independence and performance of our independent registered public accounting firm; the performance of our internal audit function; and | |
| • | our overall risk profile. |
The audit committee is also be responsible for engaging an independent registered public accounting firm, reviewing with the independent registered public accounting firm the plans and results of the audit engagement, approving professional services provided by the independent registered public accounting firm, including all audit and non-audit services, reviewing the independence of the independent registered public accounting firm, considering the range of audit and non-audit fees and reviewing the adequacy of our internal accounting controls. The audit committee also prepares the audit committee report required by SEC regulations to be included in our annual proxy statement.
Compensation Committee
Upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, our compensation committee will consist of Messrs. Barber, DeAgazio and Gaw, with Mr. Barber serving as chairman. We have adopted a compensation committee charter, which details the principal functions of the compensation committee, including:
| • | reviewing and approving on an annual basis the corporate goals and objectives relevant to our co-chief executive officers’ compensation, evaluating our co-chief executive officers’ performance in light of such goals and objectives and determining and approving the remuneration of our co-chief executive officers based on such evaluation; | |
| • | reviewing and approving the compensation, if any, of all of our other officers; | |
| • | reviewing our executive compensation policies and plans; | |
| • | implementing and administering our incentive compensation equity-based remuneration plans; | |
| • | assisting management in complying with our proxy statement and annual report disclosure requirements; | |
| • | producing a report on executive compensation to be included in our annual proxy statement; and | |
| • | reviewing, evaluating and recommending changes, if appropriate, to the remuneration for directors. |
Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee
Upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, our nominating and corporate governance committee will consist of Messrs. Barber, DeAgazio and Gaw, with Mr. DeAgazio serving as chairman. We have adopted a nominating and corporate governance committee charter, which details the principal functions of the nominating and corporate governance committee, including:
| • | identifying and recommending to the full board of directors qualified candidates for election as directors to fill vacancies on the board or at the annual meeting of stockholders; | |
| • | developing and recommending to our board of directors corporate governance guidelines and implementing and monitoring such guidelines; | |
| • | reviewing and making recommendations on matters involving the general operation of our board of directors, including board size and composition, and committee composition and structure; |
103
| • | recommending to our board of directors nominees for each committee of our board of directors; | |
| • | annually facilitating the assessment of our board of directors’ performance as a whole and of the individual directors, as required by applicable law, regulations and the NYSE MKT corporate governance listing standards; and | |
| • | overseeing our board of directors’ evaluation of management. |
In identifying and recommending nominees for election as directors, the nominating and corporate governance committee may consider diversity of relevant experience, expertise and background.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
Our board of directors has established a code of business conduct and ethics that applies to our officers, directors and employees. Among other matters, our code of business conduct and ethics is designed to deter wrongdoing and to promote:
| • | honest and ethical conduct, including the ethical handling of actual or apparent conflicts of interest between personal and professional relationships; | |
| • | full, fair, accurate, timely and understandable disclosure in our SEC reports and other public communications; compliance with laws, rules and regulations; | |
| • | prompt internal reporting of violations of the code to appropriate persons identified in the code; and | |
| • | accountability for adherence to the code of business conduct and ethics. |
Any waiver of the code of business conduct and ethics for our executive officers or directors must be approved by a majority of our independent directors, and any such waiver shall be promptly disclosed as required by law or NYSE MKT regulations.
Stockholders Agreement with Torchlight
Immediately upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, we intend to enter into a stockholders’ agreement with Torchlight, or the Stockholders Agreement, in order to establish various arrangements and restrictions with respect to governance of our company and certain rights that will be granted to Torchlight in connection with the Torchlight Transactions.
Pursuant to the terms of the Stockholders Agreement, as long as Torchlight maintains beneficial ownership of at least 2.5% of our then outstanding shares of common stock, Torchlight will be entitled to nominate one director to our board of directors. In connection with this board nomination right, the size of our board will be increased to seven directors and the vacancy will be filled by Torchlight’s nominee. In addition, the Stockholders Agreement will provide that, for so long as Torchlight’s level of beneficial ownership is equal to or greater than 2.5% of our outstanding common stock, we will be prohibited from issuing preferred stock of any class.
Under the Stockholders Agreement, Torchlight is also entitled, subject to certain exceptions, to certain customary registration rights. In addition, Torchlight will have a pre-emptive right to participate in future issuances of common stock by the company for so long as Torchlight maintains beneficial ownership of at least 2.5% of our outstanding common stock to maintain Torchlight’s fully-diluted ownership position in the company.
If Torchlight’s beneficial ownership of our outstanding common stock falls below the percentage threshold set forth above, Torchlight will promptly cause its nominated director to resign from our board of directors and all of the rights set forth above shall be terminated, even if Torchlight subsequently acquires additional shares of our common stock through the exercise of warrants or otherwise.
Limitation of Liability and Indemnification
We intend to enter into indemnification agreements with each of our directors and executive officers that will obligate us, if a director or executive officer is or is threatened to be made a party to, or witness in, any proceeding by reason of such director’s or executive officer’s status as a present or former director, officer, employee or agent of our company or as a director, trustee, officer, partner, manager, member, fiduciary, employee or agent of another enterprise that the director or executive officer served in such capacity at our request, to indemnify such director or executive officer, and advance expenses actually and reasonably incurred by him or her, or on his or her behalf, unless it has been established that:
| • | the act or omission of the director or executive officer was material to the matter giving rise to the proceeding and was committed in had faith or was the result of active and deliberate dishonesty; | |
| • | the director or executive officer actually received an improper personal benefit in money, property or services; or | |
| • | with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, the director or executive officer had reasonable cause to believe his or her conduct was unlawful. |
In addition, except as described below, our directors and executive officers will not be entitled to indemnification pursuant to the indemnification agreement:
| • | if the proceeding was one brought by us or on our behalf and the director or executive officer is adjudged to be liable to us; | |
| • | if the director or executive officer is adjudged to be liable on the basis that personal benefit was improperly received in a proceeding charging improper personal benefit to the director or executive officer; or | |
| • | in any proceeding brought against us by the director or executive officer other than to enforce his or her rights under the indemnification agreement, and then only to the extent provided by the agreement, and except as may be expressly provided in our charter, our bylaws, a resolution of our board of directors or of our stockholders entitled to vote generally in the election of directors or an agreement approved by our board of directors. |
104
Notwithstanding the limitations on indemnification described above, on application by a director or executive officer of our company to a court of appropriate jurisdiction, the court may order indemnification of such director or executive officer if the court determines that such director or executive officer is fairly and reasonably entitled to indemnification in view of all the relevant circumstances, whether or not the director or executive officer (1) has met the standards of conduct set forth above or (2) has been adjudged liable for receipt of an “improper personal benefit.” Under Maryland law, any such indemnification is limited to the expenses actually and reasonably incurred by him or her, or on his or her behalf, in connection with any proceeding by or on behalf of our company or in which the officer or director was adjudged liable for receipt of an improper personal benefit. If the court determines the director or executive officer is so entitled to indemnification, the director or executive officer will also be entitled to recover from us the expenses of securing such indemnification.
Notwithstanding, and without limiting, any other provision of the indemnification agreements, if a director or executive officer is made a party to any proceeding by reason of such director’s or executive officer’s status as a director, officer, employee or agent of our company or as a director, trustee, officer, partner, manager, member, fiduciary, employee or agent of another entity that the director or executive officer served in such capacity at our request, and such director or executive officer is successful, on the merits or otherwise, as to one or more (even if less than all) claims, issues or matters in such proceeding, we must indemnify such director or executive officer for all expenses actually and reasonably incurred by him or tier, or on his or her behalf, in connection with each successfully resolved claim, issue or matter, including any claim, issue or matter in such a proceeding that is terminated by dismissal, with or without prejudice.
In addition, the indemnification agreements will require us to advance reasonable expenses incurred by the indemnitee within ten days of the receipt by us of a statement from the indemnitee requesting the advance, provided the statement evidences the expenses and is accompanied by:
| • | a written affirmation of the indemnitee’s good faith belief that he or she has met the standard of conduct necessary for indemnification; and | |
| • | a written undertaking to reimburse us if a court of competent jurisdiction determines that the director or executive officer is not entitled to indemnification. |
The indemnification agreements will also provide for procedures for the determination of entitlement to indemnification, including a requirement that such determination be made by independent counsel after a change of control of us.
Our charter permits us and our bylaws obligate us, to the maximum extent permitted by Maryland law, to indemnify and to pay or reimburse reasonable expenses in advance of final disposition of a proceeding to (1) any of our present or former directors or officers who is made or threatened to be made a party to, or witness in, the proceeding by reason of his or her service in that capacity or (2) any individual who, while serving as our director or officer and at our request, serves or has served as a director, officer, partner, trustee, member or manager of another corporation, real estate investment trust, limited liability company, partnership, joint venture, trust, employee benefit plan or other enterprise, and who is made or threatened to be made a party to, or witness in, the proceeding by reason of his or her service in that capacity.
Generally, Maryland law permits a Maryland corporation to indemnify its present and former directors and officers except in instances where the person seeking indemnification acted in bad faith or with active and deliberate dishonesty, actually received an improper personal benefit in money, property or services or, in the case of a criminal proceeding, had reasonable cause to believe that his or her actions were unlawful. Under Maryland law, a Maryland corporation also may not indemnify a director or officer in a suit by or on behalf of the corporation in which the director or officer was adjudged liable to the corporation or for a judgment of liability on the basis that a personal benefit was improperly received. A court may order indemnification if it determines that the director or officer is fairly and reasonably entitled to indemnification, even though the director or officer did not meet the prescribed standard of conduct; however, indemnification for an adverse judgment in a suit by us or on our behalf, or for a judgment of liability on the basis that personal benefit was improperly received, is limited to expenses.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers or persons controlling our company pursuant to the foregoing provisions, we have been informed that, in the opinion of the SEC, such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is therefore unenforceable.
In addition, our directors and officers may be entitled to indemnification pursuant to the terms of the partnership agreement of our operating partnership. See “Description of the Partnership Agreement of Plymouth Industrial OP, LP.”
105
EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
This section discusses the material components of the executive compensation program for our executive officers who are named in the “Summary Compensation Table” below. Applicable SEC rules require that a registrant provide information regarding the material components of its executive compensation program with respect to the last completed fiscal year. Set forth below is an overview of the expected initial components of our named executive officer compensation program, including annual cash compensation, equity awards and health and retirement benefits, to be provided following the completion of this offering. Our “named executive officers” during 2016 were:
| • | Jeffrey E. Witherell, Chief Executive Officer; | |
| • | Pendleton P. White, Jr., President and Chief Investment Officer; and | |
| • | Daniel C. Wright, Chief Financial Officer. |
This discussion may contain forward-looking statements that are based on our current plans, considerations, expectations and determinations regarding future compensation programs. We are continuing to assess the identity of our named executive officers and to formulate our compensation philosophy and its appropriate components and levels and, accordingly, actual compensation programs that we adopt following the completion of this offering may differ materially from the currently planned programs summarized in this discussion.
Summary Compensation Table
Below is a Summary Compensation Table setting forth certain compensation that we paid our named executive officers during the year ended December 31, 2016.
| Name and Principal Position | Annual
Salary |
Bonus | Stock
Awards |
All Other Compensation(3) |
Total | |||||||||||||
| Jeffrey E. Witherell— | $ | 300,000 | — | (1)(2) | $ | — | $ | 2,000 | $ | 302,000 | ||||||||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pendleton P. White, Jr.— | $ | 250,000 | — | (1)(2) | $ | — | $ | 21,000 | $ | 271,000 | ||||||||
| President and Chief | ||||||||||||||||||
| Investment Officer | ||||||||||||||||||
| Daniel C. Wright— | $ | 200,000 | — | (1)(2) | $ | — | $ | 19,000 | $ | 219,000 | ||||||||
| Executive Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||
| and Chief Financial Officer | ||||||||||||||||||
_______________________
| (1) | Bonus amounts to be determined by our compensation committee in its sole discretion. |
| (2) | Upon completion of this offering, our compensation committee will establish specific metrics to measure future cash bonus payments. |
| (3) | Represents reimbursement of up to $10,000 annually for reasonable professional expenses and advice from professional advisors and amounts paid by us for healthcare benefits for each officer. |
Base Salaries
Our named executive officers earn annualized base salaries that are commensurate with their positions and are expected to provide a steady source of income sufficient to permit these officers to focus their time and attention on their work duties and responsibilities. The annual base salaries of our named executive officers, which will be effective as of the completion of this offering, are set forth in the Summary Compensation Table above.
Cash Bonuses
Following the completion of this offering, we expect that our named executive officers and certain employees will be eligible to earn annual bonuses based on the attainment of specified performance objectives established by our compensation committee. Eligibility to receive these cash bonuses is expected to incentivize our named executive officers to strive to attain company and/or individual performance goals that further our interests and the interests of our stockholders. The applicable terms and conditions of the cash bonuses will be determined by our compensation committee.
106
Other Elements of Compensation Retirement Plans
The Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, allows eligible employees to defer a portion of their compensation, within prescribed limits, on a pre-tax basis through contributions to a 401(k) plan. We expect to establish a 401(k) retirement savings plan for our employees, including our named executive officers, who satisfy certain eligibility requirements. We expect that our named executive officers will be eligible to participate in the 401(k) plan on the same terms as other full-time employees.
Employee Benefits and Perquisites
We expect that our full-time employees, including our named executive officers, will be eligible to participate in health and welfare benefit plans, which will provide medical, dental, prescription and other health and related benefits. We may also implement additional benefit and other perquisite programs as our compensation committee determines appropriate, though we do not expect any such additional benefits and perquisites to constitute a material component of our named executive officers’ compensation package.
Additional Compensation Components
Following the completion of this offering, as we formulate and implement our compensation program, we may provide different and/or additional compensation components, benefits and/or perquisites to our named executive officers, to ensure that we provide a balanced and comprehensive compensation structure. We believe that it is important to maintain flexibility to adapt our compensation structure at this time to properly attract, motivate and retain the top executive talent for which we compete.
Executive Compensation Arrangements
In April 2017, we entered into new employment agreements with certain executive officers of the company, including Messrs. Witherell, White and Wright. The new employment agreements extend the employment terms of our officers to April 2020, and are otherwise consistent with the employment agreements executed in September 2014. The following is a summary of the material terms of the employment agreements.
Under the employment agreements, Mr. Witherell serves as Chief Executive Officer of our company, Mr. White serves as President and Chief Investment Officer of our company and Mr. Wright serves as Chief Financial Officer of our company. Each will report directly to the board. The initial term of the employment agreements will end on the third anniversary of the date thereof. On that date, and on each subsequent one year anniversary of such date, the term of the employment agreements will automatically be extended for one year, unless earlier terminated. Pursuant to the employment agreements, during the terms of Messrs. Witherell’s and White’s employment, we will nominate each for election as a director.
Under the employment agreements, Messrs. Witherell, White and Wright receive initial annual base salaries in the amounts reflected in the “Summary Compensation Table” above, which are subject to increase at the discretion of our compensation committee. In addition, each of Messrs. Witherell, White and Wright will be eligible to receive an annual discretionary cash performance bonus targeted at 100% of the executive’s then-current annual base salary. The actual amount of any such bonuses will be determined by reference to the attainment of applicable company and/or individual performance objectives, as determined by our compensation committee. In connection with entering into the employment agreements and as described above, Messrs. Witherell, White and Wright will each be granted an award of restricted shares of our common stock. These restricted stock awards will vest in four equal, annual installments on each of the first four anniversaries of the date of the closing of this offering, subject to each executive’s continued service through the applicable vesting date. In addition, beginning in calendar year 2017 and for each calendar year thereafter, Messrs. Witherell, White and Wright will each be eligible to receive an annual equity award, as determined by our compensation committee in its sole discretion. Messrs. Witherell, White and Wright will also be eligible to participate in customary health, welfare and fringe benefit plans, and, subject to certain restrictions, healthcare benefits will be provided to them and their eligible dependents at our sole expense. Each of Messrs. Witherell, White and Wright will accrue four weeks of paid vacation per year.
Pursuant to the terms of the employment agreements, if Mr. Witherell’s, Mr. White’s or Mr. Wright’s employment is terminated by our company without “cause,” by the executive for “good reason” (each as defined in the applicable employment agreement) or because our company elects not to renew the term of the employment agreement then, in addition to any accrued amounts, the executive will be entitled to receive the following:
| • | An amount, payable over a 12-month period, equal to (a) three times with respect to Mr. Witherell and (b) two times with respect to Messrs. White and Wright the sum of (1) the executive’s annual base salary then in effect, (2) the average annual bonus earned by the executive for the two prior fiscal years (substituting target bonus in the average for any fiscal year not yet completed if fewer than two fiscal years have been completed) and (3) the average value of any annual equity awards(s) made to the executive during the prior two fiscal years (excluding the initial grant of restricted stock described above, any award(s) granted pursuant to a multi-year, outperformance or long-term performance program and any other non-recurring awards), or if fewer than two years have elapsed, over such lesser number of years; and |
107
| • | accelerated vesting of all outstanding equity awards held by the executive as of the termination date; and company-paid continuation healthcare coverage for 18 months after the termination date. |
The executive’s right to receive the severance payments and benefits described above is subject to his delivery and non-revocation of an effective general release of claims in favor of our company. The employment agreements also contain customary confidentiality and non-solicitation provisions.
Upon a termination of employment by reason of death or disability, the executive or his estate will be entitled to accelerated vesting of all outstanding equity awards held by the executive as of the termination date, in addition to any accrued amounts. In addition, upon a change in control of our company (as defined in the Plan described below), Messrs. Witherell, White and Wright will be entitled to accelerated vesting of all outstanding equity awards held by such executive as of the date of the change in control. In addition, under the employment agreements, to the extent that any change in control payment or benefit would be subject to an excise tax imposed in connection with Section 4999 of the Code, such payments and/or benefits may be subject to a “best pay cap” reduction to the extent necessary so that the executive receives the greater of the (a) net amount of the change in control payments and benefits reduced such that such payments and benefits will not be subject to the excise tax and (b) net amount of the change in control payments and benefits without such reduction.
Director Compensation
Our board of directors has approved a compensation program for our non-employee directors, which will take effect upon completion of this offering and will consist of annual retainer fees and long-term equity awards. The material terms of the program are described below:
Cash Compensation
Under the program, each non-employee director will be entitled to receive an annual cash retainer of $25,000. In addition, each committee chairperson will receive a $5,000 annual cash retainer and, in the event we have a lead independent director, he or she will receive a $25,000 annual cash retainer. Annual retainers will be paid in cash quarterly in arrears.
Equity Compensation
Under the program, each non-employee director will receive an award of restricted stock in connection with the completion of this offering in a denominated dollar value equal to $75,000. These awards will vest in substantially equal one-third installments on each of the first, second and third anniversaries of the completion of this offering, subject to continued service on our board of directors through the applicable vesting date.
In addition, under the program, each non-employee director who is currently serving on our board of directors following the completion of this offering, and each director who is serving on our board of directors as of the date of each annual meeting of stockholders, will be granted an award of restricted stock in a denominated dollar value equal to $35,000 (or, with respect to awards to initially elected or appointed non-employee directors, a pro-rated value to reflect any partial year service). These awards will vest on the earlier to occur of (a) the date of the annual meeting of stockholders immediately following the grant date and (b) the first anniversary of the grant date, subject in each case to continued service on our board of directors.
2014 Incentive Award Plan
In April 2014, our board of directors adopted, and in June 2014 our stockholders approved, the 2014 Incentive Award Plan, or Plan, under which we may grant cash and equity incentive awards to eligible service providers in order to attract, motivate and retain the talent for which we compete. The material terms of the Plan are summarized below. On May 1, 2017, our board of directors approved an amendment to the Plan solely to reduce the number of shares available for issuance under the Plan from 750,000 to 375,000.
Eligibility and Administration. Our employees, consultants and directors, and employees, consultants and directors of our operating partnership, our services company and our respective subsidiaries will be eligible to receive awards under the Plan. Initially, the Plan will be administered by our board of directors but following our initial public offering the Plan will be administered by our board of directors with respect to awards to non-employee directors and by our compensation committee with respect to other participants, each of which may delegate its duties and responsibilities to committees of our directors and/or officers (referred to collectively as the plan administrator below), subject to certain limitations that may be imposed under Section 162(m) of the Code Section 16 of the Exchange Act, the MGCL and/or stock exchange rules, as applicable. The plan administrator has the authority to make all determinations and interpretations under, prescribe all forms for use with, and adopt rules for the administration of, the Plan, subject to its express terms and conditions. The plan administrator also sets the terms and conditions of all awards under the Plan, including any vesting and vesting acceleration conditions.
108
Limitation on Awards and Shares Available. The aggregate number of shares of our common stock and/or LTIP units of partnership interest in our operating partnership, or LTIP units, that are available for issuance under awards granted pursuant to the Plan is 375,000 shares/LTIP units. Shares and units granted under the Plan may be authorized but unissued shares/LTIP units, or, if authorized by the board of directors, shares purchased in the open market. If an award under the Plan is forfeited, expires or is settled for cash, any shares/LTIP units subject to such award may, to the extent of such forfeiture, expiration or cash settlement, be used again for new grants under the Plan. However, the following shares/LTIP units may not be used again for grant under the Plan: (1) shares/LTIP units tendered or withheld to satisfy grant or exercise price or tax withholding obligations associated with an award; (2) shares subject to a stock appreciation right, or SAR, that are not issued in connection with the stock settlement of the SAR on its exercise; and (3) shares purchased on the open market with the cash proceeds from the exercise of options. The maximum number of shares that may be issued under the Plan upon the exercise of incentive stock options is 375,000.
Awards granted under the Plan upon the assumption of, or in substitution for, awards authorized or outstanding under a qualifying equity plan maintained by an entity with which we enter into a merger or similar corporate transaction will not reduce the shares available for grant under the Plan. After the expiration of a transition period that may apply following the effective date of our initial public offering, the maximum number of shares of our common stock that may be subject to one or more awards granted to any one participant pursuant to the Plan during any calendar year will be 100,000 and the maximum amount that may be paid under a cash award pursuant to the Plan to any one participant during any calendar year period will be $500,000.
Awards. The Plan provides for the grant of stock options, including incentive stock options, or ISOs, and nonqualified stock options, or NSOs, restricted stock, dividend equivalents, stock payments, restricted stock units, or RSUs, performance shares, other incentive awards, LTIP units, SARs, and cash awards. Certain awards under the Plan may constitute or provide for a deferral of compensation, subject to Section 409A of the Code, which may impose additional requirements on the terms and conditions of such awards. All awards under the Plan will be set forth in award agreements, which will detail all terms and conditions of the awards, including any applicable vesting and payment terms and post-termination exercise limitations. Awards other than cash awards and LTIP units generally will be settled in shares of our common stock, but the plan administrator may provide for cash settlement of any award. A brief description of each award type follows.
| • | Stock Options. Stock options provide for the purchase of shares of our common stock in the future at an exercise price set on the grant date. ISOs, by contrast to NSOs, may provide tax deferral beyond exercise and favorable capital gains tax treatment to their holders if certain holding period and other requirements of the Code are satisfied. The exercise price of a stock option may not be less than 100% of the fair market value of the underlying share on the date of grant (or 110% in the case of ISOs granted to certain significant stockholders), except with respect to certain substitute options granted in connection with a corporate transaction. The term of a stock option may not be longer than ten years (or five years in the case of ISOs granted to certain significant stockholders). Vesting conditions determined by the plan administrator may apply to stock options and may include continued service, performance and/or other conditions. | |
| • | SARs. SARs entitle their holder, upon exercise, to receive from us an amount equal to the appreciation of the shares subject to the award between the grant date and the exercise date. The exercise price of a SAR may not be less than 100% of the fair market value of the underlying share on the date of grant (except with respect to certain substitute SARs granted in connection with a corporate transaction) and the term of a SAR may not be longer than ten years. Vesting conditions determined by the plan administrator may apply to SARs and may include continued service, performance and/or other conditions. | |
| • | Restricted Stock, RSUs and Performance Shares. Restricted stock is an award of nontransferable shares of our common stock that remain forfeitable unless and until specified conditions are met, and which may be subject to a purchase price. RSUs are contractual promises to deliver shares of our common stock in the future, which may also remain forfeitable unless and until specified conditions are met. Delivery of the shares underlying RSUs may be deferred under the terms of the award or at the election of the participant, if the plan administrator permits such a deferral. Performance shares are contractual rights to receive a range of shares of our common stock in the future based on the attainment of specified performance goals, in addition to other conditions which may apply to these awards. Conditions applicable to restricted stock, RSUs and performance shares may be based on continuing service, the attainment of performance goals and/or such other conditions as the plan administrator may determine. |
109
| • | Stock Payments, Other Incentive Awards, LTIP Units and Cash Awards. Stock payments are awards of fully vested shares of our common stock that may, but need not, be made in lieu of base salary, bonus, fees or other cash compensation otherwise payable to any individual who is eligible to receive awards. Other incentive awards are awards other than those enumerated in this summary that are denominated in, linked to or derived from shares of our common stock or value metrics related to our shares, and may remain forfeitable unless and until specified conditions are met. LTIP units are awards of units of limited partnership interest in our operating partnership intended to constitute “profits interests” within the meaning of the relevant IRS guidance, which may be convertible into shares of our common stock. Cash awards are cash incentive bonuses subject to performance goals. | |
| • | Dividend Equivalents. Dividend equivalents represent the right to receive the equivalent value of dividends paid on shares of our common stock and may be granted alone or in tandem with awards other than stock options or SARs. Dividend equivalents are credited as of dividend record dates during the period between the date an award is granted and the date such award vests, is exercised, is distributed or expires, as determined by the plan administrator. Dividend equivalents may not be paid on performance awards granted under the Plan unless and until such performance awards have vested. |
Performance Awards. Performance awards include any of the foregoing awards that are granted subject to vesting and/or payment based on the attainment of specified performance goals. The plan administrator will determine whether performance awards are intended to constitute “qualified performance-based compensation,” or QPBC, within the meaning of Section 162(m) of the Code, in which case the applicable performance criteria will be selected from the list below in accordance with the requirements of Section 162(m) of the Code.
Section 162(m) of the Code imposes a $1,000,000 cap on the compensation deduction that a public company may take in respect of compensation paid to its “covered employees” (which should include its chief executive officer and its next three most highly compensated employees other than its chief financial officer), but excludes from the calculation of amounts subject to this limitation any amounts that constitute QPBC. Under current tax law, we do not expect Section 162(m) of the Code to apply to certain awards under the Plan until the earliest to occur of (1) our annual stockholders’ meeting at which members of our board of directors are to be elected that occurs in 2017; (2) a material modification of the Plan; (3) an exhaustion of the share/unit supply under the Plan; or (4) the expiration of the Plan. However, QPBC performance criteria may be used with respect to performance awards that are not intended to constitute QPBC. In addition, our company may issue awards that are not intended to constitute QPBC even if such awards might be non-deductible as a result of Section 162(m) of the Code.
In order to constitute QPBC under Section 162(m) of the Code, in addition to certain other requirements, the relevant amounts must be payable only upon the attainment of pre-established, objective performance goals set by our compensation committee and linked to stockholder-approved performance criteria. For purposes of the Plan, one or more of the following performance criteria will be used in setting performance goals applicable to QPBC, and may be used in setting performance goals applicable to other performance awards: (1) net earnings (either before or after one or more of the following: (a) interest, (b) taxes, (c) depreciation, (d) amortization and (e) non-cash equity-based compensation expense); (2) gross or net sales or revenue; (3) net income (either before or after taxes); (4) adjusted net income; (5) operating earnings or profit; (6) cash flow (including, but not limited to, operating cash flow and free cash flow); (7) return on assets; (8) return on capital; (9) return on stockholders’ equity; (10) total stockholder return; (11) return on sales; (12) gross or net profit or operating margin; (13) costs; (14) funds from operations; (15) expenses; (16) working capital; (17) earnings per share; (18) adjusted earnings per share; (19) price per share of common stock; (20) leasing activity; (21) implementation or completion of critical projects; (22) market share; (23) economic value; (24) debt levels or reduction; (25) sales-related goals; (26) comparisons with other stock market indices; (27) operating efficiency; (28) financing and other capital raising transactions; (29) recruiting and maintaining personnel; (30) year-end cash; (31) acquisition activity; (32) investment sourcing activity; (33) customer service; and (34) marketing initiatives, any of which may be measured either in absolute terms for us or any operating unit of our company or as compared to any incremental increase or decrease or as compared to results of a peer group or to market performance indicators or indices. The Plan also permits the plan administrator to provide for objectively determinable adjustments to the applicable performance criteria in setting performance goals for QPBC awards.
110
Equity Compensation. We expect to make grants of restricted stock pursuant to the Plan, to certain of our employees, including our named executive officers and our non-employee directors, in connection with this offering. We anticipate that the awards granted to our named executive officers in connection with this offering will vest as to 25% of the number of shares subject to the award on each of the first, second, third and fourth anniversaries of the date of grant, based on the executive’s continued service with us through the applicable vesting date. In addition, the restricted stock awards granted to Messrs. Witherell, White and Wright in connection with this offering will be subject to accelerated vesting provisions set forth in the executive’s employment agreement, as described in further detail below under “Executive Compensation Arrangements.” Each restricted stock award granted in connection with this offering is expected to be denominated as a specified dollar value, and the actual number of shares issued will be calculated at or prior to grant by dividing the total denominated dollar value of the award by $19.00. We expect that the aggregate denominated dollar value of all restricted stock awards granted to non-employee directors and executive officers in connection with this offering will be $2,500,000, including the following grants to our named executive officers:
| Named Executive Officer | Approximate Restricted Stock Denominated Grant Value | |||
| Jeffrey E. Witherell | $ | 950,000 | ||
| Pendleton P. White, Jr. | $ | 750,000 | ||
| Daniel C. Wright | $ | 500,000 | ||
Certain Transactions. The plan administrator has broad discretion to take action under the Plan, as well as make adjustments to the terms and conditions of existing and future awards, to prevent the dilution or enlargement of intended benefits and facilitate necessary or desirable changes in the event of certain transactions and events affecting our common stock and/or LTIP units, such as stock dividends, stock splits, mergers, acquisitions, consolidations and other corporate transactions. In addition, in the event of certain non-reciprocal transactions with our stockholders known as “equity restructurings,” our board of directors will make equitable adjustments to the Plan and outstanding awards. In the event of a change in control of our company (as defined in the Plan), to the extent that the surviving entity declines to continue, convert, assume or replace outstanding awards, then all such awards will become fully vested and exercisable in connection with the transaction. Upon or in anticipation of a change of control, the plan administrator may cause any outstanding awards to terminate at a specified time in the future and give the participant the right to exercise such awards during a period of time determined by the plan administrator in its sole discretion. Individual award agreements may provide for additional accelerated vesting and payment provisions.
Foreign Participants, Claw-Back Provisions, Transferability, and Participant Payments. The plan administrator may modify award terms, establish subplans and/or adjust other terms and conditions of awards, subject to the share/unit limits described above, in order to facilitate grants of awards subject to the laws and/or stock exchange rules of countries outside of the United States. All awards will be subject to the provisions of any claw-back policy implemented by our company to the extent set forth in such claw-back policy and/or in the applicable award agreement. With limited exceptions for estate planning, domestic relations orders, certain beneficiary designations and the laws of descent and distribution, awards under the Plan are generally non-transferable prior to vesting, and are exercisable only by the participant. With regard to tax withholding, exercise price and purchase price obligations arising in connection with awards under the Plan, the plan administrator may, in its discretion, accept cash or check, shares of our common stock that meet specified conditions, a “market sell order” or such other consideration as it deems suitable.
Plan Amendment and Termination. Our board of directors may amend or terminate the Plan at any time; however, except in connection with certain changes in our capital structure, stockholder approval will be required for any amendment that increases the number of shares/units available under the Plan, “reprices” any stock option or SAR, or cancels any stock option or SAR in exchange for cash or another award when the option or SAR price per share exceeds the fair market value of the underlying shares. After the tenth anniversary of the date on which we adopt the Plan, no automatic annual increases to the Plan’s share limit will occur and no incentive stock options may be granted; however, the Plan does not have a specified expiration and will otherwise continue in effect until terminated by our company.
Additional REIT Restrictions. The Plan provides that no participant will be granted, become vested in the right to receive or acquire or be permitted to acquire, or will have any right to acquire, shares under an award if such acquisition would be prohibited by the restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock contained in our charter or would impair our status as a REIT.
111
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS
Employment Agreements
We have entered into employment agreements with our executive officers, which provide for salary, bonus and other benefits, including severance upon a termination of employment under certain circumstances. The material terms of the agreements are described under “Executive Compensation—Executive Compensation Arrangements.”
2014 Incentive Award Plan
In anticipation of this offering, we adopted the Plan for our directors, officers, employees and consultants. An aggregate of 375,000 shares of our common stock and LTIP units will be available for issuance under awards granted pursuant to the Plan. We expect that the aggregated denominated dollar value of all restricted stock awards granted under the Plan to executive officers and non-employee directors in connection with this offering will be $2,500,000. See “Executive Compensation.”
Indemnification of Officers and Directors
Effective upon completion of this offering, our charter and bylaws will provide for certain indemnification rights for our directors and officers and we will enter into an indemnification agreement with each of our executive officers and directors, providing for procedures for indemnification and advancements by us of certain expenses and costs relating to claims, suits or proceedings arising from their service to us or, at our request, service to other entities, as officers, directors, partners, trustees, managers or members to the maximum extent permitted by Maryland law. See “Management—Limitation of Liability and Indemnification.”
Review and Approval of Future Transactions with Related Persons
Upon completion of this offering, we will adopt a written policy for the review and approval of related person transactions requiring disclosure under Rule 404(a) of Regulation S-K. We expect this policy to provide that the nominating and corporate governance committee will be responsible for reviewing and approving or disapproving all interested transactions, meaning any transaction, arrangement or relationship in which (a) the amount involved may be expected to exceed $120,000 in any fiscal year, (b) our company will be a participant, and (c) a related person has a direct or indirect material interest. A related person will be defined as an executive officer, director or nominee for election as director, or a greater than 5% beneficial owner of our common stock, or an immediate family member of the foregoing. The policy may deem certain interested transactions to be preapproved.
Relationship with Torchlight
Upon completion of this offering, DOF IV Plymouth PM, LLC, an entity managed by Torchlight Investors, LLC, will become a related person by virtue of its beneficial ownership of greater than 5% of our outstanding common stock. See “Structure of Our Company—Torchlight Transactions” and “Principal Stockholders”.
112
STRUCTURE OF OUR COMPANY
Our Structure
Our Company
We were formed as a Maryland corporation in March 2011 and previously conducted business as Plymouth Opportunity REIT, Inc. We conduct our business through an UPREIT structure in which our properties are owned by our operating partnership directly or through subsidiaries, as described below under “—Our Operating Partnership.” We are the sole general partner of our operating partnership and, upon completion of this offering, we will own 100% of the units of limited partnership interest, or OP units, in our operating partnership. Our board of directors oversees our business and affairs.
Prior to May 2014, we were externally managed by Plymouth Real Estate Investors, Inc., or the advisor, an affiliate of our company, pursuant to the terms of an advisory agreement. The advisory agreement was terminated in May 2014 with no consideration being paid to the advisor as a result of such termination.
Our Operating Partnership
Substantially all of our assets are held by, and our operations are conducted through, our operating partnership. We will contribute the net proceeds from this offering to our operating partnership in exchange for OP units therein. Our interest in our operating partnership will generally entitle us to share in cash distributions from, and in the profits and losses of, our operating partnership in proportion to our percentage ownership. As the sole general partner of our operating partnership, we will generally have the exclusive power under the partnership agreement to manage and conduct its business and affairs, subject to certain limited approval and voting rights of the limited partners, which are described more fully below in “Description of the Partnership Agreement of Plymouth Industrial OP, LP.”
Torchlight Transactions
Redemption of Preferred Interests in Joint Venture
We and Torchlight are party to a joint venture agreement with respect to Plymouth Industrial 20, dated as of October 17, 2016. Each of the properties in the Company Portfolio is owned by Plymouth Industrial 20, in which we currently own a 0.5% interest and Torchlight owns a 99.5% interest, or the Preferred Interests. We have the right to redeem the Preferred Interests on or before June 16, 2017, for $25.0 million, which will be paid by a combination of $20.0 million in cash with proceeds from this offering and 263,158 shares of the common stock to be issued in a private placement concurrently with the closing of this offering. See “Use of Proceeds.” The 263,158 shares issued in connection with the redemption will not be immediately freely tradeable and may only be sold pursuant to Rule 144 under the Securities Act or another exemption from registration. These shares will be registered for resale following the first anniversary of the closing of this offering. The shares issuable upon exercise of the warrants will be registered for resale following the first anniversary of the closing of this offering. See “Shares Eligible for Future Sale.”
Termination of Participation Right
As partial consideration for making the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan, Plymouth Industrial 20, the borrower under the Torchlight Mezzanine Loan, granted Torchlight, in its capacity as lender, a profit participation in the form of the right to receive 25% of net income and capital proceeds generated by the Company Portfolio following debt service payments and associated costs, or the TL Participation. Pursuant to the Letter Agreement between Torchlight and us, dated as of March 3, 2017, or the Letter Agreement, we have the right to terminate the TL Participation in consideration for the private issuance of warrants to Torchlight to acquire 250,000 shares of our common stock, which we expect to issue concurrently with the closing of this offering. The warrants will have an exercise price of $23.00 per share and will be exercisable for a five year period commencing upon the completion of this offering. See “Description of Capital Stock—Warrants.” The warrants will not be freely tradeable and may only be sold pursuant to Rule 144 or another exemption from registration. See “Shares Eligible for Future Sale.”
113
Consequences of this Offering and the Torchlight Transactions
The completion of this offering, and the application of the net proceeds thereof in accordance with the description under “Use of Proceeds,” will have the following consequences:
| • | Through our interest in our operating partnership and its wholly owned subsidiaries, we will indirectly own a 100% fee simple interest in the 20 industrial buildings in the Company Portfolio. | |
| • | Purchasers of shares of our common stock in this offering will own 80.0% of our outstanding common stock or 82.1% of our outstanding common stock if the underwriters’ over-allotment option is exercised in full. | |
| • | We will be the sole general partner of our operating partnership and own a 0.1% general partner interest and a 99.9% limited partner interest in our operating partnership. | |
| • | We expect to have total consolidated indebtedness of approximately $150 million. | |
| • | The Torchlight Entities will own 7.3% of our outstanding common stock or 6.5% of our outstanding common stock if the underwriters’ overallotment option is exercised in full. |
Corporate Structure
The chart below reflects our organizational structure immediately following completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions.

________________
| (1) | Reflects (a) an aggregate of 115,790 restricted shares of common stock to be granted to our executive officers and (b) an aggregate of 15,789 restricted shares of common stock to be granted to our independent directors, in each case, concurrently with the completion of this offering. | |
| (2) | Reflects an aggregate of 263,158 shares of our common stock to be issued to DOF IV Plymouth PM, LLC in the Torchlight Transactions, and excludes warrants exercisable for 250,000 shares of common stock to be issued to DOF IV REIT Holdings, LLC in the Torchlight Transactions. |
114
POLICIES WITH RESPECT TO CERTAIN ACTIVITIES
The following is a discussion of our investment policies and our policies with respect to certain other activities, including financing matters and conflicts of interest. These policies may be amended or revised from time to time at the discretion of our board of directors, without a vote of our stockholders. Any change to any of these policies by our board of directors, however, would be made only after a thorough review and analysis of that change, in light of then-existing business and other circumstances, and then only if, in the exercise of its business judgment, our board of directors believes that it is advisable to do so in our and our stockholders’ best interests. We cannot assure you that our investment objectives will be attained.
Investments in Real Estate or Interests in Real Estate
We intend to conduct substantially all of our investment activities through our operating partnership and its subsidiaries. Our goal is to generate attractive risk-adjusted returns for our stockholders by acquiring Class B distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties, primarily located in secondary markets and select primary markets across the Eastern half of the U.S. and Texas.
We do not have a specific policy to acquire assets primarily for capital gain or primarily for income. From time to time, we may make investments that support our objectives but do not provide current cash flow. We believe that investments that do not generate current cash flow may be, in certain instances, consistent with our objective to achieve sustainable long-term growth in earnings and FFO.
There are no limitations on the amount or percentage of our total assets that may be invested in any one property. Additionally, no limits have been set on the concentration of investments in any one location or facility type.
Additional criteria with respect to our properties are described in “Business.”
Investments in Mortgages, Structured Financings and Other Lending Policies
While the Company Portfolio consists of, and our business objectives emphasize, equity investments in real estate, we may, at the discretion of our board of directors, invest in mortgages and other types of real estate interests consistent with our qualifications as a REIT. We do not currently invest, or intend to invest, in mortgages or deeds of trust, but may acquire such interests as a strategy for acquiring ownership of a property or the economic equivalent thereof and/or invest in participating or convertible mortgages if we conclude that we may benefit from the gross revenues or any appreciation in value of the property. These mortgages may or may not be guaranteed or insured as to principal or interest by any government agency or otherwise. Investments in real estate mortgages run the risk that one or more borrowers may default under the mortgages and that the collateral securing those mortgages may not be sufficient to enable us to recoup our full investment.
Investments in Securities of or Interests in Persons Primarily Engaged in Real Estate Activities and Other Issuers
Generally speaking, we do not expect to engage in any significant investment activities with other entities, although we may consider joint venture investments with other investors. We may also invest in the securities of other issuers in connection with acquisitions of indirect interests in properties (normally general or limited partnership interests in special purpose partnerships owning properties). We may in the future acquire some, all or substantially all of the securities or assets of other REITs or similar entities where that investment would be consistent with our investment policies and the REIT qualification requirements. There are no limitations on the amount or percentage of our total assets that may be invested in any one issuer, other than those imposed by the gross income and asset tests that we must satisfy to qualify as a REIT. However, we do not anticipate investing in other issuers of securities for the purpose of exercising control or acquiring any investments primarily for sale in the ordinary course of business or holding any investments with a view to making short-term profits from their sale. In any event, we do not intend that our investments in securities will require us to register as an “investment company” under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, or the 1940 Act, and we intend to divest securities before any registration would be required.
We do not intend to engage in trading, underwriting, agency distribution or sales of securities of other issuers.
Disposition Policy
We may from time to time dispose of certain properties, based upon management’s periodic review of the Company Portfolio, if our board of directors determines that such action would be in our best interests. The tax consequences to our directors and executive officers who hold units resulting from a proposed disposition of a property may influence their decision as to the desirability of such proposed disposition. See “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Organizational Structure—Conflicts of interest may exist or could arise in the future between the interests of our stockholders and the interests of holders of OP units, which may impede business decisions that could benefit our stockholders.”
115
Financing and Leverage Policies
We anticipate using a number of different sources to finance our acquisitions and operations, including cash flows from operations, asset sales, seller financing, issuance of debt securities, private financings (such as additional bank credit facilities, which may or may not be secured by our assets), property-level mortgage debt, common or preferred equity issuances or any combination of these sources, to the extent available to us, or other sources that may become available from time to time. Any debt that we incur may be recourse or non-recourse and may be secured or unsecured. We also may take advantage of joint venture or other partnering opportunities as such opportunities arise in order to acquire properties that would otherwise be unavailable to us. We may use the proceeds of our borrowings to acquire assets, to refinance existing debt or for general corporate purposes.
Although we are not required to maintain any particular leverage ratio, we intend, when appropriate, to employ prudent amounts of leverage, which we define as a debt-to-EBITDA multiple of less than 7.0, and to use debt as a means of providing additional funds for the acquisition of assets, to refinance existing debt or for general corporate purpose. We expect to use leverage conservatively, assessing the appropriateness of new equity or debt capital based on market conditions, including prudent assumptions regarding future cash flow, the creditworthiness of tenants and future rental rates. Our charter and bylaws do not limit the amount of debt that we may incur. Our board of directors has not adopted a policy limiting the total amount of debt that we may incur.
Our board of directors will consider a number of factors in evaluating the amount of debt that we may incur. If we adopt a debt policy, our board of directors may from time to time modify such policy in light of then-current economic conditions, relative costs of debt and equity capital, market values of our properties, general conditions in the market for debt and equity securities, fluctuations in the market price of our common stock, growth and acquisition opportunities and other factors. Our decision to use leverage in the future to finance our assets will be at our discretion and will not be subject to the approval of our stockholders, and we are not restricted by our governing documents or otherwise in the amount of leverage that we may use.
Lending Policies
We may consider offering purchase money financing in connection with the sale of properties where the provision of that financing will increase the value to be received by us for the property sold. We also may make loans to joint ventures in which we participate. However, we do not intend to engage in significant lending activities. Any loan we make will be consistent with maintaining our status as a REIT.
Equity Capital Policies
To the extent that our board of directors determines to obtain additional capital, we may issue debt or equity securities, including additional units or senior securities of our operating partnership, retain earnings (subject to provisions in the Code requiring distributions of income to maintain REIT qualification) or pursue a combination of these methods. As long as our operating partnership is in existence, we will generally contribute the proceeds of all equity capital raised by us to our operating partnership in exchange for partnership interests in our operating partnership, which will dilute the ownership interests of the limited partners in our operating partnership.
Existing stockholders will have no preemptive rights to common or preferred stock or units issued in any securities offering by us, and any such offering might cause a dilution of a stockholder’s investment in us. Although we have no current plans to do so, we may in the future issue shares of common stock or cause our operating partnership to issue OP units in connection with acquisitions of property.
We may, under certain circumstances, purchase shares of our common stock or other securities in the open market or in private transactions with our stockholders, provided that those purchases are approved by our board of directors. Our board of directors has no present intention of causing us to repurchase any shares of our common stock or other securities, and any such action would only be taken in conformity with applicable federal and state laws and the applicable requirements for qualification as a REIT.
116
Conflict of Interest Policy
Overview. Conflicts of interest could arise in the future as a result of the relationships between us and our affiliates, on the one hand, and our operating partnership or any partner thereof, on the other. Our directors and officers have duties to our company under applicable Maryland law in connection with their management of our company. At the same time, we, as the general partner of our operating partnership, have fiduciary duties and obligations to our operating partnership and its other partners under Delaware law and the partnership agreement in connection with the management of our operating partnership. Our fiduciary duties and obligations, as the general partner of our operating partnership, may come into conflict with the duties of our directors and officers to our company.
Under Delaware law, a general partner of a Delaware limited partnership has fiduciary duties of loyalty and care to the partnership and its partners and must discharge its duties and exercise its rights as general partner under the partnership agreement or Delaware law consistently with the obligation of good faith and fair dealing. The duty of loyalty requires a general partner of a Delaware limited partnership to account to the partnership and hold as trustee for any property, profit, or benefit derived by the general partner in the conduct of the partnership business or derived from a use by the general partner of partnership property, including the appropriation of a partnership opportunity, to refrain from dealing with the partnership in the conduct of the partnership’s business as or on behalf of a party having an interest adverse to the partnership and to refrain from competing with the partnership in the conduct of the partnership business, although the partnership agreement may identify specific types or categories of activities that do not violate the duty of loyalty. The partnership agreement provides that, in the event of a conflict between the interests of our operating partnership or any partner, on the one hand, and the separate interests of our company or our stockholders, on the other hand, we, in our capacity as the general partner of our operating partnership, may give priority to the separate interests of our company or our stockholders (including with respect to tax consequences to limited partners, assignees or our stockholders), and, in the event of such a conflict, any action or failure to act on our part or on the part of our directors that gives priority to the separate interests of our company or our stockholders that does not result in a violation of the contract rights of the limited partners of our operating partnership under its partnership agreement does not violate the duty of loyalty or any other duty that we, in our capacity as the general partner of our operating partnership, owe to our operating partnership and its partners, or violate the obligation of good faith and fair dealing. We, in our capacity as the general partner of our operating partnership, may, but are not obligated to, take into account the tax consequences to any partner of our operating partnership of any action we take or fail to take, and any such action or failure to act that does not take into account any such tax consequences that does not violate the contract rights of the limited partners of our operating partnership under the partnership agreement does not violate the duty of loyalty or any other duty that we, in our capacity as the general partner of our operating partnership, owe to our operating partnership or its partners, or violate the obligation of good faith and fair dealing. Further, any action that we undertake or fail to take in the good faith belief that the action or inaction is necessary or advisable to protect our ability to continue to qualify as a REIT, for us to otherwise satisfy the requirements for qualifying as a REIT under the Code, for us to avoid incurring income taxes under the Code or for any of our affiliates to continue to qualify as a “qualified REIT subsidiary” under the Code or a “taxable REIT subsidiary” under the Code does not violate the duty of loyalty or any other duty or obligation, fiduciary or otherwise, that we, in our capacity as the general partner of our operating partnership, owe to our operating partnership or any other partner. The duty of care requires a general partner to refrain from engaging in grossly negligent or reckless conduct, intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law, and this duty may not be unreasonably reduced by the partnership agreement.
The partnership agreement provides that we will not be liable to our operating partnership or any partner for any action or omission taken in our capacity as general partner for the debts or liabilities of our operating partnership or for the obligations of the operating partnership under the partnership agreement, except for liability for our fraud, willful misconduct or gross negligence, pursuant to any express indemnity we may give to our operating partnership. The partnership agreement also provides that any obligation or liability in our capacity as the general partner of our operating partnership that may arise at any time under the partnership agreement or any other instrument, transaction or undertaking contemplated by the partnership agreement will be satisfied, if at all, out of our assets or the assets of our operating partnership only, and no obligation or liability of the general partner will be personally binding upon any of our directors, stockholders, officers, employees or agents, regardless of whether such obligation or liability is in the nature of contract, tort or otherwise, and none of our directors or officers will be directly liable or accountable in damages or otherwise to the partnership, any partner or any assignee of a partner for losses sustained, liabilities incurred or benefits not derived as a result of errors in judgment or mistakes of fact or law or any act or omission or by reason of their service as such. Our operating partnership must indemnify us, our directors and officers, officers of our operating partnership and any other person designated by us against any and all losses, claims, damages, liabilities (whether joint or several), expenses (including, without limitation, attorneys’ fees and other legal fees and expenses), judgments, fines, settlements and other amounts arising from any and all claims, demands, actions, suits or proceedings, whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative, that relate to the operations of our operating partnership, unless (1) an act or omission of the person was material to the matter giving rise to the action and either was committed in bad faith or was the result of active and deliberate dishonesty, (2) for any transaction for which such person actually received an improper personal benefit in violation or breach of any provision of the partnership agreement or (3) in the case of a criminal proceeding, the person had reasonable cause to believe the act or omission was unlawful.
117
Our operating partnership must also pay or reimburse the reasonable expenses of any such person in advance of a final disposition of the proceeding upon its receipt of a written affirmation of the person’s good faith belief that the standard of conduct necessary for indemnification has been met and a written undertaking to repay any amounts paid or advanced if it is ultimately determined that the person did not meet the standard of conduct for indemnification. Our operating partnership is not required to indemnify or advance funds to any person with respect to any action initiated by the person seeking indemnification without our approval (except for any proceeding brought to enforce such person’s right to indemnification under the partnership agreement) or if the person is found to be liable to our operating partnership on any portion of any claim in the action.
Policies Applicable to All Directors and Officers. Our charter and bylaws do not restrict any of our directors, officers, stockholders or affiliates from having a pecuniary interest in an investment or transaction that we have an interest in or from conducting, for their own account, business activities of the type we conduct. We intend, however, to adopt policies that are designed to eliminate or minimize potential conflicts of interest, including a policy for the review, approval or ratification of any related party transactions. This policy will provide that the audit committee of our board of directors will review the relevant facts and circumstances of each related party transaction, including if the transaction is on terms comparable to those that could be obtained in arm’s length dealings with an unrelated third party before approving such transaction. Our code of business conduct and ethics provides that all of our directors, officers and employees are prohibited from taking for themselves opportunities that are discovered through the use of corporate property, information or position without our consent. See “Management—Code of Business Conduct and Ethics.” However, we cannot assure you that these policies or provisions of law will always be successful in eliminating the influence of such conflicts, and if they are not successful, decisions could be made that might fail to reflect fully the interests of all stockholders.
Interested Director and Officer Transactions
Pursuant to the MGCL, a contract or other transaction between us and a director or between us and any other corporation or other entity in which any of our directors is a director or has a material financial interest is not void or voidable solely on the grounds of such common directorship or interest, the presence of such director at the meeting at which the contract or transaction is authorized, approved or ratified or the counting of the director’s vote in favor thereof, provided that:
| • | the fact of the common directorship or interest is disclosed or known to our board of directors or a committee of our board, and our board or such committee authorizes, approves or ratifies the contract or transaction by the affirmative vote of a majority of disinterested directors, even if the disinterested directors constitute less than a quorum; | |
| • | the fact of the common directorship or interest is disclosed or known to our stockholders entitled to vote thereon, and the transaction or contract is authorized, approved or ratified by a majority of the votes cast by the stockholders entitled to vote other than the votes of shares owned of record or beneficially by the interested director or corporation, firm or other entity; or | |
| • | the transaction or contract is fair and reasonable to us at the time it is authorized, ratified or approved. |
Furthermore, under Delaware law (where our operating partnership is formed), we, as general partner, have a fiduciary duty of loyalty to our operating partnership and its partners and, consequently, such transactions also are subject to the duties that we, as general partner, owe to our operating partnership and its limited partners (as such duties have been modified by the partnership agreement).
We will also adopt a policy that requires that all contracts and transactions between us, our operating partnership or any of our subsidiaries, on the one hand, and any of our directors or executive officers or any entity in which such director or executive officer is a director or has a material financial interest, on the other hand, must be approved by the affirmative vote of a majority of our disinterested directors even if less than a quorum. Where appropriate, in the judgment of the disinterested directors, our board of directors may obtain a fairness opinion or engage independent counsel to represent the interests of non-affiliated security holders, although our board of directors will have no obligation to do so.
118
Policies With Respect To Other Activities
We will have authority to offer common stock, preferred stock or options to purchase stock in exchange for property and to repurchase or otherwise acquire our common stock or other securities in the open market or otherwise, and we may engage in such activities in the future. As described in “Description of the Partnership Agreement of Plymouth Industrial OP, LP,” we expect, but are not obligated, to issue common stock to holders of OP units upon exercise of their redemption rights. Our board of directors has the authority, without further stockholder approval, to amend our charter to increase or decrease the number of authorized shares of common stock or preferred stock and to authorize us to issue additional shares of common stock or preferred stock, in one or more series, including senior securities, in any manner, and on the terms and for the consideration, it deems appropriate. See “Description of Stock.” We have not engaged in trading, underwriting or agency distribution or sale of securities of other issuers other than our operating partnership and do not intend to do so. At all times, we intend to make investments in such a manner as to maintain our qualification as a REIT, unless because of circumstances or changes in the Code, or the Treasury regulations, our board of directors determines that it is no longer in our best interest to maintain our qualification as a REIT. In addition, we intend to make investments in such a way that we will not be treated as an investment company under the 1940 Act.
Reporting Policies
Generally speaking, we intend to make available to our stockholders audited annual financial statements and annual reports. Following completion of this offering, we will be subject to the information reporting requirements of the Exchange Act. Pursuant to these requirements, we will file periodic reports, proxy statements and other information, including audited financial statements, with the SEC.
119
PRINCIPAL STOCKHOLDERS
The following table sets forth certain information, upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, regarding the ownership of shares of our common stock by:
| • | each of the persons who will be a director upon completion of this offering; | |
| • | each of our executive officers; | |
| • | each person who will be the beneficial owner of more than 5% of our outstanding common stock; and | |
| • | all directors and executive officers as a group. |
In accordance with SEC rules, each listed person’s beneficial ownership includes:
| • | all shares the person actually owns beneficially or of record; | |
| • | all shares over which the person has or shares voting or dispositive control (such as in the capacity as a general partner of an investment fund); and | |
| • | all shares the person has the right to acquire within 60 days (such as restricted shares of common stock that are currently vested or which are scheduled to vest within 60 days). |
Unless otherwise indicated, all shares are owned directly, and the indicated person has sole voting and investment power. Except as indicated in the footnotes to the table below, the business address of the stockholders listed below is the address of our principal executive office, 260 Franklin Street, 6th floor, Boston, Massachusetts 02110.
| Number
of Shares Beneficially Owned(1) | Percent of All Shares | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | Pre-Offering | Post-Offering | Pre-Offering(2) | Post-Offering(3) | |||||||||||||
| Jeffrey E. Witherell | 14,269 | (4) | 64,269 | * | 1.8% | ||||||||||||
| Pendleton P. White, Jr. | 14,186 | (5) | 53,660 | * | 1.5% | ||||||||||||
| Daniel C. Wright | — | 26,316 | — | * | |||||||||||||
| Martin Barber | — | 3,948 | — | * | |||||||||||||
| Philip S. Cottone | 2,987 | 6,934 | * | * | |||||||||||||
| Richard J. DeAgazio | 3,184 | 7,131 | * | * | |||||||||||||
| David G. Gaw | 3,585 | 7,532 | * | * | |||||||||||||
| Total Held by Executive Officers and Directors as a Group | 32,040 | 169,790 | 9.7% | 4.7% | |||||||||||||
| Torchlight Entities (6) | — | 513,158 | (7) | — | 13.2% | (8) | |||||||||||
_______________________
* Less than 1.0%.
| (1) | As used herein, “beneficially owned” means the power to vote or direct the voting of shares and/or the power to dispose or direct the disposition of shares. |
| (2) | Percentage ownership calculations are based on 331,965 shares of our common stock outstanding prior to the completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions. |
| (3) | Unless otherwise noted, percentage ownership calculations are based on 3,626,702 shares of our common stock outstanding upon completion of this offering, the issuance of 131,579 shares of common stock to our executive officers and independent directors upon the closing of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions. |
| (4) | Includes 14,135 shares of common stock owned by Plymouth Group Real Estate of which Mr. Witherell may be deemed to be the beneficial owner. |
| (5) | Includes 14,135 shares of common stock owned by Plymouth Group Real Estate of which Mr. White may be deemed to be the beneficial owner. |
| (6) | Torchlight Investors, LLC has the sole voting and dispositive power with respect to the shares owned by the Torchlight Entities. The address of the principal business office of Torchlight Investors is 475 5th Avenue, 12th Floor, New York, NY 10017. The following individuals, as members of the Management Committee of Torchlight Investors, have shared voting and investment power over the common stock directly owned by various entities affiliated with Torchlight Investors: Samuel Chang, Daniel Heflin, Gianluca Montalti, Steven Schwartz, Marc Young. Messrs. Chang, Heflin, Montalti, Schwartz and Young disclaim beneficial ownership of the shares of common stock and the warrants held by the Torchlight Entities. |
| (7) | Includes 263,158 shares of common stock to be issued to DOF IV Plymouth, LLC, an entity managed by Torchlight Investors, LLC, and 250,000 shares of common stock issuable to DOF IV REIT Holdings, LLC, an entity managed by Torchlight Investors, LLC, upon the exercise of the warrants to be issued in connection with the Torchlight Transactions. |
| (8) | Percentage ownership calculation is based on 3,876,702 shares of our common stock outstanding upon completion of this offering, the issuance of 131,579 shares of common stock to our executive officers and independent directors upon the closing of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions and the issuance of 250,000 shares of our common stock upon the full exercise of the warrants to be issued in connection with the Torchlight Transactions. |
120
DESCRIPTION OF CAPITAL STOCK
The following summary of the material terms of our shares of capital stock does not purport to be complete and is subject to and qualified in its entirety by reference to the MGCL, and to our charter and bylaws, copies of which are filed as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is part. See “Where You Can Find More Information.”
General
Our charter provides that we may issue up to 900,000,000 shares of common stock, $0.01 par value per share, or our common stock, and up to 100,000,000 shares of preferred stock, $0.01 par value per share, or our preferred stock. Our charter authorizes our board of directors, with the approval of a majority of the entire board of directors and without any action by our common stockholders, to amend our charter to increase or decrease the aggregate number of authorized shares of stock or the number of authorized shares of any class or series of our stock. Upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, 3,626,702 shares of our common stock will be issued and outstanding, and no shares of our preferred stock will be issued and outstanding.
Under Maryland law, stockholders generally are not personally liable for our debts or obligations solely as a result of their status as stockholders.
Common Stock
All of the shares of our common stock offered in this offering will be duly authorized, validly issued, fully paid and nonassessable. Subject to the preferential rights of any other class or series of our stock and to the provisions of our charter regarding the restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock, holders of shares of our common stock are entitled to receive dividends and other distributions on such shares if, as and when authorized by our board of directors out of assets legally available therefor and declared by us and to share ratably in the assets of our company legally available for distribution to our stockholders in the event of our liquidation, dissolution or winding up after payment or establishment of reserves for all known debts and liabilities of our company.
Subject to the provisions of our charter regarding the restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock and except as may otherwise be specified in the terms of any class or series of our common stock, each outstanding share of our common stock entitles the holder to one vote on all matters submitted to a vote of stockholders, including the election of directors, and, except as provided with respect to any other class or series of stock, the holders of shares of our common stock will possess the exclusive voting power. There is no cumulative voting in the election of our directors. Directors are elected by a plurality of all of the votes cast in the election of directors.
Holders of shares of our common stock have no preference, conversion, exchange, sinking fund or redemption rights and have no preemptive rights to subscribe for any securities of our company. Our charter provides that our common stockholders generally have no appraisal rights unless our board of directors determines prospectively that appraisal rights will apply to one or more transactions in which holders of our common stock would otherwise be entitled to exercise appraisal rights. Subject to the provisions of our charter regarding the restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock, holders of our common stock will have equal dividend, liquidation and other rights.
Under the MGCL, a Maryland corporation generally cannot dissolve, amend its charter, merge, consolidate, sell all or substantially all of its assets or engage in a statutory share exchange unless declared advisable by its board of directors and approved by the affirmative vote of stockholders entitled to cast at least two-thirds of all of the votes entitled to be cast on the matter unless a lesser percentage (but not less than a majority of all of the votes entitled to be cast on the matter) is set forth in the corporation’s charter. Our charter provides for approval of any of these matters by the affirmative vote of stockholders entitled to cast a majority of the votes entitled to be cast on such matters, except that the affirmative vote of stockholders entitled to cast at least two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast generally in the election of directors is required to remove a director (and such removal must be for cause) and the affirmative vote of stockholders entitled to cast at least two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast on such matter is required to amend the provisions of our charter relating to the removal of directors, relating to the restrictions on the transfer and ownership of shares or the vote required to amend such provisions. Maryland law also permits a Maryland corporation to transfer all or substantially all of its assets without the approval of the stockholders of the corporation to an entity if all of the equity interests of the entity are owned, directly or indirectly, by the corporation. Because our operating assets may be held by our operating partnership or its subsidiaries, these subsidiaries may be able to merge or transfer all or substantially all of their assets without the approval of our stockholders.
Our charter authorizes our board of directors to reclassify any unissued shares of our common stock into other classes or series of stock, to establish the designation and number of shares of each class or series and to set, subject to the provisions of our charter relating to the restrictions on ownership and transfer of our capital stock, the preferences, conversion and other rights, voting powers, restrictions, limitations as to dividends and other distributions, qualifications and terms and conditions of redemption of each such class or series.
121
Warrants
As consideration for the termination of the TL Participation (see "Structure of Our Company-Torchlight Transactions-Termination of Participation Right"), we will be privately issuing warrants to Torchlight to acquire 250,000 shares of our common stock. The warrants will be issued concurrently with the closing of this offering. Each warrant will initially represent the right to purchase one share of our common stock. The number of shares deliverable upon the exercise of the warrants is subject to adjustment and certain anti-dilution protection as provided in the warrant agreement. The initial exercise price applicable to each warrant is $23.00 per share of common stock for which the warrant may be exercised. All or any portion of the warrants may be exercised in whole or in part at any time and from time to time on or before 5:00 p.m. New York City time on the date that is five years following the completion of this offering. At the election of the holder, the exercise price may be paid by the withholding by us of a number of shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of the warrants equal to the value of the aggregate exercise price of the warrants so exercised, determined by reference to the market price of our common stock on the trading day on which the warrants are exercised. Any value of the warrants so exercised in excess of the number of shares withheld by us will be paid to the holder of the exercised warrants in shares of our common stock valued by reference to the same market price. We will at all times reserve the aggregate number of shares of our common stock for which the warrants may be exercised. The warrant holders will have no rights or privileges of holders of our common stock, including any voting rights and rights to dividend payments, until (and then only to the extent) the warrants have been exercised. Issuance of any shares of common stock deliverable upon the exercise of the warrants will be made without charge to the warrant holder for any issue or transfer tax or other incidental expenses in respect of the issuance of those shares. The holders of the common stock deliverable upon the exercise of the warrants will be entitled to certain customary registration rights.
Preferred Stock
Our charter authorizes our board of directors to classify any unissued shares of our preferred stock and to reclassify any previously classified but unissued shares into one or more classes or series of stock. Prior to issuance of shares of each new class or series, our board of directors is required by the MGCL and our charter to set, subject to the provisions of our charter regarding the restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock, the preferences, conversion and other rights, voting powers, restrictions, limitations as to dividends and other distributions, qualifications and terms and conditions of redemption of each such class or series. As a result, our board of directors could authorize the issuance of shares of preferred stock that have priority over shares of our common stock with respect to dividends or other distributions or rights upon liquidation, exclusive or class voting rights or with other terms and conditions that could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a transaction or a change of control of our company that might involve a premium price for holders of our common stock or that our common stockholders otherwise believe to be in their best interests. As of the date hereof, no shares of our preferred stock are outstanding and we have no present plans to issue any preferred stock. Pursuant to the Stockholders Agreement, we will be prohibited from issuing shares of preferred stock until Torchlight owns less than 2.5% of our common stock.
Power to Increase or Decrease Authorized Shares of Our Common Stock and Issue Additional Shares of Our Common and Preferred Stock
We believe that the power of our board of directors to amend our charter to increase or decrease the aggregate number of authorized shares of stock, to authorize us to issue additional authorized but unissued shares of our common stock or preferred stock and to classify or reclassify unissued shares of our common stock or preferred stock and thereafter to authorize us to issue such classified or reclassified shares of stock will provide us with increased flexibility in structuring possible future financings and acquisitions and in meeting other needs that might arise. The additional classes or series, as well as the additional authorized shares of our common stock, will be available for issuance without further action by our stockholders, unless such action is required by applicable law, the terms of any class or series of preferred stock that we may issue in the future or the rules of any stock exchange or automated quotation system on which our securities may be listed or traded. Although our board of directors does not currently intend to do so, it could authorize us to issue a class or series of stock that could, depending upon the terms of the particular class or series, delay, defer or prevent a transaction or a change of control of our company that might involve a premium price for holders of our common stock or that our common stockholders otherwise believe to be in their best interests. See “Material Provisions of Maryland Law and of Our Charter and Bylaws—Anti-takeover Effect of Certain Provisions of Maryland Law and of Our Charter and Bylaws.”
Restrictions On Ownership and Transfer
In order for us to qualify as a REIT under the Code, our stock must be beneficially owned by 100 or more persons during at least 335 days of a taxable year of 12 months (other than the first year for which an election to be a REIT has been made) or during a proportionate part of a shorter taxable year. Also, not more than 50% of the value of the outstanding shares of stock (after taking into account options to acquire shares of stock) may be owned, directly, indirectly or through application of certain attribution rules by five or fewer individuals (as defined in the Code to include certain entities such as qualified pension plans) at any time during the last half of a taxable year (other than the first year for which an election to be a REIT has been made).
Our charter contains restrictions on the ownership and transfer of our stock that are intended to assist us in complying with these requirements and continuing to qualify as a REIT. The relevant sections of our charter provide that, subject to the exceptions described below, no person or entity may actually or beneficially own, or be deemed to own by virtue of the applicable constructive ownership provisions of the Code, more than 9.8% (in value or in number of shares, whichever is more restrictive) of the outstanding shares of any class or series of our capital stock, excluding any shares of stock that are not treated as outstanding for federal income tax purposes. We refer to this restriction as the “ownership limit.” A person or entity that would have acquired actual, beneficial or constructive ownership of our stock but for the application of the ownership limit or any of the other restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock discussed below is referred to as a “prohibited owner.”
The constructive ownership rules under the Code are complex and may cause stock owned actually or constructively by a group of related individuals and/or entities to be owned constructively by one individual or entity. As a result, the acquisition of less than 9.8% of our common stock (or the acquisition of an interest in an entity that owns, actually or constructively, our common stock) by an individual or entity, could, nevertheless cause that individual or entity, or another individual or entity, to own constructively in excess of 9.8% of our outstanding common stock and thereby violate the applicable ownership limit.
122
Our board of directors, in its sole and absolute discretion, prospectively or retroactively, may exempt a person from the limit described in the paragraph above and may establish or increase an excepted holder percentage limit for that person. The person seeking an exemption must provide to our board of directors any representations, covenants and undertakings that our board of directors may deem appropriate in order to conclude that granting the exemption will not cause us to lose our status as a REIT. Our board of directors may not grant an exemption to any person if that exemption would result in our failing to qualify as a REIT. Our board of directors must waive the ownership limit with respect to a particular person if it: (i) determines that such ownership will not cause any individual’s beneficial ownership of shares of our stock to violate the ownership limit and that any exemption from the ownership limit will not jeopardize our status as a REIT; and (ii) determines that such stockholder does not and will not own, actually or constructively, an interest in a tenant of ours (or a tenant of any entity whose operations are attributed in whole or in part to us) that would cause us to own, actually or constructively, more than a 9.8% interest (as set forth in Section 856(d)(2)(B) of the Code) in such tenant or that any such ownership would not cause us to fail to qualify as a REIT under the Code. Our board of directors may require a ruling from the IRS or an opinion of counsel, in either case in form and substance satisfactory to our board of directors, in its sole discretion, in order to determine or ensure our status as a REIT.
As a condition of the exception, our board of directors may require an opinion of counsel or IRS ruling, in either case in form and substance satisfactory to our board of directors, in its sole and absolute discretion, in order to determine or ensure our status as a REIT and representations and undertakings from the person seeking the exemption or excepted holder limit in order to make the determinations above. Our board of directors may impose such conditions or restrictions as it deems appropriate in connection with such an exception.
Our board of directors may, in its sole and absolute discretion, increase or decrease the ownership limit for one or more persons, except that a decreased ownership limit will not be effective for any person whose actual, beneficial or constructive ownership of our stock exceeds the decreased ownership limit at the time of the decrease until the person’s actual, beneficial or constructive ownership of our stock equals or falls below the decreased ownership limit, although any further acquisition of shares of our stock or beneficial or constructive ownership of our stock will violate the decreased ownership limit. Our board of directors may from time to time increase or decrease any ownership limit if, among other limitations, the new ownership limit would not prevent five or fewer persons to actually or beneficially own more than 49.9% in value of our outstanding stock.
Our charter further prohibits:
| • | any person from actually, beneficially or constructively owning shares of our stock that could result in us being “closely held” under Section 856(h) of the Code (without regard to whether the ownership interest is held during the last half of a taxable year) or otherwise cause us to fail to qualify as a REIT (including, but not limited to, actual, beneficial or constructive ownership of shares of our stock that could result in us owning (actually or constructively) an interest in a tenant that is described in Section 856(d)(2)(B) of the Code if the income we derive from such tenant, taking into account our other income that would not qualify under the gross income requirements of Section 856(c) of the Code, would cause us to fail to satisfy any such gross income requirements imposed on REITs); and | |
| • | any person from transferring shares of our stock if such transfer would result in shares of our stock being beneficially owned by fewer than 100 persons (determined without reference to any rules of attribution). |
Any person who acquires or attempts or intends to acquire actual, beneficial or constructive ownership of shares of our stock that will or may violate the ownership limit or any of the other restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock described above must give written notice immediately to us or, in the case of a proposed or attempted transaction, provide us at least 15 days prior written notice, and provide us with such other information as we may request in order to determine the effect of such transfer on our status as a REIT.
The ownership limit and other restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock described above will not apply until the completion of this offering and will not apply if our board of directors determines that it is no longer in our best interests to attempt to qualify, or to continue to qualify, as a REIT or that compliance is no longer required in order for us to qualify as a REIT.
123
Pursuant to our charter, if any purported transfer of our stock or any other event would otherwise result in any person violating the ownership limits or such other limit established by our board of directors, or could result in us being “closely held” within the meaning of Section 856(h) of the Code (without regard to whether the ownership interest is held during the last half of a taxable year) or otherwise failing to qualify as a REIT, then that number of shares causing the violation (rounded up to the nearest whole share) will be automatically transferred to, and held by, a charitable trust for the exclusive benefit of one or more charitable organizations selected by us. The prohibited owner will have no rights in shares of our stock held by the trustee. The automatic transfer will be effective as of the close of business on the business day prior to the date of the violative transfer or other event that results in the transfer to the trust. Any dividend or other distribution paid to the prohibited owner, prior to our discovery that the shares had been automatically transferred to a trust as described above, must be repaid to the trustee upon demand. If the transfer to the trust as described above is not automatically effective, for any reason, to prevent violation of the applicable restriction on ownership and transfer of our stock, then that transfer of the number of shares that otherwise would cause any person to violate the above restrictions will be void. If any transfer of our stock would result in shares of our stock being beneficially owned by fewer than 100 persons (determined without reference to any rules of attribution), then any such purported transfer will be void and of no force or effect and the intended transferee will acquire no rights in the shares.
Shares of our stock transferred to the trustee are deemed offered for sale to us, or our designee, at a price per share equal to the lesser of (i) the price per share in the transaction that resulted in the transfer of the shares to the trust (or, in the event of a gift, devise or other such transaction, the last reported sale price on the day of the transfer or other event that resulted in the transfer of such shares to the trust) and (ii) the last reported sale price on the date we accept, or our designee accepts, such offer. We may reduce the amount payable to the prohibited owner by the amount of dividends and distributions paid to the prohibited owner and owed by the prohibited owner to the trustee and pay the amount of such reduction to the trustee for the benefit of the charitable beneficiary. We have the right to accept such offer until the trustee has sold the shares of our stock held in the trust. Upon a sale to us, the interest of the charitable beneficiary in the shares sold terminates and the trustee must distribute the net proceeds of the sale to the prohibited owner and any dividends or other distributions held by the trustee with respect to such stock will be paid to the charitable beneficiary.
If we do not buy the shares, the trustee must, within 20 days of receiving notice from us of the transfer of shares to the trust, sell the shares to a person or persons designated by the trustee who could own the shares without violating the ownership limits or other restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock. Upon such sale, the trustee must distribute to the prohibited owner an amount equal to the lesser of (i) the price paid by the prohibited owner for the shares (or, if the prohibited owner did not give value in connection with the transfer or other event that resulted in the transfer to the trust (e.g., a gift, devise or other such transaction), the last reported sale price on the day of the transfer or other event that resulted in the transfer of such shares to the trust) and (ii) the sales proceeds (net of commissions and other expenses of sale) received by the trustee for the shares. The trustee may reduce the amount payable to the prohibited owner by the amount of dividends and other distributions paid to the prohibited owner and owed by the prohibited owner to the trustee. Any net sales proceeds in excess of the amount payable to the prohibited owner will be immediately paid to the charitable beneficiary, together with any dividends or other distributions thereon. In addition, if prior to our discovery that shares of our stock have been transferred to the trustee, such shares of stock are sold by a prohibited owner, then such shares shall be deemed to have been sold on behalf of the trust and, to the extent that the prohibited owner received an amount for or in respect of such shares that exceeds the amount that such prohibited owner was entitled to receive, such excess amount shall be paid to the trustee upon demand.
The trustee will be designated by us and will be unaffiliated with us and with any prohibited owner. Prior to the sale of any shares by the trust, the trustee will receive, in trust for the charitable beneficiary, all dividends and other distributions paid by us with respect to such shares, and may exercise all voting rights with respect to such shares for the exclusive benefit of the charitable beneficiary.
Subject to Maryland law, effective as of the date that the shares have been transferred to the trust, the trustee may, at the trustee’s sole discretion:
| • | rescind as void any vote cast by a prohibited owner prior to our discovery that the shares have been transferred to the trust; and | |
| • | recast the vote in accordance with the desires of the trustee acting for the benefit of the beneficiary of the trust. |
However, if we have already taken irreversible corporate action, then the trustee may not rescind and recast the vote.
If our board of directors or a committee thereof determines that a proposed transfer or other event has taken place that violates the restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock set forth in our charter, our board of directors or such committee may take such action as it deems advisable in its sole and absolute discretion to refuse to give effect to or to prevent such transfer, including, but not limited to, causing us to redeem shares of stock, refusing to give effect to the transfer on our books or instituting proceedings to enjoin the transfer.
124
Every owner of 5% or more (or such lower percentage as required by the Code or the Treasury regulations promulgated thereunder) in number or value of the outstanding shares of our stock, within 30 days after the end of each taxable year, must give written notice to us stating the name and address of such owner, the number of shares of each class and series of our stock that the owner beneficially owns and a description of the manner in which the shares are held. Each such owner also must provide us with any additional information that we request in order to determine the effect, if any, of the person’s actual or beneficial ownership on our status as a REIT and to ensure compliance with the ownership limits. In addition, any person that is an actual owner, beneficial owner or constructive owner of shares of our stock and any person (including the stockholder of record) who is holding shares of our stock for an actual owner, beneficial owner or constructive owner must, on request, disclose to us such information as we may request in good faith in order to determine our status as a REIT and comply with requirements of any taxing authority or governmental authority or to determine such compliance and to ensure compliance with the ownership limits.
Any certificates representing shares of our stock will bear a legend referring to the restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock described above.
These restrictions on ownership and transfer could delay, defer or prevent a transaction or a change of control of our company that might involve a premium price for our common stock that our stockholders believe to be in their best interest.
Transfer Agent and Registrar
The transfer agent and registrar for our common stock is Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company.
125
MATERIAL PROVISIONS OF MARYLAND LAW AND OF OUR CHARTER AND BYLAWS
The following summary of certain provisions of Maryland law and of our charter and bylaws does not purport to be complete and is subject to and qualified in its entirety by reference to Maryland law and our charter and bylaws, copies of which are filed as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is part. See “Where You Can Find More Information.”
Our Board of Directors
Our charter and bylaws provide that the number of directors of our company may be established, increased or decreased only by a majority of our entire board of directors but may not be fewer than the minimum number required under the MGCL, which is one, or, unless our bylaws are amended, more than fifteen. We have five directors.
Our charter also provides that, at such time as we become eligible to elect to be subject to certain elective provisions of the MGCL (which we expect will be upon completion of this offering) and except as may be provided by our board of directors in setting the terms of any class or series of stock, any vacancy may be filled only by a majority of the remaining directors, even if the remaining directors do not constitute a quorum. Any director so elected will serve for the remainder of the full term of the directorship in which the vacancy occurred and until a successor is duly elected and qualifies.
Each of our directors is elected by our stockholders to serve until the next annual meeting of stockholders and until his or her successor is duly elected and qualifies under the MGCL. Holders of shares of our common stock will have no right to cumulative voting in the election of directors. Directors are elected by a plurality of the votes cast. Consequently, at each annual meetings of stockholders, the holders of the majority of the shares of our common stock will be able to elect all of our directors.
Removal of Directors
Our charter provides that, subject to the rights of holders of one or more classes or series of preferred stock to elect or remove one or more directors, a director may be removed only for cause (as defined in our charter) and only by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast generally in the election of directors. This provision, when coupled with the exclusive power of our board of directors to fill vacant directorships, may preclude stockholders from removing incumbent directors except for cause and by a substantial affirmative vote and filling the vacancies created by such removal with their own nominees.
Business Combinations
Under the MGCL, certain “business combinations” (including a merger, consolidation, share exchange or, in certain circumstances specified under the statute, an asset transfer or issuance or reclassification of equity securities) between a Maryland corporation and any interested stockholder, or an affiliate of such an interested stockholder, are prohibited for five years after the most recent date on which the interested stockholder becomes an interested stockholder. Maryland law defines an interested stockholder as:
| • | any person who beneficially owns, directly or indirectly, 10% or more of the voting power of the corporation’s outstanding voting stock; or | |
| • | an affiliate or associate of the corporation who, at any time within the two-year period prior to the date in question, was the beneficial owner of 10% or more of the voting power of the then outstanding voting stock of the corporation. |
A person is not an interested stockholder under the statute if the board of directors approved in advance the transaction by which the person otherwise would have become an interested stockholder.
In approving a transaction, however, a board of directors may provide that its approval is subject to compliance, at or after the time of the approval, with any terms and conditions determined by it.
After such five-year period, any such business combination must be recommended by the board of directors of the corporation and approved by the affirmative vote of at least:
| • | 80% of the votes entitled to be cast by holders of outstanding shares of voting stock of the corporation; and | |
| • | two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast by holders of voting stock of the corporation other than shares held by the interested stockholder with whom (or with whose affiliate) the business combination is to be effected or held by an affiliate or associate of the interested stockholder. |
These supermajority approval requirements do not apply if, among other conditions, the corporation’s common stockholders receive a minimum price (as defined in the MGCL) for their shares and the consideration is received in cash or in the same form as previously paid by the interested stockholder for its shares.
126
These provisions of the MGCL do not apply, however, to business combinations that are approved or exempted by a corporation’s board of directors prior to the time that the interested stockholder becomes an interested stockholder. Our board of directors has adopted a resolution opting out of the business combination provisions of the MGCL. This resolution provides that any alteration or repeal of the resolution by the board of directors shall be valid only if approved, at a meeting duly called, by the affirmative vote of a majority of votes cast by stockholders entitled to vote generally for directors. Our bylaws provide that any such alteration or repeal of the resolution will be valid only if approved, at a meeting duly called, by the affirmative vote of a majority of votes cast by stockholders entitled to vote generally for directors.
We do not have a “poison pill” or stockholder rights plan. We intend to seek prior stockholder approval before adopting a stockholder rights plan unless, due to timing constraints or other reasons, a majority of the directors who qualify as independent directors under NYSE MKT corporate governance standards determines that it would be in the best interests of stockholders to adopt a plan before obtaining stockholder approval. We also intend that any stockholder rights plan we adopt without prior stockholder approval would either be ratified by stockholders or must expire, without being renewed or replaced, within one year.
Control Share Acquisitions
The MGCL provides that holders of “control shares” of a Maryland corporation acquired in a “control share acquisition” have no voting rights with respect to their control shares except to the extent approved by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast in the election of directors, generally, excluding shares of stock in a corporation in respect of which any of the following persons is entitled to exercise or direct the exercise of the voting power of such shares in the election of directors: (1) the person who made or proposes to make a control share acquisition, (2) an officer of the corporation or (3) an employee of the corporation who is also a director of the corporation. “Control shares” are voting shares of stock that, if aggregated with all other such shares of stock previously acquired by the acquirer or in respect of which the acquirer is able to exercise or direct the exercise of voting power (except solely by virtue of a revocable proxy), would entitle the acquirer to exercise voting power in electing directors within one of the following ranges of voting power:
| • | one-tenth or more but less than one-third; | |
| • | one-third or more but less than a majority; or | |
| • | a majority or more of all voting power. |
Control shares do not include shares that the acquiring person is then entitled to vote as a result of having previously obtained stockholder approval. A “control share acquisition” means the acquisition, directly or indirectly, of ownership of, or the power to direct the exercise of voting power with respect to, issued and outstanding control shares, subject to certain exceptions.
A person who has made or proposes to make a control share acquisition, upon satisfaction of certain conditions (including an undertaking to pay expenses and making an “acquiring person statement” as described in the MGCL), may compel the corporation to call a special meeting of stockholders to be held within 50 days of demand to consider the voting rights of the control shares. If no request for a special meeting is made, the corporation may itself present the question at any stockholders meeting.
If voting rights of control shares are not approved at the meeting or if the acquiring person does not deliver an “acquiring person statement” as required by the statute, then, subject to certain conditions and limitations, the corporation may redeem any or all of the control shares (except those for which voting rights have previously been approved) for fair value determined, without regard to the absence of voting rights for the control shares, as of the date of the last control share acquisition by the acquirer or of any meeting of stockholders at which the voting rights of such shares are considered and not approved. If voting rights for control shares are approved at a stockholders meeting and the acquirer becomes entitled to vote a majority of the shares entitled to vote, all other stockholders may exercise appraisal rights. The fair value of the shares as determined for purposes of such appraisal rights may not be less than the highest price per share paid by the acquirer in the control share acquisition.
The control share acquisition statute does not apply to: (1) shares acquired in a merger, consolidation or share exchange if the corporation is a party to the transaction or (2) acquisitions approved or exempted by the charter or bylaws of the corporation.
Our bylaws contain a provision exempting from the control share acquisition statute any and all acquisitions by any person of shares of our stock. Our bylaws provide that any amendment, alteration or repeal of this provision shall be valid only if approved, at a meeting duly called, by the affirmative vote of a majority of votes cast by stockholders entitled to vote generally for directors. There can be no assurance that such provision will not be amended or eliminated at any time in the future.
127
Subtitle 8
Subtitle 8 of Title 3 of the MGCL permits a Maryland corporation with a class of equity securities registered under the Exchange Act and at least three independent directors to elect to be subject, by provision in its charter or bylaws or a resolution of its board of directors and notwithstanding any contrary provision in the charter or bylaws, to any or all of the following five provisions:
| • | a classified board; | |
| • | a two-thirds vote requirement for removing a director; | |
| • | a requirement that the number of directors be fixed only by vote of the directors; | |
| • | a requirement that a vacancy on the board be filled only by the remaining directors and for the remainder of the full term of the class of directors in which the vacancy occurred; or | |
| • | a majority requirement for the calling of a special meeting of stockholders. |
Our charter provides that, at such time as we become eligible to make a Subtitle 8 election (which we expect will be upon the completion of this offering) and except as may be provided by our board of directors in setting the terms of any class or series of stock, we elect to be subject to the provisions of Subtitle 8 relating to the filling of vacancies on our board of directors. Through provisions in our charter and bylaws unrelated to Subtitle 8, we already (1) require a two-thirds vote for the removal of any director from the board, (2) vest in the board the exclusive power to fix the number of directorships, subject to limitations set forth in our charter and bylaws, and (3) require, unless called by the chairman of our board of directors, our president, our chief executive officer or our board of directors, the request of stockholders entitled to cast not less than a majority of all votes entitled to be cast on a matter at such meeting to call a special meeting to consider and vote on any matter that may properly be considered at a meeting of stockholders. Our bylaws provide that we may not create a classified board. Our bylaws provide that any amendment, alteration or repeal of this provision shall be valid only if approved, at a meeting duly called, by the affirmative vote of a majority of votes cast by stockholders entitled to vote generally for directors. There can be no assurance that such provision will not be amended or eliminated at any time in the future.
Amendments to Our Charter and Bylaws
Other than amendments to certain provisions of our charter described below and amendments permitted to be made without stockholder approval under Maryland law or by a specific provision in the charter, our charter may be amended only if such amendment is declared advisable by our board of directors and approved by the affirmative vote of stockholders entitled to cast a majority of all of the votes entitled to be cast on the matter. The provisions of our charter relating to the removal of directors, the restrictions on the transfer and ownership of shares or the vote required to amend such provisions may be amended only if such amendment is declared advisable by our board of directors and approved by the affirmative vote of stockholders entitled to cast not less than two-thirds of all of the votes entitled to be cast on the matter. Our board of directors has the exclusive power to adopt, alter or repeal any provision of our bylaws or to make new bylaws.
Meetings of Stockholders
Under our bylaws, annual meetings of stockholders must be held each year at a date, time and place determined by our board of directors. Special meetings of stockholders may be called by the chairman of our board of directors, our chief executive officer, our president and our board of directors. Subject to the provisions of our bylaws, a special meeting of stockholders to act on any matter that may properly be considered at a meeting of stockholders must be called by our secretary upon the written request of stockholders entitled to cast a majority of all of the votes entitled to be cast on the matter at such meeting who have requested the special meeting in accordance with the procedures specified in our bylaws and provided the information and certifications required by our bylaws. Only matters set forth in the notice of a special meeting of stockholders may be considered and acted upon at such a meeting.
Advance Notice of Director Nominations and New Business
Our bylaws provide that:
| • | with respect to an annual meeting of stockholders, nominations of individuals for election to the board of directors and the proposal of business to be considered by stockholders at the annual meeting may be made only: |
| o | pursuant to our notice of the meeting; |
| o | by or at the direction of our board of directors; or |
| o | by a stockholder who was a stockholder of record both at the time of giving of the notice required by our bylaws and at the time of the annual meeting, who is entitled to vote at the meeting in the election of each individual so nominated or on such other business and who has provided the information and certifications required by the advance notice procedures set forth in our bylaws. |
128
| • | with respect to special meetings of stockholders, only the business specified in our notice of meeting may be brought before the meeting of stockholders, and nominations of individuals for election to our board of directors may be made only: |
| o | by or at the direction of our board of directors; or |
| o | provided that the meeting has been called for the purpose of electing directors, by a stockholder who is a stockholder of record both at the time of giving of the notice required by our bylaws and at the time of the meeting, who is entitled to vote at the meeting in the election of each individual so nominated and who has provided the information and certifications required by the advance notice procedures set forth in our bylaws. |
The purpose of requiring stockholders to give advance notice of nominations and other proposals is to afford our board of directors the opportunity to consider the qualifications of the proposed nominees or the advisability of the other proposals and, to the extent considered necessary by our board of directors, to inform stockholders and make recommendations regarding the nominations or other proposals. The advance notice procedures also permit a more orderly procedure for conducting our stockholder meetings.
Anti-takeover Effect of Certain Provisions of Maryland Law and of Our Charter and Bylaws
The restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock, the provisions of our charter regarding the removal of directors, the exclusive power of our board of directors to fill vacancies on the board and the advance notice provisions of the bylaws could delay, defer or prevent a transaction or a change of control of our company that might involve a premium price for holders of our common stock or otherwise be in their best interests. Likewise, if our board of directors were to opt in to the business combination provisions of the MGCL or the provisions of Subtitle 8 of Title 3 of the MGCL providing for a classified board of directors, or if the provision in our bylaws opting out of the control share acquisition provisions of the MGCL were amended or rescinded, these provisions of the MGCL could have similar anti-takeover effects.
Indemnification and Limitation of Directors’ and Officers’ Liability
Maryland law permits a Maryland corporation to include in its charter a provision limiting the liability of its directors and officers to the corporation and its stockholders for money damages except for liability resulting from actual receipt of an improper benefit or profit in money, property or services or active and deliberate dishonesty that is established by a final judgment and is material to the cause of action. Our charter contains a provision that eliminates such liability to the maximum extent permitted by Maryland law.
The MGCL requires a Maryland corporation (unless its charter provides otherwise, which our charter does not) to indemnify a director or officer who has been successful, on the merits or otherwise, in the defense of any proceeding to which he or she is made a party by reason of his or her service in that capacity. The MGCL permits a Maryland corporation to indemnify its present and former directors and officers, among others, against judgments, penalties, fines, settlements and reasonable expenses actually incurred by them in connection with any proceeding to which they may be made or are threatened to be made a party by reason of their service in those or other capacities unless it is established that:
| • | the act or omission of the director or officer was material to the matter giving rise to the proceeding and: |
| o | was committed in bad faith; or |
| o | was the result of active and deliberate dishonesty; |
| • | the director or officer actually received an improper personal benefit in money, property or services; or | |
| • | in the case of any criminal proceeding, the director or officer had reasonable cause to believe that the act or omission was unlawful. |
However, under the MGCL, a Maryland corporation may not indemnify a director or officer for an adverse judgment in a suit by or on behalf of the corporation or if the director or officer was adjudged liable on the basis that personal benefit was improperly received, unless in either case a court orders indemnification and then only for expenses. In addition, the MGCL permits a Maryland corporation to advance reasonable expenses to a director or officer, without requiring a preliminary determination of the director’s or officer’s ultimate entitlement to indemnification, upon the corporation’s receipt of:
| • | a written affirmation by the director or officer of his or her good faith belief that he or she has met the standard of conduct necessary for indemnification by the corporation; and | |
| • | a written undertaking by the director or officer or on the director’s or officer’s behalf to repay the amount paid or reimbursed by the corporation if it is ultimately determined that the director or officer did not meet the standard of conduct. |
129
Our charter authorizes us to obligate our company and our bylaws obligate us, to the fullest extent permitted by Maryland law in effect from time to time, to indemnify and to pay or reimburse reasonable expenses in advance of final disposition of a proceeding, without requiring a preliminary determination of the director’s or officer’s ultimate entitlement to indemnification, to:
| • | any present or former director or officer who is made or threatened to be made a party to the proceeding by reason of his or her service in that capacity; or | |
| • | any individual who, while serving as a director or officer and at our request, serves or has served as a director, officer, partner, trustee, member or manager of another corporation, real estate investment trust, limited liability company, partnership, joint venture, trust, employee benefit plan or other enterprise and who is made or threatened to be made a party to the proceeding by reason of his or her service in that capacity. |
Our charter and bylaws also permit us, with the approval of our board of directors, to indemnify and advance expenses to any person who served a predecessor of ours in any of the capacities described above and to any employee or agent of our company or a predecessor of our company.
The partnership agreement also provides that we, as general partner, and our directors, officers, employees, agents and designees are indemnified to the extent provided therein. See “Description of the Partnership Agreement of Plymouth Industrial OP, LP.”
Insofar as the foregoing provisions permit indemnification of directors, officers or persons controlling us for liability arising under the Securities Act, we have been informed that in the opinion of the SEC, this indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is therefore unenforceable.
Indemnification Agreements
We intend to enter into indemnification agreements with each of our executive officers and directors as described in “Management—Limitation of Liability and Indemnification.”
Restrictions on Ownership and Transfer
Subject to certain exceptions, our charter provides that no person or entity may actually or beneficially own, or be deemed to own by virtue of the applicable constructive ownership provisions of the Code, more than 9.8% (in value or number of shares, whichever is more restrictive) of the outstanding shares of any class or series of our capital stock. For a fuller description of this and other restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock, see “Description of Stock—Restrictions on Ownership and Transfer.”
REIT Qualification
Our charter provides that our board of directors may revoke or otherwise terminate our REIT election, without approval of our stockholders, if it determines that it is no longer in our best interests to continue to be qualified as a REIT. Our charter also provides that our board of directors may determine that compliance with one or more of the restrictions on ownership and transfer of our stock is no longer required in order for us to qualify as a REIT.
130
SHARES ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE
General
Upon completion of this offering and the Torchlight Transactions, we will have 3,626,702 shares of our common stock outstanding (4,061,702 shares if the underwriters’ over-allotment option is exercised in full).
Of these shares, 3,231,965 shares, including the 2,900,000 shares sold in this offering (3,666,965 shares if the underwriters’ over-allotment option is exercised in full), will be freely transferable without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act, subject to the limitations on ownership set forth in our charter, except for any shares purchased in this offering by our “affiliates,” as that term is defined by Rule 144 under the Securities Act. The shares of common stock owned by our affiliates, the shares of common stock and warrants privately issued to the Torchlight Entities in connection with the Torchlight Transactions, and the shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of such warrants, are not freely transferable and may only be resold in compliance with Rule 144 or pursuant to another exemption from registration under the Securities Act. The shares of common stock issued in connection with redemption of the Preferred Interests will be registered for resale following the first anniversary of the closing of this offering. The shares issuable upon the exercise of the warrants will be registered for resale following the first anniversary of the closing of this offering. See “Structure of Our Company—Torchlight Transactions—Termination of Participation Right.”
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock. We have applied to list our common stock on the NYSE MKT. No assurance can be given as to (1) the likelihood that an active market for our shares of common stock will develop, (2) the liquidity of any such market, (3) the ability of the stockholders to sell the shares or (4) the prices that stockholders may obtain for any of the shares. No prediction can be made as to the effect, if any, that future sales of shares, or the availability of shares for future sale, will have on the market price prevailing from time to time. Sales of substantial amounts of our common stock (including shares issued upon the exchange of units tendered for redemption or the exercise of stock options), or the perception that such sales could occur, may adversely affect prevailing market prices of our common stock. See “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Common Stock and this Offering.” For a description of certain restrictions on ownership and transfer of our shares of common stock, see “Description of Stock—Restrictions on Ownership and Transfer.”
Rule 144
Under Rule 144 as currently in effect, beginning 90 days after the date of this prospectus, a person who is not deemed to have been an affiliate of ours at any time during the three months preceding a sale and who has beneficially owned shares considered to be restricted securities under Rule 144 for at least six months would be entitled to sell those shares, subject only to the availability of current public information about us. A non-affiliated person who has beneficially owned shares considered to be restricted securities under Rule 144 for at least one year would be entitled to sell those shares without regard to the provisions of Rule 144.
An affiliate of ours who has beneficially owned shares of our common stock for at least six months would be entitled to sell, within any three-month period, a number of shares that does not exceed the greater of:
| • | 1.0% of the shares of our common stock then outstanding, which will equal approximately 36,267 shares immediately after this offering (40,617 shares if the underwriters exercise their over-allotment option in full); or | |
| • | the average weekly trading volume of our common stock on the NYSE MKT during the four calendar weeks preceding the date on which notice of the sale is filed with the SEC. |
Sales under Rule 144 by our affiliates or persons selling shares on behalf of our affiliates are also subject to manner of sale provisions, notice requirements and the availability of current public information about us.
2014 Incentive Award Plan
We have adopted the Plan in anticipation of this offering. The Plan provides for the grant of incentive awards to our employees, officers, directors and consultants of our company and our subsidiaries. We reserved shares of common stock and LTIP units for issuance under the Plan.
We intend to file with the SEC a Registration Statement on Form S-8 covering the shares of our common stock issuable under the Plan. Shares of our common stock issuable under the Plan covered by this registration statement will be eligible for transfer or resale without restriction under the Securities Act unless held by an affiliate.
131
Lock-up Periods
Each of our executive officers and directors and their respective affiliates, and Torchlight, have agreed not to sell or otherwise transfer any shares of our common stock owned by them at the completion of this offering or thereafter acquired by them for a period of 180 days after the date of this prospectus without the prior written consent of D.A. Davidson & Co.
However, in addition to certain other exceptions, (1) each of our directors, executive officers and their respective affiliates, as well as certain of our prior investors, may transfer or dispose of his or her shares during the lock-up period in the case of gifts or for estate planning purposes, and (2) each of the prior investors that is an entity may distribute its shares to its limited partners, members or stockholders or to its affiliates or to any investment fund or other entity controlled or managed by it, provided in each case that each transferee agrees to a similar lock-up agreement for the remainder of the lock-up period, the transfer does not involve a disposition for value, no report is required to be filed by the transferor under the Exchange Act as a result of the transfer and the transferor does not voluntarily effect any public filing or report regarding such transfer.
132
DESCRIPTION OF THE PARTNERSHIP AGREEMENT OF PLYMOUTH INDUSTRIAL OP, LP.
A summary of the material terms and provisions of the Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of Plymouth Industrial OP, LP., which we refer to as the “partnership agreement,” is set forth below. This summary is not complete and is subject to and qualified in its entirety by reference to the applicable provisions of Delaware law and the partnership agreement. For more detail, please refer to the partnership agreement itself a copy of which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is part. See “Where You Can Find More Information.”
General
Our operating partnership was formed in March 2011 to acquire, own and operate properties on our behalf. It is the operating partnership of an UPREIT, which structure is utilized generally to provide for the acquisition of real property from owners who desire to defer taxable gain that would otherwise be recognized by them upon the disposition of their property. These owners may also desire to achieve diversity in their investment and other benefits afforded to owners of stock in a REIT. For purposes of satisfying the asset and income tests for qualification as a REIT for tax purposes, the REIT’s proportionate share of the assets and income of an UPREIT, such as our operating partnership, will be deemed to be assets and income of the REIT.
A property owner may generally contribute property to an UPREIT in exchange for OP units on a tax-deferred basis. In addition, our operating partnership will be structured to make distributions with respect to OP units that will be equivalent to the distributions made to holders of our common stock. Finally, a limited partner may later redeem his OP units in our operating partnership for cash or, at our option, shares of our common stock in a taxable transaction.
The partnership agreement for our operating partnership contains provisions that would allow, under certain circumstances, other entities to merge into our operating partnership. In the event of such a merger, our limited partnership would issue additional OP units that would be entitled to the same exchange rights as other holders of OP units. As a result, any such merger ultimately could result in the issuance of a substantial number of shares of our common stock, thereby diluting the percentage ownership interest of other stockholders.
We intend to hold substantially all of our assets through our operating partnership. We may, however, own investments through entities other than our operating partnership if limited partners of our operating partnership that are not affiliated with us and who hold more than 50% of the OP units held by all limited partners not affiliated with us approve the ownership of a property through another entity. We are the sole general partner of our operating partnership and own an approximately 0.1% partnership interest in our operating partnership. Our subsidiary, Plymouth OP Limited, LLC, is the only limited partner and the owner of the other approximately 99.9% partnership interest in our operating partnership. As the general partner to our operating partnership, we have the exclusive power to manage and conduct the business of our operating partnership.
The following is a summary of certain provisions of the partnership agreement of our operating partnership. This summary is not complete and is qualified by the specific language in the partnership agreement.
Capital Contributions
As we accept subscriptions for shares, we transfer (directly or through our wholly-owned subsidiary) substantially all of the net proceeds of the offering to our operating partnership as a capital contribution; however, we are deemed to have made capital contributions in the amount of the gross offering proceeds received from investors. Our operating partnership is deemed to have simultaneously paid the selling commissions and other costs associated with the offering. If our operating partnership requires additional funds at any time in excess of capital contributions made by us, it may borrow funds from us or other lenders. In addition, we are authorized to cause our operating partnership to issue partnership interests for less than fair market value if we conclude in good faith that such issuance is in the best interests of us and our operating partnership.
Operations
The partnership agreement requires that our operating partnership be operated in a manner that will enable us to (1) satisfy the requirements for being classified as a REIT for tax purposes, (2) avoid any federal income or excise tax liability and (3) ensure that our operating partnership will not be classified as a “publicly traded partnership” for purposes of Section 7704 of the Code, which classification could result in our operating partnership being taxed as a corporation, rather than as a partnership. See “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations—Tax Aspects of Our Operating Partnership” elsewhere in this prospectus.
133
Distributions
The partnership agreement provides that our operating partnership will distribute cash flow as follows:
| • | First, to us until we have received aggregate distributions with respect to the current fiscal year equal to the minimum amount necessary for us to distribute to our stockholders to enable us to maintain our status as a REIT (and avoid the imposition of federal income and excise taxes) under the Code with respect to such fiscal year; | |
| • | Next, to the limited partners until our limited partners have received aggregate distributions equal to the amount that would have been distributed to them with respect to all prior fiscal years had each limited partner held a number of our common shares equal to the number of OP units that it holds; | |
| • | Next, after the establishment of reasonable cash reserves for our expenses and obligations of our operating partnership, to us and to the limited partners until each partner has received aggregate distributions with respect to the current fiscal year and all fiscal years had each limited partner held a number of common shares equal to the number of OP units that it holds; and | |
| • | Finally, to us and the limited partners in accordance with the partners’ percentage interests in our operating partnership. |
Similarly, the partnership agreement of our operating partnership provides that taxable income is generally allocated to the partners of our operating partnership in accordance with their relative percentage interests such that a holder of one unit of partnership interest in our operating partnership will be allocated taxable income for each taxable year in an amount generally equal to the amount of taxable income to be recognized by a holder of one of our shares, subject to compliance with the provisions of Sections 704(b) and 704(c) of the Code and corresponding Treasury regulations. Losses, if any, will generally be allocated among the partners in accordance with their respective percentage interests in our operating partnership. We are authorized to amend the partnership agreement to allocate income or loss of our operating partnership in a manner so as to avoid the characterization of operating income allocable to certain tax-exempt partners as “unrelated business taxable income,” as defined in the Code.
Upon the liquidation of our operating partnership, after payment of debts and obligations, any remaining assets of our operating partnership will be distributed to partners with positive capital accounts in accordance with their respective positive capital account balances. If we were to have a negative balance in our capital account following a liquidation, we might be obligated to contribute cash to our operating partnership up to an amount not exceeding such negative balance.
In addition to the administrative and operating costs and expenses incurred by our operating partnership in acquiring and operating real properties, to the extent not paid by us, our operating partnership will pay all of our administrative costs and expenses, and such expenses will be treated as expenses of our operating partnership. Such expenses will include:
| • | all expenses relating to the formation and continuity of our existence; | |
| • | all expenses relating to the public offering and registration of securities by us; | |
| • | all expenses associated with the preparation and filing of any periodic reports by us under federal, state or local laws or regulations; | |
| • | all expenses associated with compliance by us with applicable laws, rules and regulations; | |
| • | all costs and expenses relating to any issuance or redemption of partnership interests or shares of our common stock; and | |
| • | all our other operating or administrative costs incurred in the ordinary course of our business on behalf of our operating partnership. |
Exchange Rights
The limited partners of our operating partnership, including Plymouth OP Limited, LLC, have the right to cause their OP units to be redeemed by our operating partnership or purchased by us for cash. In either event, the cash amount to be paid will be equal to the cash value of the number of our shares that would be issuable if the OP units were exchanged for our shares on a one-for-one basis. Alternatively, we may elect to purchase the OP units by issuing one share of our common stock for each limited partnership unit exchanged. If we list our shares of common stock on a national securities exchange, the cash value of a share of our common stock would equal the average of the daily closing price of a share of common stock for the ten consecutive trading days immediately preceding the date on which the cash value is determined. If our shares of common stock are not listed, then the cash value of a share of our common stock will equal the then applicable redemption price per share in our share redemption program. In the event that there is no such applicable redemption price per share then the cash value of a share of our common stock will be determined by our management in good faith.
134
These exchange rights may not be exercised, however, if and to the extent that the delivery of shares upon exercise would (1) result in any person owning shares in excess of our ownership limits, (2) result in shares being owned by fewer than 100 persons, (3) cause us to be “closely held” within the meaning of Section 856(h) of the Code, (4) cause us to own 10% or more of the ownership interests in a tenant within the meaning of Section 856(d)(2)(B) of the Code, or (5) cause the acquisition of shares by a redeemed limited partner to be “integrated” with any other distribution of our shares for purposes of complying with the Securities Act.
Subject to the foregoing, limited partners of our operating partnership may exercise their exchange rights at any time after one year following the date of issuance of their partnership units. However, a limited partner may not deliver more than two exchange notices each calendar year and may not exercise an exchange right for less than 1,000 OP units, unless such limited partner holds less than 1,000 OP units, in which case, it must exercise his exchange right for all of its OP units. We do not expect to issue any of the shares of common stock offered hereby to limited partners of our operating partnership in exchange for their OP units. Rather, in the event a limited partner of our operating partnership exercises its exchange rights, and we elect to purchase the OP units with shares of our common stock, we expect to issue unregistered shares of common stock, or subsequently registered shares of common stock, in connection with such transaction.
Transferability of Interests
We may not (1) voluntarily withdraw as the general partner of our operating partnership, (2) engage in any merger, consolidation or other business combination or (3) transfer the general partnership interest in our operating partnership (except to another of our wholly owned subsidiaries), unless the transaction in which such withdrawal, business combination or transfer occurs results in the limited partners receiving or having the right to receive an amount of cash, securities or other property equal in value to the amount they would have received if they had exercised their exchange rights immediately prior to such transaction or unless, in the case of a merger or other business combination, the successor entity contributes substantially all of its assets to our operating partnership in return for an interest in our operating partnership and agrees to assume all obligations of the general partner of our operating partnership. We may also enter into a business combination or transfer the general partnership interest upon the receipt of the consent of a majority-in-interest of the limited partners of our operating partnership other than Plymouth OP Limited, LLC. With certain exceptions, a limited partner may not transfer its interests in our operating partnership, in whole or in part, without our written consent, acting as general partner.
Voting Rights
The holders of limited partnership interests have limited voting rights. The consent of a majority-in-interest of the limited partners is required only to approve (1) any amendment that would affect the conversion or exchange rights of the limited partnership interests, (2) any amendment to the partnership agreement that would adversely affect the rights of the limited partners to receive distributions, (3) any amendment that would alter the partnership’s allocations of profit and loss and (4) any amendment that would impose any obligation on the limited partners to make additional capital contributions to the partnership.
135
MATERIAL U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS
The following is a summary of the current material U.S. federal income tax considerations regarding our company and holders of our common stock. For the purposes of this discussion, references to “we,” “our” and “us” mean only Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc., and do not include any of its subsidiaries, except as otherwise indicated. This summary is for general information only and is not tax advice. The information in this summary is based on:
| • | the Code; | |
| • | current, temporary and proposed Treasury regulations promulgated under the Code; | |
| • | the legislative history of the Code; | |
| • | current administrative interpretations and practices of the IRS; and | |
| • | court decisions |
in each case, as of the date of this prospectus. In addition, the administrative interpretations and practices of the IRS include its practices and policies as expressed in private letter rulings that are not binding on the IRS except with respect to the particular taxpayers who requested and received those rulings. Future legislation, Treasury regulations, administrative interpretations and practices and/or court decisions may adversely affect the tax considerations contained in this discussion. Any such change could apply retroactively to transactions preceding the date of the change. Except as expressly provided below, we have not requested and do not intend to request a ruling from the IRS that we qualify as a REIT, and the statements in this prospectus are not binding on the IRS or any court. Thus, we can provide no assurance that the tax considerations contained in this discussion will not be challenged by the IRS or will be sustained by a court if challenged by the IRS. This summary does not discuss any state, local or non-U.S. tax consequences, or any tax consequences arising under any U.S. federal tax other than the income tax, associated with the purchase, ownership, or disposition of our common stock, or our election to be taxed as a REIT.
You are urged to consult your tax advisors regarding the tax consequences to you of:
| • | the purchase, ownership or disposition of our common stock including the federal, state, local, non-U.S. and other tax consequences; |
| • | our election to be taxed as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes; and |
| • | potential changes in applicable tax laws. |
Taxation of Our Company
General
We inadvertently filed a U.S. federal income tax return for the taxable year ended December 31, 2011, on IRS Form 1120-REIT. As a result, we inadvertently made a REIT election for the taxable year ended December 31, 2011. After seeking relief from the IRS, the IRS issued a private letter ruling to us on February 5, 2015, in which the IRS concluded that we will be treated as if we had not made the REIT election for the taxable year ended December 31, 2011. We elected to be taxed as a REIT under the Code by filing IRS Form 1120-REIT for the taxable year ended December 31, 2012. Although the private letter ruling that the IRS issued to us does not address our election to be taxed as a REIT for the taxable year ended December 31, 2012, we believe we have effectively elected to be taxed as, and have operated in a manner to allow us to qualify as, a REIT under the Code commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2012. We have not requested a ruling from the IRS as to our qualification as a REIT, and no assurance can be given that we will operate in a manner so as to qualify or remain qualified as a REIT.
Dentons US LLP has acted as our tax counsel in connection with this offering. Dentons US LLP will render an opinion to us to the effect that, commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2012, and subject to certain assumptions and qualifications, we have been organized in conformity with the requirements for qualification and taxation as a REIT under the Code, and that our actual and proposed method of operation has enabled and will continue to enable us to meet the requirements for qualification and taxation as a REIT under the Code for such taxable year and thereafter. In addition, it must be emphasized that the opinion of Dentons US LLP will be based on various assumptions and representations as to factual matters, including representations made by us in a factual certificate provided by one of our officers. In addition, the opinion will be based upon our factual representations set forth in this prospectus. The opinion of Dentons US LLP is not binding upon the IRS or any court. Moreover, our qualification and taxation as a REIT depend upon our ability to meet the various qualification tests imposed under the Code, which are discussed below, including through actual annual operating results, asset composition, distribution levels and diversity of stock ownership, the results of which have not been and will not be reviewed by Dentons US LLP. Accordingly, no assurance can be given that the actual results of our operations for any particular taxable year will satisfy such requirements. Further, the anticipated U.S. federal income tax treatment described in this prospectus may be changed, perhaps retroactively, by legislative, administrative or judicial action at any time. Dentons US LLP has no obligation to update its opinion subsequent to the date of such opinion.
136
Subject to the foregoing, commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2012, we believe that we were organized and operated, and will continue to be organized and operated, in a manner that will allow us to qualify for taxation as a REIT under the Code. However, in addition to the issues discussed above, qualification and taxation as a REIT depend upon our ability to meet various tests imposed under the Code, including through actual annual operating results, asset composition, distribution levels and diversity of stock ownership. Accordingly, no assurance can be given that we have been organized and will operate, or will continue to be organized and operate, in a manner so as to qualify or remain qualified as a REIT. See “—Taxation of Our Company—Failure to Qualify.”
The sections of the Code and the corresponding Treasury regulations that relate to qualification and taxation as a REIT are highly technical and complex. The following sets forth the material aspects of the sections of the Code that govern the federal income tax treatment of a REIT and the holders of its common stock. This summary is qualified in its entirety by the applicable Code provisions, relevant rules and regulations promulgated under the Code, and administrative and judicial interpretations of the Code and these rules and regulations.
Provided we qualify for taxation as a REIT, we generally will not be required to pay federal corporate income taxes on our net income that is currently distributed to our stockholders. This treatment substantially eliminates the “double taxation” that ordinarily results from investment in a C corporation. A C corporation is a corporation that generally is required to pay tax at the corporate level. Double taxation means taxation once at the corporate level when income is earned and once again at the stockholder level when the income is distributed.
We may, however, be required to pay U.S. federal tax as follows:
| • | First, we will be required to pay tax at regular corporate rates on any undistributed net taxable income, including undistributed net capital gains. | |
| • | Second, we may be required to pay the “alternative minimum tax” on our items of tax preference under some circumstances. | |
| • | Third, if we have (1) net income from the sale or other disposition of “foreclosure property” held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business or (2) other non-qualifying income from foreclosure property, we will be required to pay tax at the highest corporate rate on this income. To the extent that income from foreclosure property is otherwise qualifying income for purposes of the 75% gross income test, as described below, this tax is not applicable. Subject to certain other requirements, foreclosure property generally is defined as property we acquired through foreclosure or after a default on a loan secured by the property or a lease of the property. | |
| • | Fourth, we will be required to pay a 100% tax on any net income from prohibited transactions. Prohibited transactions are, in general, sales or other taxable dispositions of property, other than foreclosure property, held as inventory or primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business. | |
| • | Fifth, if we fail to satisfy the 75% gross income test or the 95% gross income test, as described below, but have otherwise maintained our qualification as a REIT because certain other requirements are met, we will be required to pay a tax equal to (1) the greater of (A) the amount by which we fail to satisfy the 75% gross income test and (B) the amount by which we fail to satisfy the 95% gross income test, multiplied by (2) a fraction intended to reflect our profitability. | |
| • | Sixth, in the event of a failure of the asset tests (other than a de minimis failure of the 5% asset test or the 10% asset test), as long as (1) the failure was due to reasonable cause and not to willful neglect, (2) we file a description of each asset that caused such failure with the IRS, and (3) we dispose of the assets causing the failure or otherwise comply with the asset tests within six months after the last day of the quarter in which we identify such failure, we may retain our REIT qualification but will be required to pay a tax equal to the greater of $50,000 or the highest corporate tax rate multiplied by the net income from the non-qualifying assets that caused us to fail such test. | |
| • | Seventh, if we fail to satisfy any provision of the Code that would result in our failure to qualify as a REIT (other than a violation of the gross income tests or certain violations of the asset tests, as described below) and the violation is due to reasonable cause and not due to willful neglect, we may retain our REIT qualification but we will be required to pay a penalty of $50,000 for each such failure. | |
| • | Eighth, we will be required to pay a 4% excise tax to the extent we fail to distribute during each calendar year at least the sum of (1) 85% of our ordinary income for the year, (2) 95% of our capital gain net income for the year, and (3) any undistributed taxable income from prior periods. |
137
| • | Ninth, if we acquire any asset from a corporation that is or has been a C corporation in a transaction in which the basis of the asset in our hands is less than the fair market value of the asset, in each case determined at the time we acquired the asset, and we subsequently recognize gain on the disposition of the asset during the five-year period beginning on the date on which we acquired the asset, then we will be required to pay tax at the highest regular corporate tax rate on this gain to the extent of the excess of (1) the fair market value of the asset over (2) our adjusted basis in the asset, in each case determined as of the date on which we acquired the asset. This built-in gains tax does not apply to any gain from the sale of property acquired by us in an exchange under Section 1031 (a like kind exchange) or Section 1033 (an involuntary conversion) of the Code. | |
| • | Tenth, entities we own that are C corporations, including any “taxable REIT subsidiaries,” generally will be required to pay federal corporate income tax on their earnings. | |
| • | Eleventh, we will be required to pay a 100% tax on any “redetermined rents,” “redetermined deductions,” “excess interest,” or “redetermined TRS service income.” See “Taxation of Our Company—Penalty Tax.” In general, redetermined rents are rents from real property that are overstated as a result of services furnished to any of our tenants by a taxable REIT subsidiary of ours. Redetermined deductions and excess interest generally represent amounts that are deducted by a taxable REIT subsidiary of ours for amounts paid to us that are in excess of the amounts that would have been deducted based on arm’s length negotiations. Redetermined TRS service income generally represents income of a taxable REIT subsidiary that is understated as a result of services provided to us or on our behalf. | |
| • | Twelfth, we may elect to retain and pay income tax on our net capital gain. In that case, a U.S. holder would include its proportionate share of our undistributed capital gain (to the extent that we make a timely designation of such gain to the holder) in its income, would be deemed to have paid the tax that we paid on such gain, and would be allowed a credit for its proportionate share of the tax deemed to have been paid, and an adjustment would be made to increase the basis of the holder in our common stock. | |
| • | Thirteenth, if we are treated for tax purposes as a Subchapter C corporation prior to our REIT election, then we would generally be subject to a corporate-level tax on a taxable disposition of any appreciated asset we hold as of the effective date of our REIT election. Specifically, if we dispose of a built-in-gain asset in a taxable transaction prior to the fifth anniversary of the effective date of our REIT election, we generally would be subject to tax at the highest regular corporate federal income tax rate on the gain. | |
| • | Fourteenth, notwithstanding our status as a REIT, we may also have to pay certain state and local income taxes, because not all states and localities treat REITs in the same manner that they are treated for federal income tax purposes. Moreover, as further described below, domestic taxable REIT subsidiaries will be subject to federal, state, and local corporate income tax on their taxable income. |
Requirements for Qualification as a REIT
The Code defines a REIT as a corporation, trust or association:
| (1) | that is managed by one or more trustees or directors; |
| (2) | that issues transferable shares or transferable certificates of beneficial interest to evidence its beneficial ownership; |
| (3) | that would be taxable as a domestic corporation, but for Sections 856 through 860 of the Code; |
| (4) | that is not a financial institution or an insurance company within the meaning of certain provisions of the Code; |
| (5) | that is beneficially owned by 100 or more persons; |
| (6) | not more than 50% in value of the outstanding stock of which is owned, directly or indirectly, by five or fewer individuals, including certain specified entities, during the last half of each taxable year; |
| (7) | that elects to be a REIT, or has made such election for a previous taxable year, and satisfies all relevant filing and other administrative requirements established by the IRS that must be met to elect and maintain REIT status; |
| (8) | that uses a calendar year for U.S. federal income tax purposes; and |
| (9) | that meets other tests, described below, regarding the nature of its income and assets and the amount of its distributions. |
138
The Code provides that conditions (1) to (4), inclusive, must be met during the entire taxable year and that condition (5) must be met during at least 335 days of a taxable year of 12 months, or during a proportionate part of a taxable year of less than 12 months. Conditions (5) and (6) do not apply until after the first taxable year for which an election is made to be taxed as a REIT. For purposes of condition (6), the term “individual” includes a supplemental unemployment compensation benefits plan, a private foundation or a portion of a trust permanently set aside or used exclusively for charitable purposes, but generally does not include a qualified pension plan or profit sharing trust.
We believe we have been organized, have operated and have issued sufficient shares of common stock with sufficient diversity of ownership to allow us to satisfy conditions (1) through (9) inclusive, during the relevant time periods. In addition, our charter provides for restrictions regarding ownership and transfer of our shares which are intended to assist us in continuing to satisfy the share ownership requirements described in (5) and (6) above. These share ownership and transfer restrictions are described under “Description of Stock—Restrictions on Ownership and Transfer” in this prospectus. These restrictions, however, do not ensure that we will, in all cases, satisfy the share ownership requirements described in (5) and (6) above. If we fail to satisfy these share ownership requirements, except as provided in the next sentence, our status as a REIT will terminate. If, however, we comply with the rules contained in applicable Treasury regulations that require us to ascertain the actual ownership of our shares and we do not know, or would not have known through the exercise of reasonable diligence, that we failed to meet the requirement described in condition (6) above, we will be treated as having met this requirement. See “—Taxation of Our Company—Failure to Qualify.”
Ownership of Interests in Partnerships, Limited Liability Companies and Qualified REIT Subsidiaries
In the case of a REIT which is a partner in a partnership or a member in a limited liability company treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes, Treasury regulations provide that the REIT will be deemed to own its proportionate share of the assets of the partnership or limited liability company, as the case may be, based on its interest in partnership capital, subject to special rules relating to the 10% asset test described below. Also, the REIT will be deemed to be entitled to its proportionate share of the income of that entity. The assets and gross income of the partnership or limited liability company retain the same character in the hands of the REIT for purposes of Section 856 of the Code, including satisfying the gross income tests and the asset tests. Thus, during periods in which our operating partnership is treated as a partnership for federal income tax purposes, our pro rata share of the assets and items of income of our operating partnership, including our operating partnership’s share of these items of any partnership or limited liability company treated as a partnership or disregarded entity for U.S. federal income tax purposes in which it owns an interest, is treated as our assets and items of income for purposes of applying the requirements described in this discussion, including the gross income and asset tests described below. During periods in which our operating partnership is treated as a disregarded entity for federal income tax purposes, it will not be treated as a separate entity and all assets, liabilities and items of income, gain, loss, deduction and credit of the operating partnership will be treated as our assets, liabilities and items of income, gain, loss, deduction and credit. A brief summary of the rules governing the U.S. federal income taxation of partnerships and limited liability companies is set forth below in “—Tax Aspects of Our Operating Partnership, the Subsidiary Partnerships and the Limited Liability Companies.”
We have control of our operating partnership and intend to control any of its subsidiary partnerships and limited liability companies, and we intend to operate them in a manner consistent with the requirements for our qualification as a REIT. We may from time to time be a limited partner or non-managing member in a partnership or limited liability company. If a partnership or limited liability company in which we own an interest takes or expects to take actions that could jeopardize our status as a REIT or require us to pay tax, we may be forced to dispose of our interest in such entity. In addition, it is possible that a partnership or limited liability company could take an action which could cause us to fail a gross income or asset test, and that we would not become aware of such action in time to dispose of our interest in the partnership or limited liability company or take other corrective action on a timely basis. In that case, we could fail to qualify as a REIT unless we were entitled to relief, as described below.
We may from time to time own and operate certain properties through wholly owned subsidiaries that we intend to be treated as “qualified REIT subsidiaries” under the Code. A corporation will qualify as our qualified REIT subsidiary if we own 100% of the corporation’s outstanding stock and do not elect with the subsidiary to treat it as a “taxable REIT subsidiary,” as described below. A qualified REIT subsidiary is not treated as a separate corporation, and all assets, liabilities and items of income, gain, loss, deduction and credit of a qualified REIT subsidiary are treated as assets, liabilities and items of income, gain, loss, deduction and credit of the parent REIT for all purposes under the Code, including all REIT qualification tests. Thus, in applying the federal tax requirements described in this discussion, any qualified REIT subsidiaries we own are ignored, and all assets, liabilities and items of income, gain, loss, deduction and credit of such corporations are treated as our assets, liabilities and items of income, gain, loss, deduction and credit. A qualified REIT subsidiary is not subject to federal income tax, and our ownership of the stock of a qualified REIT subsidiary does not violate the restrictions on ownership of securities, as described below under “—Taxation of Our Company—Asset Tests.”
139
Ownership of Interests in Taxable REIT Subsidiaries
We may own interests in one or more taxable REIT subsidiaries in the future. A taxable REIT subsidiary is a corporation other than a REIT in which a REIT directly or indirectly holds stock, and that has made a joint election with such REIT to be treated as a taxable REIT subsidiary. If a taxable REIT subsidiary owns more than 35% of the total voting power or value of the outstanding securities of another corporation, such other corporation will also be treated as a taxable REIT subsidiary. Other than some activities relating to lodging and health care facilities, a taxable REIT subsidiary may generally engage in any business, including the provision of customary or non-customary services to tenants of its parent REIT. A taxable REIT subsidiary is subject to federal income tax as a regular C corporation. In addition, a taxable REIT subsidiary may be prevented from deducting interest on debt funded directly or indirectly by its parent REIT if certain tests regarding the taxable REIT subsidiary’s debt-to-equity ratio and interest expense are not satisfied. A REIT’s ownership of securities of a taxable REIT subsidiary is not subject to the 5% or 10% asset test described below, and their operations will be subject to the provisions described above. See “—Taxation of Our Company—Asset Tests.”
Income Tests
We must satisfy two gross income requirements annually to maintain our qualification as a REIT. First, in each taxable year, we must derive directly or indirectly at least 75% of our gross income (excluding gross income from prohibited transactions, certain hedging transactions and certain foreign currency gains) from investments relating to real property or mortgages on real property, including “rents from real property,” interest on obligations adequately secured by mortgages on real property, and certain types of temporary investments. Qualifying income for purposes of that 75% gross income test generally includes:
| • | rents from real property; | |
| • | interest on debt secured by mortgages on real property, or on interests in real property, and interest on debt secured by mortgages on both real and personal property if the fair market value of such personal property does not exceed 15% of the total fair market value of all such property; | |
| • | dividends or other distributions on, and gain from the sale of, shares in other REITs; | |
| • | income derived from foreclosure property; | |
| • | gain from the sale of real estate assets that are not inventory or dealer property; and | |
| • | income derived from the temporary investment of new capital that is attributable to the issuance of our shares of common stock or a public offering of our debt with a maturity date of at least five years and that we receive during the one-year period beginning on the date on which we received such new capital. |
Second, in each taxable year we must derive at least 95% of our gross income (excluding gross income from prohibited transactions, certain hedging transactions and certain foreign currency gains) from the real property investments described above or dividends, interest and gain from the sale or disposition of stock or securities, or from any combination of the foregoing.
Rents we receive from a tenant will qualify as “rents from real property” for the purpose of satisfying the gross income requirements for a REIT described above only if all of the following conditions are met:
| • | The amount of rent is not based in whole or in part on the income or profits of any person. However, an amount we receive or accrue generally will not be excluded from the term “rents from real property” solely because it is based on a fixed percentage or percentages of receipts or sales; | |
| • | Neither we nor an actual or constructive owner of 10% or more of our stock actually or constructively owns 10% or more of the interests in the assets or net profits of a non-corporate tenant, or, if the tenant is a corporation, 10% or more of the total combined voting power of all classes of stock entitled to vote or 10% or more of the total value of all classes of stock of the tenant. Rents we receive from such a tenant that is a taxable REIT subsidiary of ours, however, will not be excluded from the definition of “rents from real property” as a result of this condition if at least 90% of the space at the property to which the rents relate is leased to third parties, and the rents paid by the taxable REIT subsidiary are substantially comparable to rents paid by our other tenants for comparable space. Whether rents paid by a taxable REIT subsidiary are substantially comparable to rents paid by other tenants is determined at the time the lease with the taxable REIT subsidiary is entered into, extended, and modified, if such modification increases the rents due under such lease. Notwithstanding the foregoing, however, if a lease with a “controlled taxable REIT subsidiary” is modified and such modification results in an increase in the rents payable by such taxable REIT subsidiary, any such increase will not qualify as “rents from real property.” For purposes of this rule, a “controlled taxable REIT subsidiary” is a taxable REIT subsidiary in which the parent REIT owns stock possessing more than 50% of the voting power or more than 50% of the total value of the outstanding stock of such taxable REIT subsidiary; |
140
| • | Rent attributable to personal property, leased in connection with a lease of real property, is not greater than 15% of the total rent received under the lease. If this condition is not met, then the portion of the rent attributable to personal property will not qualify as “rents from real property” and will not qualify for either the 75% or 95% gross income tests. The rent attributable to the personal property leased in connection with the lease of real property is the amount that bears the same ratio to total rent for the property in the taxable year as the average of the fair market values of the personal property at the beginning and at the end of the taxable year bears to the average of the aggregate fair market values of both the real and personal property at the beginning and at the end of such taxable year, or “the personal property ratio.” We believe that the personal property ratio of our properties will be less than 15% or that any income attributable to excess personal property will not jeopardize our ability to qualify as a REIT; and | |
| • | We generally do not operate or manage the property or furnish or render services to our tenants, subject to a 1% de minimis exception and except as provided below. We are permitted, however, to perform directly certain services that are “usually or customarily rendered” in connection with the rental of space for occupancy only and are not otherwise considered “rendered to the occupant” of the property. Examples of these permitted services include the provision of light, heat, or other utilities, trash removal and general maintenance of common areas. In addition, we are permitted to employ an independent contractor from whom we derive no revenue or a taxable REIT subsidiary, which may be wholly or partially owned by us, to provide both customary and non-customary services to our tenants without causing the rent we receive from those tenants to fail to qualify as “rents from real property.” Any amounts we receive from a taxable REIT subsidiary with respect to the taxable REIT subsidiary’s provision of non-customary services will, however, be non-qualifying income under the 75% gross income test and, except to the extent received through the payment of dividends, the 95% gross income test. |
We generally do not intend, and as a general partner of our operating partnership, do not intend to permit our operating partnership, to take actions we believe will cause us to fail to satisfy the rental conditions described above. However, we may intentionally fail to satisfy some of these conditions to the extent the failure will not, based on the advice of our tax counsel, jeopardize our tax status as a REIT. In addition, with respect to the limitation on the rental of personal property, we have not obtained appraisals of the real property and personal property leased to tenants. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that the IRS will not disagree with our determinations of the value of such property.
Income we receive that is attributable to the use of parking spaces at the properties will generally constitute rents from real property for purposes of the gross income tests if certain services we provide with respect to the parking spaces are performed by independent contractors from whom we derive no revenue, either directly or indirectly, or by a taxable REIT subsidiary, and certain other conditions are met. We believe that the income we receive that is attributable to parking spaces meets these tests and, accordingly, will constitute rents from real property for purposes of the gross income tests.
For purposes of the gross income tests, the term “interest” generally does not include any amount received or accrued, directly or indirectly, if the determination of all or some of the amount depends in any way on the income or profits of any person. However, an amount received or accrued generally will not be excluded from the term “interest” solely by reason of being based on a fixed percentage or percentages of receipts or sales. Interest income constitutes qualifying mortgage interest for purposes of the 75% gross income test to the extent that the underlying obligation is secured by a mortgage on real property. If we receive interest income with respect to a mortgage loan that is secured by both real property and personal property and the fair market value of the personal property does not exceed 15% of the total fair market value of all such property, then the interest income will be treated as qualifying mortgage interest for purposes of the 75% gross income test. If, however, the fair market value of the personal property exceeds 15% of the total fair market value of all of the real and personal property securing the mortgage loan, then the loan will not be treated as fully secured by real property, the interest income must be apportioned between the real property and the other property, and our income from the arrangement will qualify for purposes of the 75% gross income test only to the extent that the interest is allocable to the real property security. In this case, we would be required to apportion our annual interest income to the real property security based on a fraction, the numerator of which is the value of the real property securing the loan, determined when we commit to acquire the loan, and the denominator of which is the highest “principal amount” of the loan during the year. Even if a loan is not secured by real property or is undersecured, the income that it generates may nonetheless qualify for purposes of the 95% gross income test.
141
From time to time, we may enter into hedging transactions with respect to one or more of our assets or liabilities. Our hedging activities may include entering into interest rate swaps, caps, and floors, options to purchase these items, and futures and forward contracts. Income from a hedging transaction, including gain from the sale or disposition of such a transaction, that is clearly identified as a hedging transaction as specified in the Code, will not constitute gross income and thus will be exempt from the 75% and 95% gross income tests. The term “hedging transaction,” as used above, generally means any transaction we enter into in the normal course of our business primarily to manage risk of (1) interest rate changes or fluctuations with respect to borrowings made or to be made by us to acquire or carry real estate assets, (2) currency fluctuations with respect to an item of qualifying income under the 75% or 95% gross income test, or (3) new transactions entered into to hedge the income or loss from prior hedging transactions, where the property or indebtedness which was the subject of the prior hedging transaction was disposed of or extinguished. To the extent that we do not properly identify such transactions as hedges or we hedge with other types of financial instruments, the income from those transactions is not likely to be treated as qualifying income for purposes of the gross income tests. We intend to structure any hedging transactions in a manner that does not jeopardize our status as a REIT.
To the extent we receive dividends from a taxable REIT subsidiary, we generally will derive our allocable share of such dividend income through our interest in our operating partnership. Such dividend income will qualify under the 95%, but not the 75%, gross income test.
We will monitor the amount of our non-qualifying income and will take actions intended to keep such income within the limitations of the gross income tests. Although we expect these actions will be sufficient to prevent a violation of the gross income tests, we cannot guarantee that such actions will in all cases prevent such a violation.
If we fail to satisfy one or both of the 75% or 95% gross income tests for any taxable year, we may nevertheless qualify as a REIT for the year if we are entitled to relief under certain provisions of the Code. We generally may make use of the relief provisions if:
| • | following our identification of the failure to meet the 75% or 95% gross income tests for any taxable year, we file a schedule with the IRS setting forth each item of our gross income for purposes of the 75% or 95% gross income tests for such taxable year in accordance with applicable Treasury regulations; and | |
| • | our failure to meet these tests was due to reasonable cause and not due to willful neglect. |
It is not possible, however, to state whether in all circumstances we would be entitled to the benefit of these relief provisions. For example, if we fail to satisfy the gross income tests because non-qualifying income that we intentionally accrue or receive exceeds the limits on non-qualifying income, the IRS could conclude that our failure to satisfy the tests was not due to reasonable cause. If these relief provisions do not apply to a particular set of circumstances, we will not qualify as a REIT. As discussed above in “—Taxation of Our Company—General,” even if these relief provisions apply, and we retain our status as a REIT, a tax would be imposed with respect to our non-qualifying income. We may not always be able to comply with the gross income tests for REIT qualification despite periodic monitoring of our income.
Prohibited Transaction Income
Any gain that we realize on the sale of property held as inventory or otherwise held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business, including our share of any such gain realized by our operating partnership, either directly or through its subsidiary partnerships and limited liability companies, will be treated as income from a prohibited transaction that is subject to a 100% penalty tax, unless certain safe harbor exceptions apply. Under existing law, whether property is held as inventory or primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of a trade or business is a question of fact that depends on all the facts and circumstances surrounding the particular transaction. Our operating partnership intends to hold its properties for investment with a view to long-term appreciation, to engage in the business of acquiring, developing and owning its properties and to make occasional sales of the properties as are consistent with our operating partnership’s investment objectives. We do not intend to enter into any sales that are prohibited transactions. However, the IRS may successfully contend that some or all of the sales made by our operating partnership or its subsidiary partnerships or limited liability companies are prohibited transactions. We would be required to pay the 100% penalty tax on our allocable share of the gains resulting from any such sales.
142
Penalty Tax
Any redetermined rents, redetermined deductions, excess interest or redetermined TRS service income we generate will be subject to a 100% penalty tax. In general, redetermined rents are rents from real property that are overstated as a result of any services furnished to any of our tenants by a taxable REIT subsidiary of ours. Rents we receive will not constitute redetermined rents if they qualify for certain safe harbor provisions contained in the Code. Redetermined deductions and excess interest represent any amounts that are deducted by a taxable REIT subsidiary of ours for amounts paid to us that are in excess of the amounts that would have been deducted based on arm’s length negotiations. Redetermined TRS service income means gross income of a taxable REIT subsidiary attributable to service provided to or on behalf of a REIT, to the extent that the taxable REIT subsidiary’s income should be increased to reflect arms’ length charges for such services.
If a taxable REIT subsidiary of ours provides services to our tenants, we intend to set the fees paid to any such taxable REIT subsidiary for such services at arm’s length rates, although the fees paid may not satisfy the safe-harbor provisions referenced above. These determinations are inherently factual, and the IRS has broad discretion to assert that amounts paid between related parties should be reallocated to clearly reflect their respective incomes. If the IRS successfully made such an assertion, we would be required to pay a 100% penalty tax on the excess of an arm’s length fee for tenant services over the amount actually paid.
Asset Tests
At the close of each calendar quarter of our taxable year, we must also satisfy five tests relating to the nature and diversification of our assets. First, at least 75% of the value of our total assets must be represented by:
| • | cash or cash items, including certain receivables; | |
| • | government securities; | |
| • | interests in real property, including leaseholds and options to acquire real property and leaseholds; | |
| • | interests in mortgage loans on real property or on interests in real property; | |
| • | interests in mortgage loans secured by both real property and personal property if the fair market value of such personal property does not exceed 15% of the total fair market value of all such property; | |
| • | stock in other REITs; | |
| • | investments in stock or debt instruments during the one-year period following our receipt of new capital that we raise through equity offerings or offerings of debt with at least a five-year term; | |
| • | debt instruments of publicly offered REITs; and | |
| • | personal property leased in connection with a lease of real property for which the rent attributable to personal property is not greater than 15% of the total rent received under the lease. |
Second, not more than 25% of the value of our total assets may be represented by securities (including securities of one or more taxable REIT subsidiaries), other than those securities includable in the 75% asset test.
Third, of the investments included in the 25% asset class, and except for investments in any other REITs, any qualified REIT subsidiaries and taxable REIT subsidiaries, the value of any one issuer’s securities may not exceed 5% of the value of our total assets, and we may not own more than 10% of the total voting power or value of the outstanding securities of any one issuer except, in the case of the 10% value test, securities satisfying the “straight debt” safe-harbor or securities issued by a partnership that itself would satisfy the 75% income test if it were a REIT. Certain types of securities we may own are disregarded as securities solely for purposes of the 10% value test, including, but not limited to, any loan to an individual or an estate, any obligation to pay rents from real property and any security issued by a REIT. In addition, solely for purposes of the 10% value test, the determination of our interest in the assets of a partnership or limited liability company in which we own an interest will be based on our proportionate interest in any securities issued by the partnership or limited liability company, excluding for this purpose certain securities described in the Code.
Fourth, not more than 25% (20% for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017) of the value of our total assets may be represented by the securities of one or more taxable REIT subsidiaries. Our operating partnership may own the stock of certain corporations that elect, together with us, to be treated as our taxable REIT subsidiaries. So long as each of these companies qualifies as a taxable REIT subsidiary, we will not be subject to the 5% asset test, the 10% voting securities limitation or the 10% value limitation with respect to our ownership of their stock. We intend that the aggregate value of our taxable REIT subsidiaries will not exceed 25% (20% for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017) of the aggregate value of our gross assets. There can be no assurance that the IRS will not disagree with our determinations of value of such assets.
143
Fifth, not more than 25% of the value of our total assets may be represented by debt instruments of publicly offered REITs to the extent those debt instruments would not be real estate assets but for the inclusion of debt instruments of publicly offered REITs in the meaning of real estate assets effective for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2015.
In the event that we invest in a mortgage loan that is not fully secured by real property, the mortgage loan will nonetheless be treated as a real estate asset for purposes of the 75% asset test as long as the fair market value of the personal property does not exceed 15% of the total fair market value of the real and personal property securing the mortgage loan. To the extent that the fair market value of the personal property securing the mortgage loan exceeds 15% of the total fair market value of the real and personal property securing the mortgage loan, then only a portion of the mortgage loan may be treated as a real estate asset for purposes of the 75% asset test.
The asset tests must be satisfied at the close of each calendar quarter of our taxable year in which we (directly or through our operating partnership) acquire securities in the applicable issuer, and also at the close of each calendar quarter in which we increase our ownership of securities of such issuer (including as a result of increasing our interest in our operating partnership). For example, our indirect ownership of securities of each issuer will increase as a result of our capital contributions to our operating partnership or as limited partners exercise their redemption/exchange rights. After initially meeting the asset tests at the close of any quarter, we will not lose our status as a REIT for failure to satisfy the asset tests at the end of a later quarter solely by reason of changes in asset values. If we fail to satisfy an asset test because we acquire securities or other property during a quarter (including as a result of an increase in our interest in our operating partnership), we may cure this failure by disposing of sufficient non-qualifying assets within 30 days after the close of that quarter. We intend to maintain adequate records of the value of our assets to ensure compliance with the asset tests. If we fail to cure any noncompliance with the asset tests within the 30 day cure period, we would cease to qualify as a REIT unless we are eligible for certain relief provisions discussed below.
Certain relief provisions may be available to us if we discover a failure to satisfy the asset tests described above after the 30-day cure period. Under these provisions, we will be deemed to have met the 5% and 10% asset tests if the value of our non-qualifying assets (i) does not exceed the lesser of (a) 1% of the total value of our assets at the end of the applicable quarter or (b) $10,000,000, and (ii) we dispose of the non-qualifying assets or otherwise satisfy such tests within (a) six months after the last day of the quarter in which the failure to satisfy the asset tests is discovered or (b) the period of time prescribed by Treasury regulations to be issued. For violations of any of the asset tests due to reasonable cause and not due to willful neglect and that are, in the case of the 5% and 10% asset tests, in excess of the de minimis exception described above, we may avoid disqualification as a REIT after the 30 day cure period by taking steps including (i) the disposition of sufficient non-qualifying assets, or the taking of other actions, which allow us to meet the asset tests within (a) six months after the last day of the quarter in which the failure to satisfy the asset tests is discovered or (b) the period of time prescribed by Treasury regulations to be issued, (ii) paying a tax equal to the greater of (a) $50,000 or (b) the highest corporate tax rate multiplied by the net income generated by the non-qualifying assets, and (iii) disclosing certain information to the IRS.
Although we intend to satisfy the asset tests described above and plan to take steps to ensure that we satisfy such tests for any quarter with respect to which retesting is to occur, there can be no assurance we will always be successful, or will not require a reduction in our operating partnership’s overall interest in an issuer (including in a taxable REIT subsidiary). If we fail to cure any non-compliance with the asset tests in a timely manner, and the relief provisions described above are not available, we would cease to qualify as a REIT.
Annual Distribution Requirements
To maintain our qualification as a REIT, we are required to distribute dividends, other than capital gain dividends, to our stockholders in an amount at least equal to the sum of:
| • | 90% of our “REIT taxable income;” and | |
| • | 90% of our after-tax net income, if any, from foreclosure property; minus | |
| • | the excess of the sum of certain items of non-cash income over 5% of our “REIT taxable income.” |
For these purposes, our “REIT taxable income” is computed without regard to the dividends paid deduction and our net capital gain. In addition, for purposes of this test, non-cash income means income attributable to leveled stepped rents, original issue discount on purchase money debt, cancellation of indebtedness, or a like-kind exchange that is later determined to be taxable.
Also, our “REIT taxable income” will be reduced by any taxes we are required to pay on any gain we recognize from the disposition of any asset we acquired from a corporation which is or has been a C corporation in a transaction in which our basis in the asset is less than the fair market value of the asset, in each case determined at the time we acquired the asset, within the five-year period following our acquisition of such asset.
144
We generally must pay, or be treated as paying, the distributions described above in the taxable year to which they relate. At our election, a distribution will be treated as paid in a taxable year if it is declared before we timely file our tax return for such year and paid on or before the first regular dividend payment after such declaration, provided such payment is made during the 12-month period following the close of such year. These distributions are treated as received by our stockholders in the year in which paid even though these distributions relate to the prior year for purposes of the 90% distribution requirement. In order to be taken into account for purposes of our distribution requirement, unless we qualify as a “publicly offered REIT,” the amount distributed must not be preferential—i.e., every stockholder of the class of stock to which a distribution is made must be treated the same as every other stockholder of that class, and no class of stock may be treated other than according to its dividend rights as a class. We believe that we are, and expect we will continue to be, a “publicly offered REIT.” To the extent that we do not distribute all of our net capital gain, or distribute at least 90%, but less than 100%, of our “REIT taxable income,” as adjusted, we will be required to pay tax on the undistributed amount at regular corporate tax rates. We intend to make timely distributions sufficient to satisfy these annual distribution requirements and to minimize our corporate tax obligations. In this regard, the partnership agreement of our operating partnership authorizes us, as general partner of our operating partnership, to take such steps as may be necessary to cause our operating partnership to distribute to its partners an amount sufficient to permit us to meet these distribution requirements and to minimize our corporate tax obligation.
We expect that our REIT taxable income will be less than our cash flow because of depreciation and other non-cash charges included in computing REIT taxable income. Accordingly, we anticipate that we generally will have sufficient cash or liquid assets to enable us to satisfy the distribution requirements described above. However, from time to time, we may not have sufficient cash or other liquid assets to meet these distribution requirements due to timing differences between the actual receipt of income and actual payment of deductible expenses, and the inclusion of income and deduction of expenses in determining our taxable income. In addition, we may decide to retain our cash, rather than distribute it, in order to repay debt or for other reasons. In these cases, we may borrow funds to pay dividends or pay dividends through the distribution of other property in order to meet the distribution requirements while preserving our cash.
Under certain circumstances, we may be able to rectify an inadvertent failure to meet the 90% distribution requirement for a year by paying “deficiency dividends” to our stockholders in a later year, which may be included in our deduction for dividends paid for the earlier year. Thus, we may be able to avoid being taxed on amounts distributed as deficiency dividends, subject to the 4% excise tax described below. However, we will be required to pay interest to the IRS based upon the amount of any deduction claimed for deficiency dividends. While the payment of a deficiency dividend will apply to a prior year for purposes of our REIT distribution requirements, it will be treated as an additional distribution to our stockholders in the year such dividend is paid.
Furthermore, we will be required to pay a 4% excise tax to the extent we fail to distribute during each calendar year at least the sum of 85% of our ordinary income for such year, 95% of our capital gain net income for the year and any undistributed taxable income from prior periods. Any ordinary income and net capital gain on which this excise tax is imposed for any year is treated as an amount distributed during that year for purposes of calculating such tax.
For purposes of the 90% distribution requirement and excise tax described above, dividends declared during the last three months of the taxable year, payable to stockholders of record on a specified date during such period and paid during January of the following year, will be treated as paid by us and received by our stockholders on December 31 of the year in which they are declared.
In addition, in order to qualify as a REIT, we may not have, at the end of any taxable year, any undistributed earnings and profits accumulated in any non-REIT taxable year. Any earnings and profits we accumulated before the effective date of our REIT election were distributed to stockholders of record before the end of the first taxable year for which we elected REIT status.
Like-Kind Exchanges
We may dispose of properties in transactions intended to qualify as like-kind exchanges under the Code. Such like-kind exchanges are intended to result in the deferral of gain for U.S. federal income tax purposes. The failure of any such transaction to qualify as a like-kind exchange could subject us to U.S. federal income tax, possibly including the 100% prohibited transaction tax, depending on the facts and circumstances surrounding the particular transaction.
145
Failure To Qualify
If we discover a violation of a provision of the Code that would result in our failure to qualify as a REIT, specified cure provisions may be available to us. Except with respect to violations of the gross income tests and asset tests (for which the cure provisions are described above), and provided the violation is due to reasonable cause and not due to willful neglect, these cure provisions generally impose a $50,000 penalty for each violation in lieu of a loss of REIT status. If we fail to satisfy the requirements for taxation as a REIT in any taxable year, and the relief provisions do not apply, we will be required to pay tax, including any applicable alternative minimum tax, on our taxable income at regular corporate rates. Distributions to stockholders in any year in which we fail to qualify as a REIT will not be deductible by us, and we will not be required to distribute any amounts to our stockholders. As a result, we anticipate that our failure to qualify as a REIT would reduce the cash available for distribution by us to our stockholders. In addition, if we fail to qualify as a REIT, all distributions to stockholders will be taxable as regular corporate dividends to the extent of our current and accumulated earnings and profits. In this event, corporate distributees may be eligible for the dividends-received deduction. In addition, non-corporate stockholders, including individuals, may be eligible for the preferential tax rates on qualified dividend income. Unless entitled to relief under specific statutory provisions, we will also be ineligible to elect to be treated as a REIT for the four taxable years following the year for which we lost our qualification. It is not possible to state whether in all circumstances we would be entitled to this statutory relief.
Tax Aspects of Our Operating Partnership, the Subsidiary Partnerships and the Limited Liability Companies
General
All of our investments will be held indirectly through our operating partnership. In addition, our operating partnership will hold certain of its investments indirectly through subsidiary partnerships and limited liability companies which we expect will be treated as partnerships or disregarded entities for U.S. federal income tax purposes. In general, entities that are treated as partnerships or disregarded entities for U.S. federal income tax purposes are “pass-through” entities which are not required to pay U.S. federal income tax. Rather, partners or members of such entities are allocated their shares of the items of income, gain, loss, deduction and credit of the partnership or limited liability company, and are potentially required to pay tax on this income, without regard to whether they receive a distribution from the partnership or limited liability company. We will include in our income our share of these partnership and limited liability company items for purposes of the various gross income tests, the computation of our REIT taxable income, and the REIT distribution requirements. Moreover, for purposes of the asset tests, we will include our pro rata share of assets held by our operating partnership, including its share of its subsidiary partnerships and limited liability companies, based on our capital interests in each such entity. See “—Taxation of Our Company—General.”
Entity Classification
Our interests in our operating partnership and the subsidiary partnerships and limited liability companies involve special tax considerations, including the possibility that the IRS might challenge the status of these entities as partnerships or disregarded entities. For example, an entity that would otherwise be classified as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes may nonetheless be taxable as a corporation if it is a “publicly traded partnership” and certain other requirements are met. A partnership or limited liability company would be treated as a publicly traded partnership if its interests are traded on an established securities market or are readily tradable on a secondary market or a substantial equivalent thereof, within the meaning of applicable Treasury regulations. Interests in a partnership are not treated as readily tradable on a secondary market, or the substantial equivalent thereof, if all interests in the partnership were issued in one or more transactions that were not required to be registered under the Securities Act, and the partnership does not have more than 100 partners at any time during the taxable year of the partnership, taking into account certain ownership attribution and anti-avoidance rules (the “100 Partner Safe Harbor”). Our operating partnership is currently disregarded from us for U.S. federal income tax purposes and will not be subject to these rules. However, in the event our operating partnership admits additional partners, then our operating partnership will become a partnership subject to these rules and may not qualify for the 100 Partner Safe Harbor. However, interests in our operating partnership will nonetheless be viewed as not readily tradable on a secondary market or the substantial equivalent thereof if the sum of the percentage interests in capital or profits of our operating partnership transferred during any taxable year of our operating partnership does not exceed 2% of the total interests in our operating partnership’s capital or profits, subject to certain exceptions. For purpose of this 2% trading safe harbor, our interests in our operating partnership are excluded from the determination of the percentage interests in capital or profits of our operating partnership. In addition, this 2% trading safe harbor does not apply to transfers by a limited partner in one or more transactions during any 30-day period representing in the aggregate more than 2% of the total interests in our operating partnership’s capital or profits. We, as general partner of our operating partnership, have the authority to take any steps we determine necessary to prevent any trading of interests in our operating partnership that would cause our operating partnership to become a publicly traded partnership, including any steps necessary to ensure compliance with this 2% trading safe harbor.
146
We believe our operating partnership and each of our other partnerships and limited liability companies will be classified as partnerships or disregarded entities for U.S. federal income tax purposes, and we do not anticipate that our operating partnership or any subsidiary partnership or limited liability company will be treated as a publicly traded partnership that is taxable as a corporation. However, if our operating partnership is treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes, it does not qualify for the 100 Partner Safe Harbor, and certain other safe harbor provisions of applicable Treasury regulations are not available, our operating partnership could be classified as a publicly traded partnership.
If our operating partnership or any of our other partnerships or limited liability companies were to be treated as a publicly traded partnership, it would be taxable as a corporation unless it qualified for the statutory “90% qualifying income exception.” Under that exception, a publicly traded partnership is not subject to corporate-level tax if 90% or more of its gross income consists of dividends, interest, “rents from real property” (as that term is defined for purposes of the rules applicable to REITs, with certain modifications), gain from the sale or other disposition of real property, and certain other types of qualifying income. However, if any such entity did not qualify for this exception or was otherwise taxable as a corporation, it would be required to pay an entity-level tax on its income. In this situation, the character of our assets and items of gross income would change and could prevent us from satisfying the REIT asset tests and possibly the REIT income tests. See “—Taxation of Our Company—Asset Tests” and “—Taxation of Our Company—Income Tests.” This, in turn, could prevent us from qualifying as a REIT. See “—Taxation of Our Company—Failure to Qualify” for a discussion of the effect of our failure to meet these tests. In addition, a change in the tax status of our operating partnership or a subsidiary partnership or limited liability company might be treated as a taxable event. If so, we might incur a tax liability without any related cash payment.
Allocations of Income, Gain, Loss and Deduction
A partnership agreement will generally determine the allocation of income and loss among partners. These allocations, however, will be disregarded for tax purposes if they do not comply with the provisions of Section 704(b) of the Code and the Treasury regulations thereunder. Generally, Section 704(b) of the Code and the Treasury regulations thereunder require that partnership allocations respect the economic arrangement of the partners. If an allocation of partnership income or loss does not comply with the requirements of Section 704(b) of the Code and the Treasury regulations thereunder, the item subject to the allocation will be reallocated in accordance with the partners’ interests in the partnership. This reallocation will be determined by taking into account all of the facts and circumstances relating to the economic arrangement of the partners with respect to such item. Our operating partnership’s allocations of taxable income and loss are intended to comply with the requirements of Section 704(b) of the Code and the Treasury regulations thereunder.
Tax Allocations With Respect to the Properties
Under Section 704(c) of the Code, income, gain, loss and deduction attributable to appreciated or depreciated property that is contributed to a partnership in exchange for an interest in the partnership, must be allocated in a manner so that the contributing partner is charged with the unrealized gain or benefits from the unrealized loss associated with the property at the time of the contribution. The amount of the unrealized gain or unrealized loss generally is equal to the difference between the fair market value or book value and the adjusted tax basis of the contributed property at the time of contribution, as adjusted from time to time. These allocations are solely for U.S. federal income tax purposes and do not affect the book capital accounts or other economic or legal arrangements among the partners. Treasury regulations issued under Section 704(c) of the Code provide partnerships with a choice of several methods of accounting for book-tax differences.
Basis in Partnership Interest
Our adjusted tax basis in any partnership interest we own generally will be:
| • | the amount of cash and the basis of any other property we contribute to the partnership; | |
| • | increased by our distributive share of the partnership’s income (including tax-exempt income) and any increase in our allocable share of indebtedness of the partnership; and | |
| • | reduced, but not below zero, by our distributive share of the partnership’s loss (including any non-deductible items), the amount of cash and the basis of property distributed to us, and any reduction in our allocable share of indebtedness of the partnership. |
Loss allocated to us in excess of our basis in a partnership interest will not be taken into account for U.S. federal income tax purposes until we again have basis sufficient to absorb the loss. A reduction of our allocable share of partnership indebtedness will be treated as a constructive cash distribution to us, and will reduce our adjusted tax basis in the partnership interest. Distributions, including constructive distributions, in excess of the basis of our partnership interest will constitute taxable income to us. Such distributions and constructive distributions normally will be characterized as long-term capital gain.
147
Sale of a Partnership’s Property
Generally, any gain realized by a partnership on the sale of property held for more than one year will be long-term capital gain, except for any portion of the gain treated as depreciation or cost recovery recapture. Our share of any partnership’s gain from the sale of inventory or other property held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of the partnership’s trade or business will be treated as income from a prohibited transaction subject to a 100% tax. See “—Taxation of Our Company—Income Tests.”
Partnership Audit Rules
The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015 changed the rules applicable to U.S. federal income tax audits of partnerships. Under the new rules (which are generally effective for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017), among other changes and subject to certain exceptions, any audit adjustment to items of income, gain, loss, deduction, or credit of a partnership (and any partner’s distributive share thereof) is determined, and taxes, interest, or penalties attributable thereto are assessed and collected, at the partnership level. Although it is uncertain how these new rules will be implemented, it is possible that they could result in partnerships (including our operating partnership) in which we directly or indirect invest being required to pay additional taxes, interest and penalties as a result of an audit adjustment, and we, as a direct or indirect partner of these partnerships, could be required to bear the economic burden of those taxes, interest, and penalties even though we, as a REIT, may not otherwise have been required to pay additional corporate-level taxes as a result of the related audit adjustment. The changes created by these new rules are sweeping and in many respects dependent on the promulgation of future regulations or other guidance by the U.S. Treasury. Investors are urged to consult their tax advisors with respect to these changes and their potential impact on their investment in our common stock.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations for Holders of Our Common Stock
The following summary describes the material U.S. federal income tax considerations to you of purchasing, owning and disposing of our common stock. This summary assumes you hold shares of our common stock as a “capital asset” (generally, property held for investment within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code). It does not address all the tax consequences that may be relevant to you in light of your particular circumstances. In addition, this discussion does not address the tax consequences relevant to persons who receive special treatment under the U.S. federal income tax law, except where specifically noted. Holders receiving special treatment include, without limitation:
| • | financial institutions, banks and thrifts; | |
| • | insurance companies; | |
| • | tax exempt entities (except to the extent discussed in “—Taxation of Tax-Exempt Holders of our Common Stock”); | |
| • | “S” corporations; | |
| • | traders in securities that elect to mark to market; | |
| • | partnerships, pass-through entities and persons holding our common stock through a partnership or other pass-through entity; | |
| • | holders subject to the alternative minimum tax; | |
| • | regulated investment companies and REITs; | |
| • | non-U.S. corporations or partnerships, and persons who are not residents or citizens of the United States; | |
| • | broker-dealers or dealers in securities or currencies; | |
| • | U.S. expatriates; | |
| • | persons holding our common stock as part of a hedge, straddle, conversion, integrated or other risk reduction or constructive sale transaction; | |
| • | U.S. persons whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar; or | |
| • | persons who receive our common stock through the exercise of employee stock options or otherwise as compensation. |
148
If you are considering purchasing our common stock, you should consult your tax advisors concerning the application of U.S. federal income tax laws to your particular situation as well as any consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of our common stock arising under the laws of any state, local or non-U.S. taxing jurisdiction.
When we use the term “U.S. holder,” we mean a holder of shares of our common stock who, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, is:
| • | an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States; | |
| • | a corporation or partnership, including an entity treated as a corporation or partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes, created or organized in or under the laws of the United States or of any state thereof or in the District of Columbia unless, in the case of a partnership, Treasury regulations provide otherwise; | |
| • | an estate the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income taxation regardless of its source; or | |
| • | a trust, if (A) a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over its administration, and one or more U.S. persons, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, have the authority to control all of its substantial decisions, or (2) it has a valid election in place to be treated as a U.S. person. |
If you hold shares of our common stock and are not a U.S. holder, a partnership or an entity classified as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes, you are a “non-U.S. holder.”
If a partnership or other entity treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds shares of our common stock, the tax treatment of a partner generally will depend on the status of the partner and on the activities of the partnership. Partners of partnerships holding shares of our common stock are encouraged to consult their tax advisors.
Taxation of Taxable U.S. Holders of Our Common Stock
Distributions Generally
Distributions out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits will be treated as dividends and, other than with respect to capital gain dividends and certain amounts which have previously been subject to corporate level tax, as discussed below, will be taxable to our taxable U.S. holders as ordinary income when actually or constructively received. See “—Tax Rates” below. As long as we qualify as a REIT, these distributions will not be eligible for the dividends-received deduction in the case of U.S. holders that are corporations, nor, except to the extent provided in “—Tax Rates” below, the preferential rates on qualified dividend income applicable to non-corporate U.S. holders, including individuals. For purposes of determining whether distributions to holders of our stock are out of current or accumulated earnings and profits, our earnings and profits will be allocated first to our outstanding preferred stock and then to our outstanding common stock.
To the extent that we make distributions on our common stock in excess of our current and accumulated earnings and profits allocable to such stock, these distributions will be treated first as a tax-free return of capital to a U.S. holder. This treatment will reduce the U.S. holder’s adjusted tax basis in such shares of stock by the amount of the distribution, but not below zero. Distributions in excess of our current and accumulated earnings and profits and in excess of a U.S. holder’s adjusted tax basis in its shares will be taxable as capital gain. Such gain will be taxable as long-term capital gain if the shares have been held for more than one year. Dividends we declare in October, November, or December of any year and which are payable to a holder of record on a specified date in any of these months will be treated as both paid by us and received by the holder on December 31 of that year, provided we actually pay the dividend on or before January 31 of the following year.
Capital Gain Dividends
Dividends that we properly designate as capital gain dividends will be taxable to our taxable U.S. holders as a gain from the sale or disposition of a capital asset held for more than one year, to the extent that such gain does not exceed our actual net capital gain for the taxable year and, for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2015, may not exceed our dividends paid for the taxable year, including dividends paid the following year that are treated as paid in the current year. U.S. holders that are corporations may, however, be required to treat up to 20% of certain capital gain dividends as ordinary income. If we properly designate any portion of a dividend as a capital gain dividend then, except as otherwise required by law, we presently intend to allocate a portion of the total capital gain dividends paid or made available to holders of all classes of our capital stock for the year to the holders of each class of our capital stock in proportion to the amount that our total dividends, as determined for U.S. federal income tax purposes, paid or made available to the holders of each such class of our capital stock for the year bears to the total dividends, as determined for U.S. federal income tax purposes, paid or made available to holders of all classes of our capital stock for the year. In addition, except as otherwise required by law, we will make a similar allocation with respect to any undistributed long term capital gains which are to be included in our stockholders’ long term capital gains, based on the allocation of the capital gains amount which would have resulted if those undistributed long term capital gains had been distributed as “capital gain dividends” by us to our stockholders.
149
Retention of Net Capital Gains
We may elect to retain, rather than distribute as a capital gain dividend, all or a portion of our net capital gains. If we make this election, we would pay tax on our retained net capital gains. In addition, to the extent we so elect, a U.S. holder generally would:
| • | include its pro rata share of our undistributed net capital gains in computing its long-term capital gains in its return for its taxable year in which the last day of our taxable year falls, subject to certain limitations as to the amount that is includable; | |
| • | be deemed to have paid its share of the capital gains tax imposed on us on the designated amounts included in the U.S. holder’s income as long-term capital gain; | |
| • | receive a credit or refund for the amount of tax deemed paid by it; | |
| • | increase the adjusted basis of its stock by the difference between the amount of includable gains and the tax deemed to have been paid by it; and | |
| • | in the case of a U.S. holder that is a corporation, appropriately adjust its earnings and profits for the retained capital gains in accordance with Treasury regulations to be promulgated by the IRS. |
Net Operating Losses
Holders may not include in their individual income tax returns any of our net operating or capital losses. Instead these losses are generally carried over by us for potential offset against our future income.
Passive Activity Losses and Investment Interest Limitations
Distributions we make and gain arising from the sale or exchange by a U.S. holder of our common stock will not be treated as passive activity income. As a result, U.S. holders generally will not be able to apply any “passive losses” against this income or gain. A U.S. holder may elect to treat capital gain dividends, capital gains from the disposition of our common stock and income designated as qualified dividend income, as investment income for purposes of computing the investment interest limitation, but in such case, the holder will be taxed at ordinary income rates on such amount. Other distributions made by our company, to the extent they do not constitute a return of capital, generally will be treated as investment income for purposes of computing the investment interest limitation.
Dispositions of Our Common Stock
A U.S. holder that sells or disposes of shares of common stock will recognize gain or loss for federal income tax purposes in an amount equal to the difference between the amount of cash and the fair market value of any property received on the sale or other disposition and the holder’s adjusted basis in the shares of common stock for tax purposes. Except as provided below, this gain or loss will be long-term capital gain or loss if the holder has held such common stock for more than one year. However, if a U.S. holder recognizes loss upon the sale or other disposition of common stock that it has held for six months or less, after applying certain holding period rules, the loss recognized will be treated as a long-term capital loss to the extent the U.S. holder received distributions from us which were required to be treated as long-term capital gains.
Redemption or Repurchase by Us
A redemption or repurchase of shares of our common stock will be treated under Section 302 of the Code as a distribution (and taxable as a dividend to the extent of our current and accumulated earnings and profits as described above) unless the redemption or repurchase satisfies one of the tests set forth in Section 302(b) of the Code and is therefore treated as a sale or exchange of the redeemed or repurchased shares. The redemption or repurchase generally will be treated as a sale or exchange if it:
| (i) | is “substantially disproportionate” with respect to the U.S. stockholder; |
| (ii) | results in a “complete termination” of the U.S. stockholder’s stock interest in us; or |
| (iii) | is “not essentially equivalent to a dividend” with respect to the U.S. stockholder, |
all within the meaning of Section 302(b) of the Code.
150
In determining whether any of these tests has been met, shares of our capital stock, including common stock and other equity interests in us, considered to be owned by the U.S. stockholder by reason of certain constructive ownership rules set forth in the Code, as well as shares of our capital stock actually owned by the U.S. stockholder, must generally be taken into account. Because the determination as to whether any of the alternative tests of Section 302(b) of the Code will be satisfied with respect to the U.S. stockholder depends upon the facts and circumstances at the time that the determination must be made, U.S. stockholders are advised to consult their tax advisors to determine such tax treatment.
If a redemption or repurchase of shares of our common stock is treated as a distribution taxable as a dividend, the amount of the distribution will be measured by the amount of cash and the fair market value of any property received. A U.S. stockholder’s adjusted basis in the redeemed or repurchased shares of the stock for tax purposes generally will be transferred to its remaining shares of our common stock, if any. If a U.S. stockholder owns no other shares of our capital stock, under certain circumstances, such basis may be transferred to a related person or it may be lost entirely. Proposed Treasury regulations issued in 2009, if enacted in their current form, would affect the basis recovery rules described above. It is not clear whether these proposed regulations will be enacted in their current form or at all. Prospective investors should consult their tax advisors regarding the federal income tax consequences of a redemption or repurchase of our common stock.
If a redemption or repurchase of shares of our common stock is not treated as a distribution taxable as a dividend, it will be treated as a taxable sale or exchange in the manner described under “—Dispositions of Our Common Stock.”
Foreign Accounts
Certain payments made to “foreign financial institutions” in respect of accounts of U.S. holders at such financial institutions may be subject to withholding at a rate of 30%. U.S. holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the effect, if any, of this withholding provision on their ownership and disposition of our common stock and the effective date of such provision. See “—Foreign Accounts.”
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
We are required to report to our U.S. holders and the IRS the amount of dividends paid during each calendar year, and the amount of any tax withheld. Under the backup withholding rules, a U.S. holder may be subject to backup withholding with respect to dividends paid unless the U.S. holder is a corporation or comes within certain other exempt categories and, when required, demonstrates this fact, or provides a taxpayer identification number, certifies as to no loss of exemption from backup withholding, and otherwise complies with applicable requirements of the backup withholding rules. A U.S. holder that does not provide us with its correct taxpayer identification number may also be subject to penalties imposed by the IRS. Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amount paid as backup withholding will be creditable against the U.S. holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability, provided the required information is timely furnished to the IRS. In addition, we may be required to withhold a portion of capital gain distributions to any holders who fail to certify their non-foreign status. See “—Taxation of Non-U.S. Holders of our Common Stock.”
Taxation of Tax-Exempt Holders of Our Common Stock
Dividend income from us and gain arising upon a sale of our shares of common stock generally will not be unrelated business taxable income to a tax-exempt holder, except as described below. This income or gain will be unrelated business taxable income, however, if a tax-exempt holder holds its shares as “debt-financed property” within the meaning of the Code. Generally, “debt-financed property” is property the acquisition or holding of which was financed through a borrowing by the tax-exempt holder.
For tax-exempt holders which are social clubs, voluntary employee benefit associations, supplemental unemployment benefit trusts, or qualified group legal services plans exempt from U.S. federal income taxation under Sections 501(c)(7), (c)(9), (c)(17) or (c)(20) of the Code, respectively, income from an investment in our shares will constitute unrelated business taxable income unless the organization is able to properly claim a deduction for amounts set aside or placed in reserve for specific purposes so as to offset the income generated by its investment in our shares. These prospective investors should consult their tax advisors concerning these “set aside” and reserve requirements.
Notwithstanding the above, however, a portion of the dividends paid by a “pension-held REIT” may be treated as unrelated business taxable income as to certain trusts that hold more than 10%, by value, of the interests in the REIT. A REIT will not be a “pension-held REIT” if it is able to satisfy the “not closely held” requirement without relying on the “look-through” exception with respect to certain trusts or if such REIT is not “predominantly held” by “qualified trusts.” As a result of restrictions on the transfer and ownership of our stock contained in our charter, we do not expect to be classified as a “pension-held REIT,” and as a result, the tax treatment described above should be inapplicable to our holders. However, because our stock is publicly traded, we cannot guarantee that this will always be the case.
151
Taxation of Non-U.S. Holders of Our Common Stock
The following discussion addresses the rules governing U.S. federal income taxation of the purchase, ownership and disposition of our common stock by non-U.S. holders. These rules are complex, and no attempt is made herein to provide more than a brief summary of such rules. Accordingly, the discussion does not address all aspects of U.S. federal income taxation and does not address state, local or non-U.S. tax consequences that may be relevant to a non-U.S. holder in light of its particular circumstances. We urge non-U.S. holders to consult their tax advisors to determine the impact of federal, state, local and non-U.S. income tax laws on the purchase, ownership, and disposition of shares of our common stock, including any reporting requirements.
Distributions Generally
Distributions that are neither attributable to gain from sales or exchanges by us of U.S. real property interests, or “USRPIs,” nor designated by us as capital gain dividends (except as described below) will be treated as dividends of ordinary income to the extent that they are made out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits. Such distributions ordinarily will be subject to withholding of U.S. federal income tax at a 30% rate or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty, unless the distributions are treated as effectively connected with the conduct by the non-U.S. holder of a U.S. trade or business (through a U.S. permanent establishment, where applicable). Under certain treaties, however, lower withholding rates generally applicable to dividends do not apply to dividends from a REIT. If such a distribution is treated as effectively connected with the non-U.S. holder’s conduct of a U.S. trade or business, the non-U.S. holder generally will be subject to federal income tax on the distribution at graduated rates, in the same manner as U.S. holders are taxed on distributions, and also may be subject to the 30% branch profits tax in the case of a corporate non-U.S. holder.
Except as otherwise provided below, we expect to withhold U.S. federal income tax at the rate of 30% on any distributions made to a non-U.S. holder unless:
| 1) | a lower treaty rate applies and the non-U.S. holder files with us an IRS Form W-8BEN (or Form W-8BEN-E, as applicable) evidencing eligibility for that reduced treaty rate; or |
| 2) | the non-U.S. holder files an IRS Form W-8ECI with us claiming that the distribution is income effectively connected with the non-U.S. holder’s trade or business. |
Distributions in excess of our current and accumulated earnings and profits will not be taxable to a non-U.S. holder to the extent that such distributions do not exceed the adjusted basis of the holder’s common stock, but rather will reduce the adjusted basis of such stock. To the extent that such distributions exceed the non-U.S. holder’s adjusted basis in such common stock, they will give rise to gain from the sale or exchange of such stock, the tax treatment of which is described below. Under FIRPTA (discussed below), we may be required to withhold 15% of the portion of any distribution that exceeds our current and accumulated earnings and profits. That being said, for withholding purposes, we expect to treat all distributions as made out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits. However, amounts withheld should generally be refundable if it is subsequently determined that the distribution was, in fact, in excess of our current and accumulated earnings and profits, provided that certain conditions are met.
Capital Gain Dividends and Distributions Attributable to a Sale or Exchange of USRPIs
Distributions to a non-U.S. holder that we properly designate as capital gain dividends, other than those arising from the disposition of USRPI, generally should not be subject to U.S. federal income taxation, unless:
| 1) | the investment in our stock is treated as effectively connected with the non-U.S. holder’s U.S. trade or business (through a U.S. permanent establishment, where applicable), in which case the non-U.S. holder will be subject to the same treatment as U.S. holders with respect to such gain, except that a non-U.S. holder that is a non-U.S. corporation may also be subject to the 30% branch profits tax or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty, as discussed above; or |
| 2) | the non-U.S. holder is a nonresident alien individual who is present in the United States for 183 days or more during the taxable year and certain other conditions are met, in which case the non-U.S. holder will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at a rate of 30% on the non-U.S. holder’s capital gains (or such lower rate specified by an applicable income tax treaty), which may be offset by U.S. source capital losses of such non-U.S. holder (even though the individual is not considered a resident of the United States), provided the non-U.S. holder has timely filed U.S. federal income tax returns with respect to such losses. |
152
Pursuant to the Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act of 1980, which is referred to as “FIRPTA,” distributions to a non-U.S. holder that are attributable to gain from sales or exchanges by us of USRPI, whether or not designated as capital gain dividends, will cause the non-U.S. holder to be treated as recognizing such gain as income effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business. Non-U.S. holders would generally be taxed at the same rates applicable to U.S. holders, subject to any applicable alternative minimum tax, and any non-U.S. holder that is a foreign corporation may also be subject to the 30% branch profits tax or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty. We also will be required to withhold and to remit to the IRS 35% (or 20% to the extent provided in Treasury regulations) of any distribution to non-U.S. holders attributable to gain from sales or exchanges by us of USRPIs. The amount withheld is creditable against the non-U.S. holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability. However, any distribution with respect to any class of stock which is “regularly traded” on an established securities market located in the U.S. is not subject to FIRPTA, and therefore, not subject to the 35% U.S. withholding tax described above, if the non-U.S. holder did not own more than 10% of such class of stock at any time during the one-year period ending on the date of the distribution. Instead, such distributions generally will be treated as ordinary dividend distributions and subject to withholding in the manner described above with respect to ordinary dividends. In addition, distributions to certain non-U.S. publicly traded holders of our common stock that meet certain record-keeping and other requirements (“qualified stockholders”) are exempt from FIRPTA, except to the extent owners of such qualified holders that are not also qualified holders own, actually or constructively, more than 10% of our capital stock. Furthermore, distributions to “qualified foreign pension funds” or entities all of the interests of which are held by “qualified foreign pension funds” are exempt from FIRPTA. Non-U.S. holders of our common stock should consult their tax advisors regarding the application of these rules.
Retention of Net Capital Gains
Although the law is not clear on the matter, it appears that amounts designated by us as retained net capital gains in respect of the stock held by U.S. holders generally should be treated with respect to non-U.S. holders in the same manner as actual distributions of capital gain dividends. Under this approach, the non-U.S. holders would be able to offset as a credit against their U.S. federal income tax liability resulting from their proportionate share of the tax paid by us on such retained net capital gains and to receive from the IRS a refund to the extent their proportionate share of such tax paid by us exceeds their actual U.S. federal income tax liability, provided the non-U.S. holder furnishes required information to the IRS on a timely basis. If we designate any portion of our net capital gain as retained net capital gain, a non-U.S. stockholder should consult its tax advisor regarding the taxation of such retained net capital gain.
Sale of Our Common Stock
Except as described below, gain recognized by a non-U.S. holder upon the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of our common stock generally will not be subject to U.S. taxation unless such stock constitutes a URSPI. In general, stock of a domestic corporation that constitutes a “U.S. real property holding corporation,” or USRPHC, will constitute a USRPI. We believe that we are a USRPHC. Our common stock will not, however, constitute a USRPI so long as we are a “domestically controlled qualified investment entity.” A “domestically controlled qualified investment entity” includes a REIT in which at all times during a specified testing period less than 50% in value of its stock is held directly or indirectly by non-U.S. holders, subject to certain rules. For purposes of determining whether a REIT is a “domestically controlled qualified investment entity,” a person who at all applicable times holds less than 5% of a class of stock that is “regularly traded” is treated as a U.S. person unless the REIT has actual knowledge that such person is not a U.S. person. We believe, but cannot guarantee, that we are a “domestically controlled qualified investment entity.” Because our stock is (and, we anticipate, will continue to be) publicly traded, no assurance can be given that we will continue to be a “domestically controlled qualified investment entity.”
Notwithstanding the foregoing, gain from the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of our common stock not otherwise subject to FIRPTA will be taxable to a non-U.S. holder if either (a) the investment in our common stock is treated as effectively connected with the non-U.S. holder’s U.S. trade or business (through a U.S. permanent establishment, where applicable), in which case the non-U.S. holder will be subject to the same treatment as U.S. holders with respect to such gain, except that a non-U.S. holder that is a foreign corporation may also be subject to the 30% branch profits tax or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty, or (b) the non-U.S. holder is a nonresident alien individual who is present in the U.S. for 183 days or more during the taxable year and certain other conditions are met, in which case the nonresident alien individual will be subject to a 30% tax on the individual’s capital gains (reduced by certain capital losses). In addition, even if we are a domestically controlled qualified investment entity, upon disposition of our common stock, a non-U.S. holder may be treated as having gain from the sale or other taxable disposition of a USRPI if the non-U.S. holder (1) disposes of our common stock within a 30-day period preceding the ex-dividend date of a distribution, any portion of which, but for the disposition, would have been treated as gain from the sale or exchange of a USRPI and (2) acquires, or enters into a contract or option to acquire, or is deemed to acquire, other shares of that stock during the 61-day period beginning with the first day of the 30-day period described in clause (1). The preceding sentence shall not apply to a non-U.S. holder if the non-U.S. holder did not own more than 5% of the stock at any time during the one-year period ending on the date of the distribution described in clause (1) of the preceding sentence and the class of stock as “regularly traded,” as defined by applicable Treasury regulations.
153
Even if we do not qualify as a “domestically controlled qualified investment entity” at the time a non-U.S. holder sells our common stock, gain arising from the sale or other taxable disposition by a non-U.S. holder of such common stock would not be subject to U.S. taxation under FIRPTA as a sale of a USRPI if:
| 1) | such class of common stock is “regularly traded,” as defined by applicable Treasury regulations, on an established securities market such as the NYSE MKT; and |
| 2) | such non-U.S. holder owned, actually and constructively, 10% or less of such class of common stock throughout the shorter of the five-year period ending on the date of the sale or exchange or the non-U.S. holder’s holding period. |
In addition, dispositions of our common stock by qualified stockholders are exempt from FIRPTA, except to the extent owners of such qualified stockholders that are not also qualified stockholders own, actually or constructively, more than 10% of our common stock. An actual or deemed disposition of our common stock by such stockholders may also be treated as a dividend. Furthermore, dispositions of our common stock by “qualified foreign pension funds” or entities all of the interests of which are held by “qualified foreign pension funds” are exempt from FIRPTA. Non-U.S. holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the application of these rules.
If gain on the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of our common stock were subject to taxation under FIRPTA, the non-U.S. holder would be required to file a U.S. federal income tax return and would be subject to regular U.S. federal income tax with respect to such gain in the same manner as a taxable U.S. holder (subject to any applicable alternative minimum tax and a special alternative minimum tax in the case of nonresident alien individuals). In addition, if the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of our common stock were subject to taxation under FIRPTA, and if shares of the applicable class of our common stock were not “regularly traded” on an established securities market, the purchaser of such common stock would be required to withhold and remit to the IRS 15% of the purchase price.
Redemption or Repurchase by Us
A redemption or repurchase of shares of our common stock will be treated under Section 302 of the Code as a distribution (and taxable as a dividend to the extent of our current and accumulated earnings and profits) unless the redemption or repurchase satisfies one of the tests set forth in Section 302(b) of the Code and is therefore treated as a sale or exchange of the redeemed or repurchased shares. See “—Taxation of Taxable U.S. Holders of Our Common Stock—Redemption or Repurchase by Us.” If the redemption or repurchase of shares is treated as a distribution, the amount of the distribution will be measured by the amount of cash and the fair market value of any property received. See “—Taxation of Non-U.S. Holders of Our Common Stock—Distributions Generally.” If the redemption or repurchase of shares is not treated as a distribution, it will be treated as a taxable sale or exchange in the manner described under “—Taxation of Non-U.S. Holders of Our Common Stock—Sale of Our Common Stock.”
Information Reporting Requirements and Backup Withholding
We will report to our stockholders and to the IRS the amount of distributions we pay during each calendar year and the amount of tax we withhold, if any. Under the backup withholding rules, a holder of our common stock may be subject to backup withholding (at a rate of 28%) with respect to distributions unless the holder:
| · | is a corporation or comes within certain other exempt categories and, when required, demonstrates this fact; or |
| · | provides a taxpayer identification number, certifies as to no loss of exemption from backup withholding, and otherwise complies with the applicable requirements of the backup withholding rules. |
A holder who does not provide us with its correct taxpayer identification number also may be subject to penalties imposed by the IRS. Any amount paid as backup withholding generally may be claimed as a credit against the holder’s income tax liability. In addition, we may be required to withhold a portion of capital gain distributions to any holders who fail to certify their non-foreign status to us.
Backup withholding will generally not apply to payments of dividends made by us or our paying agents, in their capacities as such, to a non-U.S. holder provided that the non-U.S. holder furnishes to us or our paying agent the required certification as to its non-U.S. status, such as providing a valid IRS Form W-8BEN or W-8ECI, or certain other requirements are met. Notwithstanding the foregoing, backup withholding may apply if either we or our paying agent has actual knowledge, or reason to know, that the holder is a U.S. person that is not an exempt recipient. Payments of the proceeds from a disposition or a redemption that occurs outside the U.S. by a non-U.S. holder made by or through a foreign office of a broker generally will not be subject to information reporting or backup withholding. However, information reporting (but not backup withholding) generally will apply to such a payment if the broker has certain connections with the U.S. unless the broker has documentary evidence in its records that the beneficial owner is a non-U.S. holder and specified conditions are met or an exemption is otherwise established. Payment of the proceeds from a disposition by a non-U.S. holder of common stock made by or through the U.S. office of a broker is generally subject to information reporting and backup withholding unless the non-U.S. holder certifies under penalties of perjury that it is not a U.S. person and satisfies certain other requirements, or otherwise establishes an exemption from information reporting and backup withholding.
154
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules may be refunded or credited against the holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability if certain required information is furnished to the IRS. Holders of our common stock should consult their own tax advisers regarding application of backup withholding to them and the availability of, and procedure for obtaining an exemption from, backup withholding.
Tax Rates
The maximum tax rate for non-corporate taxpayers for long-term capital gains, including certain “capital gain dividends,” is generally 20% (although depending on the characteristics of the assets which produced these gains and on designations which we may make, certain capital gain dividends may be taxed at a 25% rate). Capital gain dividends will only be eligible for the rates described above to the extent they are properly designated by us as “capital gain dividends.” In general, dividends payable by a REIT that are not “capital gains dividends” are subject to tax at the tax rates applicable to ordinary income. Dividends that a REIT properly designates as “qualified dividend income,” however, are subject to a maximum tax rate of 20% in the case of non-corporate taxpayers. In general, dividends payable by a REIT are only eligible to be taxed as qualified dividend income to the extent that the taxpayer satisfies certain holding requirements with respect to the REIT’s stock and the REIT’s dividends are attributable to dividends received by the REIT from certain taxable corporations (such as its taxable REIT subsidiaries) or to income that was subject to tax at the corporate/REIT level (for example, if the REIT distributed taxable income that it retained and paid tax on in the prior taxable year). In addition, certain U.S. stockholders that are individuals, estates or trusts are required to pay an additional 3.8% Medicare tax on, among other things, dividends and capital gains from the sale or other disposition of stock. Prospective investors should consult their tax advisors regarding the tax rates applicable to them in light of their particular circumstances.
Additional Withholding Tax on Payments Made to Foreign Accounts
Withholding taxes may be imposed under Sections 1471 to 1474 of the Code (such sections commonly referred to as the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act, or FATCA) on certain types of payments made to non-U.S. financial institutions and certain other non-U.S. entities (including payments to U.S. holders who hold shares of our common stock through such a foreign financial institution or non-U.S. entity). Specifically, a 30% withholding tax may be imposed on dividends on our common stock, interest on our debt securities, or gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of our common stock or debt securities, in each case paid to a “foreign financial institution” or a “non-financial foreign entity” (each as defined in the Code), unless (1) the foreign financial institution undertakes certain diligence and reporting obligations, (2) the non-financial foreign entity either certifies it does not have any “substantial United States owners” (as defined in the Code) or furnishes identifying information regarding each substantial United States owner, or (3) the foreign financial institution or non-financial foreign entity otherwise qualifies for an exemption from these rules. If the payee is a foreign financial institution and is subject to the diligence and reporting requirements in clause (1) above, it must enter into an agreement with the U.S. Department of the Treasury under which it undertakes, among other things, to identify accounts held by certain “specified United States persons” or “United States-owned foreign entities” (each as defined in the Code), annually report certain information about such accounts, and withhold 30% on certain payments to non-compliant foreign financial institutions and certain other account holders. Foreign financial institutions located in jurisdictions that have an intergovernmental agreement with the United States governing FATCA may be subject to different rules.
Under the applicable Treasury regulations and administrative guidance, withholding under FATCA generally applies to payments of dividends on our common stock or interest on our debt securities, and will apply to payments of gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of such stock or debt securities on or after January 1, 2019.
Prospective investors should consult their tax advisors regarding the potential application of withholding under FATCA to their investment in our capital stock or debt securities.
Possible Legislative or Other Actions Affecting Tax Consequences
Prospective stockholders should recognize that the present U.S. federal income tax treatment of an investment in us may be modified by legislative, judicial or administrative action at any time and that any such action may affect investments and commitments previously made. The rules dealing with U.S. federal income taxation are constantly under review by persons involved in the legislative process, the IRS and the U.S. Treasury Department, resulting in revisions of regulations and revised interpretations of established concepts as well as statutory changes. Revisions in U.S. federal tax laws and interpretations of these laws could adversely affect the tax consequences of your investment.
Other Tax Consequences
State, local and non-U.S. income tax laws may differ substantially from the corresponding federal income tax laws, and this discussion does not purport to describe any aspect of the tax laws of any state, local or non-U.S. jurisdiction, or any federal tax other than the income tax. Prospective investors should consult their tax advisor regarding the effect of state, local and non-U.S. tax laws with respect to our tax treatment as a REIT and on an investment in our common stock.
155
UNDERWRITING
Under the terms and subject to the conditions in an underwriting agreement dated the date of this prospectus, the underwriters named below, for whom D.A. Davidson & Co. is acting as representative, have severally agreed to purchase, and we have agreed to sell them, severally, the number of shares of common stock indicated below.
| Underwriter | Number
of shares |
||
| D.A. Davidson & Co. | 1,160,000 | ||
| BB&T Capital Markets, a Division of BB&T Securities, LLC | 435,000 | ||
| Oppenheimer & Co. Inc. | 435,000 | ||
| National Securities Corporation | 348,000 | ||
| Wedbush Securities Inc. | 261,000 | ||
| Janney Montgomery Scott LLC | 261,000 | ||
| Total | 2,900,000 |
The underwriters and the representative are collectively referred to as the “underwriters” and the “representative,” respectively. The underwriters are offering the shares of common stock subject to their acceptance of the shares from us and subject to prior sale. The underwriting agreement provides that the obligations of the several underwriters to pay for and accept delivery of the shares of common stock offered by this prospectus are subject to the approval of certain legal matters by their counsel and to certain other conditions. The underwriters are obligated to take and pay for all of the shares of common stock offered by this prospectus if any such shares are taken. However, the underwriters are not required to take or pay for the shares covered by the underwriters’ over-allotment option described below.
The underwriters initially propose to offer part of the shares of common stock directly to the public at the offering price listed on the cover page of this prospectus and part to certain dealers. After the initial offering of the shares of common stock, the offering price, and other selling terms may from time to time be varied by the representative.
We have granted to the underwriters an option, exercisable for 30 days from the date of this prospectus, to purchase up to 435,000 additional shares of common stock at the public offering price listed on the cover page of this prospectus, less underwriting discounts and commissions. The underwriters may exercise this option solely for the purpose of covering over-allotments, if any, made in connection with the offering of the shares of common stock by this prospectus. To the extent the option is exercised, each underwriter will become obligated, subject to certain conditions, to purchase about the same percentage of the additional shares of common stock as the number listed next to the underwriter’s name in the preceding table bears to the total number of shares of common stock listed next to the names of all underwriters in the preceding table.
The following table shows the per share and total public offering price, underwriting discounts and commissions, and proceeds before expenses to the common stock. These amounts are shown assuming both no exercise and full exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase up to an additional 435,000 shares of common stock.
| Per Share | Without Option | With Option | ||||||||
| Public offering price | $ | 19.00 | $ | 55,100,000 | $ | 63,365,000 | ||||
| Underwriting discounts and commissions | $ | 1.33 | $ | 3,857,000 | $ | 4,435,550 | ||||
| Proceeds, before expenses | $ | 17.67 | $ | 51,243,000 | $ | 58,929,450 | ||||
The estimated offering expenses payable by us, exclusive of underwriting discounts and commissions, are approximately $1,150,000. In addition, we have agreed to reimburse the underwriters for certain of their expenses, including reasonable fees of counsel in connection with review by FINRA, in an amount not to exceed $150,000.
Our common stock has been approved for listing, subject to official notice of issuance, on the NYSE MKT under the trading symbol “PLYM.”
We, each of our directors and executive officers, and Torchlight, have agreed that, without the prior written consent of D.A. Davidson & Co., on behalf of the underwriters, they will not, during the period ending 180 days after the date of this prospectus:
| • | offer, pledge, sell, contract to sell, sell any option or contract to purchase, purchase any option or contract to sell, grant any option, right or warrant to purchase, lend or otherwise transfer or dispose of, directly or indirectly, any shares of common stock or any securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for shares of common stock, | |
| • | file any registration statement with the SEC relating to the offering of any shares of common stock, or any securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for shares of common stock; or | |
| • | enter into any swap or other arrangement that transfers to another, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of ownership of the shares of common stock, whether any such transaction described above is to be settled by delivery of shares of common stock or such other securities, in cash or otherwise. |
156
In order to facilitate the offering of the shares of common stock, the underwriters may engage in transactions that stabilize, maintain or otherwise affect the price of the shares of common stock. Specifically, the underwriters may sell more shares than they are obligated to purchase under the underwriting agreement, creating a short position. A short sale is covered if the short position is no greater than the number of shares available for purchase by the underwriters under the over-allotment option. The underwriters can close out a covered short sale by exercising the over-allotment option or purchasing shares in the open market. In determining the source of shares to close out a covered short sale, the underwriters will consider, among other things, the open market price of shares compared to the price available under the over-allotment option. The underwriters may also sell shares in excess of the over-allotment option, creating a naked short position. The underwriters must close out any naked short position by purchasing shares in the open market. A naked short position is more likely to be created if the underwriters are concerned that there may be downward pressure on the price of the shares of common stock in the open market after pricing that could adversely affect investors who purchase in this offering. As an additional means of facilitating this offering, the underwriters may bid for, and purchase, shares of common stock in the open market to stabilize the price of the shares of common stock. These activities may raise or maintain the market price of the shares of common stock above independent market levels or prevent or retard a decline in the market price of the shares of common stock. The underwriters are not required to engage in these activities and may end any of these activities at any time.
We and the underwriters have agreed to indemnify each other against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act.
A prospectus in electronic format may be made available on websites maintained by one or more underwriters, or selling group members, if any, participating in this offering. The representative may agree to allocate a number of shares of common stock to underwriters for sale to their online brokerage account holders. Internet distributions will be allocated by the representative to underwriters that may make Internet distributions on the same basis as other allocations.
Pricing of the Offering
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for the shares of common stock. The price was determined by negotiations between us and the representative. Among the factors considered in determining the price were our future prospects and those of its industry in general, the company’s revenues, earnings and certain other financial and operating information in recent periods, and the price-earnings ratios, price-sales ratios, market prices of securities, and certain financial and operating information of companies engaged in activities similar to our activities.
157
LEGAL MATTERS
Certain legal matters will be passed upon for us by Winston & Strawn LLP and for the underwriters by Morrison & Foerster LLP.
EXPERTS
The following financial statements have been audited by Marcum LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in its report included in this prospectus, and have been included in this prospectus in reliance on such report, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting: the historical consolidated financial statements of our company as of and for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We maintain a web site at www.plymouthreit.com. Information contained on, or accessible through our website is not incorporated by reference into and does not constitute a part of this prospectus or any other report or documents we file with or furnish to the SEC.
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-11, including exhibits and schedules filed with the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, under the Securities Act, with respect to the shares of common stock to be sold in this offering. This prospectus does not contain all of the information set forth in the registration statement and exhibits and schedules to the registration statement. For further information with respect to us and the shares of common stock to be sold in this offering, reference is made to the registration statement, including the exhibits and schedules to the registration statement. Copies of the registration statement, including the exhibits and schedules to the registration statement, may be examined without charge at the public reference room of the SEC, 100 F Street, N.E., Room 1580, Washington, D.C. 20549. Information about the operation of the public reference room may be obtained by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0300. Copies of all or a portion of the registration statement may be obtained from the public reference room of the SEC upon payment of prescribed fees. Our SEC filings, including our registration statement, are also available to you, free of charge, on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
Additionally, we file annual, quarterly and current reports and proxy statements with the SEC. The periodic reports and other confirmation are available for inspection and copying at the SEC’s public reference facilities and the website of the SEC referred to above. We will make available to our stockholders annual reports containing audited financial information for each year and quarterly reports for the first three quarters of each fiscal year containing unaudited interim financial information.
158
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. | |
| Explanatory Note | F-2 |
| Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements: | |
| Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet as of March 31, 2017 | F-3 |
| Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Statement of Operations for the Three Months Ended March 31, 2017 | F-4 |
| Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Statement of Operations for the Year Ended December 31, 2016 | F-5 |
| Notes to Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements | F-6 |
| Consolidated Historical Financial Statements: | |
| Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets as of March 31, 2017 Unaudited and December 31, 2016 | F-7 |
| Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the Three Months Ended March 31, 2017 and 2016 Unaudited | F-8 |
| Condensed Consolidated Statements of Changes in Deficit for the Three Months Ended March 31, 2017 Unaudited | F-9 |
| Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for Three Months Ended March 31, 2017 and 2016 Unaudited | F-10 |
| Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements | F-11 |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | F-22 |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 | F-23 |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations for the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 | F-24 |
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Deficit for the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 | F-25 |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 | F-26 |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | F-27 |
| Financial Statement Schedule | |
| Schedule III. Real Estate Properties and Accumulated Depreciation | F-40 |
F-1
Explanatory Note
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc., or the Company, a Maryland corporation, is a full service, vertically integrated, self-administered and self-managed Maryland corporation focused on the acquisition, ownership and management of single and multi-tenant Class B industrial properties, including distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties, primarily located in secondary and select primary markets across the U.S.
The Company has elected to be taxed as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes commencing with the Company’s taxable year ended December 31, 2012. As a REIT, the Company generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax to the extent it distributes its REIT taxable income to its stockholders, subject to other statutory provisions in the Internal Revenue Code of 1986.
The accompanying unaudited pro forma condensed consolidated financial statements have been derived from the historical condensed consolidated financial statements of the Company. The unaudited pro forma condensed consolidated balance sheet as of March 31, 2017 is presented to reflect adjustments to the Company’s historical balance sheet as if the Company’s initial public offering of its common stock, or the offering, and the concurrent private placement to affiliates of Torchlight Investors, LLC, or Torchlight, and the concurrent issuance of warrants to Torchlight, or together, the Torchlight Transactions, were completed on March 31, 2017. The unaudited pro forma condensed consolidated statements of operations for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and for the year ended December 31, 2016 are presented as if the Offering and the Torchlight Transactions were completed on the first day of the period presented.
The accompanying unaudited pro forma condensed consolidated financial statements and unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements as of March 31, 2017 and 2016 and the three months then ended, should be read in conjunction with (i) the Company’s historical consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 and historical consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015; and (ii) the “Risk Factors,” “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” sections in this prospectus. The Company has based the unaudited pro forma adjustments on available information and assumptions that it believes are reasonable. The following unaudited pro forma condensed consolidated financial statements are presented for informational purposes only and are not necessarily indicative of what the Company’s actual financial position would have been as of March 31, 2017 assuming the offering and the Torchlight Transactions had been completed on March 31, 2017, what actual results of operations would have been for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and the year ended December 31, 2016 assuming the offering and the Torchlight Transactions were completed on the first day of the period presented, and are not indicative of future results of operations or financial condition and should not be viewed as indicative of future results of operations or financial condition.
F-2
Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Balance
Sheet
As of March 31, 2017
(Unaudited and in thousands)
| Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. | Proceeds from IPO and Private Placement | Redemption of Preferred Member Interest | Company Pro Forma | |||||||||||||
| (A) | (B) | (C) | ||||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||||
| Real estate properties | $ | 139,123 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 139,123 | ||||||||
| Less Accumulated Depreciation | (17,916 | ) | (17,916 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Real estate properties, net | 121,207 | — | — | 121,207 | ||||||||||||
| Cash | 1,151 | 50,093 | (20,000 | ) | 31,244 | |||||||||||
| Restricted Cash | 771 | 771 | ||||||||||||||
| Cash held in escrow | 3,103 | 3,103 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred leasing intangibles | 9,610 | 9,610 | ||||||||||||||
| Other current assets | 1,601 | 1,601 | ||||||||||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 137,443 | $ | 50,093 | $ | (20,000 | ) | $ | 167,536 | |||||||
| Liabilities & Equity (Deficit) | ||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||
| Senior secured debt, net | $ | 116,258 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 116,258 | ||||||||
| Mezzanine debt to investor, net | 29,292 | 29,292 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred interest | 207 | 207 | ||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable and other liabilities | 4,870 | 4,870 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred leasing-intangibles | 1,278 | 1,278 | ||||||||||||||
| Redeemable preferred member interest in subsidiary | 25,000 | (5,000 | ) | (20,000 | ) | — | ||||||||||
| Total Liabilities | 176,905 | (5,000 | ) | (20,000 | ) | 151,905 | ||||||||||
| Equity | ||||||||||||||||
| Common Shares | 3 | 32 | 35 | |||||||||||||
| Additional Paid in Capital | 12,477 | 55,061 | 59,005 | 126,543 | ||||||||||||
| Accumulated Deficit | (110,947 | ) | (110,947 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Total Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. stockholders' deficit | (98,467 | ) | 55,093 | 59,005 | 15,631 | |||||||||||
| Non-controlling deficit | 59,005 | (59,005 | ) | — | ||||||||||||
| Total equity (deficit) | (39,462 | ) | 55,093 | — | 15,631 | |||||||||||
| Total Liabilities and Equity | $ | 137,443 | $ | 50,093 | $ | (20,000 | ) | $ | 167,536 | |||||||
F-3
Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Statement
of Operations
For the Three Months Ended March 31, 2017
(Unaudited and in thousands)
| Plymouth | ||||||||||||
| Industrial | Pro Forma | Pro | ||||||||||
| REIT, Inc. | Adjustments | Forma | ||||||||||
| (A) | (B) | |||||||||||
| Revenues: | ||||||||||||
| Rental revenue | $ | 4,938 | $ | — | $ | 4,938 | ||||||
| Other Income | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Total revenues | 4,939 | — | 4,939 | |||||||||
| Operating Expenses: | ||||||||||||
| Property | 1,408 | 1,408 | ||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | — | 2,772 | |||||||||
| General and administrative | 724 | 162 | 886 | |||||||||
| Acquisition expenses | — | — | — | |||||||||
| Total expenses | 4,904 | 162 | 5,066 | |||||||||
| Operating income | 35 | (162 | ) | (127 | ) | |||||||
| Other expense : | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (2,941 | ) | 338 | (2,603 | ) | |||||||
| Total other expense | (2,941 | ) | 338 | (2,603 | ) | |||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | 176 | $ | (2,730 | ) | ||||
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest | $ | (2,465 | ) | $ | 2,465 | $ | — | |||||
| Net loss attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. common stockholders | $ | (441 | ) | $ | (2,289 | ) | $ | (2,730 | ) | |||
| Loss per share | $ | (1.33 | ) | $ | (0.78 | ) | ||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding | 331,965 | 3,163,158 | 3,495,123 | |||||||||
F-4
Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Statement
of Operations
For the Year Ended December 31, 2016
(Unaudited and in thousands)
| Plymouth | ||||||||||||
| Industrial | Pro Forma | Pro | ||||||||||
| REIT, Inc. | Adjustments | Forma | ||||||||||
| (A) | (B) | |||||||||||
| Revenues: | ||||||||||||
| Rental revenue | $ | 19,658 | $ | — | $ | 19,658 | ||||||
| Other income | 230 | — | 230 | |||||||||
| Total revenues | 19,888 | — | 19,888 | |||||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||
| Property | 5,927 | 5,927 | ||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 11,674 | — | 11,674 | |||||||||
| General and administrative | 3,742 | 650 | 4,392 | |||||||||
| Acquisition expenses | — | — | — | |||||||||
| Total Operating expenses | 21,343 | 650 | 21,993 | |||||||||
| Operating loss | (1,455 | ) | (650 | ) | (2,105 | ) | ||||||
| Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||
| Gain on disposition of equity investment | 2,846 | 2,846 | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | (40,679 | ) | 490 | (40,189 | ) | |||||||
| Total other expense | (37,833 | ) | 490 | (37,343 | ) | |||||||
| Net loss | (39,288 | ) | (160 | ) | (39,448 | ) | ||||||
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest | (2,301 | ) | 2,301 | — | ||||||||
| Net loss attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. | (36,987 | ) | (2,461 | ) | (39,448 | ) | ||||||
| Loss per share | $ | (111.42 | ) | $ | (11.29 | ) | ||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding | 331,965 | 3,163,158 | 3,495,123 | |||||||||
F-5
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Unaudited Pro Forma
Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(dollars in thousands)
1. Notes to the Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet as of March 31, 2017
(A) Reflects the historical Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet of Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. as of March 31, 2017.
(B) Reflects the net proceeds of the offering in the amount of $50,093 for the issuance of 2,900,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.01, at $19 per share. It also reflects the private placement in which 263,158 shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, will be issued to Torchlight in partial satisfaction ($5,000) of the redemption of the Preferred Member Interest and an aggregate of 115,790 restricted shares of the Company’s common stock to be granted to the Company’s executive officers and an aggregate of 15,789 restricted shares of the Company’s common stock to be granted to the Company’s independent directors, in each case, upon the closing of this offering.
(C) Reflects the agreed redemption of the Preferred Member Interest at the time of the offering. The non-controlling interest is eliminated effective with the redemption of the Preferred Member Interest.
2. Notes to the Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Statement of Operations for the three months ended March 31, 2017
(A) Reflects the historical condensed consolidated statement of operations of Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. for the three months ended March 31, 2017.
(B) Reflects an adjustment for the elimination of interest expense related to the Preferred Member Interest considered redeemed as of the first day of the period ended March 31, 2017 and reflects stock-based compensation associated with the issuance of an aggregate of 131,579 shares of the Company’s common stock to be issued to the Company’s executive officers and independent directors upon the closing of this offering which is recognized over the applicable annual vesting and related service period of the 115,790 shares to be granted to the Company’s executive officers (four years) and the 15,789 shares to be granted to the Company’s independent directors (three years).
As part of the Torchlight transactions the Company granted Torchlight warrants to purchase 250,000 shares of the Company’s common stock at $23 per share. The warrants expire five years from the closing of the offering. The weighted average shares outstanding for the period ended March 31, 2017 does not include the 131,579 shares of common stock to be issued to the Company’s executive officers and independent directors upon the closing of the offering. There were no vested shares for the three months ended March 31, 2017 on a pro forma basis.
3. Notes to the Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Statement of Operations for the year ended December 31, 2016
(A) Reflects the historical consolidated statement of operations of Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. for the year ended December 31, 2016.
(B) Reflects an adjustment for the elimination of interest expense related to the preferred member interest considered redeemed as of the first day of the year ended December 31, 2016 and reflects stock-based compensation associated with the issuance of an aggregate of 131,579 shares of the Company’s common stock to be issued to the Company’s executive officers and independent directors upon the closing of the offering which is recognized over the applicable annual vesting and related service period of the 115,790 shares to be granted to the Company’s executive officers (four years) and the 15,789 shares to be granted to the Company’s independent directors (three years).
As part of the Torchlight transactions the Company granted Torchlight warrants to purchase 250,000 shares of common stock at $23 per share. The warrants expire five years from the closing of the offering. The weighted average shares outstanding for the year ended December 31, 2016 does not include the 131,579 shares of the Company’s common stock to be issued to the Company’s executive officers and independent directors upon the closing of this offering. There were no vested shares for the year ended December 31, 2016 on a pro forma basis.
F-6
PLYMOUTH INDUSTRIAL REIT, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
| March 31, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| (Unaudited) | ||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||
| Real estate properties | $ | 139,123 | $ | 139,086 | ||||
| Less Accumulated Depreciation | (17,916 | ) | (16,027 | ) | ||||
| Real estate properties, net | 121,207 | 123,059 | ||||||
| Cash | 1,151 | 941 | ||||||
| Restricted cash | 771 | 6,353 | ||||||
| Cash held in escrow | 3,103 | 2,907 | ||||||
| Deferred lease intangibles, net | 9,610 | 10,533 | ||||||
| Other assets | 1,601 | 1,953 | ||||||
| Total assets | $ | 137,443 | $ | 145,746 | ||||
| Liabilities and deficit | ||||||||
| Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Senior secured debt, net | $ | 116,258 | $ | 116,053 | ||||
| Mezzanine debt to investor, net | 29,292 | 29,262 | ||||||
| Deferred interest | 207 | 207 | ||||||
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities | 4,870 | 5,352 | ||||||
| Deferred lease intangibles, net | 1,278 | 1,405 | ||||||
| Redeemable preferred member interest in subsidiary | 25,000 | 31,043 | ||||||
| Total | 176,905 | 183,322 | ||||||
| Deficit: | ||||||||
| Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. Stockholders' Deficit: | ||||||||
| Preferred stock, par value $0.01 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; none issued and outstanding | ||||||||
| Common stock, $0.01 par value: 900,000,000 shares authorized; 331,965 shares issued and outstanding | 3 | 3 | ||||||
| Additional paid in capital | 12,477 | 12,477 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (110,947 | ) | (110,506 | ) | ||||
| Total Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. stockholders' deficit | (98,467 | ) | (98,026 | ) | ||||
| Non-controlling interest | 59,005 | 60,450 | ||||||
| Total deficit | (39,462 | ) | (37,576 | ) | ||||
| Total liabilities and deficit | $ | 137,443 | $ | 145,746 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-7
PLYMOUTH INDUSTRIAL REIT, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
UNAUDITED
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
| For the Period | ||||||||
| Ended March 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Rental revenue | $ | 4,938 | $ | 4,808 | ||||
| Other Income | 1 | 30 | ||||||
| Total revenues | 4,939 | 4,838 | ||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||
| Property | 1,408 | 1,412 | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 3,028 | ||||||
| General and administrative | 724 | 911 | ||||||
| Acquisition costs | — | 19 | ||||||
| Total operating expenses | 4,904 | 5,370 | ||||||
| Operating Income (loss) | 35 | (532 | ) | |||||
| Other expense: | ||||||||
| Interest expense | (2,941 | ) | (13,784 | ) | ||||
| Total other expense | (2,941 | ) | (13,784 | ) | ||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | ||
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest | $ | (2,465 | ) | $ | — | |||
| Net loss attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. | $ | (441 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | ||
| Net loss per share attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. common stockholders | $ | (1.33 | ) | $ | (43.13 | ) | ||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding basic and diluted | 331,965 | 331,965 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-8
PLYMOUTH INDUSTRIAL REIT, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN DEFICIT
UNAUDITED
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
| Additional | Total Plymouth Industrial REIT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock, $0.01 Par Value | Paid in | Accumulated | Stockholders' | Non-controlling | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Capital | Deficit | Deficit | Interest | Deficit | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance January 1, 2017 | 331,965 | $ | 3 | $ | 12,477 | $ | (110,506 | ) | $ | (98,026 | ) | $ | 60,450 | $ | (37,576 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Non cash capital contribution by investor related to adjustment of Redemption Price of redeemable preferred interest | 1,020 | 1,020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | (441 | ) | (441 | ) | (2,465 | ) | (2,906 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Balance, March 31, 2017 | 331,965 | $ | 3 | $ | 12,477 | $ | (110,947 | ) | $ | (98,467 | ) | $ | 59,005 | $ | (39,462 | ) | ||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-9
PLYMOUTH INDUSTRIAL REIT, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
UNAUDITED
(In thousands)
| Three Months Ended | Three Months Ended | |||||||
| March 31, | March 31, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Operating activities | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,906 | ) | $ | (14,316 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,772 | 3,028 | ||||||
| Straight line rent adjustment | (45 | ) | (75 | ) | ||||
| Intangible amortization in rental revenue, net | (82 | ) | (89 | ) | ||||
| Equity investment (income) loss | — | (30 | ) | |||||
| Accretion of interest and deferred interest | 794 | 2,700 | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
| Security deposits | — | 7 | ||||||
| Other assets | 397 | 53 | ||||||
| Cash held in escrow | 202 | — | ||||||
| Deferred leasing costs | (6 | ) | — | |||||
| Deferred interest | — | 7,615 | ||||||
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities | (482 | ) | 1,543 | |||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 644 | 436 | ||||||
| Investing activities | ||||||||
| Real estate improvements | (36 | ) | (258 | ) | ||||
| Increase in cash held in escrow | (398 | ) | — | |||||
| Distributions from investment in joint ventures | — | 49 | ||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (434 | ) | (209 | ) | ||||
| Net increase in cash | 210 | 227 | ||||||
| Cash at beginning of period | 941 | 698 | ||||||
| Cash at end of period | $ | 1,151 | $ | 925 | ||||
| Supplemental Cash Flow Disclosures: | ||||||||
| Interest paid | $ | 2,147 | $ | 1,390 | ||||
| Supplemental Non-cash Financing and Investing Activities: | ||||||||
| Application of restricted cash to redeemable preferred membership interest | $ | 5,582 | $ | — | ||||
| Improvements to real estate included in accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities | $ | — | $ | 59 | ||||
| Non cash capital contribution by investor related to adjustment of Redemption Price of redeemable preferred interest | $ | 1,020 | $ | — | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-10
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
1. Nature of the Business and Basis of Presentation
Business
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc., (the “Company” or the “REIT”) is a Maryland corporation formed on March 7, 2011. The Company is a full service, vertically integrated, self-administered and self-managed organization. The Company is focused on the acquisition, ownership and management of single and multi-tenant Class B industrial properties, including distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties, primarily located in secondary and select primary markets across the U.S. As of March 31, 2017, the Company through its subsidiaries owns an interest in 20 industrial properties comprising approximately 4,000,000 square feet.
On October 17, 2016, the Company completed a reorganization of its subsidiary structure simultaneously with the refinancing of the Company’s existing debt. The Company issued non-controlling interests to a financial investor and lender, Torchlight, in newly established legal entities to hold the properties. The refinancing of the Company’s debt is further discussed in Note 6.
The accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements include the following entities:
| Name | Relationship | Formation | ||
| Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. | Parent | 2011 | ||
| Plymouth Industrial OP LP | Wholly-owned subsidiary | 2011 | ||
| Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC | Wholly-owned subsidiary | 2016 | ||
| Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC (20 LLC) | Controlling interest* | 2016 | ||
| 20 individual property LLCs | Controlling interest* | 2014 |
* See note 10 for discussion of non-controlling interests.
Basis of Presentation
The Company’s condensed consolidated financial statements include its financial statements, and those of its wholly-owned subsidiaries and controlling interests. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. The Company considers the issuance of member interests in entities that hold its properties under the guidance of ASC 360 Property, Plant and Equipment (ASC 360), and ASC 976, Real Estate, (ASC 976) as referenced by ASC 810, Consolidation, (ASC 810).
These interim condensed consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP"). All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. These interim condensed consolidated financial statements include adjustments of a normal and recurring nature considered necessary by management to fairly present the Company's financial position and results of operations. These interim condensed consolidated financial statements may not be indicative of financial results for the full year. The interim condensed consolidated financial statements and notes thereto should be read in conjunction with the Company's audited financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 included elsewhere in this filing.
F-11
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
1. Nature of the Business and Basis of Presentation
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the condensed consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the condensed consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Management makes significant estimates regarding impairments. These estimates and assumptions are based on management’s best estimates and judgment. Management evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis using historical experience and other factors, including the current economic environment. The current economic environment has increased the degree of uncertainty inherent in these estimates and assumptions. Management adjusts such estimates when facts and circumstances dictate. As future events and their effects cannot be determined with precision, actual results could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
Risks and Uncertainties
The state of the overall economy can significantly impact the Company’s operational performance and thus impact its financial position. Should the Company experience a significant decline in operational performance, it may affect the Company’s ability to make distributions to its stockholders, service debt, or meet other financial obligations.
Liquidity and Going Concern
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared on a basis which assumes that the Company will continue as a going concern and which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities and commitments in the ordinary course of business.
At March 31, 2017, the Company has an accumulated deficit of $110,947 and had limited amounts of liquidity evidenced by the cash position of $1,151 as of March 31, 2017. The Company continues to maintain arrangements with certain of its vendors to limit future expenses related to certain professional services.
The Company is currently in technical violation of the net worth covenant under the terms of the AIG Loan (as defined below). On May 3, 2017, we entered into an agreement with AIG pursuant to which AIG has agreed to waive this default from October 17, 2016 up to and including June 30, 2017. If prior to June 30, 2017 the offering does not occur or we are not able to negotiate a resolution of the default with our senior lender, the lender could declare all amounts due, including default interest at a rate substantially in excess of the stated rate, under the AIG Loan immediately due and payable.
Through March 31, 2017, the Company has derived the capital required to purchase and originate real estate related investments and conduct our operations from the proceeds of our prior offering, from secured financings from banks and other lenders and from any undistributed funds from our operations.
The Company’s ability to meet its working capital needs, repay the redeemable preferred membership interest and make its required payments under its senior mortgage debt and mezzanine loan is dependent on its ability to issue additional equity or secure additional debt financing. The Company has engaged D. A. Davidson & Co., investment banking, as underwriters for a proposed initial public offering (IPO or Offering) on a firm commitment basis. There is no assurance, however, that additional debt or other forms of capital, including the proposed IPO, will be available to the Company, or on terms acceptable to the Company.
These conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern within one year after the date the condensed consolidated financial statements are issued. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
F-12
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
The accounting policies underlying the accompanying unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements are those set forth in the Company's audited financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 included elsewhere in this filing. Additional information regarding the Company’s significant accounting policies related to the accompanying interim financial statements is as follows:
Segments
The Company has one reportable segment–industrial properties. These properties have similar economic characteristics and also meet the other criteria that permit the properties to be aggregated into one reportable segment.
Revenue Recognition and Tenant Receivables and Rental Revenue Components
Minimum rental income from real estate operations is recognized on a straight-line basis. The straight-line rent calculation on leases includes the effects of rent concessions and scheduled rent increases, and the calculated straight-line rent income is recognized over the lives of the individual leases. The Company maintains allowances for doubtful accounts receivable and straight-line rents receivable, based upon estimates determined by management. Management specifically analyzes aged receivables, tenant credit-worthiness and current economic trends when evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts. At March 31, 2017 and at December 31, 2016 the Company did not recognize an allowance for doubtful accounts.
For the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, rental income was derived from various tenants. As such, future receipts are dependent upon the financial strength of the lessees and their ability to perform under the lease agreements.
The following tenants represent 10% or greater of rental revenue for the period ended March 31, 2017 and 2016:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Pier One | 12.7% | 12.3% | ||||||
| Perseus | 10.0% | 10.2% | ||||||
Rental revenue is comprised of the following:
| Period Ended | Period Ended | |||||||
| March 31, | March 31, | |||||||
| (in thousands) | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||
| Income from leases | $ | 3,517 | $ | 3,429 | ||||
| Straight-line rent adjustment | 45 | 76 | ||||||
| Reimbursable expenses | 1,293 | 1,215 | ||||||
| Amortization of above market leases | (45 | ) | (45 | ) | ||||
| Amortization of below market leases | 128 | 133 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 4,938 | $ | 4,808 | ||||
F-13
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. There were no cash equivalents at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016. The Company maintains cash and restricted cash, which includes tenant security deposits and cash collateral for its borrowings discussed in Notes 6 and 9, cash held in escrow for real estate tax, insurance and tenant capital improvement and leasing commissions, in bank deposit accounts, which at times may exceed federally insured limits. As of March 31, 2017, the Company has not realized any losses in such cash accounts and believes it is not exposed to any significant risk of loss.
Financial Instruments
The Company estimates that the carrying value of cash, restricted cash, cash held in escrow and reserves, senior secured debt, mezzanine debt to investor, redeemable preferred member interests and deferred interest, approximate their fair values based on their short-term maturity and prevailing interest rates.
Deferred Offering Costs
The Company capitalizes certain legal and other third-party fees that are directly associated with in-process equity financings as deferred offering costs until such financings are consummated. There were no deferred offering costs on the Company’s condensed consolidated balance sheet at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016.
Debt Issuance Costs
The Company adopted ASU 2015-03, Interest—Imputation of Interest (Subtopic 835-30) (“ASU 2015-03”) in 2016. In accordance with the adoption of ASU No. 2015-03, debt issuance costs are reflected as a reduction to the respective loan amounts in the form of a debt discount. Amortization of this expense is included in interest expense in the condensed consolidated statements of operations.
Debt issuance costs amounted to $4,799 at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, and related accumulated amortization amounted to $349 and $113 at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. Unamortized debt issuance costs amounted to $4,450 and $4,686 at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively.
Comprehensive Loss
Comprehensive loss includes net loss as well as other changes in deficit that result from transactions and economic events other than those with members. There was no difference between net loss and comprehensive loss for the periods ended March 31, 2017 and 2016.
Earnings per Share
Basic net loss per share is computed by dividing net loss attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. by the weighted average shares of common stock outstanding for each year, which is also presented on the condensed consolidated statements of operations. Diluted net loss per share is the same as basic net loss per share since the Company does not have any common stock equivalents such as stock options. The Company has not granted any stock options or stock-based awards under the 2014 Incentive Award Plan.
F-14
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
3. Real Estate Properties
Real estate properties consisted of the following at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016:
| March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| Land and improvements | $ | 18,117 | $ | 18,117 | ||||
| Buildings | 110,545 | 110,142 | ||||||
| Site improvements | 10,442 | 10,442 | ||||||
| Construction in process | 19 | 385 | ||||||
| 139,123 | 139,086 | |||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation | (17,916 | ) | (16,027 | ) | ||||
| Real estate properties | $ | 121,207 | $ | 123,059 | ||||
Depreciation expense was $1,888 and $1,861 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
4. Deferred Lease Intangibles
Deferred Lease Intangible assets consisted of the following at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016 :
| March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| Above market lease | $ | 1,122 | $ | 1,122 | ||||
| Lease in place | 14,289 | 14,289 | ||||||
| Tenant relationships | 2,068 | 2,068 | ||||||
| Leasing commission | 2,606 | 2,606 | ||||||
| Leasing commission after acquisition | 263 | 258 | ||||||
| 20,348 | 20,343 | |||||||
| Less Accumulated amortization | (10,738 | ) | (9,810 | ) | ||||
| Deferred lease intangibles | $ | 9,610 | $ | 10,533 | ||||
Deferred Lease Intangibles - Below Market Leases at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016:
| March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| Below market leases | $ | 2,548 | $ | 2,548 | ||||
| Less accumulated amortization | (1,270 | ) | (1,143 | ) | ||||
| Deferred lease intangibles | $ | 1,278 | $ | 1,405 | ||||
Amortization of above and below market leases was recorded as an adjustment to revenues and amounted to $82 and $89 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Amortization of all other deferred lease intangibles has been included in depreciation and amortization in the accompanying condensed consolidated statements of operations and amounted to $884 and $1,167 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
F-15
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
5. Investment in Real Estate Joint Venture
In 2013, the Company acquired a 50.3% interest in TCG 5400 FIB LP (“5400 FIB”), which owned a warehouse facility (the “Property”) in Atlanta, Georgia containing 682,750 rentable square feet of space, which was obtained in 2013 for a total of $3,900. The Company accounted for the investment under the equity method since it did not have control over the investment. The carrying value of the investment was $2,987 at December 31, 2015.
The property was sold in November 2016 and the Company received $5,582 as a return of its investment. The Company recorded a gain on the disposition of the investment in the amount of $2,846 in 2016. The Company included the cash proceeds from the investment in restricted cash in the condensed consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2016 since the amount served as collateral for the borrowing arrangements with Torchlight discussed in Notes 6 and 9. The amount was released from restricted cash in February, 2017 and applied to the redeemable preferred member interest.
6. Borrowing Arrangements
On October 17, 2016, the Company completed a reorganization of its subsidiary structure in connection with the refinancing of the Company’s existing debt. The Company issued non-controlling interests to a financial investor and lender, Torchlight, in newly established legal entities to hold the properties owned by the REIT.
Previous Borrowing Arrangement
On October 28, 2014, the Company, its wholly-owned subsidiary Plymouth Industrial OP LP, its Operating Partnership, and certain subsidiaries of its Operating Partnership entered into a senior secured loan agreement (Senior Loan) with investment entities, or the Funds, managed by Senator Investment Group LP (Senator). The Senior Loan was a $192,000 facility with $71,000 designated as Tranche A, $101,000 designated as Tranche B and $20,000 designated as Tranche C and the deemed original issue discount.
The Company borrowed $69,200 under Tranche A and $95,800 under Tranche B for a total of $165,000. At December 31, 2015, there was $165,000 of indebtedness outstanding under the Senior Loan and $20,000 of fully amortized original issue discount, which had been accreted over the initial term of the Senior Loan. Additionally, Payment-in-Kind (PIK) interest is also accreted to debt. The borrowings under the Senior Loan were scheduled to mature on April 28, 2015, however, through a series of extensions, the maturity date was extended to February 29, 2016. On February 9, 2016, an affiliate of Torchlight Investors LLC (“Torchlight”) acquired the Senior Loan from Senator in a transaction outside of the Company and assumed the rights of Senator under the Senior Loan. The Company and Torchlight entered into a forbearance agreement through April 30, 2016, which was extended to August 31, 2016. No action was taken by Torchlight after August 31, 2016 during active negotiations concluding in the refinancing on October 17, 2016.
F-16
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
6. Borrowing Arrangements (continued)
During the forbearance period, the Company undertook efforts to restructure the loan, obtain alternative debt, additional equity or other capital. The relevant terms of the borrowing arrangement during the forbearance period were as follows:
| · | The borrowings under the Senior Loan bore interest at a current pay rate equal to 7% per annum. | |
| · | The borrowings under the Senior Loan were made in tranches and also accrued PIK interest at an annual rate of 3% compounded monthly on Tranche A amounts, and at an annual rate of 8% compounded monthly on Tranche B and C amounts. The weighted average of PIK interest was approximately 5%. All PIK amounts were due at maturity. | |
| · | An additional 8% default rate of interest accrued effective March 31, 2016. | |
| · | With respect to any repayment of (a) Tranche A, a make-whole fee in an amount equal to four percent (4%) of the outstanding balance of Tranche A was payable; (b) Tranche B, a make-whole fee in an amount equal to five percent (5%) of the outstanding balance of Tranche B, and (c) Tranche C, following an event of default, a make-whole fee in an amount equal to five percent (5%) of the outstanding balance of Tranche C. The Company had fully accrued the make-whole fees due upon the initial maturity of the Senior Loan on April 28, 2016. | |
| · | The borrowings under the Senior Loan were secured by first lien mortgages on all of the Company’s existing properties and pledges of equity interests in the Operating Partnership. | |
| · | The obligations under the Senior Loan were guaranteed by the Company |
Refinancing
On October 17, 2016, the Company refinanced its Senior Loan with Torchlight, which had a carrying value of $237,751 as of that date, through the following steps:
| · | The Company, through its newly created subsidiary 20 LLC, borrowed $120,000 in the form of a senior secured loan from investment entities managed by AIG Asset Management (the “AIG Loan”). The Company used the net proceeds of these borrowings to reduce the Senior Loan with Torchlight. | |
| · | The Company, through 20 LLC, issued a mezzanine term loan (Mezzanine Loan) in the amount of $30,000 to an investment fund controlled by Torchlight, in satisfaction of $30,000 of the Senior Loan with Torchlight. | |
| · | The Company, through 20 LLC, issued a 99.5% redeemable preferred member interest in 20 LLC in the amount of $30,553 to an affiliate of Torchlight in satisfaction of the $30,553 of the Senior Loan with Torchlight. |
The value of the consideration transferred by the Company to Torchlight totaled $175,000 which consisted of (a) net cash transferred of $114,447, (b) debt satisfied in the amount of $30,000 through the issuance of the Mezzanine Loan and (c) the debt satisfied in the amount of $30,553 through the issuance of the redeemable preferred member interest.
The Company accounted for the difference between the carrying value of the Senior Loan of $237,751 and the value of the consideration transferred of $175,000, or $62,751 as a capital contribution pursuant to the guidelines of ASC 470-50-40-2 since the refinancing was between the Company and Torchlight, a related party.
The terms of the refinanced debt are discussed below and the terms of the redeemable preferred member interest in 20 LLC are discussed in Note 10.
F-17
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
6. Borrowing Arrangements (continued)
$120,000 AIG Loan
Certain indirect subsidiaries of our Operating Partnership have entered into a senior secured loan agreement with investment entities managed by AIG Asset Management (the “AIG Loan”).
As of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, there was $120,000 of indebtedness outstanding under the AIG Loan. The AIG Loan bears interest at 4.08% per annum and has a seven-year term. The AIG Loan provides for monthly payments of interest only for the first three years of the term and thereafter monthly principal and interest payments based on a 27-year amortization period.
The borrowings under the AIG Loan are secured by first lien mortgages on all of the 20 properties. The obligations under the AIG Loan are also guaranteed by our Company and each of our Operating Partnership’s wholly-owned subsidiaries.
The AIG Loan agreement contains customary representations and warranties, as well as affirmative and negative covenants. The negative covenants include restrictions on additional indebtedness, restrictions on liens, fundamental changes, dispositions, restricted payments, change in nature of business, transactions with affiliates and burdensome agreements. The AIG Loan contains financial covenants that require minimum liquidity and Net Worth. The AIG Loan is subject to acceleration upon certain specified events of defaults, including breaches of representations or covenants, failure to pay other material indebtedness, failure to pay taxes or a change of control of our company, as defined in the senior secured loan agreement. We are currently in technical violation of the net worth covenant under the terms of the AIG Loan, which we believe was the result of a drafting error. On May 3, 2017, we entered into an agreement with AIG pursuant to which AIG has agreed to waive this default from October 17, 2016 up to and including June 30, 2017. If prior to June 30, 2017 the offering does not occur or we are not able to negotiate a resolution of the default with our senior lender, the lender could declare all amounts due, including default interest at a rate substantially in excess of the stated rate, under the AIG Loan immediately due and payable.
The Company has no right to prepay all or any part of the AIG Loan before November 1, 2019. Following that date, the AIG Loan can only be paid in full, and a prepayment penalty would be assessed, as defined in the agreement.
The borrowings amounted to $116,258 and $116,053 net of $3,742 and $3,947 of unamortized debt issuance costs at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively.
$30,000 Mezzanine Loan
20 LLC has entered into a mezzanine loan agreement with Torchlight as partial payment of its prior Senior Loan. The Mezzanine Loan has an original principal amount of $30,000, and bears interest at 15% per annum, of which 7% percent is paid currently during the first four years of the term and 10% is paid for the remainder of the term, and is due on October 17, 2023. Unpaid interest accrues and is added to the outstanding principal amount of the loan. The Mezzanine Loan requires borrower to pay a prepayment premium equal to the difference between (1) the sum of 150% of the principal being repaid (excluding the accrued interest) and (2) the sum of the actual principal amount being repaid and current and accrued interest paid through the date of repayment. This repayment feature operates as a prepayment feature since the difference between (1) and (2) will be zero at maturity.
As additional consideration for the Mezzanine Loan, 20 LLC granted Torchlight under the Mezzanine Loan, a profit participation in the form of the right to receive 25% of net income and capital proceeds generated by the Company Portfolio following debt service payments and associated costs (the “TL Participation”). The profit participation was zero for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and the year ended December 31, 2016.
F-18
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
6. Borrowing Arrangements (continued)
On March 3, 2017, the Company entered into a letter of agreement with Torchlight in anticipation of the Company filing a Registration Statement on Form S-11 and completing an initial public offering, which provides the Company the right to terminate the TL Participation in consideration for the private issuance of warrants to Torchlight to acquire 250,000 shares of our common stock, which the Company expects to issue concurrently with the closing of its proposed initial public offering.
The borrowings under the Mezzanine Loan are secured by, among other things, pledges of the equity interest in 20 LLC and each of its property-owning subsidiaries.
Borrowings under the Mezzanine Loan amounted to $29,292, net of unamortized debt issuance costs of $708 at March 31, 2017. Borrowings under the Mezzanine Loan amounted to $29,262, net of unamortized debt issuance costs of $738 at December 31, 2016.
Deferred interest amounted to $207 at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, and is presented separately in the condensed consolidated balance sheets.
7. Common Stock
The Company had 900,000,000 shares of authorized common stock at $0.01 par value, of which 331,965 shares were issued and outstanding at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016.
Common stockholders have full voting rights and are entitled to one vote per share held and are entitled to receive dividends when and if declared.
There were no distributions declared or made to common stockholders during the periods ended March 31, 2017 and 2016.
8. Preferred Stock
The Company’s amended and restated charter authorizes the Company to issue up to 100,000,000 shares of its $0.01 par value preferred stock as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016. There were no shares of preferred stock issued and outstanding at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016.
F-19
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
9. Redeemable Preferred Member Interest in Subsidiary
On October 17, 2016, and in connection with its refinancing of its Senior Loan with Torchlight, the Company issued Torchlight a 99.5% redeemable preferred member interest in 20 LLC in exchange for $30,553. The preferred member interest was mandatorily redeemable at its Redemption Price, as defined below, by the Company on January 17, 2017. In the event the Company defaults under the preferred member interest, the Managing Member interests held by Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC transfers automatically to the Preferred Member for payment of one dollar.
On March 3, 2017, the Company entered into a letter of agreement with Torchlight, which included the following provisions, in anticipation of the Company filing a Registration Statement on Form S-11 and completing an initial public offering:
| · | The redemption date of the redeemable preferred member interest was extended from January 17, 2017 to May 17, 2017. | |
| · | The redemption price of the redeemable preferred member interest is fixed at $25,000 as of March 3, 2017 and the preferred interest will bear no interest or be entitled to any additional preferential returns. As consideration of the redemption price, the Company will pay Torchlight $20,000 in cash and $5,000 in shares of common stock upon the completion of the initial public offering. Restricted cash in the amount of $5,582, which was included on the condensed consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2016, was applied to the redeemable preferred member interest in February 2017. | |
| · | A non-cash capital contribution of $1,020 is related to the adjustment of the Redemption Price for the redeemable preferred member interest as set forth in the letter of agreement. | |
| · | In the event the Company does not make the required payment by May 17, 2017, Torchlight has the right to acquire the Company’s ownership in 20 LLC for $1. |
Prior to the letter of agreement, the holders of the redeemable preferred member interests were entitled to the following:
| · | the amount of the Preferred Member’s unreturned Capital Contributions, which was $30,553 at December 31, 2016, including preferential returns of $490. |
| · | a Preferred Return equal to a cumulative annual return of 7%, plus any additional Preferred Return, compounded monthly on an amount equal to the unreturned capital contributions until the date that such amount is returned to the Preferred Member. Pursuant to the March 3, 2017 agreement the balance of $25,000 will bear no further interest or additional preferred return. | |
| · | all accrued but unpaid Priority Preferred Returns on the Preferred Member’s Priority Additional Capital Contributions equal to a cumulative annual return of 20%, compounded monthly, on an amount equal to each dollar of the Preferred Member’s Priority Additional Capital Contributions until the date that such amount is returned to the Preferred Member. There were no Preferred Member’s Priority Additional Capital Contributions at March 31, 2017 or December 31, 2016. | |
| · | all other sums advanced and costs and expenses (including legal fees) incurred by the Preferred Member in connection with such redemption |
F-20
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
9. Redeemable Preferred Member Interest in Subsidiary (continued)
The Preferred member interests carry certain rights related to major decisions by 20 LLC, including, but not limited to, the acquisition of significant assets as well as a sale of 20 LLC.
The Company has classified this amount as a liability in accordance with ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (ASC 480). Because the member interest is mandatorily redeemable, the Company has concluded that its required redemption of that interest represents a continuing interest in the properties and therefore, the issuance of the redeemable preferred member interest represents a financing of 20 LLC and not a sale of the properties.
The carrying value of the redeemable preferred member interest amounted to $25,000 at March 31, 2017. All amounts are current liabilities at March 31, 2017.
The carrying value of the redeemable preferred member interest amounted to $31,043, including $490 of preferential returns, at December 31, 2016. All amounts are current liabilities at December 31, 2016.
10. Non-Controlling Interests
As discussed in Note 1, and in connection with the refinancing of the Company’s debt on October 17, 2016, the Company established the following subsidiaries:
| · | Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC |
| · | Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC, (20 LLC), as parent company and sole member of the 20 individual LLC’s for Properties |
The ownership interests and managing member or partnership status for each entity is as follows:
Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC
The REIT through its operating partnership Plymouth Industrial OP, LP is the sole member of Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC.
Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC (20 LLC)
The REIT through Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC , is the managing member in 20 LLC with a 0.5% ownership interest. An affiliate of Torchlight has the remaining 99.5% interest in 20 LLC.
20 Individual LLC’s for Properties
The individual LLC’s which hold the properties associated with the partnership interests are wholly owned subsidiaries of 20 LLC.
The Company considers guidance of ASC 360 and ASC 976, as referenced by ASC 810, for issuance of member interests prior to any deconsolidation of assets. The Company has concluded that the redemption feature of the preferred member interest represents the Company’s obligation to repurchase the ownership interest and therefore, the issuance of the preferred interest is a financing and therefore, the risks and rewards of ownership of the properties have not permanently transferred to Torchlight. In accordance with ASC 810, however, the Company has reported the preferred interests in the properties held by Torchlight as non-controlling interests.
Torchlight’s initial investment in 20 LLC consisted of its redeemable preferred member interest of $30,553 along with the non-cash capital contribution of $62,751 associated with the refinancing of the debt. In accordance with ASC 480, the Company has presented the redeemable preferred member interest as a liability. The proportionate share of the loss attributed to the non-controlling interest in each of the entities held by Torchlight amount to a $2,465 deficit for the three months ended March 31, 2017. The carrying value of the non-controlling interest amounted to $59,005 and $60,450 at March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively, and is presented in the condensed consolidated statements of changes in deficit.
11. Subsequent event
On May 1, 2017, the Company amended its charter and effected a 1-for-4 reverse stock split with respect to all then-outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock. All per share amounts and number of shares in the financial statements and related notes have been retroactively restated to reflect the reverse stock split.
On May 2, 2017, Torchlight, the holder of the preferred member interest in 20 LLC, (see Note 9) agreed to extend the redemption date from May 17, 2017 to June 16, 2017.
F-21
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders
of Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of operations, changes in deficit and cash flows for the years then ended. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule on Pages F-40 and F-41. These financial statements and schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc., as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, the related financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly in all material respects the information set forth therein.
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the financial statements, the Company’s limited liquidity, deficit and debt obligations raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans concerning these matters are also discussed in Note 1 to the financial statements. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
/s/ Marcum llp
Marcum LLP
Boston, Massachusetts
March 29, 2017, except for Note 2A, as to which the date is May 3, 2017.
F-22
PLYMOUTH INDUSTRIAL REIT, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Assets | ||||||||
| Real estate properties | $ | 139,086 | $ | 138,236 | ||||
| Less Accumulated depreciation | (16,027 | ) | (8,522 | ) | ||||
| Real estate properties, net | 123,059 | 129,714 | ||||||
| Investments in real estate joint venture | — | 2,987 | ||||||
| Cash | 941 | 698 | ||||||
| Restricted cash | 6,353 | 757 | ||||||
| Cash held in escrow | 2,907 | — | ||||||
| Deferred lease intangibles, net | 10,533 | 14,773 | ||||||
| Other assets | 1,953 | 1,122 | ||||||
| Total assets | $ | 145,746 | $ | 150,051 | ||||
| Liabilities and deficit | ||||||||
| Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Senior secured debt, net | $ | 116,053 | $ | 196,800 | ||||
| Mezzanine debt to investor, net | 29,262 | — | ||||||
| Deferred interest | 207 | 8,081 | ||||||
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities | 5,352 | 4,268 | ||||||
| Deferred lease intangibles, net | 1,405 | 1,941 | ||||||
| Redeemable preferred member interest in subsidiary | 31,043 | — | ||||||
| Total liabilities | 183,322 | 211,090 | ||||||
| Deficit: | ||||||||
| Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. stockholder’s deficit: | ||||||||
| Preferred stock; par value $0.01; 100,000,000 shares authorized; none issued and outstanding | — | — | ||||||
| Common stock, $0.01 par value: 900,000,000 shares authorized; 331,965 shares issued and outstanding | 3 | 3 | ||||||
| Additional paid in capital | 12,477 | 12,477 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (110,506 | ) | (73,519 | ) | ||||
| Total Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. stockholders' deficit | (98,026 | ) | (61,039 | ) | ||||
| Non-controlling interest | 60,450 | — | ||||||
| Total deficit | (37,576 | ) | (61,039 | ) | ||||
| Total liabilities and deficit | $ | 145,746 | $ | 150,051 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-23
PLYMOUTH INDUSTRIAL REIT, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Rental revenue | $ | 19,658 | $ | 19,290 | ||||
| Equity investment income (loss) | 230 | (85 | ) | |||||
| Total revenues | 19,888 | 19,205 | ||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||
| Property | 5,927 | 5,751 | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||
| General and administrative | 3,742 | 4,688 | ||||||
| Acquisition costs | — | 1,061 | ||||||
| Offering costs | — | 938 | ||||||
| Total operating expenses | 21,343 | 24,574 | ||||||
| Operating loss | (1,455 | ) | (5,369 | ) | ||||
| Other income (expense): | ||||||||
| Gain on disposition of equity investment | 2,846 | 1,380 | ||||||
| Interest expense | (40,679 | ) | (44,676 | ) | ||||
| Total other expense, net | (37,833 | ) | (43,296 | ) | ||||
| Net loss | (39,288 | ) | (48,665 | ) | ||||
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest | (2,301 | ) | — | |||||
| Net loss attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. | (36,987 | ) | (48,665 | ) | ||||
| Net loss per share attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. common stockholders | $ | (111.42 | ) | $ | (146.60 | ) | ||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding basic and diluted | 331,965 | 331,965 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-24
PLYMOUTH INDUSTRIAL REIT, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN DEFICIT
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
| Common Stock, $0.01 Par Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Additional Paid in Capital | Accumulated Deficit | Total Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. Stockholders’ Deficit | Non- Controlling Interest | Total Deficit | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, January 1, 2015 | 331,965 | $ | 3 | $ | 12,477 | $ | (24,854 | ) | $ | (12,374 | ) | — | $ | (12,374 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | (48,665 | ) | (48,665 | ) | — | (48,665 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2015 | 331,965 | 3 | 12,477 | (73,519 | ) | (61,039 | ) | — | (61,039 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Non-cash capital contribution by investor in connection with extinguishment of debt | — | — | — | — | — | 62,751 | 62,751 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | (36,987 | ) | (36,987 | ) | (2,301 | ) | (39,288 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2016 | 331,965 | $ | 3 | $ | 12,477 | $ | (110,506 | ) | $ | (98,026 | ) | $ | 60,450 | $ | (37,576 | ) | ||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-25
PLYMOUTH INDUSTRIAL REIT, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Operating activities | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (39,288 | ) | $ | (48,665 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 11,674 | 12,136 | ||||||
| Straight line rent adjustment | (287 | ) | (404 | ) | ||||
| Intangible amortization in rental revenue, net | (355 | ) | (351 | ) | ||||
| Equity investment (income) loss | (230 | ) | 85 | |||||
| Write-off deferred offering costs | — | 938 | ||||||
| Gain on disposition of equity investment | (2,846 | ) | (1,380 | ) | ||||
| Accretion of interest and deferred interest | 33,690 | 32,528 | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
| Security deposits | (14 | ) | (13 | ) | ||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | (530 | ) | (14 | ) | ||||
| Cash held in escrow | (1,658 | ) | — | |||||
| Deferred leasing costs | (110 | ) | (148 | ) | ||||
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities | 174 | 937 | ||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 220 | (4,351 | ) | |||||
| Investing activities | ||||||||
| Proceeds on disposition of joint ventures | 5,582 | 1,708 | ||||||
| Acquisition of properties | — | (434 | ) | |||||
| Real estate improvements | (850 | ) | (124 | ) | ||||
| Increase in restricted cash | (5,596 | ) | — | |||||
| Increase in cash held in escrow | (1,249 | ) | — | |||||
| Distributions from investment in joint ventures | 481 | 470 | ||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | (1,632 | ) | 1,620 | |||||
| Financing activities | ||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of senior secured debt | 120,000 | — | ||||||
| Repayment of senior debt to investor | (114,447 | ) | — | |||||
| Debt issuance costs | (3,898 | ) | (1,095 | ) | ||||
| Deferred offering costs | — | (450 | ) | |||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 1,655 | (1,545 | ) | |||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash | 243 | (4,276 | ) | |||||
| Cash at beginning of year | 698 | 4,974 | ||||||
| Cash at end of year | $ | 941 | $ | 698 | ||||
| Supplemental Cash Flow Disclosures: | ||||||||
| Interest paid | $ | 6,989 | $ | 12,148 | ||||
| Supplemental Non-Cash Investing and Financing Activities: | ||||||||
| Issuance of redeemable preferred member interest | $ | 30,553 | $ | 0 | ||||
| Issuance of mezzanine debt to existing investor | $ | 30,000 | $ | 0 | ||||
| Non-cash capital contribution by investor upon extinguishment of debt | $ | 62,751 | $ | 0 | ||||
| Accrued debt issuance costs | $ | 900 | — | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-26
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
1. Nature of the Business and Basis of Presentation
Business
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc., (the Company or the REIT) is a Maryland corporation formed on March 7, 2011. The Company is a full service, vertically integrated, self-administered and self-managed organization. The Company is focused on the acquisition, ownership and management of single and multi-tenant Class B industrial properties, including distribution centers, warehouses and light industrial properties, primarily located in secondary and select primary markets across the U.S. As of December 31, 2016, the Company through its subsidiaries owns 20 industrial properties comprising approximately 4,000,000 square feet.
On October 17, 2016, the Company completed a reorganization of its subsidiary structure simultaneously with the refinancing of the Company’s existing debt. The Company issued non-controlling interests into a financial investor and lender, Torchlight, in newly established legal entities to hold the properties. The refinancing of the Company’s debt is further discussed in Note 6.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the following entities:
| Name | Relationship | Formation | ||
| Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. | Parent | 2011 | ||
| Plymouth Industrial OP LP | Wholly-owned subsidiary | 2011 | ||
| Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC | Wholly-owned subsidiary | 2016 | ||
| Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC (20 LLC) | Controlling interest* | 2016 | ||
| 20 individual property LLC’s | Controlling interest* | 2014 |
* See note 10 for discussion of non-controlling interests.
Basis of Presentation
The Company’s consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“GAAP”).
Liquidity and Going Concern
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared on a basis which assumes that the Company will continue as a going concern and which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities and commitments in the ordinary course of business.
At December 31, 2016, the Company has an accumulated deficit of $110,506 and had limited amounts of liquidity evidenced by the cash position of $941 as of December 31, 2016. The Company continues to maintain arrangements with certain of its vendors to limit future expenses related to certain professional services.
We are currently in technical violation of the net worth covenant under the terms of the AIG Loan. Although we are pursuing with the lender to remediate the technical violation, which we believe was the result of a drafting error, we can provide no assurances that the lender will agree with our interpretation of the relevant language in the loan agreement or agree to amend the agreement. If we are not able to negotiate a resolution of the default with our senior lender, the lender could declare all amounts due, including default interest at a rate substantially in excess of the stated rate, under the AIG loan immediately due and payable.
Through December 31, 2016, the Company has derived the capital required to purchase and originate real estate related investments and conduct our operations from the proceeds of our prior offering, from secured financings from banks and other lenders and from any undistributed funds from our operations.
The Company’s ability to meet its working capital needs, repay the redeemable preferred membership interest and make its required payments under its senior mortgage debt and mezzanine loan is dependent on its ability to issue additional equity or secure additional debt financing. The Company has engaged D. A. Davidson & Co., investment banking, as underwriters for a proposed initial public offering (IPO or Offering) on a firm commitment basis. There is no assurance, however, that additional debt or other forms of capital, including the proposed IPO, will be available to the Company, or on terms acceptable to the Company.
These conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern within one year after the date the consolidated financial statements are issued. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
F-27
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Consolidation
The Company’s consolidated financial statements include its financial statements, and those of its wholly-owned subsidiaries and controlling interests. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. The Company considers the issuance of member interests in entities that hold its properties under the guidance of ASC 360 Property, Plant and Equipment (ASC 360), and ASC 976, Real Estate, (ASC 976) as referenced by ASC 810, Consolidation, (ASC 810). See Note 10.
Income Taxes
The Company has operated in a manner that allows it to qualify as a REIT for federal income tax purposes. The Company filed its initial Form 1120-REIT as its tax return for the tax year ended December 31, 2012. The Company utilizes an Umbrella Partnership Real Estate Investment Trust (“UPREIT”) organizational structure with the intent to hold properties and securities through an Operating Partnership.
The Company elected to be taxed as a real estate investment trust (“REIT”) under the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and has operated as such beginning with the tax year ending December 31, 2012. To qualify as a REIT, the Company must meet certain organizational and operational requirements, including a requirement to distribute at least 90% of its annual REIT taxable income to stockholders (which is computed without regard to the dividends-paid deduction or net capital gain and which does not necessarily equal net income as calculated in accordance with GAAP). As a REIT, the Company generally will not be subject to federal income tax on income that we distribute as dividends to its stockholders. If the Company fails to qualify as a REIT in any taxable year, it will be subject to federal income tax on our taxable income at regular corporate income tax rates and generally will not be permitted to qualify for treatment as a REIT for federal income tax purposes for the four tax years following the year during which qualification is lost, unless it can obtain relief under certain statutory provisions. Such an event could materially and adversely affect the net income and net cash available for distribution to stockholders. However, the Company intends to continue to operate in a manner that allows it to qualify for treatment as a REIT.
The Company files income tax returns in the U.S federal jurisdiction and various state and local jurisdictions. The statute of limitations for the Company’s income tax returns is generally three years and as such, the Company’s returns that remain subject to examination would be primarily from 2013 and thereafter.
As is more fully described in Note 6, the refinancing transaction that took place on October 17, 2016 resulted in the Company realizing cancellation of indebtedness income of $62,751 for income tax purposes. Cancellation of indebtedness income is includable in the gross income of all taxpayers under the Internal Revenue Code. The inclusion of $62,751 of cancellation of indebtedness income in the Company’s 2016 gross income would potentially result in federal alternative minimum tax and various state and local income taxes.
However, according to the Internal Revenue Code, due to the Company’s insolvency both before and after the debt refinancing transaction, cancellation of indebtedness income is excluded from the gross income of a taxpayer if the taxpayer is insolvent when the discharge takes place. As a condition of excluding cancellation of indebtedness income from the gross income, a taxpayer must reduce certain tax attributes, such as its net operating losses (NOL).
To the extent the Company does not utilize the full amount of the annual federal NOLs, the unused amount may normally be carried forward for 20 years to offset taxable income in future years. The Company had federal NOL carryforwards originating from 2012 through 2015 of approximately $59,805. The Company incurred a federal taxable loss during 2016, after exclusion of cancellation of indebtedness income, of approximately $32,049. These total net operating losses incurred from 2012 through 2016 of approximately $91,854 must be reduced per the Internal Revenue Code by the cancellation of indebtedness income realized in 2016 of approximately $62,751, resulting in net operating loss carryforwards to 2017 of approximately $29,103.
The Company’s net tax basis of real estate assets amounted to $150,506 as of December 31, 2016.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Management makes significant estimates regarding impairments. These estimates and assumptions are based on management’s best estimates and judgment. Management evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis using historical experience and other factors, including the current economic environment. The current economic environment has increased the degree of uncertainty inherent in these estimates and assumptions. Management adjusts such estimates when facts and circumstances dictate. As future events and their effects cannot be determined with precision, actual results could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
Risks and Uncertainties
The state of the overall economy can significantly impact the Company’s operational performance and thus impact its financial position. Should the Company experience a significant decline in operational performance, it may affect the Company’s ability to make distributions to its stockholders, service debt, or meet other financial obligations.
F-28
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Segments
The Company has one reportable segment–industrial properties. These properties have similar economic characteristics and also meet the other criteria that permit the properties to be aggregated into one reportable segment.
Revenue Recognition and Tenant Receivables and Rental Revenue Components
Minimum rental income from real estate operations is recognized on a straight-line basis. The straight-line rent calculation on leases includes the effects of rent concessions and scheduled rent increases, and the calculated straight-line rent income is recognized over the lives of the individual leases. The Company maintains allowances for doubtful accounts receivable and straight-line rents receivable, based upon estimates determined by management. Management specifically analyzes aged receivables, tenant credit-worthiness and current economic trends when evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts. At December 31, 2016 and 2015 the Company did not recognize an allowance for doubtful accounts.
For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, rental income was derived from various tenants. As such, future receipts are dependent upon the financial strength of the lessees and their ability to perform under the lease agreements.
The following tenants represent 10% or greater of rental revenue for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015:
| 2016 | 2015 | |
| Pier One | 12.7% | 12.3% |
| Perseus | 10.0% | 9.7% |
Rental revenue is comprised of the following:
| Year Ended | Year Ended | |||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||
| (in thousands) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Income from lease | $ | 13,865 | $ | 13,710 | ||||
| Straight-line rent adjustment | 287 | 606 | ||||||
| Reimbursable expenses | 5,151 | 4,623 | ||||||
| Amortization of above market leases | (178 | ) | (182 | ) | ||||
| Amortization of below market leases | 533 | 533 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 19,658 | $ | 19,290 | ||||
Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. There were no cash equivalents at December 31, 2016 and 2015. The Company maintains cash and restricted cash, which includes tenant security deposits and cash collateral for its borrowings discussed in Notes 6 and 9, cash held in escrow for real estate tax, insurance and tenant capital improvement and leasing commissions, in bank deposit accounts, which at times may exceed federally insured limits. As of December 31, 2016, the Company has not realized any losses in such cash accounts and believes it is not exposed to any significant risk of loss.
Financial Instruments
The Company estimates that the carrying value of cash, restricted cash, cash held in escrow and reserves, senior secured debt, mezzanine debt to investor, redeemable preferred member interests and deferred interest, approximate their fair values based on their short-term maturity and prevailing interest rates.
F-29
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Deferred Offering Costs
The Company capitalizes certain legal and other third-party fees that are directly associated with in-process equity financings as deferred offering costs until such financings are consummated. There were no deferred offering costs on the Company’s consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2016 and 2015.
The Company had capitalized $938 of costs in 2015 related to the previously proposed public offering. In 2015, the Company postponed the offering and, therefore, the costs were expensed in the year ended December 31, 2015.
Business Combinations
In accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board, (FASB), ASC 805-10 “Business Combinations”, the assets and liabilities acquired are recorded at their fair values as of the acquisition date. Acquisition related costs are recognized as expense in the periods in which incurred.
The accounting for business combinations requires estimates and judgment as to expectations for future cash flows of the acquired business, the allocation of those cash flows to identifiable intangible assets, and in determining the estimated fair value for assets acquired and liabilities assumed. The amounts allocated to lease intangibles (leases in place, leasing commissions, tenant relationships, and above and below market leases) are based on management’s estimates and assumptions, as well as other information compiled by management, including independent third party analysis and market data and are generally amortized over the remaining life of the related leases excluding renewal options, except in the case of below market fixed rate rent amounts, which are amortized over the applicable renewal period.
Real Estate and Depreciation
Real estate properties are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation of buildings and other improvements is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated remaining useful lives of the assets, which generally range from 11 to 34 years for buildings and 3 to 13 years for site improvements. If the Company determines that impairment has occurred, the affected assets are reduced to their fair value. Building improvements are capitalized, while maintenance and repair expenses are charged to expense as incurred. Significant renovations and improvements that improve or extend the useful life of the assets are capitalized.
Amortization of Deferred Lease Intangibles - Assets and Liabilities
Deferred lease intangible assets consist of leases in place, leasing commissions, tenant relationships, and above market leases. Deferred lease Intangible liabilities represent below market leases. These intangibles have been recorded at their fair market value in connection with the acquisition of 20 properties in 2014. Intangible assets are generally amortized over the remaining life of the related leases excluding renewal options, except in the case of below market fixed rate rent amounts, which are amortized over the applicable renewal period.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company assesses the carrying values of our respective long-lived assets, including goodwill, whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amounts of these assets may not be fully recoverable.
Recoverability of real estate assets is measured by comparison of the carrying amount of the asset to the estimated future undiscounted cash flows. In order to review our real estate assets for recoverability, the Company considers current market conditions, as well as our intent with respect to holding or disposing of the asset. Our intent with regard to the underlying assets might change as market conditions change, as well as other factors. Fair value is determined through various valuation techniques, including discounted cash flow models, applying a capitalization rate to estimated net operating income of a property and quoted market values and third-party appraisals, where considered necessary. If our analysis indicates that the carrying value of the real estate asset is not recoverable on an undiscounted cash flow basis, we recognize an impairment charge for the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the current estimated fair value of the real estate property. The Company has determined there is no impairment of value of long lived assets.
F-30
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Debt Issuance Costs
The Company adopted ASU 2015-03, Interest—Imputation of Interest (Subtopic 835-30) (“ASU 2015-03”) in 2016. In accordance with the adoption of ASU No. 2015-03, debt issuance costs are reflected as a reduction to the respective loan amounts in the form of a debt discount. Amortization of this expense is included in interest expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
Debt issuance costs amounted to $4,799 and $3,940 at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and related accumulated amortization amounted to $113 and $3,940 at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Unamortized debt issuance costs amounted to $4,686 and $0 at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Comprehensive Loss
Comprehensive loss includes net loss as well as other changes in deficit that result from transactions and economic events other than those with members. There was no difference between net loss and comprehensive loss for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Earnings per Share
Basic net loss per share is computed by dividing net loss attributable to Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc. by the weighted average shares of common stock outstanding for each year, which is also presented on the consolidated statements of operations. Diluted net loss per share is the same as basic net loss per share since the Company does not have any common stock equivalents such as stock options. The Company has not granted any stock options or stock-based awards under the 2014 Incentive Award Plan.
Equity Method of Accounting
The Company accounted for its 50.3% investment in a real estate joint venture made in 2013, whose property was sold in 2016, under the equity method of accounting since the Company did not, and does not, control but has the ability to exercise significant influence on the entity. Under the equity method of accounting, the Company recognized its proportional share of net income or loss as determined under GAAP in our results of operations.
Non-controlling Interests
As further discussed in Note 10, the Company has issued non-controlling interests in its subsidiaries. The net loss attributable to the non-controlling interests is presented in the Company’s consolidated results of operations since the date of initial acquisition.
Controlling Interests
The Company determines whether it holds a controlling financial interest in an entity by first evaluating whether it is required to apply the variable interest entity (“VIE”) model to the entity. Where the Company holds current or potential rights that give it the power to direct the activities of a VIE that most significantly impact the VIE’s economic performance combined with a variable interest that gives it the right to receive potentially significant benefits or the obligation to absorb potentially significant losses, the Company is the primary beneficiary of that VIE. When changes occur to the design of an entity, the Company reconsiders whether it is subject to the VIE model. The Company continuously evaluates whether it is the primary beneficiary of a consolidated VIE.
To the extent the Company is not required to apply the VIE model, the Company follows the control model for consolidation purposes and considers instances whether its ownership exceeds 50% of the voting rights of the entity and whether other investors have liquidating, kick-out or substantive participating rights.
With respect to in substance real estate transactions, the Company considers guidance of ASC 360 and ASC 976, as referenced by ASC 810, for issuance of membership interests prior to any deconsolidation of assets. See Note 10.
F-31
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) (“ASU 2014-09”), which supersedes all existing revenue recognition requirements, including most industry-specific guidance. The new standard requires a company to recognize revenue when it transfers goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration that the company expects to receive for those goods or services. The new standard will be effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017. Earlier application is permitted only for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim reporting periods within that reporting period. The Company is in the process of evaluating the impact of this pronouncement on its consolidation financial statements.
In August 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-15, Presentation of Financial Statements – Going Concern (“ASU 2014-15”), which requires a company to evaluate the existence of conditions or events that raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern within one year of the issuance date of its financial statements. The standard is effective for interim and annual periods ending after December 15, 2016 with early adoption permitted. The Company has evaluated the impact of ASU 2014-15 and and has included the appropriate disclosures herein.
In February 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-02, Consolidation (Topic 810) (“ASU 2015-02”), to address financial reporting considerations for the evaluation as to the requirement to consolidate certain legal entities. ASU 2015-02 is effective for fiscal years and for interim periods within those fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2015. The Company has evaluated the impact of ASU 2015-02 and has concluded that it has no effect on the consolidated financial statements.
In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-01, Financial Instruments – Overall: Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities. ASU 2016-01 requires equity investments (except those accounted for under the equity method of accounting, or those that result in consolidation of the investee) to be measured at fair value with changes in fair value recognized in net income, requires public business entities to use the exit price notion when measuring the fair value of financial instruments for disclosure purposes, requires separate presentation of financial assets and financial liabilities by measurement category and form of financial asset, and eliminates the requirement for public business entities to disclose the method(s) and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair value that is required to be disclosed for financial instruments measured at amortized cost. ASU 2016-01 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early application is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the potential impact that the adoption of ASU 2016-01 will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases (“ASU 2016-02”), which requires a lessee to recognize assets and liabilities on the balance sheet for operating leases and changes many key definitions, including the definition of a lease. The update includes a short-term lease exception for leases with a term of 12 months or less, in which a lessee can make an accounting policy election not to recognize lease assets and lease liabilities. Lessees and lessors are required to recognize and measure leases at the beginning of the earliest period presented using a modified retrospective approach. The modified retrospective approach includes a number of optional practical expedients that entities may elect to apply as well as transition guidance specific to nonstandard leasing transactions. ASU 2016-02 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact that the adoption of ASU 2016-02 may have on its consolidated financial statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09, Stock Compensation – Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting, (“ASU 2016-09”), which simplifies several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment transactions, including the income tax consequences, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, classification on the statement of cash flows and policy elections on the impact for forfeitures. ASU 2016-09 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016 and interim periods within those annual periods. The Company is in the process of evaluating the impact of ASU 2016-09 on its financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash (“ASU 2016-18”). The ASU requires an entity to explain the changes in the total of cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash, and restricted cash equivalents on the statement of cash flows and to provide a reconciliation of the totals in that statement to the related captions in the balance sheet when the cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash, and restricted cash equivalents are presented in more than one line item on the balance sheet. This ASU is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2017, and is required to be adopted using a retrospective approach, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact that the adoption of ASU 2016-18 may have on its consolidated financial statements.
Other accounting standards that have been issued or proposed by the FASB or other standards-setting bodies that do not require adoption until a future date are not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements upon adoption.
2A. Reverse Stock Split
On May 1, 2017, the Company amended its charter and effected a 1-for-4 reverse stock split with respect to all then-outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock. All per share amounts and number of shares in the financial statements and related notes have been retroactively restated to reflect the reverse stock split.
F-32
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
3. Real Estate Properties
Real estate properties consisted of the following at December 31, 2016 and 2015:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Land and improvements | $ | 18,117 | $ | 18,051 | ||||
| Buildings | 110,142 | 109,725 | ||||||
| Site improvements | 10,442 | 10,442 | ||||||
| Construction in process | 385 | 18 | ||||||
| 139,086 | 138,236 | |||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation | (16,027 | ) | (8,522 | ) | ||||
| Real estate properties | $ | 123,059 | $ | 129,714 | ||||
Depreciation expense was $7,505 in 2016 and $7,518 in 2015.
4. Deferred Lease Intangibles
Deferred Lease Intangible assets consisted of the following at December 31, 2016 and 2015:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Above market lease | $ | 1,122 | $ | 1,122 | ||||
| Lease in place | 14,289 | 14,289 | ||||||
| Tenant relationships | 2,068 | 2,068 | ||||||
| Leasing commission | 2,606 | 2,606 | ||||||
| Leasing commission after acquisition | 258 | 148 | ||||||
| 20,343 | 20,233 | |||||||
| Less Accumulated amortization | (9,810 | ) | (5,460 | ) | ||||
| Deferred lease intangibles | $ | 10,533 | $ | 14,773 | ||||
Deferred Lease Intangibles - Below Market Leases at December 31, 2016 and 2015 were:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Below market leases | $ | 2,548 | $ | 2,548 | ||||
| Less accumulated amortization | (1,143 | ) | (607 | ) | ||||
| Deferred lease intangibles | $ | 1,405 | $ | 1,941 | ||||
Amortization of above and below market leases was recorded as an adjustment to revenues and amounted to $355 and $351 in 2016 and 2015, respectively. Amortization of all other deferred lease intangibles has been included in depreciation and amortization in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations and amounted to $4,169 and $4,618 in 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Projected amortization of deferred lease intangibles for the next five years as of December 31, 2016 is as follows:
| Years Ending December 31, | ||||
| 2017 | $ | 3,184 | ||
| 2018 | 2,520 | |||
| 2019 | 1,852 | |||
| 2020 | 852 | |||
| 2021 | 363 | |||
F-33
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
5. Investment in Real Estate Joint Venture
In 2013, the Company acquired a 50.3% interest in TCG 5400 FIB LP (“5400 FIB”), which owned a warehouse facility (the “Property”) in Atlanta, Georgia containing 682,750 rentable square feet of space, which was obtained in 2013 for a total of $3,900. The Company accounted for the investment under the equity method since it did not have control over the investment. The carrying value of the investment was $2,987 at December 31, 2015.
The property was sold in November 2016 and the Company received $5,582 as a return of its investment. The Company recorded a gain on the disposition of the investment in the amount of $2,846 in 2016. The Company has included the cash proceeds from the investment in restricted cash in the consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2016 since the amount serves as collateral for the borrowing arrangements with Torchlight discussed in Notes 6 and 9.
6. Borrowing Arrangements
On October 17, 2016, the Company completed a reorganization of its subsidiary structure in connection with the refinancing of the Company’s existing debt. The Company issued non-controlling interests to a financial investor and lender, Torchlight, in newly established legal entities to hold the properties owned by the REIT.
Previous Borrowing Arrangement
On October 28, 2014, the Company, its its wholly-owned subsidiary Plymouth Industrial OP LP, its Operating Partnership, and certain subsidiaries of its Operating Partnership entered into a senior secured loan agreement (Senior Loan) with investment entities, or the Funds, managed by Senator Investment Group LP (Senator). The Senior Loan was a $192,000 facility with $71,000 designated as Tranche A, $101,000 designated as Tranche B and $20,000 designated as Tranche C and the deemed original issue discount.
The Company borrowed $69,200 under Tranche A and $95,800 under Tranche B for a total of $165,000. At December 31, 2015, there was $165,000 of indebtedness outstanding under the Senior Loan and $20,000 of fully amortized original issue discount, which had been accreted over the initial term of the Senior Loan. Additionally, Payment-in-Kind (PIK) interest is also accreted to debt. There was also $8,081 of deferred interest payable outstanding at December 31, 2015, respectively.
The borrowings under the Senior Loan were scheduled to mature on April 28, 2015, however, through a series of extensions, the maturity date was extended to February 29, 2016. On February 9, 2016, an affiliate of Torchlight Investors LLC (“Torchlight”) acquired the Senior Loan from Senator in a transaction outside of the Company and assumed the rights of Senator under the Senior Loan. The Company and Torchlight entered into a forbearance agreement through April 30, 2016, which was extended to August 31, 2016. No action was taken by Torchlight after August 31, 2016 during active negotiations concluding in the refinancing on October 17, 2016.
During the forbearance period, the Company undertook efforts to restructure the loan, obtain alternative debt, additional equity or other capital. The relevant terms of the borrowing arrangement during the forbearance period were as follows:
| · | The borrowings under the Senior Loan bore interest at a current pay rate equal to 7% per annum. |
| · | The borrowings under the Senior Loan were made in tranches and also accrued PIK interest at an annual rate of 3% compounded monthly on Tranche A amounts, and at an annual rate of 8% compounded monthly on Tranche B and C amounts. The weighted average of PIK interest was approximately 5%. All PIK amounts were due at maturity. |
| · | An additional 8% default rate of interest accrued effective March 31, 2016. |
| · | With respect to any repayment of (a) Tranche A, a make-whole fee in an amount equal to four percent (4%) of the outstanding balance of Tranche A was payable; (b) Tranche B, a make-whole fee in an amount equal to five percent (5%) of the outstanding balance of Tranche B, and (c) Tranche C, following an event of default, a make-whole fee in an amount equal to five percent (5%) of the outstanding balance of Tranche C. The Company had fully accrued the make-whole fees due upon the initial maturity of the Senior Loan on October 28, 2015. |
| · | The borrowings under the Senior Loan were secured by first lien mortgages on all of the Company’s existing properties and pledges of equity interests in the Operating Partnership. |
| · | The obligations under the Senior Loan were guaranteed by the Company |
F-34
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
6. Borrowing Arrangements (continued)
Refinancing
On October 17, 2016, the Company refinanced its Senior Loan with Torchlight, which had a carrying value of $237,751 as of that date, through the following steps:
| · | The Company, through its newly created subsidiary 20 LLC, borrowed $120,000 in the form of a senior secured loan from investment entities managed by AIG Asset Management (the “AIG Loan”). The Company used the net proceeds of these borrowings to reduce the Senior Loan with Torchlight. |
| · | The Company, through 20 LLC, issued a mezzanine term loan (Mezzanine Loan) in the amount of $30,000 to an investment fund controlled by Torchlight, in satisfaction of $30,000 of the Senior Loan with Torchlight. |
| · | The Company, through 20 LLC, issued a 99.5% redeemable preferred member interest in 20 LLC in the amount of $30,553 to an affiliate of Torchlight in satisfaction of the $30,553 of the Senior Loan with Torchlight. |
The value of the consideration transferred by the Company to Torchlight totaled $175,000 which consisted of (a) net cash transferred of $114,447, (b) debt satisfied in the amount of $30,000 through the issuance of the Mezzanine Loan and (c) the debt satisfied in the amount of $30,553 through the issuance of the redeemable preferred member interest.
The Company has accounted for the difference between the carrying value of the Senior Loan of $237,751 and the value of the consideration transferred of $175,000 , or $62,751 as a capital contribution pursuant to the guidelines of ASC 470-50-40-2 since the refinancing was between the Company and Torchlight, a related party.
The terms of the refinanced debt are discussed below and the terms of the redeemable preferred member interest in 20 LLC are discussed in Note 10.
$120,000 AIG Loan
Certain indirect subsidiaries of our Operating Partnership have entered into a senior secured loan agreement with investment entities managed by AIG Asset Management (the “AIG Loan”).
As of December 31, 2016, there was $120,000 of indebtedness outstanding under the AIG Loan agreement. The AIG Loan bears interest at 4.08% per annum and has a seven-year term. The AIG Loan provides for monthly payments of interest only for the first three years of the term and thereafter monthly principal and interest payments based on a 27-year amortization period.
The borrowings under the AIG Loan are secured by first lien mortgages on all of the 20 properties. The obligations under the AIG Loan are also guaranteed by our Company and each of our Operating Partnership’s wholly-owned subsidiaries.
The AIG Loan agreement contains customary representations and warranties, as well as affirmative and negative covenants. The negative covenants include restrictions on additional indebtedness, restrictions on liens, fundamental changes, dispositions, restricted payments, change in nature of business, transactions with affiliates and burdensome agreements. The AIG Loan contains financial covenants that require minimum liquidity and Net Worth.. The AIG Loan is subject to acceleration upon certain specified events of defaults, including breaches of representations or covenants, failure to pay other material indebtedness, failure to pay taxes or a change of control of our company, as defined in the senior secured loan agreement. We are currently in technical violation of the net worth covenant under the terms of the AIG Loan. Although we are pursuing with the lender to remediate the technical violation, which we believe was the result of a drafting error, we can provide no assurances that the lender will agree with our interpretation of the relevant language in the loan agreement or agree to amend the agreement. If we are not able to negotiate a resolution of the default with our senior lender, the lender could declare all amounts due, including default interest at a rate substantially in excess of the stated rate, under the AIG loan immediately due and payable.
The Company has no right to prepay all or any part of the AIG Loan before November 1, 2019. Following that date, the AIG Loan can only be paid in full, and a prepayment penalty would be assessed, as defined in the agreement.
The borrowings amounted to $120,000, net of $3,947 of unamortized debt issuance costs at December 31, 2016.
F-35
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
6. Borrowing Arrangements (continued)
$30,000 Mezzanine Loan
20 LLC, has entered into a mezzanine loan agreement with Torchlight as partial payment of its prior Senior Loan. The Mezzanine Loan has an original principal amount of $30,000, and bears interest at 15% per annum, of which 7% percent is paid currently during the first four years of the term and 10% is paid for the remainder of the term, and is due on October 17, 2023. Unpaid interest accrues and is added to the outstanding principal amount of the loan. The Mezzanine Loan requires borrower to pay a prepayment premium equal to the difference between (1) the sum of 150% of the principal being repaid (excluding the accrued interest) and (2) the sum of the actual principal amount being repaid and current and accrued interest paid through the date of repayment. This repayment feature operates as a prepayment feature since the difference between (1) and (2) will be zero at maturity.
As additional consideration for the Mezzanine Loan, 20 LLC granted Torchlight under the Mezzanine Loan, a profit participation in the form of the right to receive 25% of net income and capital proceeds generated by the Company Portfolio following debt service payments and associated costs (the “TL Participation”). The profit participation was zero for 2016.
The borrowings under the Mezzanine Loan are secured by, among other things, pledges of the equity interest in 20 LLC and each of its property-owning subsidiaries.
Borrowings under the Mezzanine Loan amounted to $29,262, net of $738 of unamortized discount, at December 31, 2016. Deferred interest amounted to $207 at December 31, 2016 and is presented separately on the consolidated balance sheets.
Principal payments on the Company’s long-term debt due in each of the next five fiscal years as of December 31, 2016 are as follows:
| Amount | ||||
| Year ending December 31: | ||||
| 2017 | $ | 0 | ||
| 2018 | 0 | |||
| 2019 | 204 | |||
| 2020 | 2,049 | |||
| 2021 | 2,497 | |||
7. Common Stock
The Company at December 31, 2016 and 2015 has 900,000,000 shares of authorized common stock at $0.01 par value, of which 331,965 shares were issued and outstanding at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Common stockholders have full voting rights and are entitled to one vote per share held and are entitled to receive dividends when and if declared.
There were no distributions declared or made to common stockholders during the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015.
8. Preferred Stock
The Company’s amended and restated charter authorizes the Company to issue up to 100,000,000 shares of its $0.01 par value preferred stock as of December 31, 2016 and 2015. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, there were no shares of preferred stock issued and outstanding.
9. Redeemable Preferred Member Interest in Subsidiary
On October 17, 2016, and in connection with its refinancing of its Senior Loan with Torchlight, the Company issued Torchlight a 99.5% redeemable preferred member interest in 20 LLC in exchange for $30,553. The significant terms of the preferred member interest are as follows:
Maturity
The preferred member interest is mandatorily redeemable at its Redemption Price, as defined below, by the Company on January 17, 2017. In the event the Company defaults under the preferred member interest, the Managing Member interests held by Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC transfers automatically to the Preferred Member for payment of one dollar. On March 3, 2017 a letter of agreement was agreed to with Torchlight extending this date to May 17, 2017 (Note 15).
F-36
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
9. Redeemable Preferred Member Interest in Subsidiary (continued)
Redemption Price
The redemption price of the redeemable preferred member interest is as follows:
| · | the amount of the Preferred Member’s unreturned Capital Contributions ($30,553 at December 31, 2016). See Note 15 regarding the letter agreement dated March 3, 2017. The Preferred Member interest is fixed at $25,000 after applying $5,582 in February, 2017. |
| · | a Preferred Return equal to a cumulative annual return of 7%, plus any additional Preferred Return, compounded monthly on an amount equal to the unreturned capital contributions until the date that such amount is returned to the Preferred Member |
| · | pursuant to the March 3, 2017 agreement (Note 15) the balance of $25,000 will bear no further interest or additional preferred return. |
| · | all accrued but unpaid Priority Preferred Returns on the Preferred Member’s Priority Additional Capital Contributions equal to a cumulative annual return of 20%, compounded monthly, on an amount equal to each dollar of the Preferred Member’s Priority Additional Capital Contributions until the date that such amount is returned to the Preferred Member. There were no Preferred Member’s Priority Additional Capital Contributions at December 31, 2016. |
| · | all other sums advanced and costs and expenses (including legal fees) incurred by the Preferred Member in connection with such redemption |
Major Decisions
The Preferred member interests carry certain rights related to major decisions by 20 LLC, including, but not limited to, the acquisition of significant assets as well as a sale of 20 LLC.
Presentation
The Company has classified this amount as a liability in accordance with ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (ASC 480). Because the member interest is mandatorily redeemable, the Company has concluded that its required redemption of that interest represents a continuing interest in the properties and therefore, the issuance of the redeemable preferred member interest represents a financing of 20 LLC and not a sale of the properties.
The carrying value of the redeemable preferred member interest amounted to $31,043, including $490 of preferential returns, at December 31, 2016. All amounts are current liabilities at December 31, 2016.
10. Non-Controlling Interests
As discussed in Note 1 and in connection with the refinancing of the Company’s debt on October 17, 2016, the Company established the following subsidiaries:
| · | Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC |
| · | Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC, as parent company and sole member of the 20 individual LLC’s for Properties |
The ownership interests and managing member or partnership status for each entity is as follows:
Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC
The REIT through its operating partnership Plymouth Industrial OP, LP is the sole member of Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC.
Plymouth Industrial 20 LLC (20 LLC)
The REIT through Plymouth Industrial 20 Financial LLC , is the managing member in 20 LLC with a 0.5% ownership interest. Torchlight has the remaining 99.5% interest in 20 LLC.
F-37
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
10. Non-Controlling Interests (continued)
20 Individual LLC’s for Properties
The individual LLC’s which hold the properties associated with the partnership interests are wholly owned subsidiaries of 20 LLC.
The Company considers guidance of ASC 360 and ASC 976, as referenced by ASC 810, for issuance of member interests prior to any deconsolidation of assets. The Company has concluded that the redemption feature of the preferred member interest represents the Company’s obligation to repurchase the ownership interest and therefore, the issuance of the preferred interest is a financing and therefore, the risks and rewards of ownership of the properties have not permanently transferred to Torchlight. In accordance with ASC 810, however, the Company has reported the preferred interests in the properties held by Torchlight as non-controlling interests.
Torchlight’s initial investment in 20 LLC consisted of its redeemable preferred member interest of $30,553 along with the non-cash capital contribution of $62,751 associated with the refinancing of the debt. In accordance with ASC 480, the Company has presented the redeemable preferred member interest as a liability. The proportionate share of the loss attributed to the non-controlling interest in each of the entities held by Torchlight amount to a $2,301 deficit in 2016. The carrying value of the non-controlling interest amounted to $60,450 at December 31, 2016 and is presented in the consolidated statements of changes in deficit.
11. Incentive Award Plan
In April 2014, the Company’s Board of Directors adopted, and in June 2014 the Company’s stockholders approved, the 2014 Incentive Award Plan, or Plan, under which the Company may grant cash and equity incentive awards to eligible service providers in order to attract, motivate and retain the talent for which we compete. The aggregate number of shares of the Company’s common stock and/or LTIP units of partnership interest in the Company’s Operating Partnership, or LTIP units that are available for issuance under awards granted pursuant to the Plan is 750,000 shares/LTIP units. Shares and units granted under the Plan may be authorized but unissued shares/LTIP units, or, if authorized by the board of directors, shares purchased in the open market. If an award under the Plan is forfeited, expires or is settled for cash, any shares/LTIP units subject to such award may, to the extent of such forfeiture, expiration or cash settlement, be used again for new grants under the Plan. However, the following shares/LTIP units may not be used again for grant under the Plan: (1) shares/LTIP units tendered or withheld to satisfy grant or exercise price or tax withholding obligations associated with an award; (2) shares subject to a stock appreciation right, or SAR, that are not issued in connection with the stock settlement of the SAR on its exercise; and (3) shares purchased on the open market with the cash proceeds from the exercise of options. The maximum number of shares that may be issued under the Plan upon the exercise of incentive stock options is 750,000.
The Plan provides for the grant of stock options, including incentive stock options, or ISOs, and nonqualified stock options, or NSOs, restricted stock, dividend equivalents, stock payments, restricted stock units, or RSUs, performance shares, other incentive awards, LTIP units, SARs, and cash awards.
No awards have been granted to date under the Plan.
12. Future Minimum Rental Receipts Under Non-Cancellable Leases
The following schedule indicates approximate future minimum rental receipts due under non-cancellable operating leases for real estate properties, by year, as of December 31, 2016:
| Year ending December 31, | Future Minimum Rental Receipts | |||
| 2017 | $ | 14,113 | ||
| 2018 | 11,456 | |||
| 2019 | 9,106 | |||
| 2020 | 5,244 | |||
| 2021 | 3,420 | |||
| Thereafter | 5,554 | |||
| Total minimum rental receipts | $ | 48,893 | ||
F-38
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(all dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
13. Commitments and Contingencies
Operating Leases
The Company leases space for its corporate office under the terms of a lease. Rental expense for operating leases, including common-area maintenance, was $292 in 2016 and $328 in 2015. Future amounts of minimum future annual rental commitments under the operating lease as of December 31, 2016 were $216 for 2017, $221 for 2018, $225 for 2019. and $57 for 2020.
Employment Agreements
The Company has entered into employment agreements with the Company’s current Chief Executive Officer, President and Chief Investment Officer, and Vice President and Chief Financial Officer. As approved by the compensation committee of the Board of Directors the agreements provide for base salaries ranging from $200 to $300 annually with discretionary cash performance awards. The agreements contain provisions for equity awards, general benefits, and termination and severance provisions, consistent with similar positions and companies.
Legal Proceedings
The Company is not currently party to any material legal proceedings. At each reporting date, the Company evaluates whether or not a potential loss amount or a potential range of loss is probable and reasonably estimable under the provisions of the authoritative guidance that addresses accounting for contingencies. The Company expense as incurred the costs related to such legal proceedings.
14. Retirement Plan
The Company in December, 2014 funded individual SEP IRA retirement accounts for all employees. The Company has accrued a contribution for 2016 in the amount of $264, which is included in accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2016. No contribution was made for 2015. The Company has no control or administrative responsibility related to the individual accounts and is not obligated to fund in future years.
15. Subsequent Events
As discussed in Note 1, on March 3, 2017, the Company entered a letter of agreement with Torchlight, which included the following provisions, in anticipation of the Company filing a Registration Statement on Form S-11 and completing an initial public offering:
| · | the redemption date of the redeemable preferred member interest was extended from January 17, 2017 to May 17, 2017. |
| · | The balance of the redeemable preferred member interest is fixed at $25,000 as of March 3, 2017 and the preferred interest will bear no interest or be entitled to any additional preferential returns. Of the amount due, the Company will pay Torchlight $20,000 in cash and $5,000 in shares of common stock upon the completion of the initial public offering. Restricted cash in the amount of $5,582, which was included on the consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2016, had been applied to the amount due under the redeemable preferred member interest in February 2017. |
| · | The Company has the right to terminate the TL Participation described in Note 6 in consideration for the private issuance of warrants to Torchlight to acquire 250,000 shares of our common stock, which we expect to issue concurrently with the closing of this offering. |
| · | In the event the Company does not make the required payment by May 17, 2017, Torchlight has the right to acquire the Company’s ownership in 20 LLC for $1. |
F-39
Schedule III
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Real Estate Properties and Accumulated Depreciation
December 31, 2016 ($ in thousands)
| Initial Costs to the Company | Gross Amounts at Close of Period | ||||||||||||
| Metro Area | Address | Encumbrances | Land | Building and Improvements | Costs capitalized Subsequent to Acquisition | Land | Building and Improvements | Total | Accumulated Depreciation (3) | Year Acquired |
Year Built/ Renovated (2) | Depreciable Life (in years) | |
| Chicago, IL | 3940 Stern Avenue | (1) | $ 1,156 | $ 5,141 | $ - | $ 1,156 | $ 5,141 | $ 6,297 | $ 736 | 2014 | 1987 | 16 | |
| Chicago, IL | 1875 Holmes Road | (1) | 1,591 | 5,205 | - | 1,591 | 5,205 | 6,796 | 792 | 2014 | 1989 | 16 | |
| Chicago, IL | 1355 Holmes Road | (1) | 1,012 | 2,789 | 132 | 1,012 | 2,921 | 3,933 | 419 | 2014 | 1975/1999 | 16 | |
| Chicago, IL | 2401 Commerce Drive | (1) | 486 | 4,598 | 188 | 486 | 4,786 | 5,272 | 447 | 2014 | 1994 | 28 | |
| Chicago, IL | 189 Seegers Road | (1) | 470 | 1,381 | 9 | 470 | 1,390 | 1,860 | 150 | 2014 | 1972 | 21 | |
| Chicago, IL | 11351 W. 183rd Street | (1) | 361 | 1,674 | - | 361 | 1,674 | 2,035 | 160 | 2014 | 2000 | 34 | |
| Cincinnati, OH | Mosteller Distribution Center | (1) | 1,501 | 9,424 | - | 1,501 | 9,424 | 10,925 | 1,611 | 2014 | 1959 | 14 | |
| Cincinnati, OH | 4115 Thunderbird Lane | (1) | 275 | 2,093 | - | 275 | 2,093 | 2,368 | 247 | 2014 | 1991 | 22 | |
| Florence, KY | 7585 Empire Drive | (1) | 644 | 2,656 | - | 644 | 2,656 | 3,300 | 585 | 2014 | 1973 | 11 | |
| Columbus, OH | 3500 Southwest Boulevard | (1) | 1,488 | 16,730 | - | 1,488 | 16,730 | 18,218 | 1,895 | 2014 | 1992 | 22 | |
| Columbus, OH | 3100 Creekside Parkway | (1) | 1,205 | 9,602 | - | 1,205 | 9,602 | 10,807 | 920 | 2014 | 2004 | 27 | |
| Columbus, OH | 8288 Green Meadows Dr. | (1) | 1,107 | 8,413 | - | 1,107 | 8,413 | 9,520 | 1,274 | 2014 | 1988 | 17 | |
| Columbus, OH | 8273 Green Meadows Dr. | (1) | 341 | 2,266 | 12 | 341 | 2,278 | 2,619 | 247 | 2014 | 1996/2007 | 27 | |
| Columbus, OH | 7001 American Pkwy | (1) | 331 | 1,416 | 28 | 331 | 1,444 | 1,775 | 197 | 2014 | 1986/2007 & 2012 | 20 | |
| Memphis, TN | 6005, 6045 & 6075 Shelby Dr. | (1) | 488 | 4,918 | 39 | 488 | 4,957 | 5,445 | 691 | 2014 | 1989 | 19 | |
| Jackson, TN | 210 American Dr. | (1) | 928 | 10,441 | 74 | 928 | 10,515 | 11,443 | 1,974 | 2014 | 1967/1981 & 2012 | 13 | |
| Atlanta, GA | 32 Dart Road | (1) | 257 | 4,453 | 215 | 257 | 4,668 | 4,925 | 620 | 2014 | 1988 | 18 | |
| Portland, ME | 56 Milliken Road | (1) | 1,418 | 7,412 | 97 | 1,418 | 7,509 | 8,927 | 1,010 | 2014 | 1966/1995, 2005, 2013 | 20 | |
| Marlton, NJ | 4 East Stow Road | (1) | 1,580 | 6,953 | 22 | 1,580 | 6,975 | 8,555 | 932 | 2014 | 1986 | 22 | |
| Cleveland, OH | 1755 Enterprise Parkway | (1) | 1,412 | 12,281 | 373 | 1,412 | 12,654 | 14,066 | 1,120 | 2014 | 1979/2005 | 27 | |
| Total Real Estate Owned | $ 18,051 | $ 119,846 | $ 1,189 | $18,051 | $ 121,035 | $139,086 | $ 16,027 | ||||||
Note (1) These properties secure the $120,000 Senior Secured Debt and $30,000 Mezzanine Debt.
Note (2) Renovation means significant upgrades, alterations, or additions to building interiors or exteriors and/or systems.
Note (3) Depreciation is calculated over the remaining useful life of the respective property as determined at the time of the purchase allocation, ranging from 11- 34 years for buildings and 3-13 years for improvements
As of December 31, 2016 the aggregate basis for Federal tax purposes of investments in real estate was approximately $150,506.
F-40
Plymouth Industrial REIT, Inc.
Real Estate Properties and Accumulated Depreciation
December 31, 2016 and 2015 ($ in thousands)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Real Estate | ||||||||
| Balance at the beginning of the year | $ | 138,236 | $ | 138,112 | ||||
| Additions during the year | 850 | 124 | ||||||
| Balance at the end of the year | $ | 139,086 | $ | 138,236 | ||||
| Accumulated Depreciation | ||||||||
| Balance at the beginning of the year | $ | 8,522 | $ | 1,004 | ||||
| Depreciation expense | 7,505 | 7,518 | ||||||
| Balance at the end of the year | $ | 16,027 | $ | 8,522 | ||||
F-41

2,900,000 Shares
Common Stock
P R O S P E C T U S
D.A. Davidson & Co.
BB&T Capital Markets
Oppenheimer & Co.
National Securities Corporation
Wedbush Securities
Janney Montgomery Scott
Until July 3, 2017 (25 days after the date of this prospectus), all dealers that effect transactions in these securities, whether or not participating in this offering, may be required to deliver a prospectus. This is in addition to the dealer's obligation to deliver a prospectus when acting as soliciting dealers with respect to their unsold allotments or subscriptions.
June 8, 2017